bio 153l eyes
1/66
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
67 Terms
rectus
straight
oblique
slanting
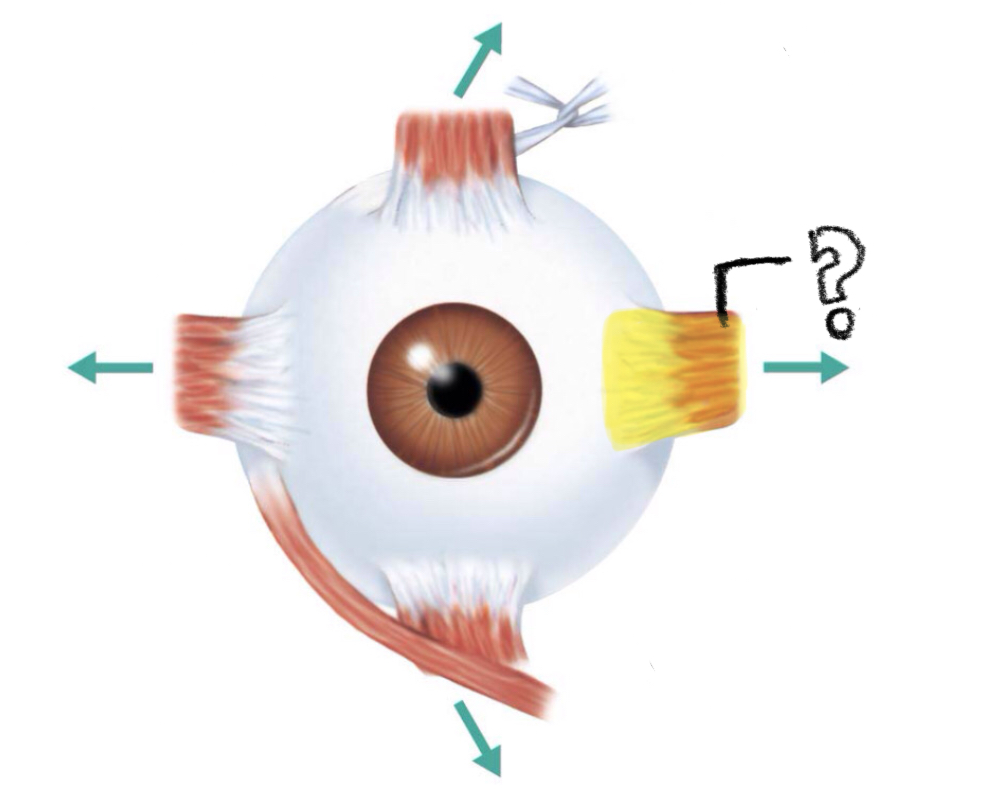
lateral rectus
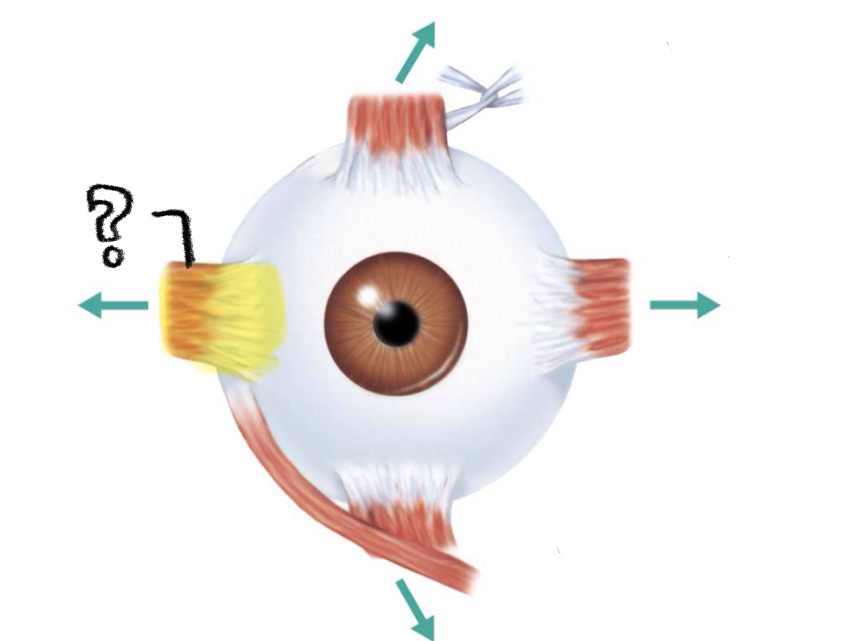
medial rectus
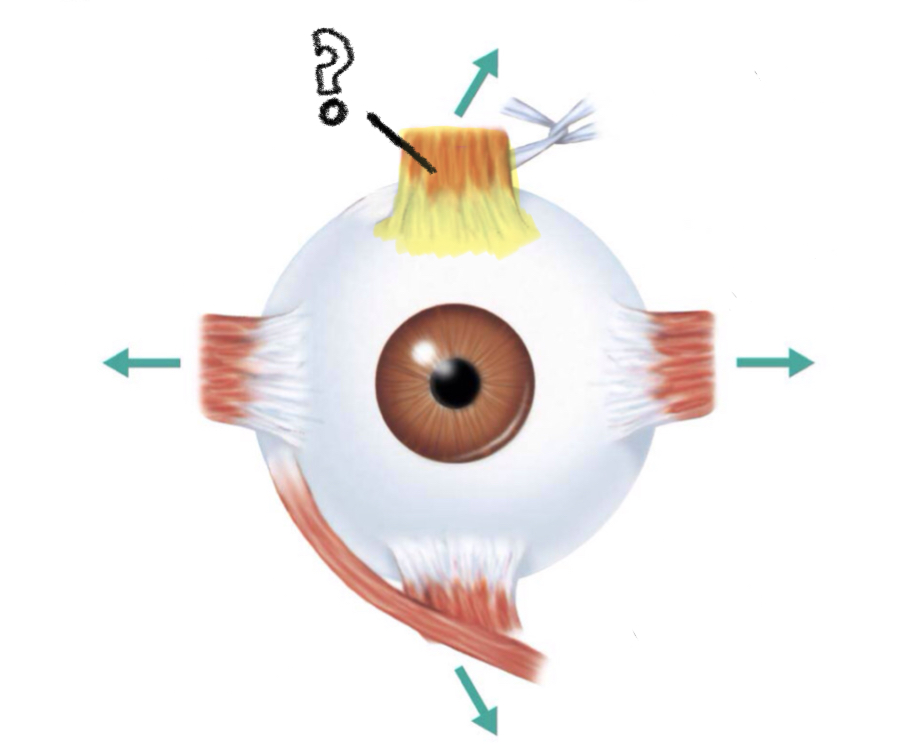
superior rectus
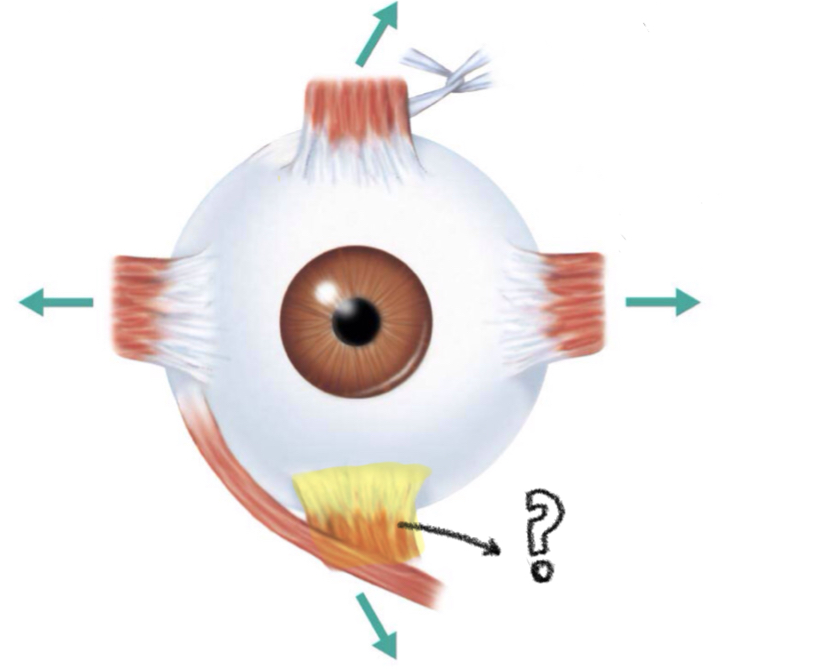
inferior rectus
superior oblique
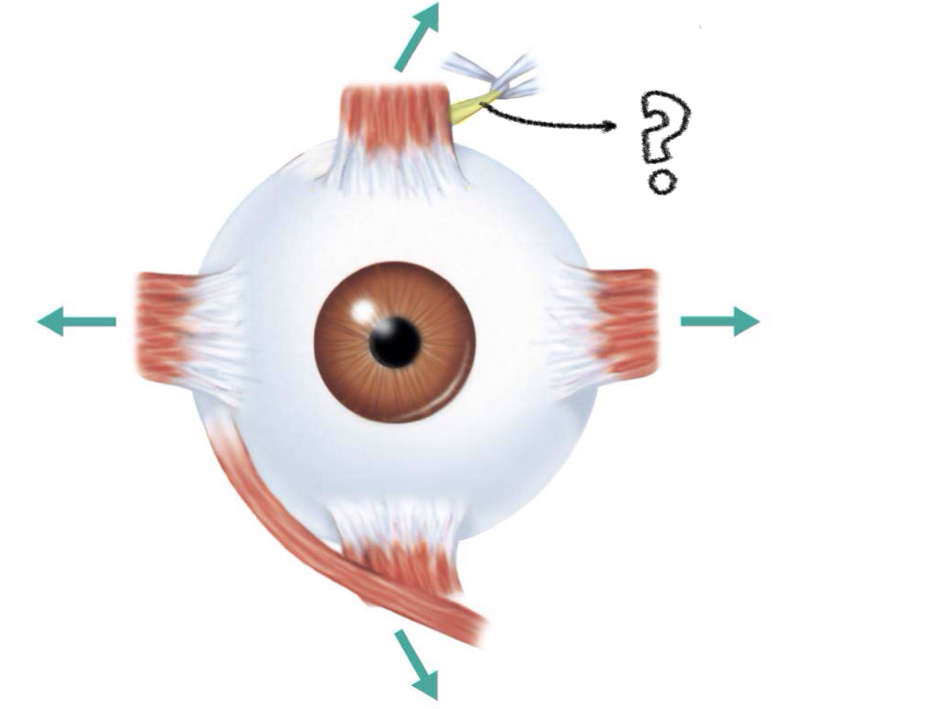
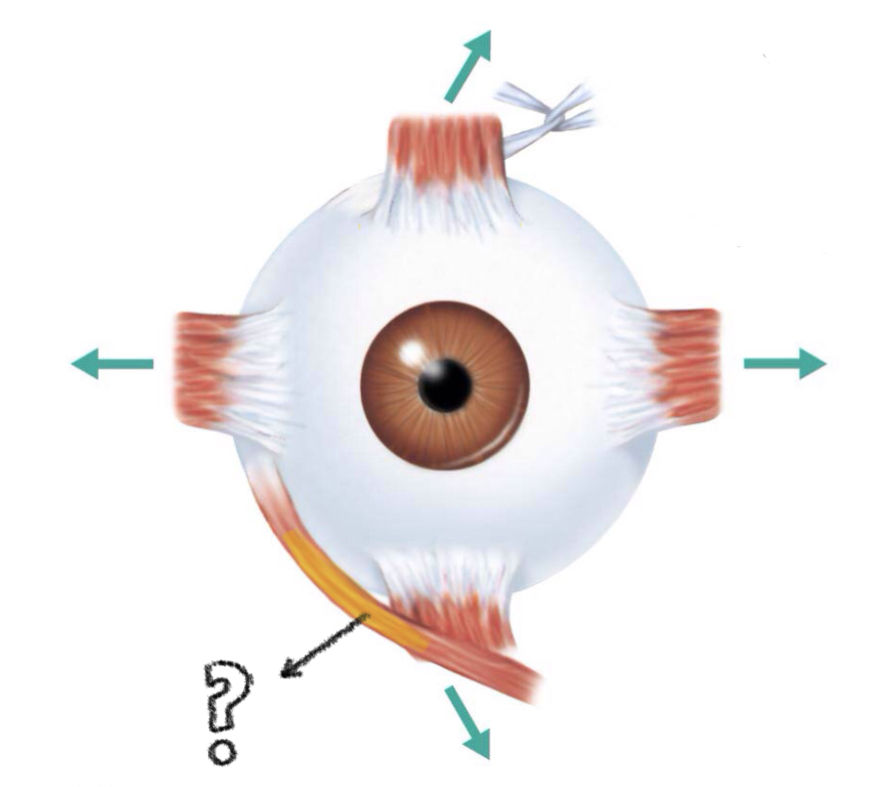
inferior oblique
moves eye laterally
action of lateral rectus
VI (abducens)
controlling cranial nerve of lateral rectus
moves eye medially
action of medial rectus
III (oculomotor)
controlling cranial nerve of medial rectus
elevates eye and turns it medially
action of superior rectus
III (oculomotor)
controlling cranial nerve of superior rectus
depresses eye and turns it medially
action of inferior rectus
III (oculomotor)
controlling cranial nerve of inferior rectus
elevates eye and turns it laterally
action of inferior oblique
III (oculomotor)
controlling cranial nerve of inferior oblique
depresses eye and turns it laterally
action of superior oblique
IV (trochlear)
controlling cranial nerve of superior obliqe
ciliary body
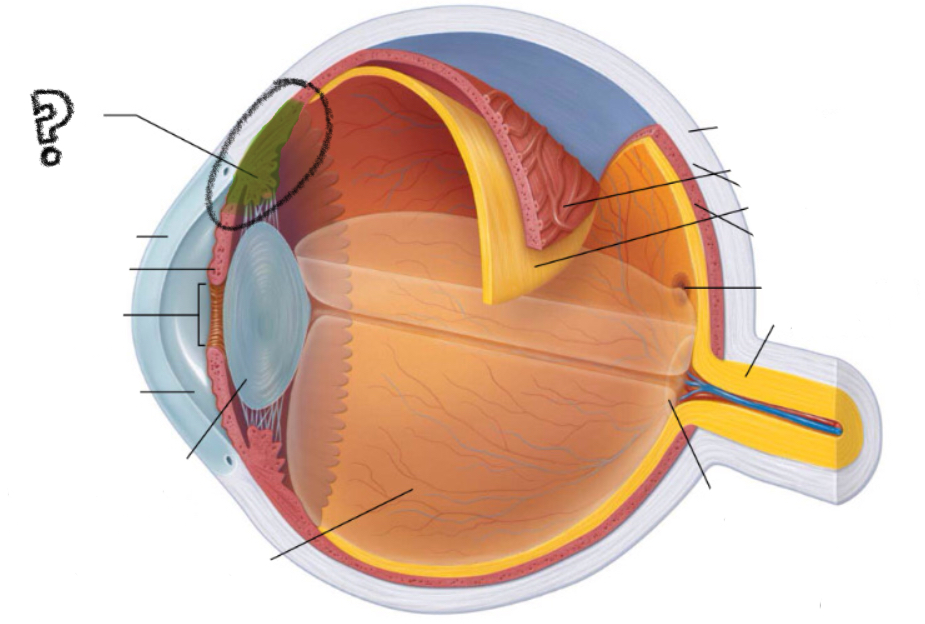
cornea
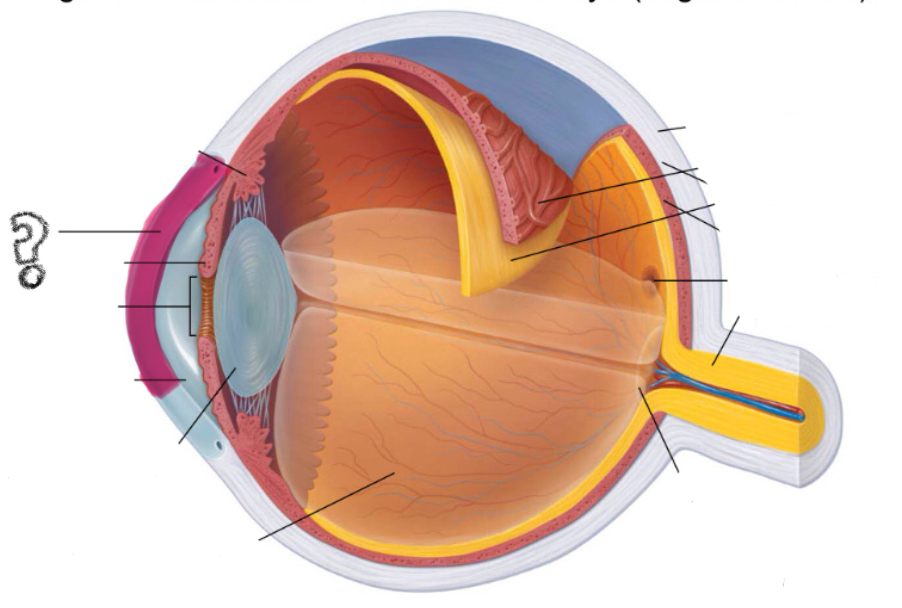
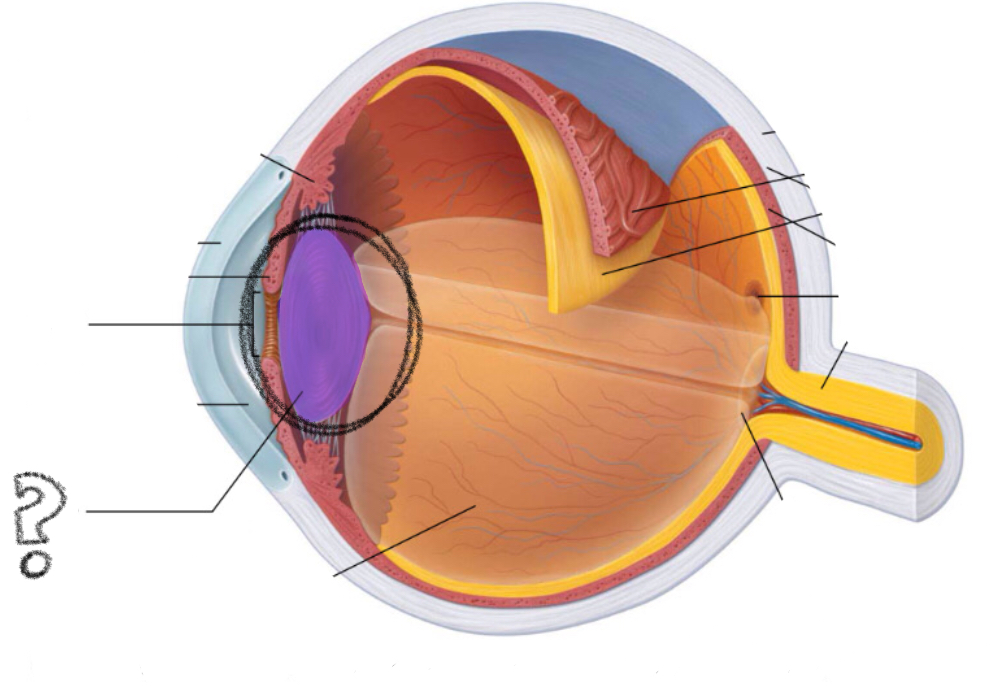
iris
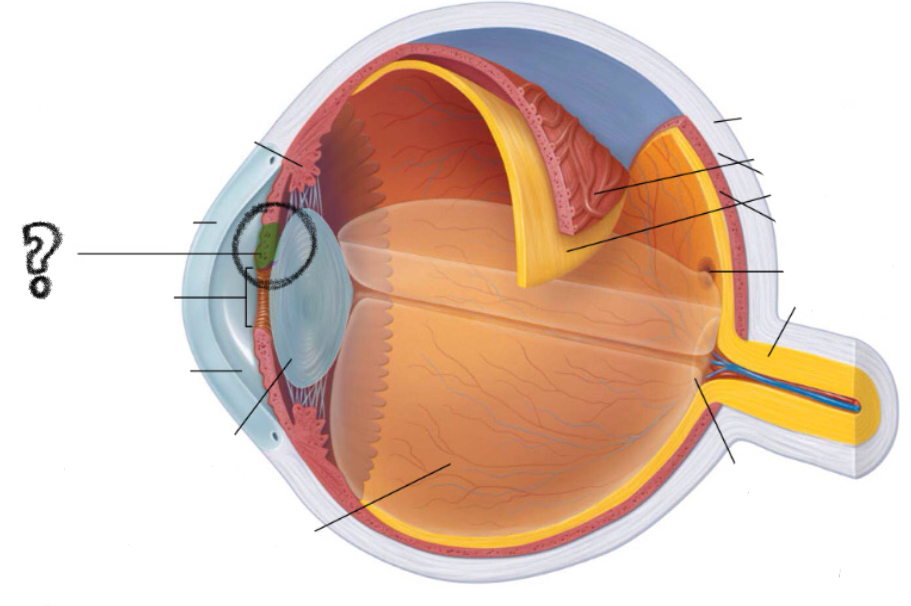
pupil
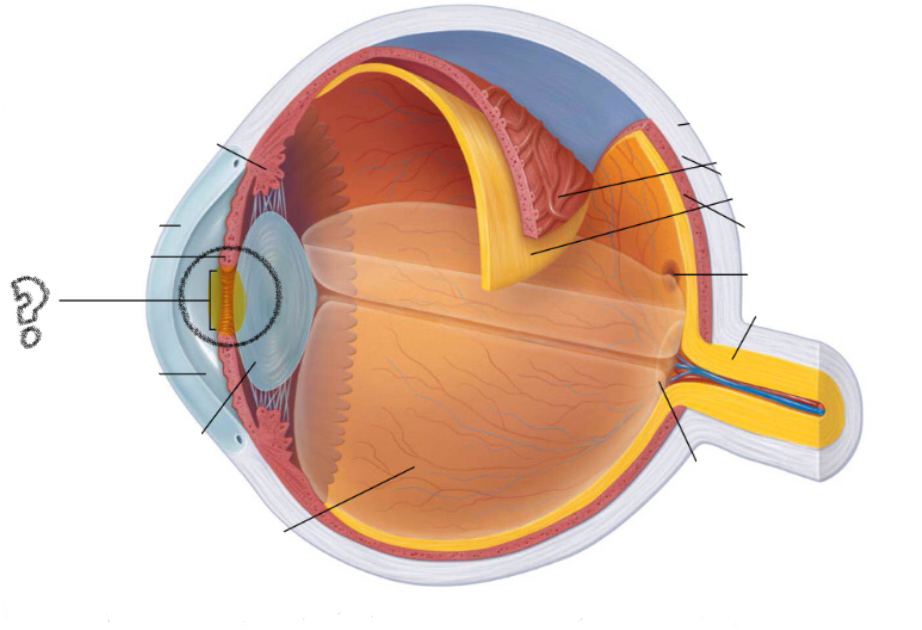
lens
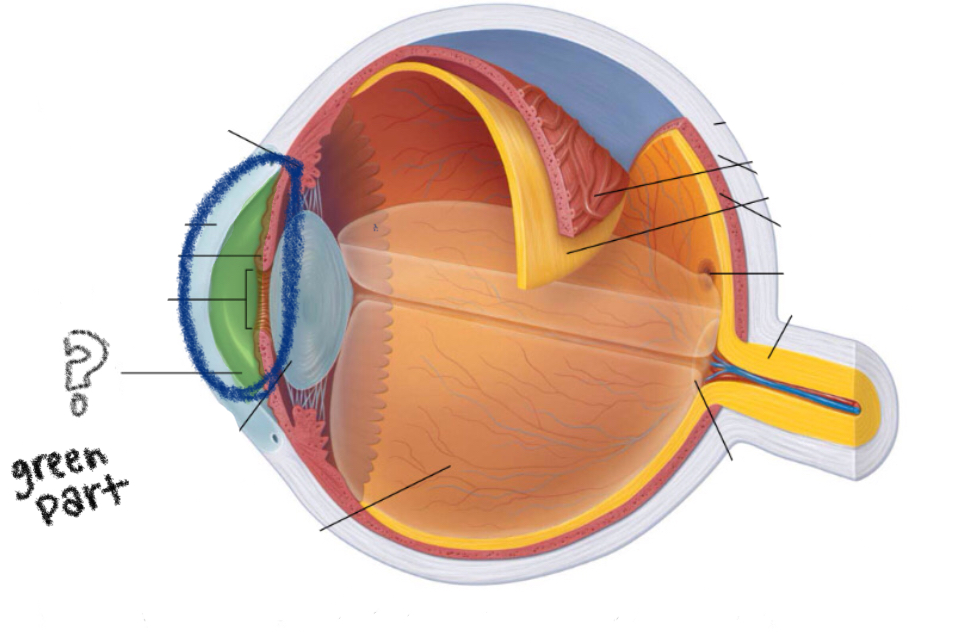
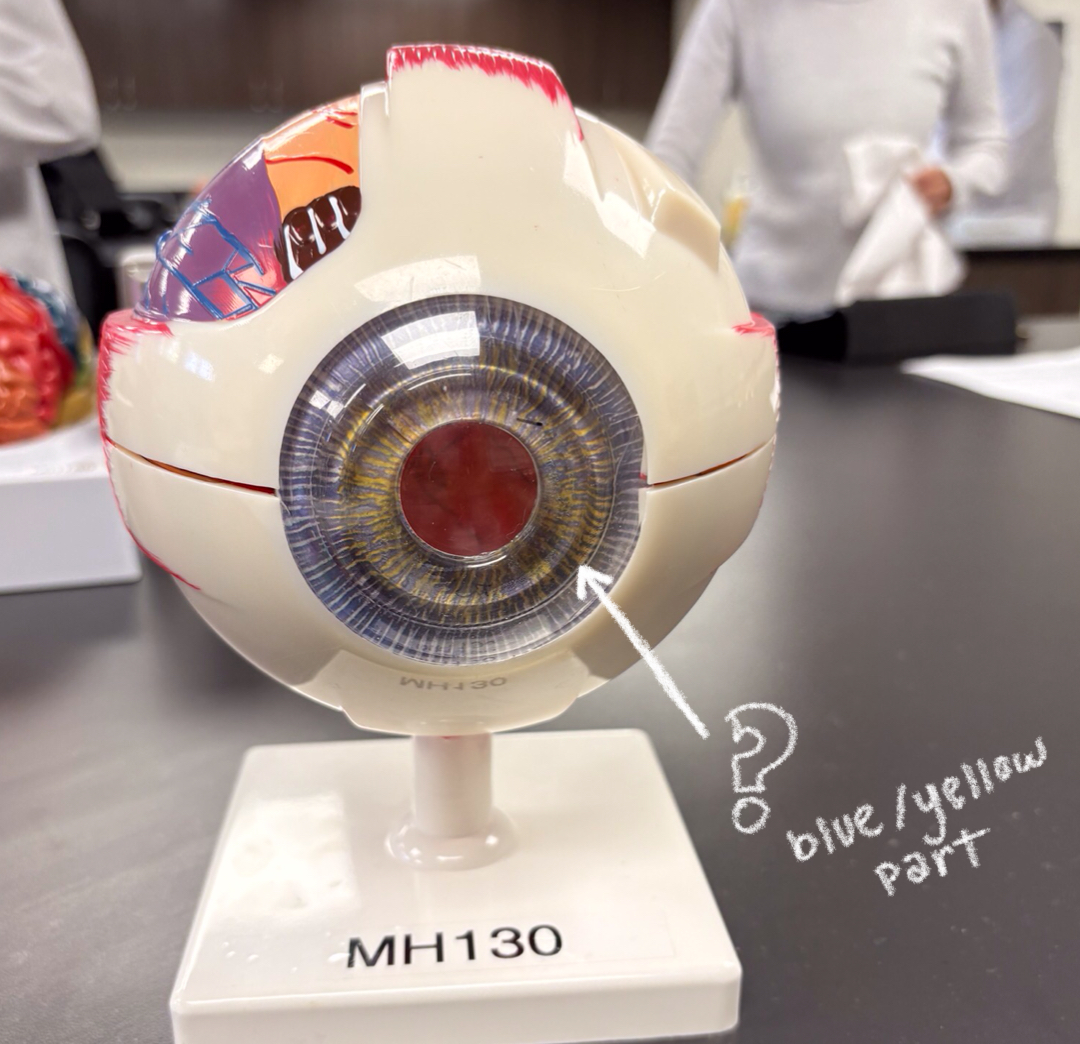
aqueous humor
i think?
sclera
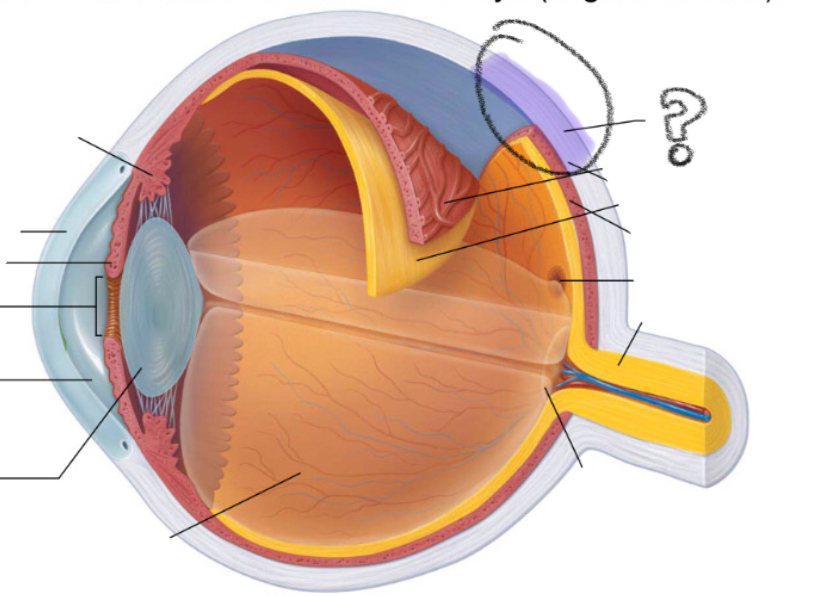
choroid
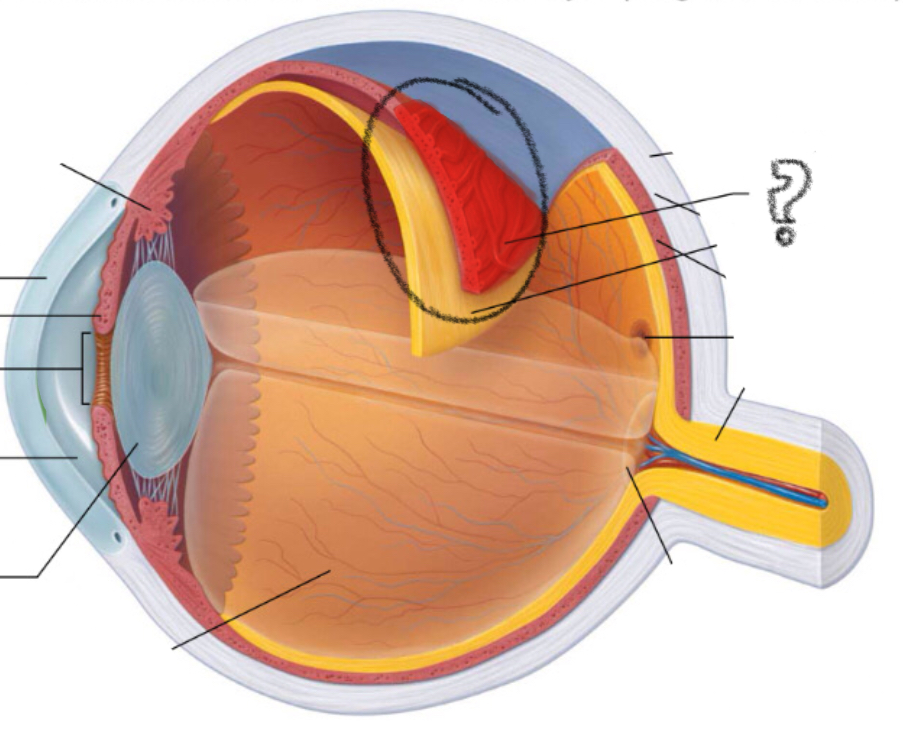
retina
optic disc
optic nerve
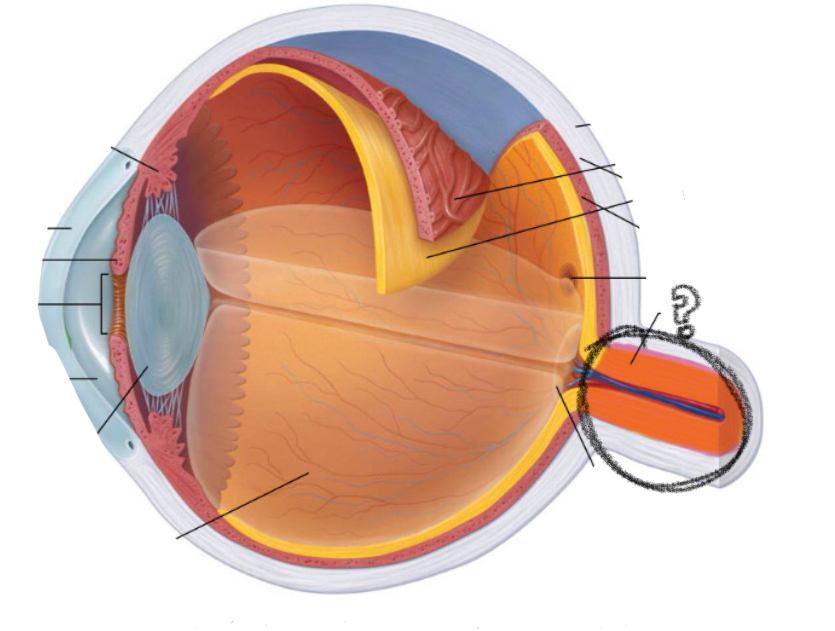
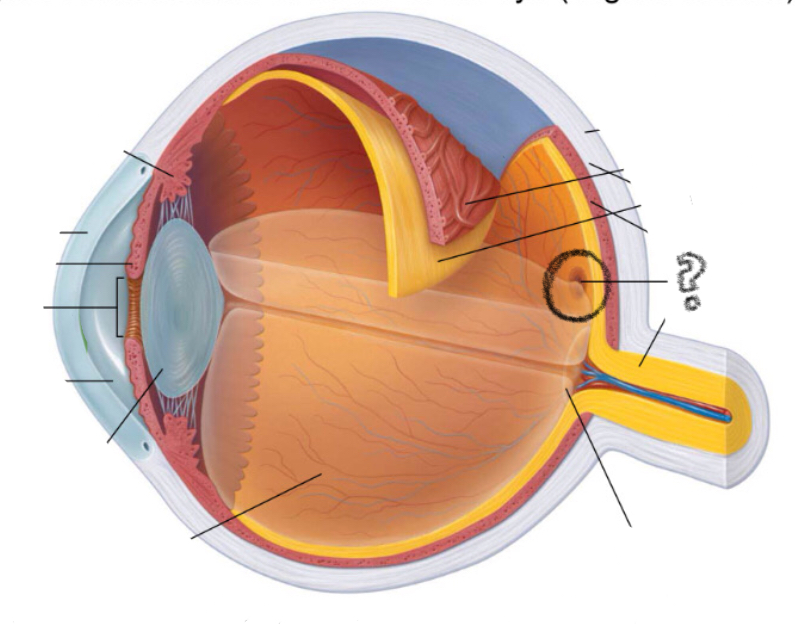
fovea centralis
rods
photoreceptor for low light/ black and white vision
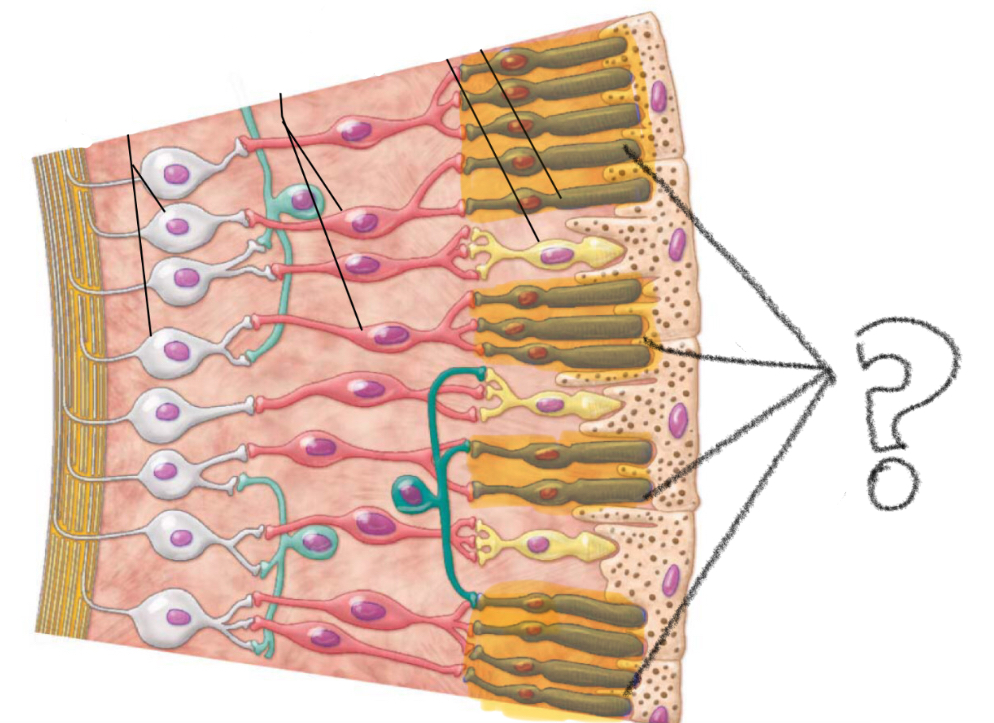
cones
photoreceptors for brighter colors/ color vision
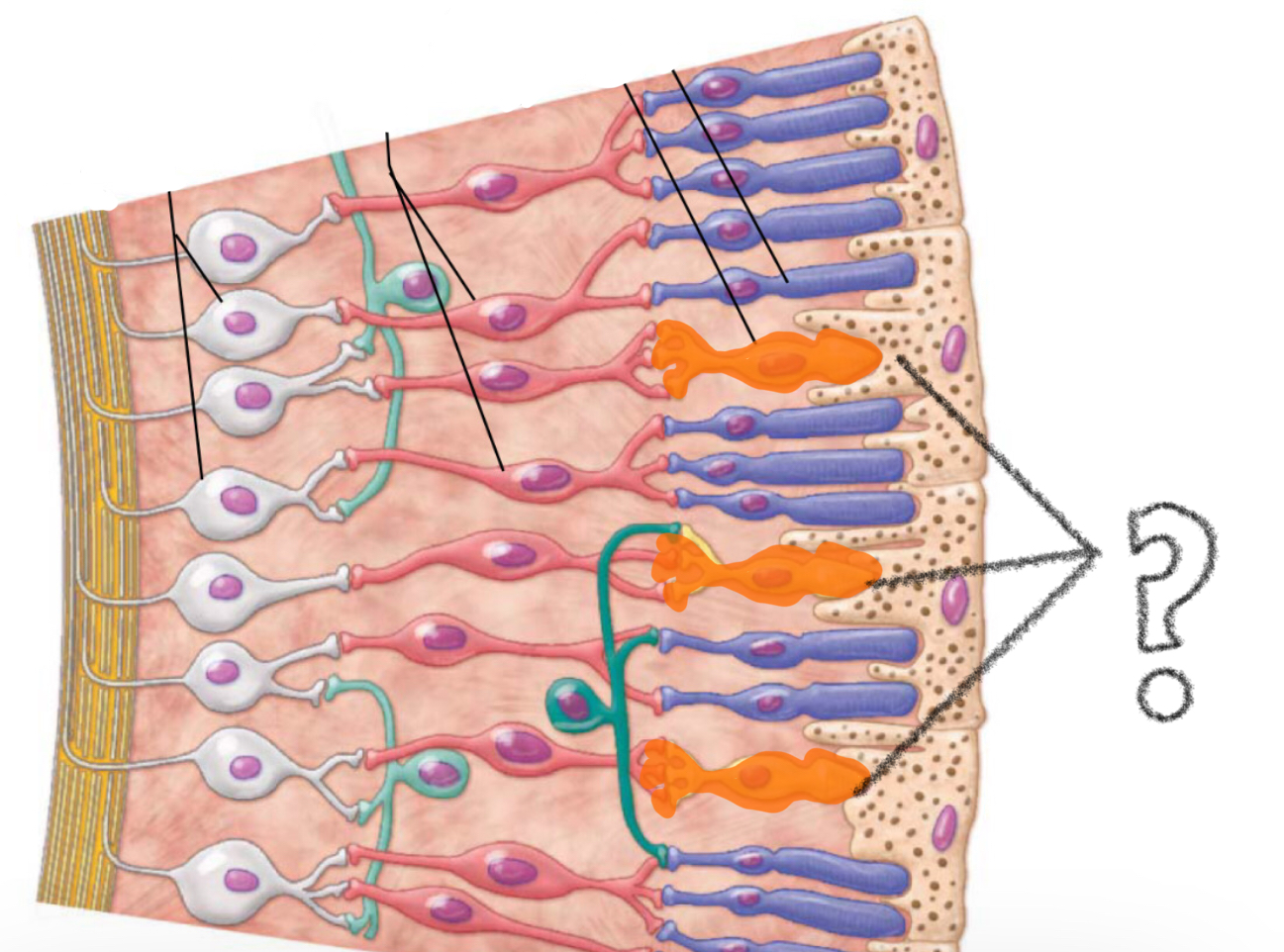
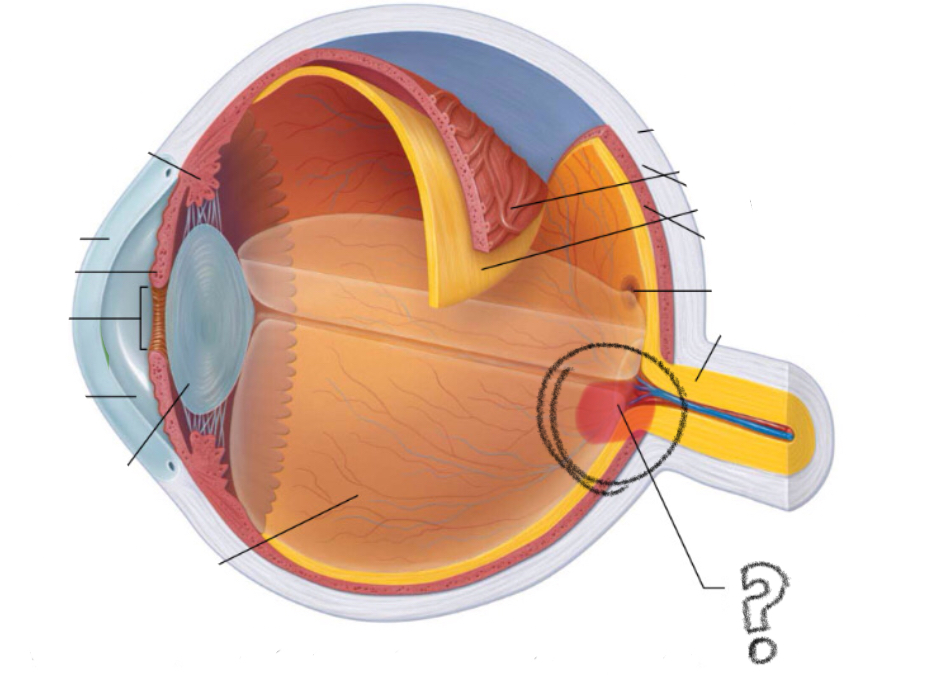
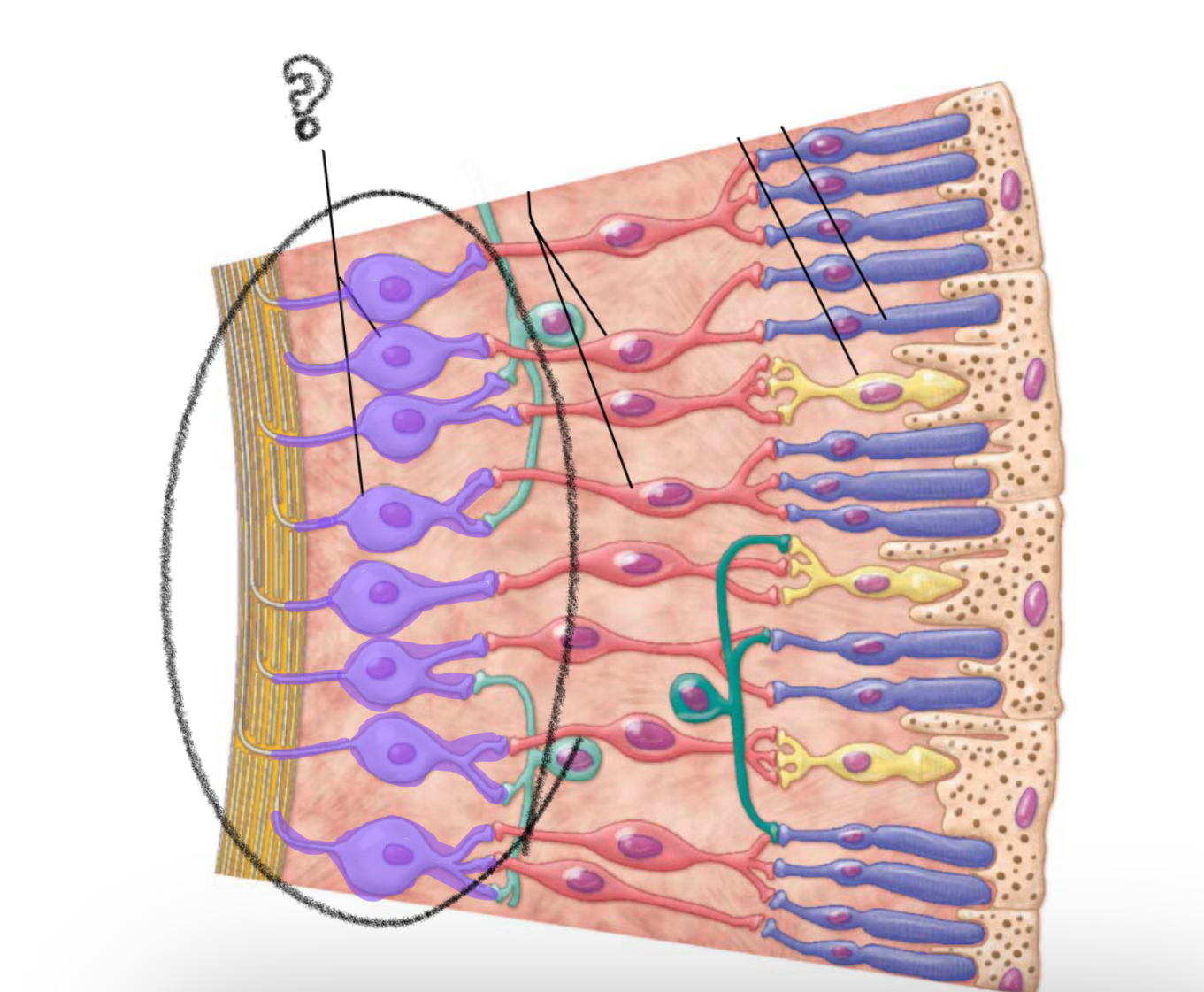
bipolar cells
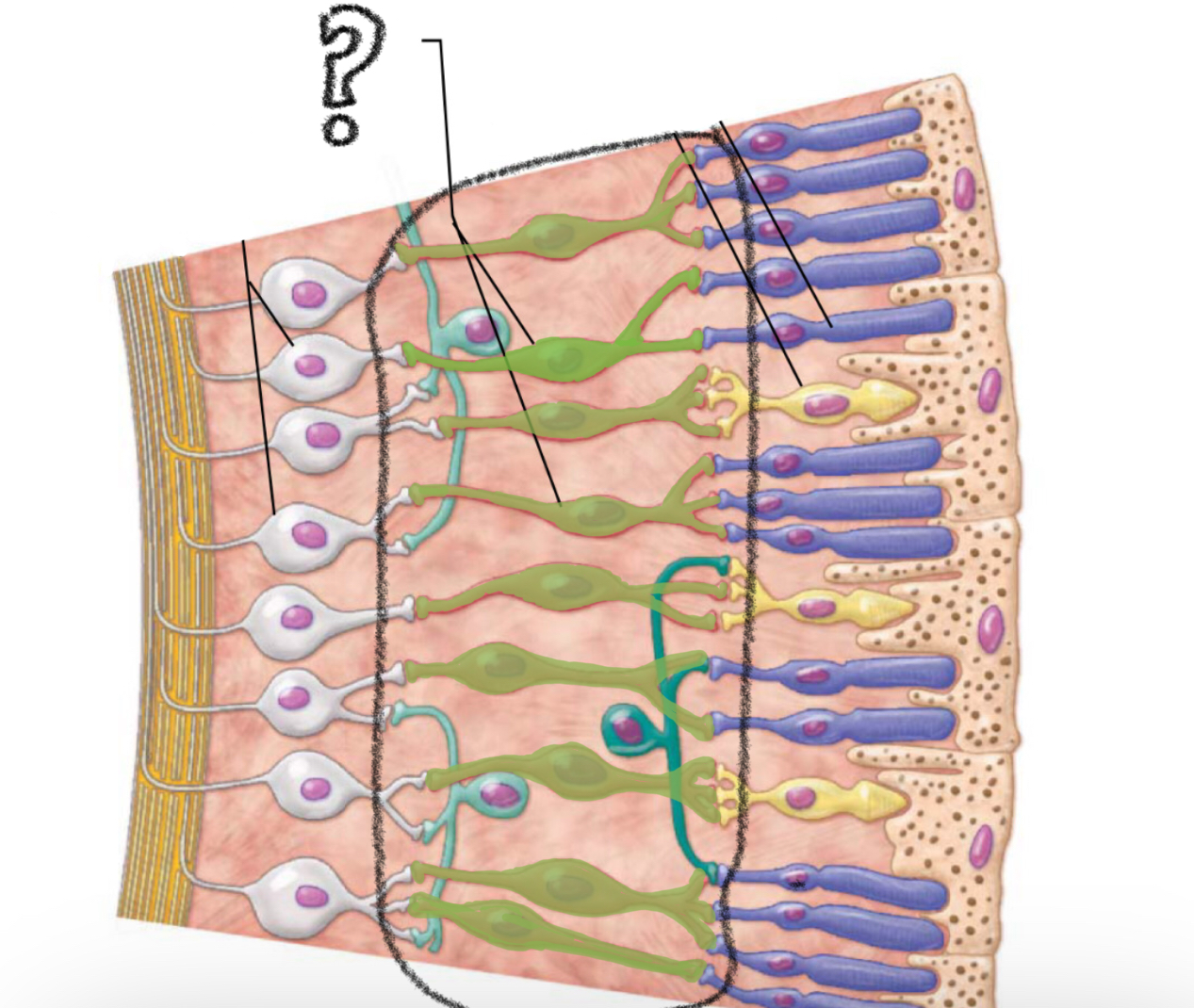
ganglion cells
(nerve cells; axons combine to form optic nerve)
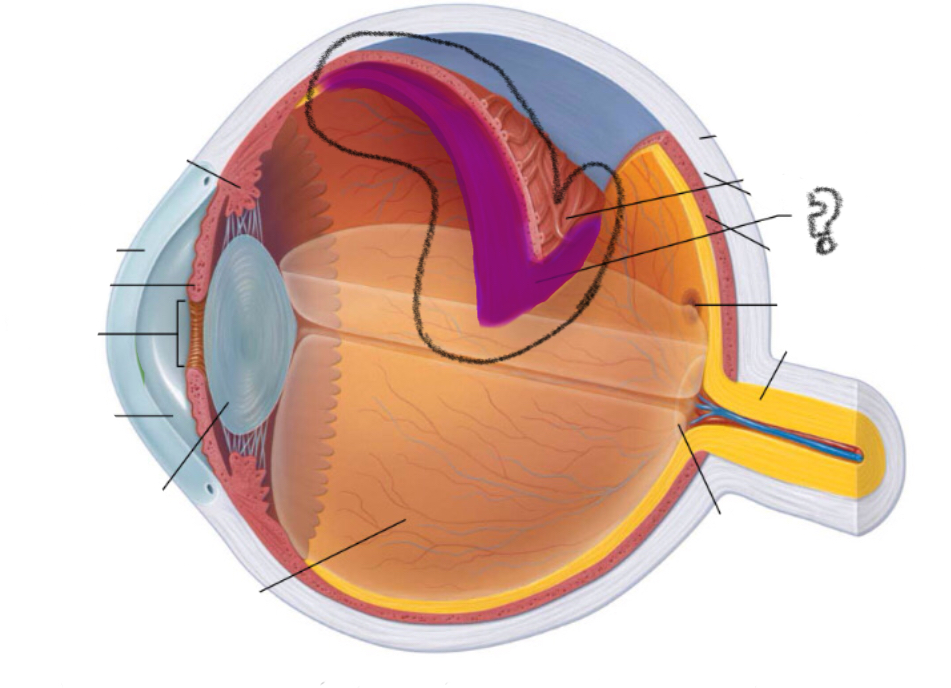
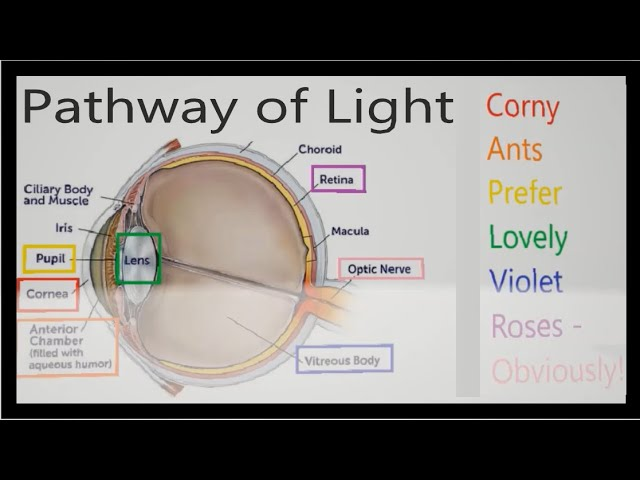
light passes thru the cornea, aqueous humor, pupil, lens and vitreous humor before reaching the retina. It passes to the back of the retina( optic nerve) where it reaches the photoreceptors cells (rods and cones)
pathway for light
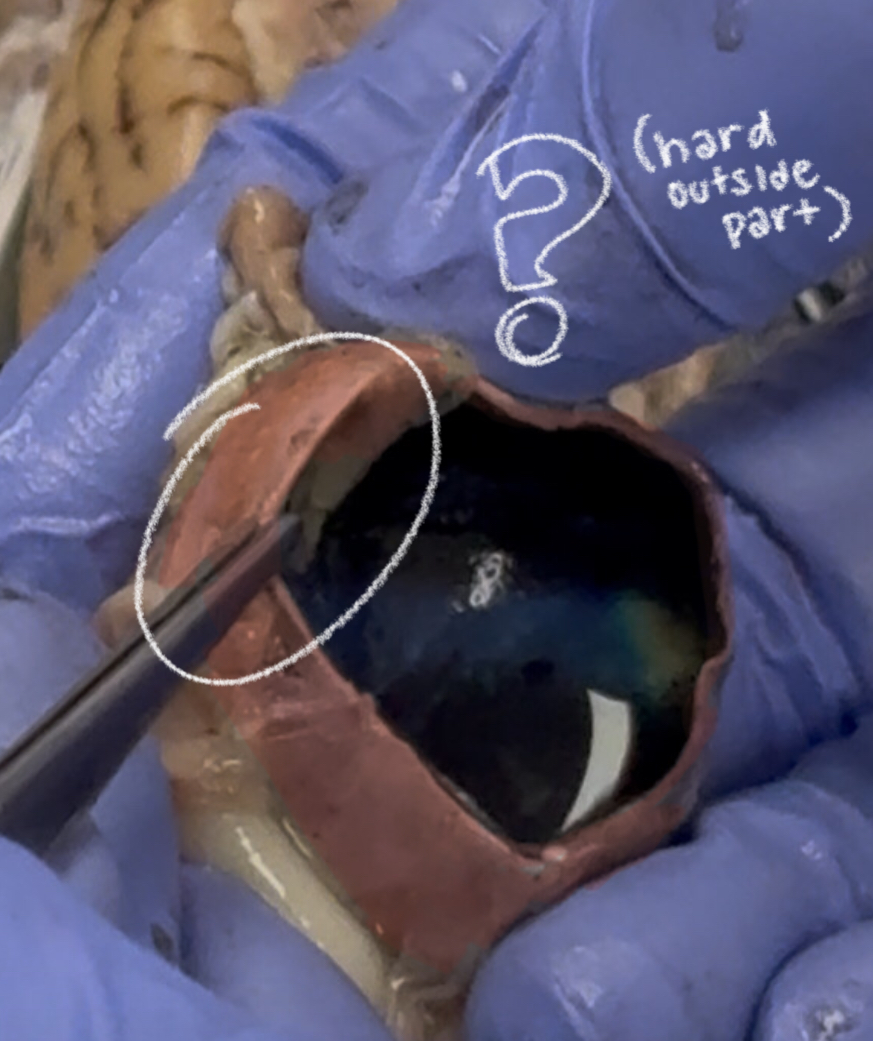
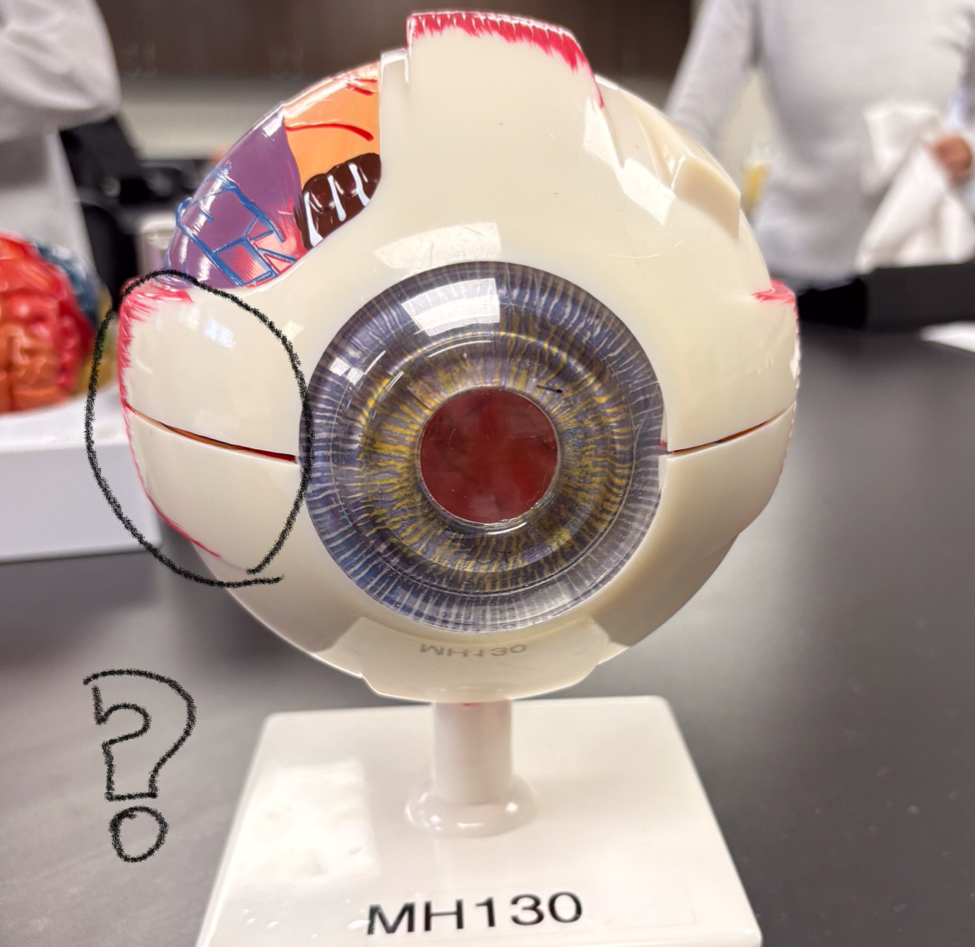
sclera (cow)
cornea (cow)
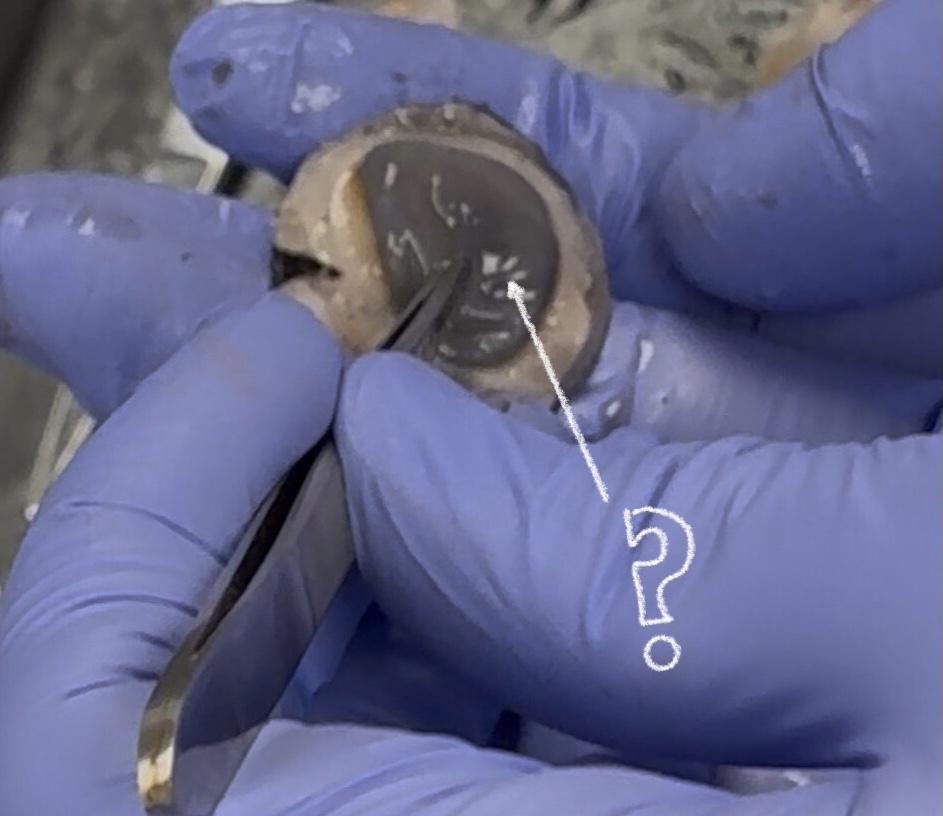

optic nerve (cow)
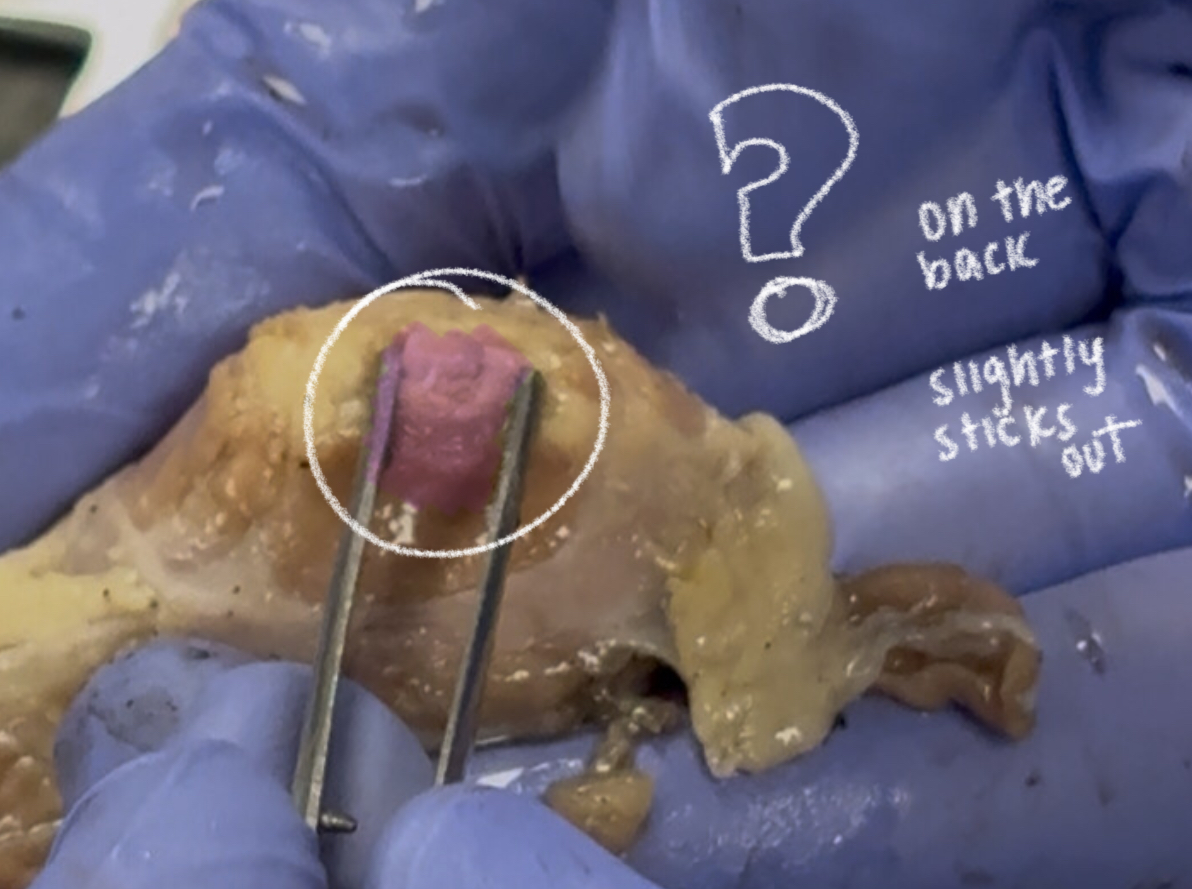
ciliary body (cow)
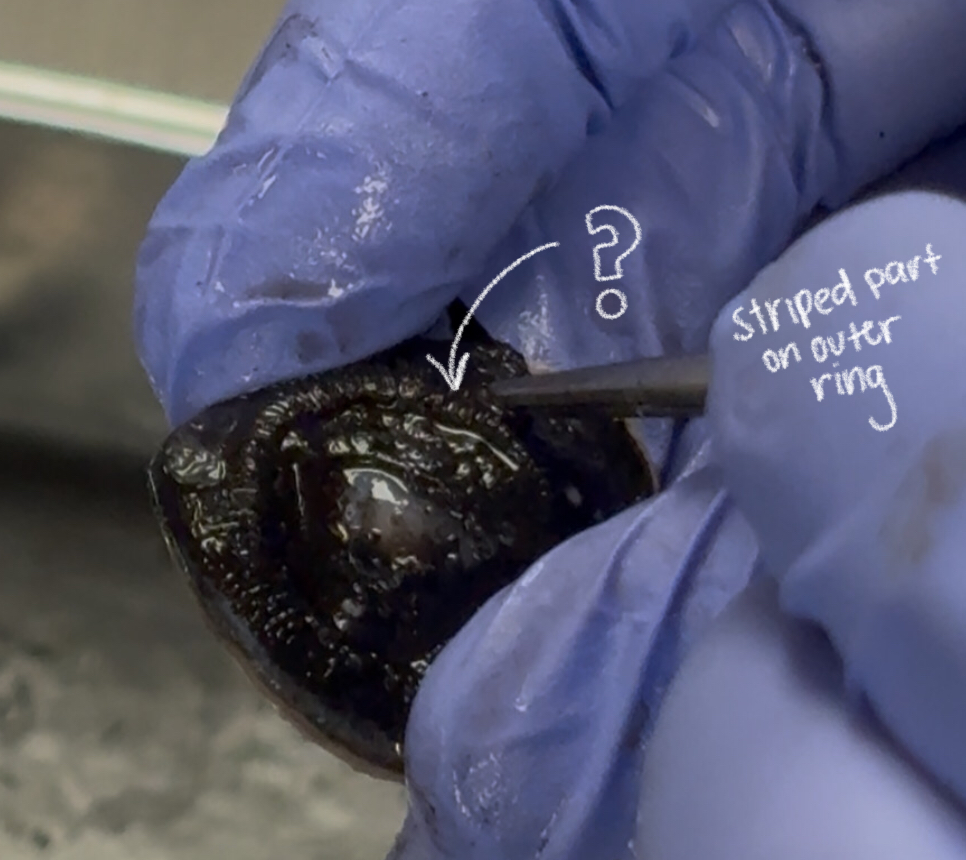

iris (cow)
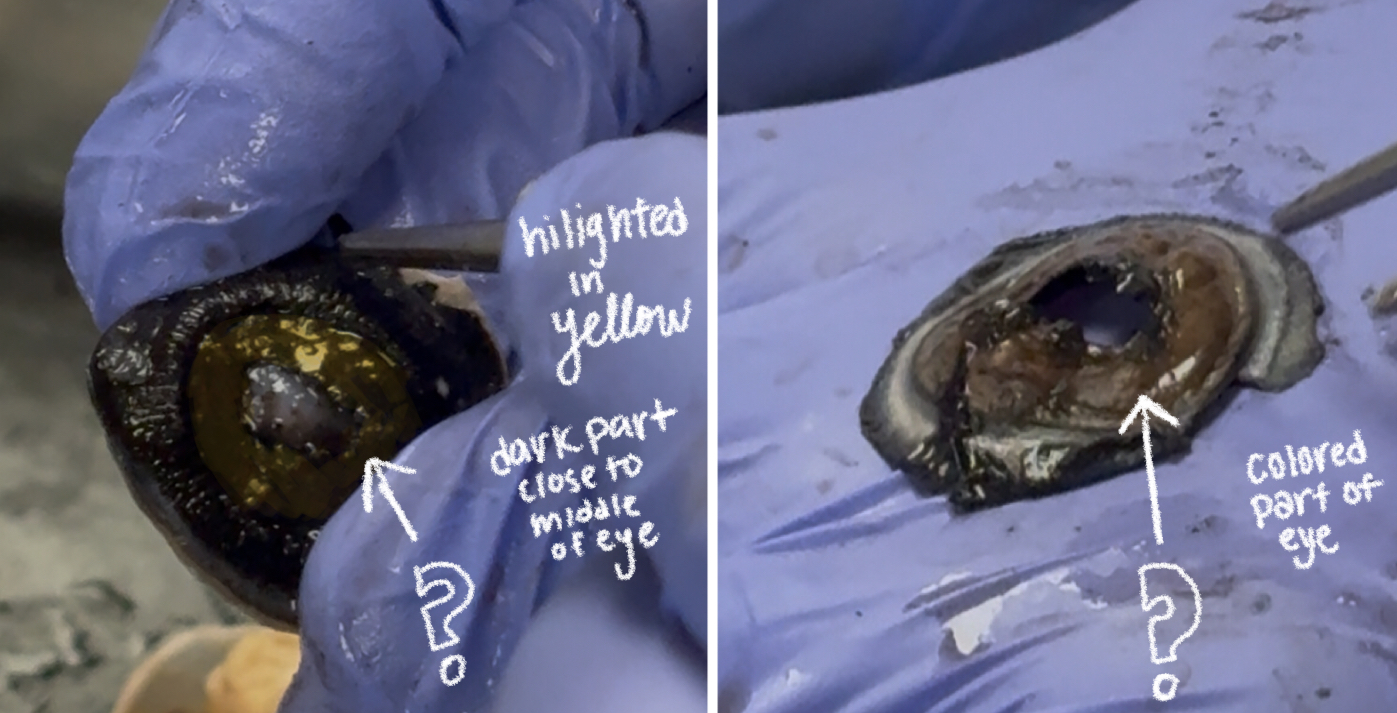
pupil (cow)

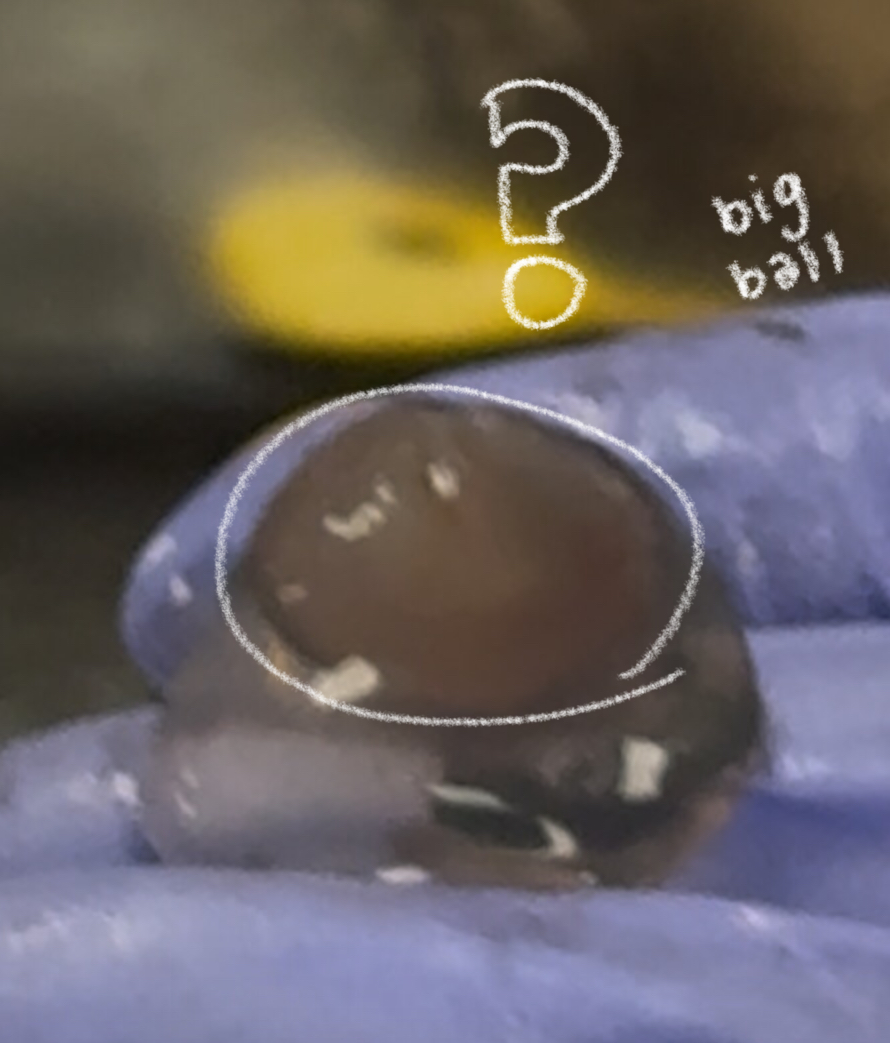
lens (cow)

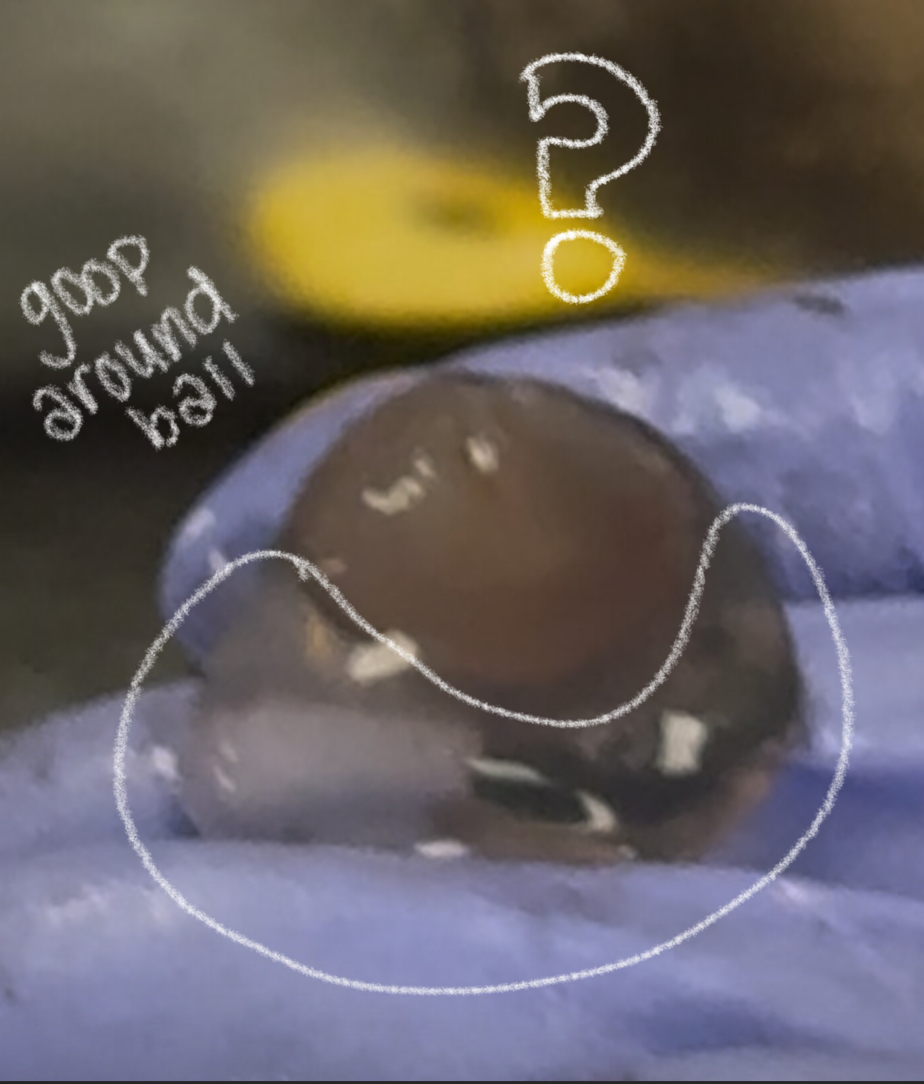
vitreous humor (cow)

retina (cow)
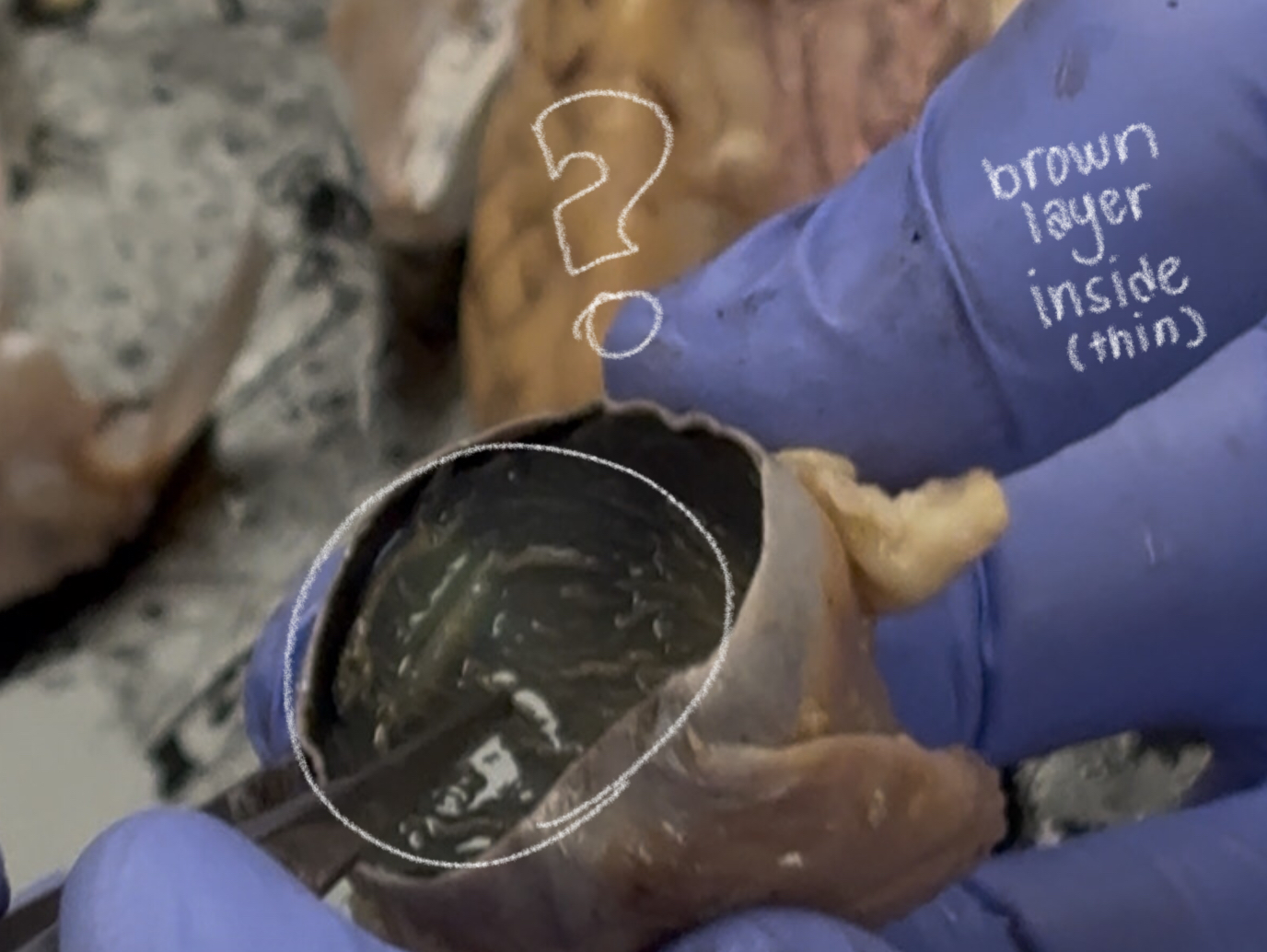

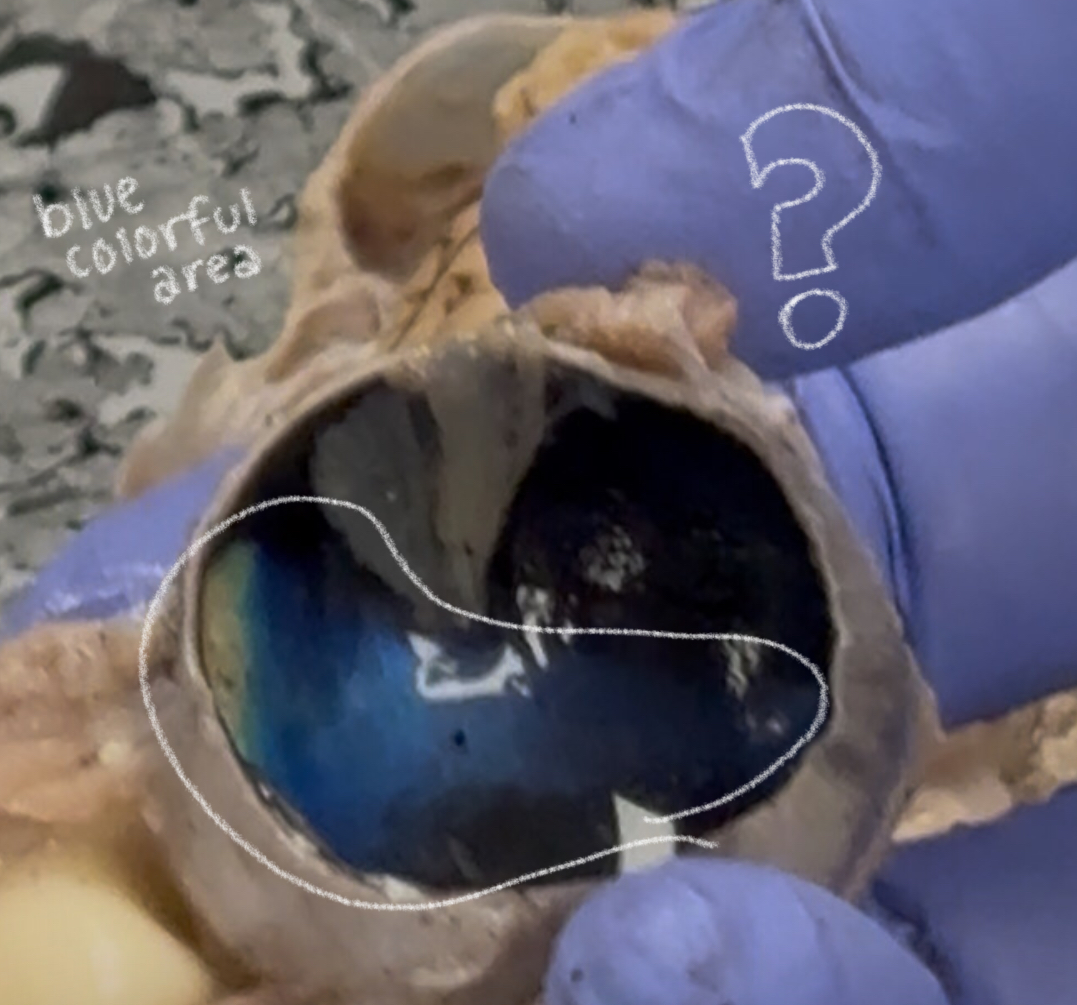
tapetum lucidum (cow)
makes cow & cat eye reflect light; improves night vision
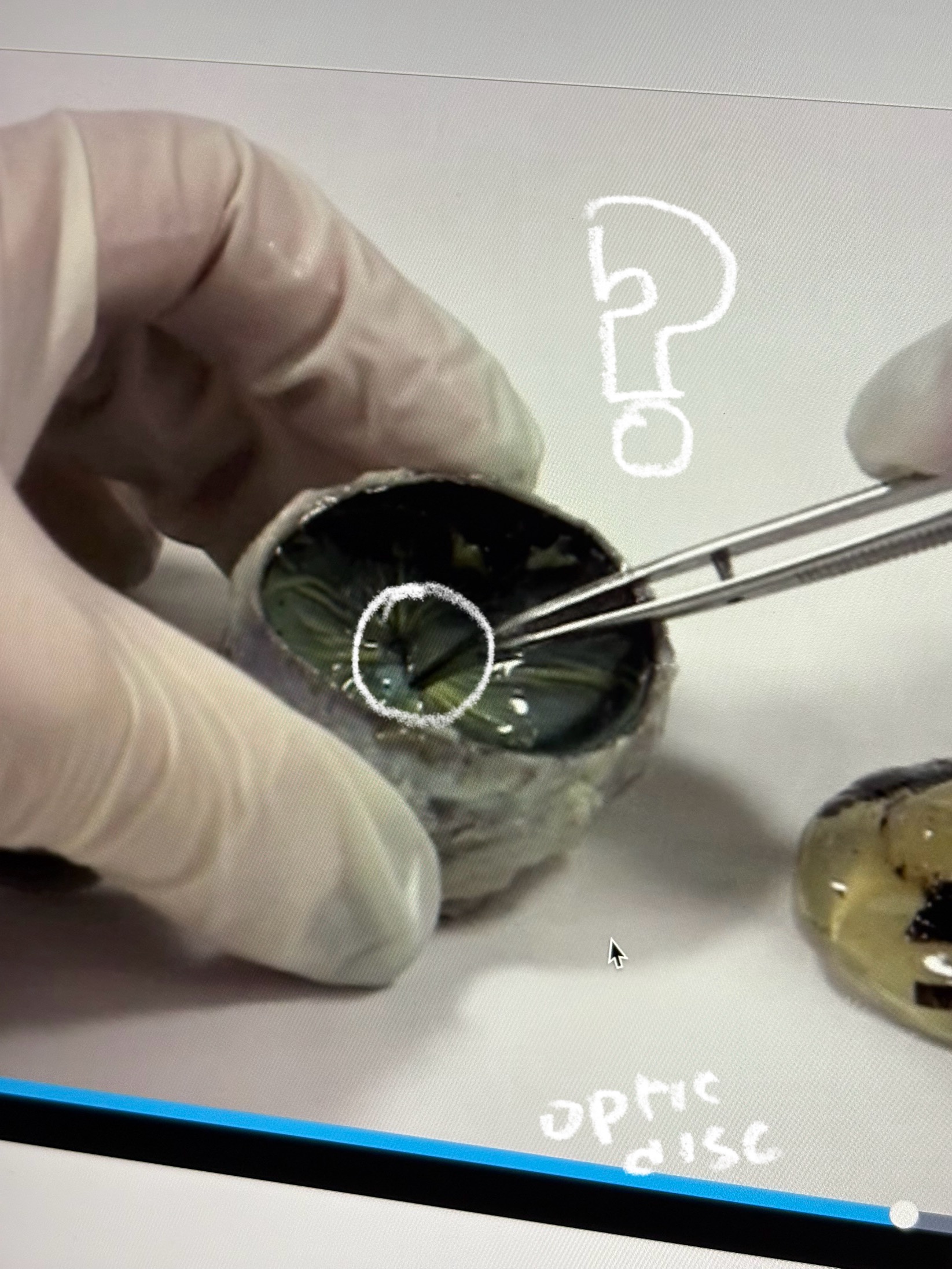
optic disc (cow)
dot in the middle??

sclera model

cornea model

pupil model
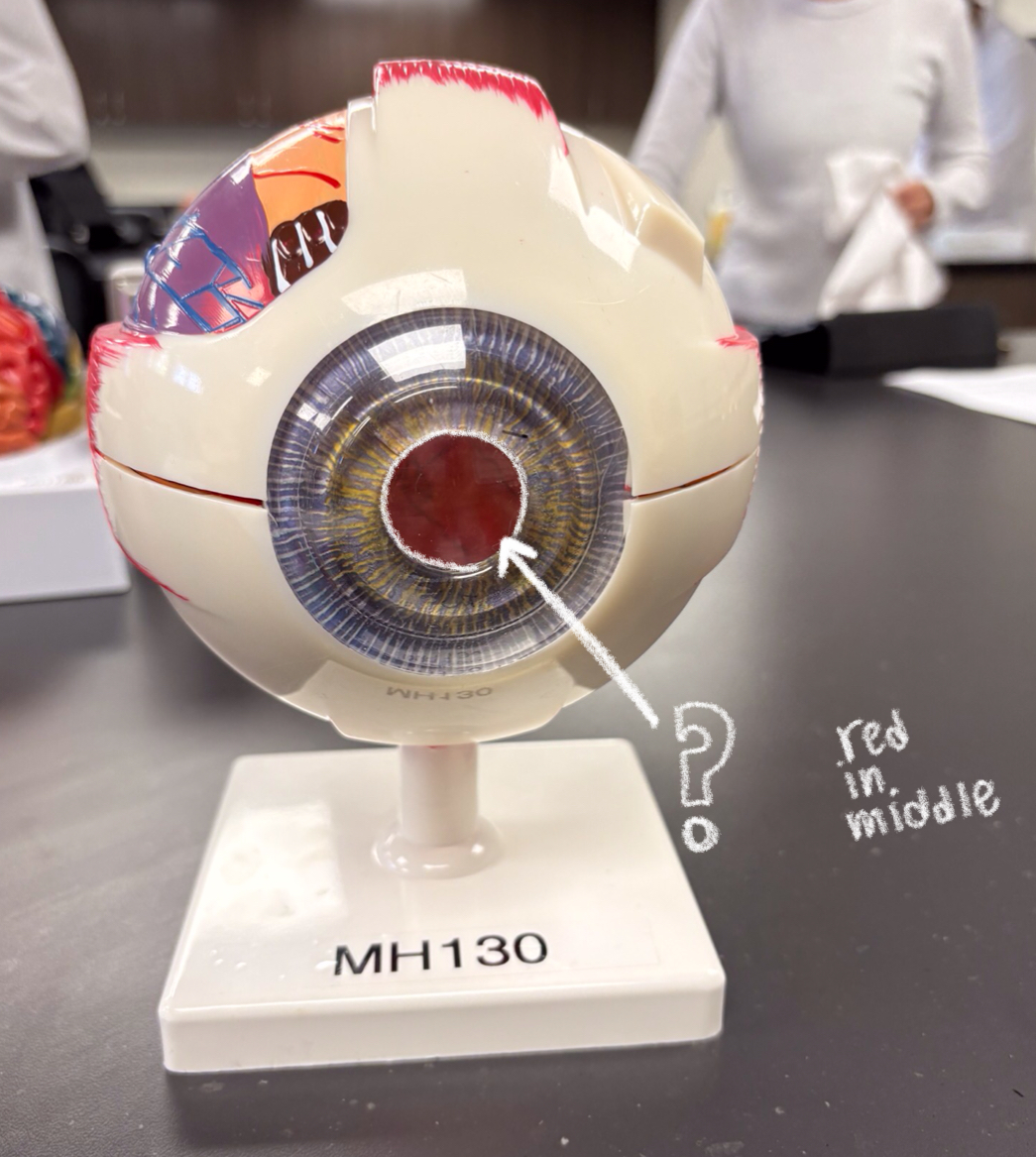
iris model
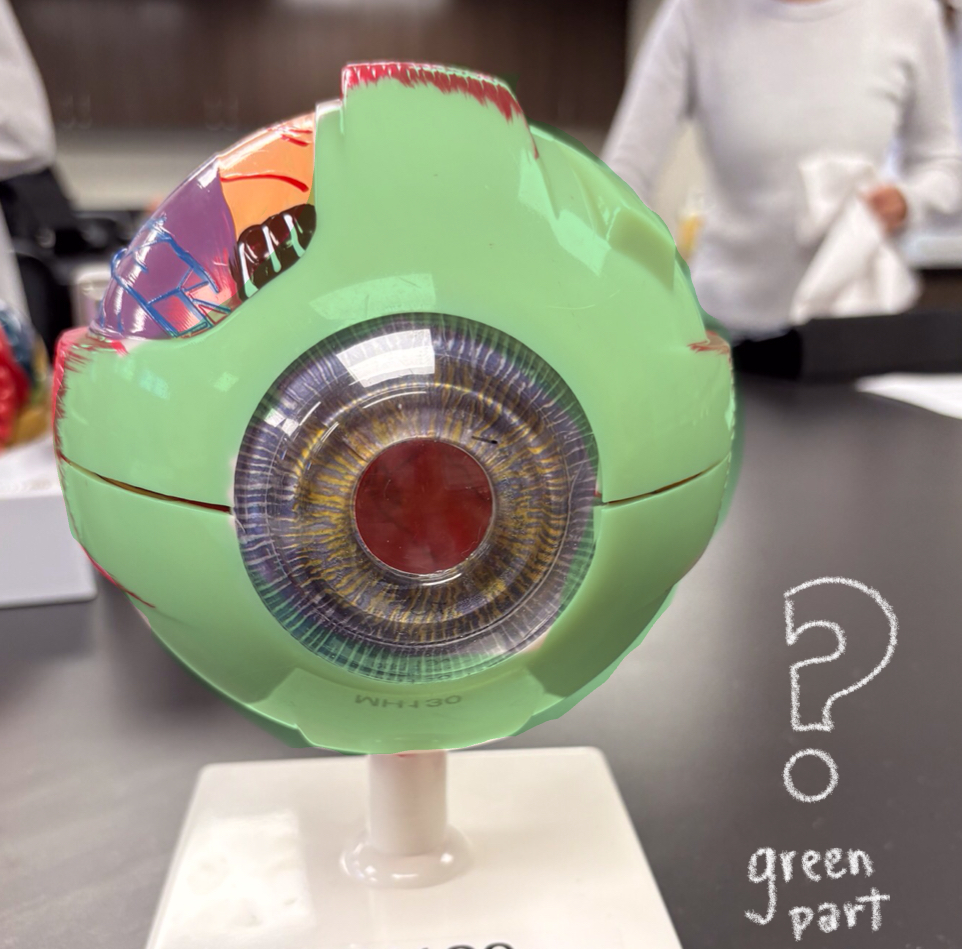
colored part of eye

chorid model
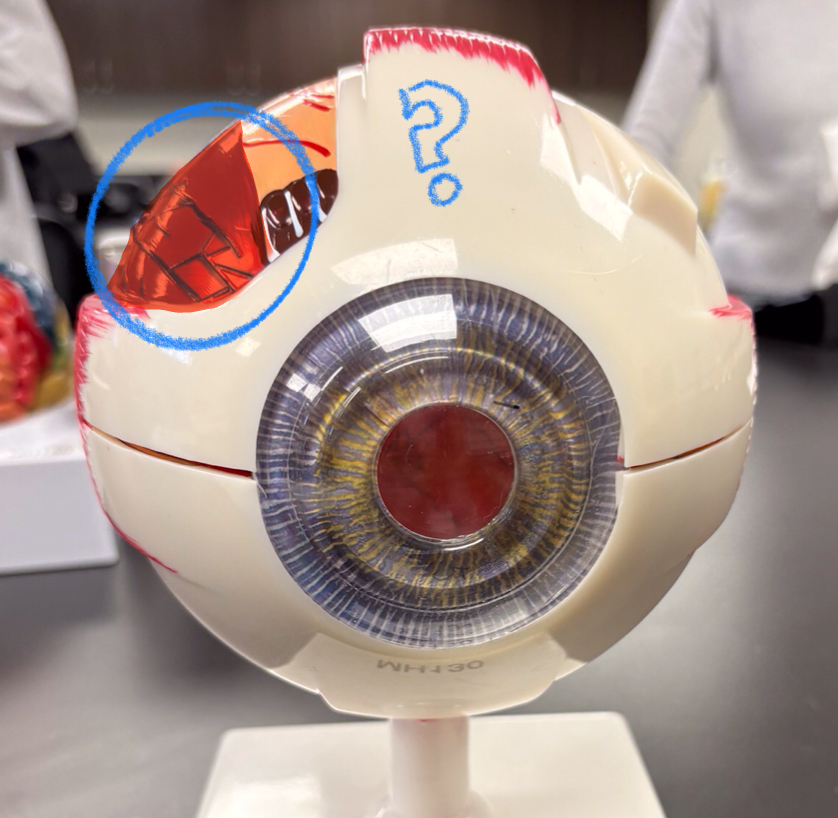
lateral rectus model

superior rectus model
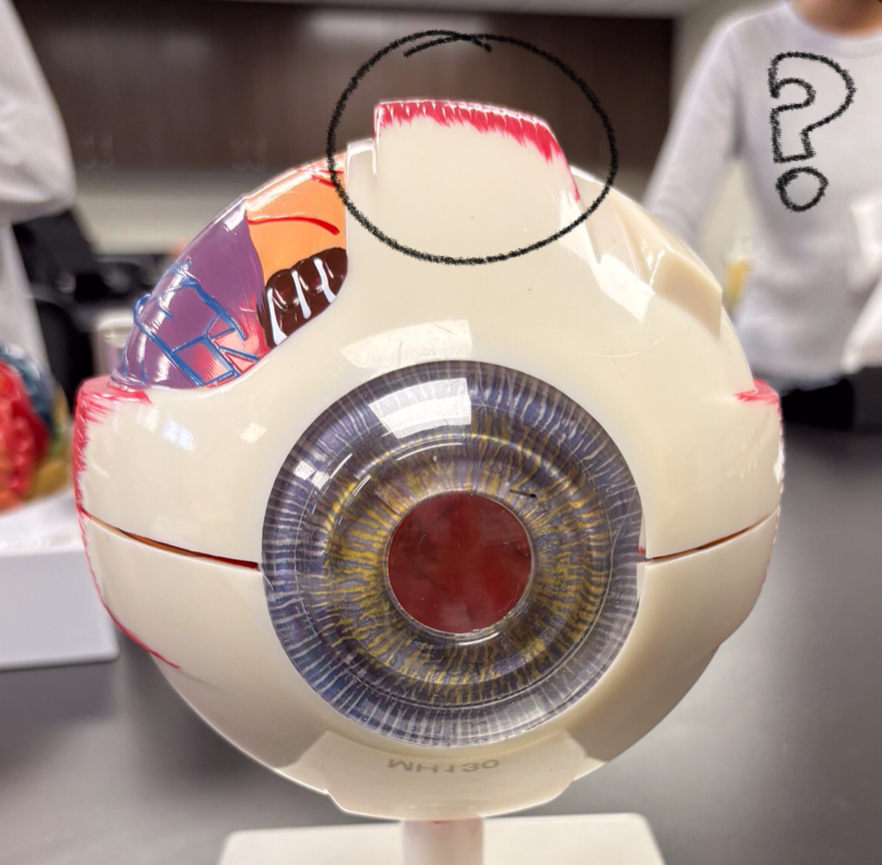

medial rectus model
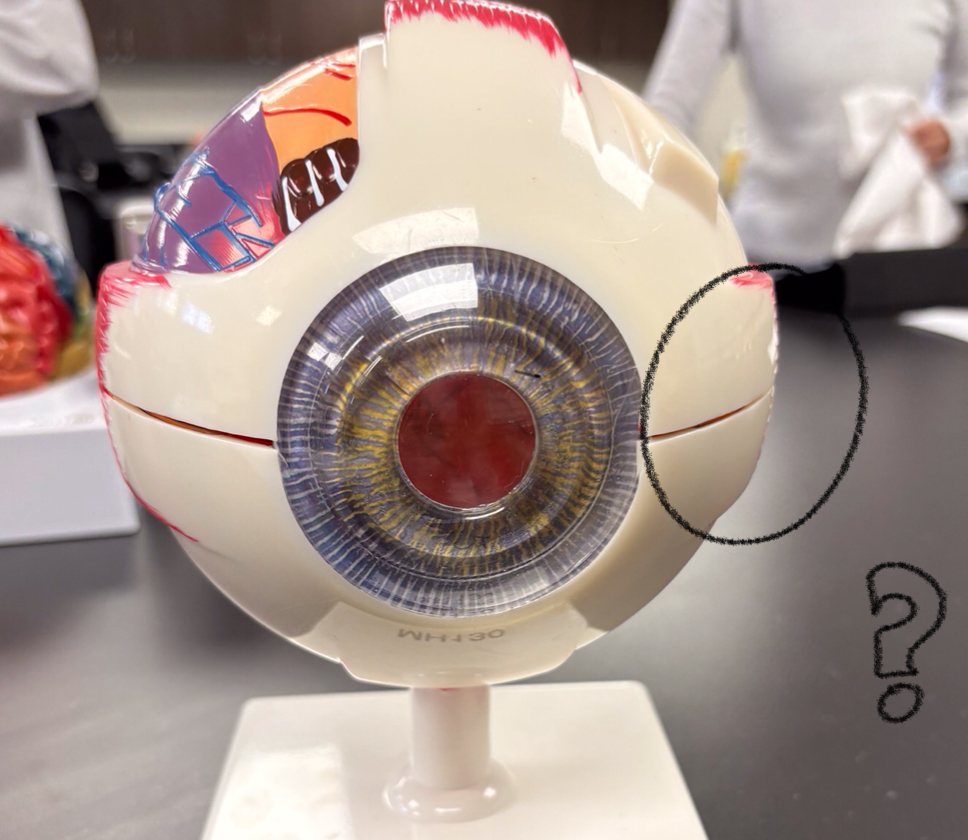
inferior rectus model
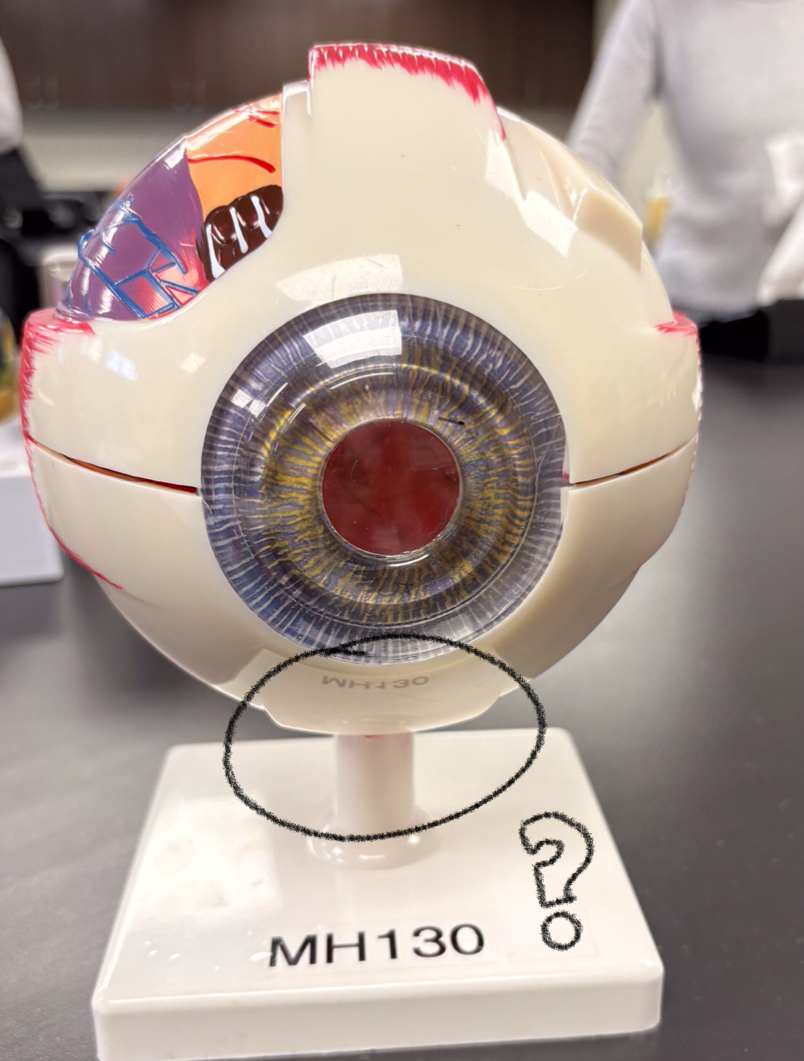

superior oblique model
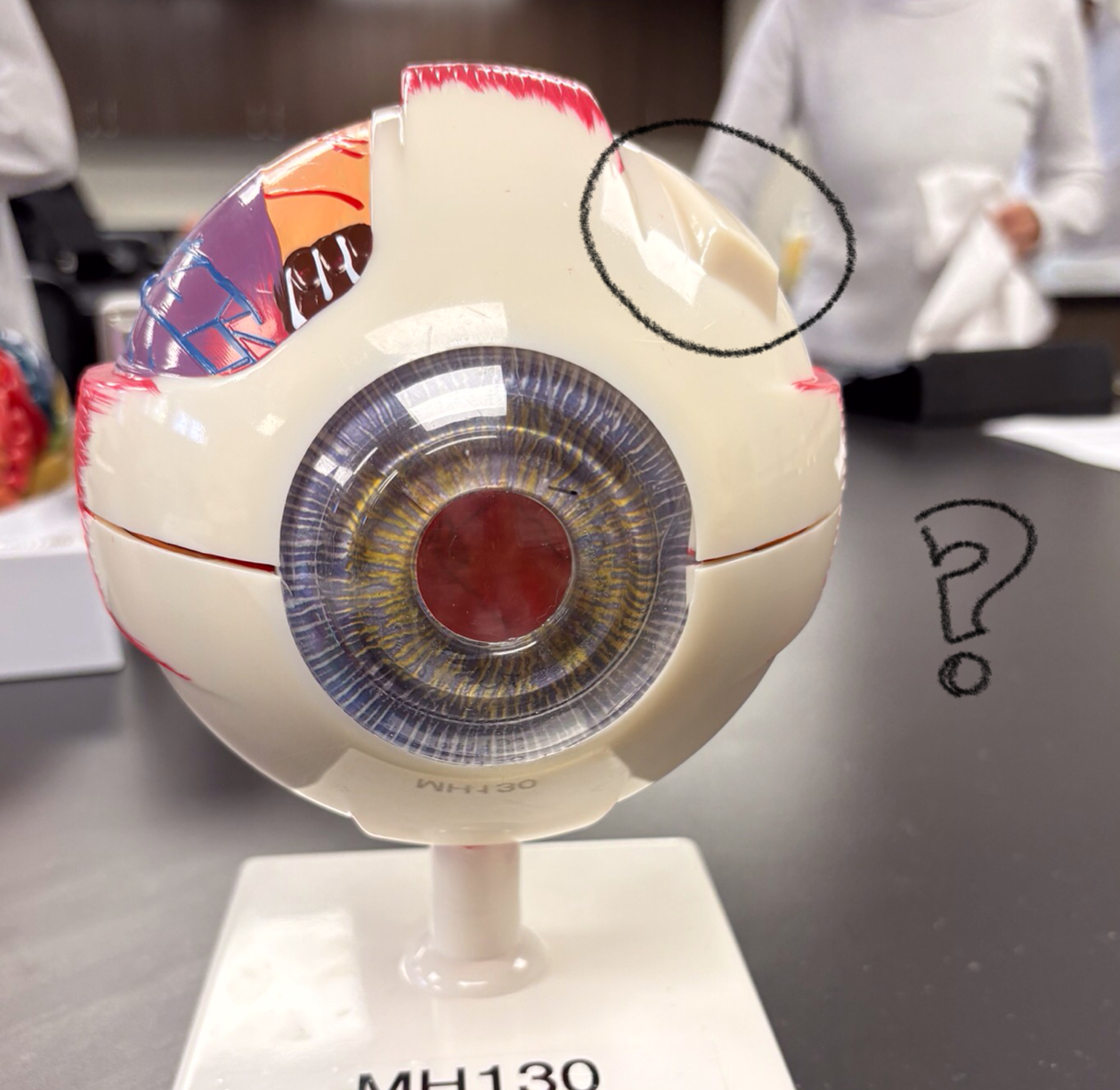

inferior oblique model
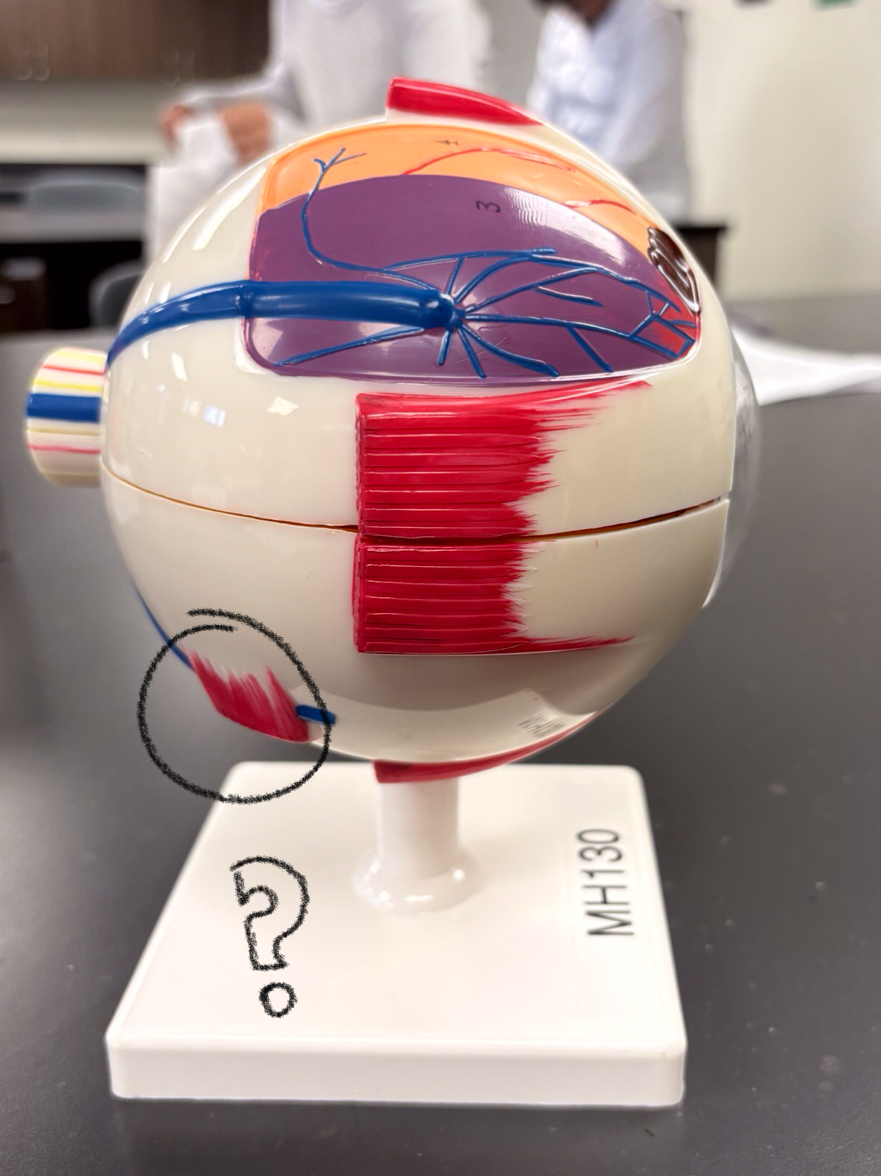

optic nerve model
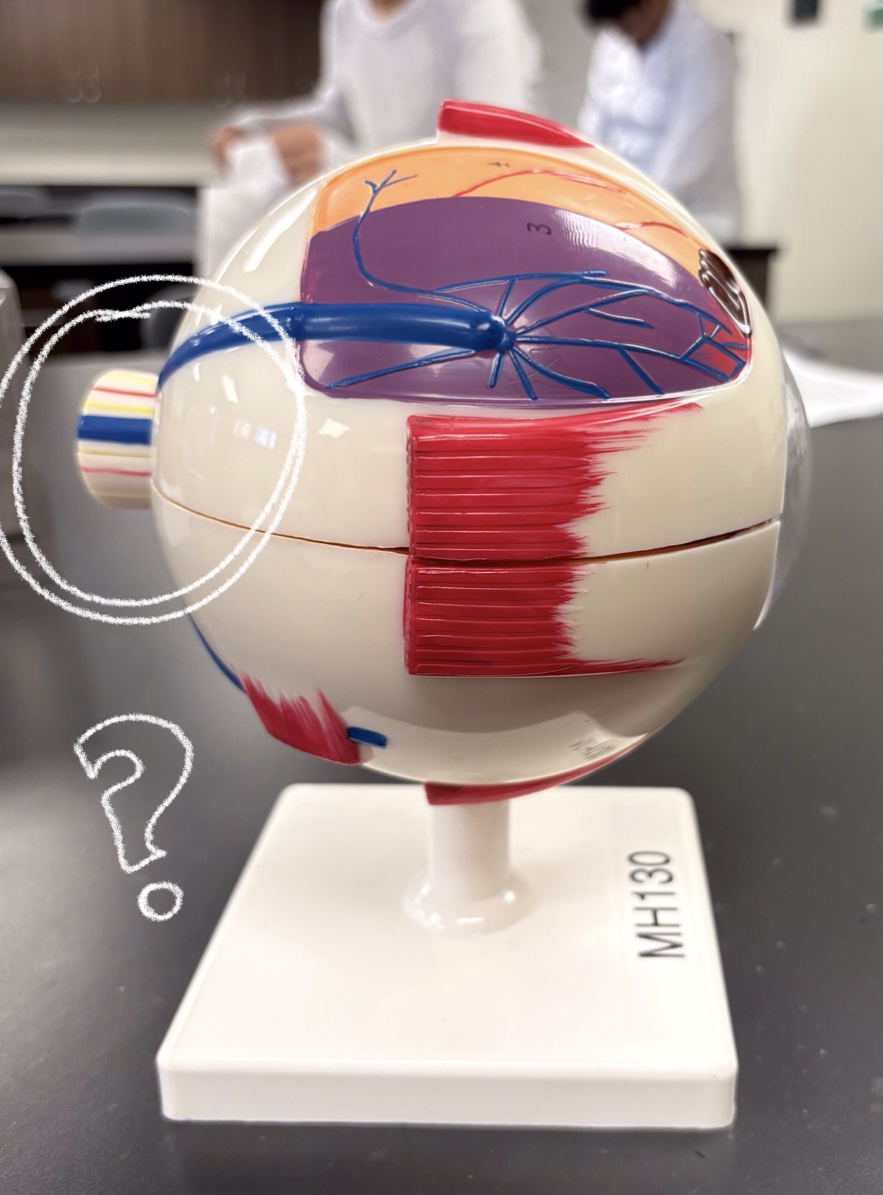

fovea centralis model
hole/ yellow part by retina (might be below white circle)
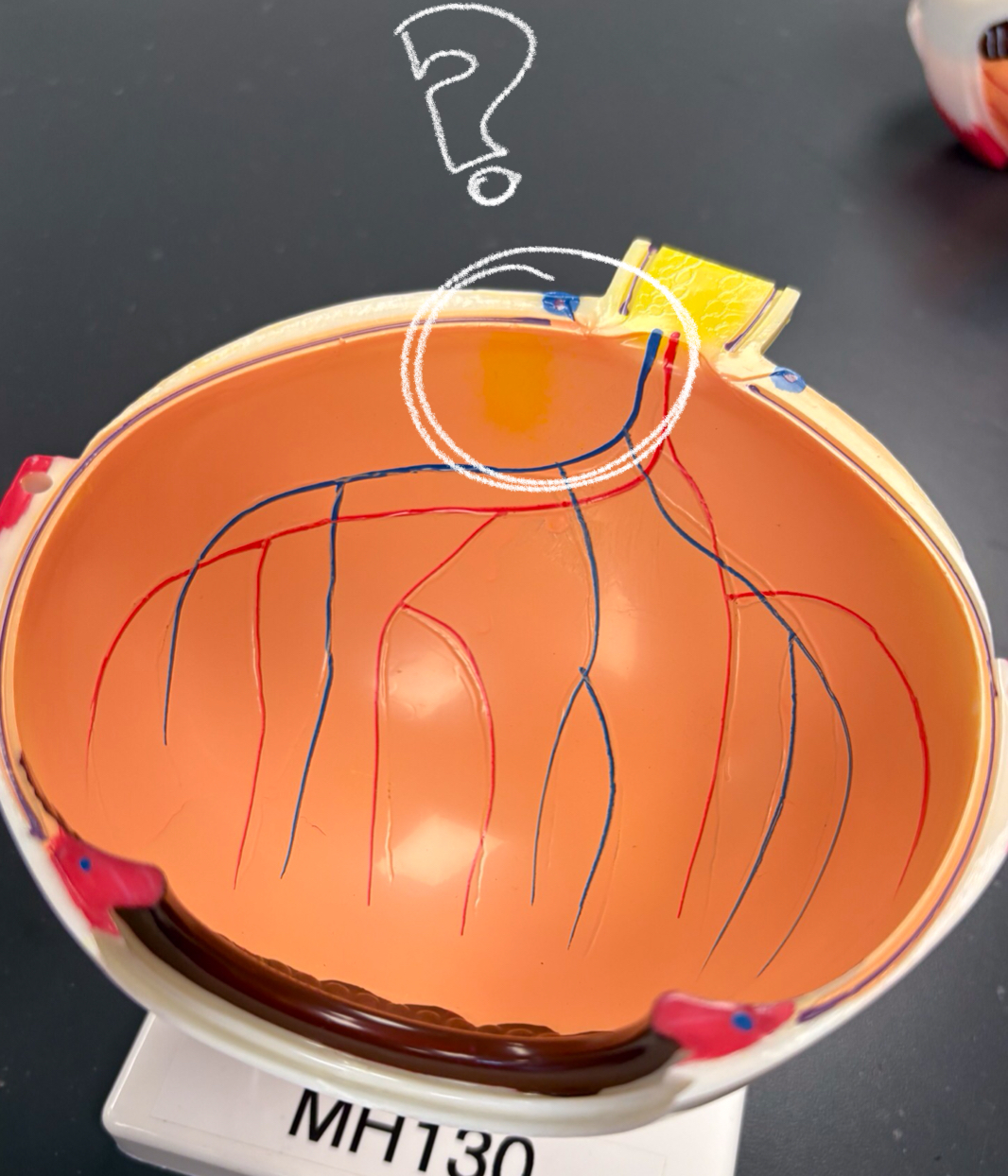

retina model
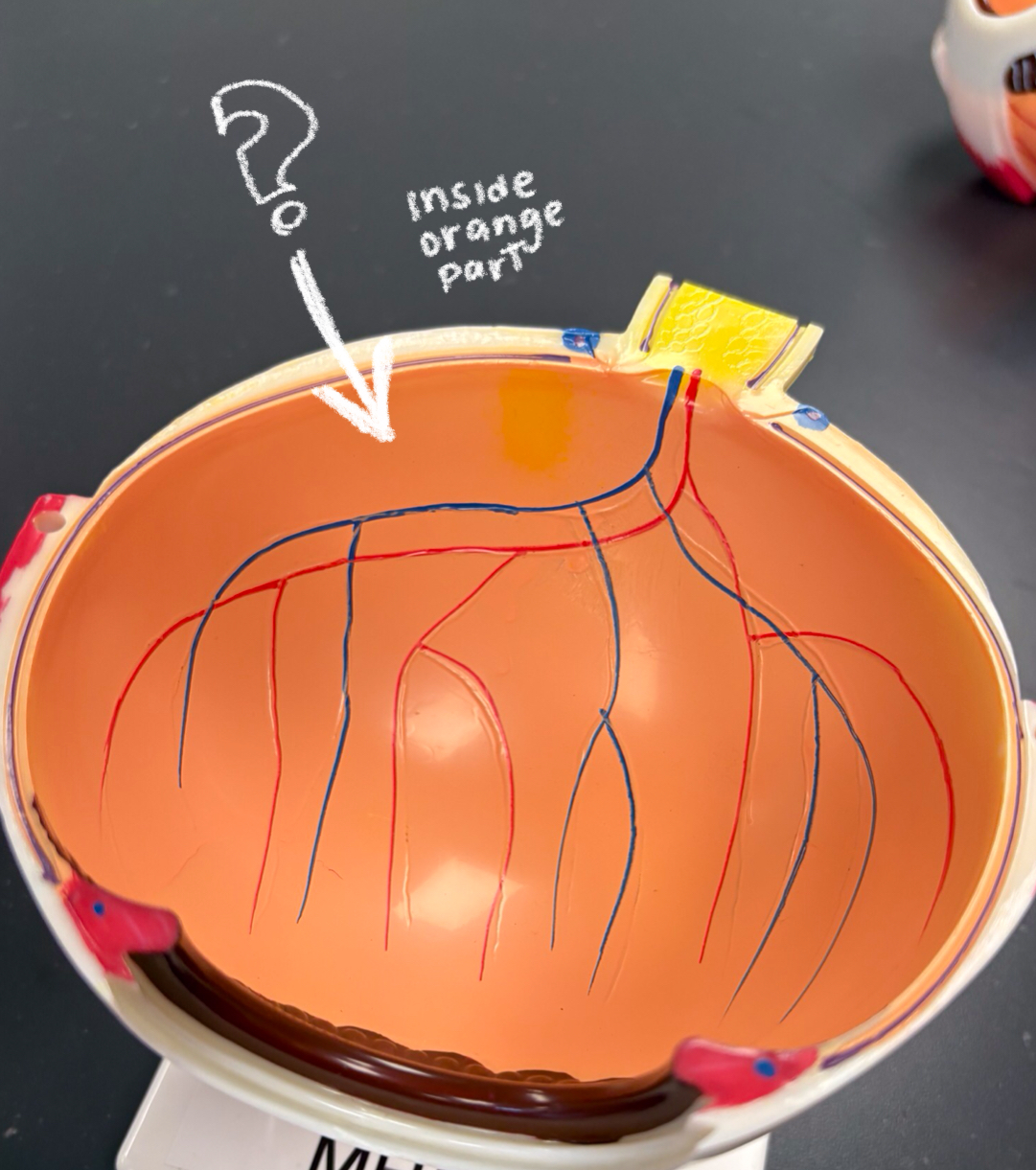

optic disc model
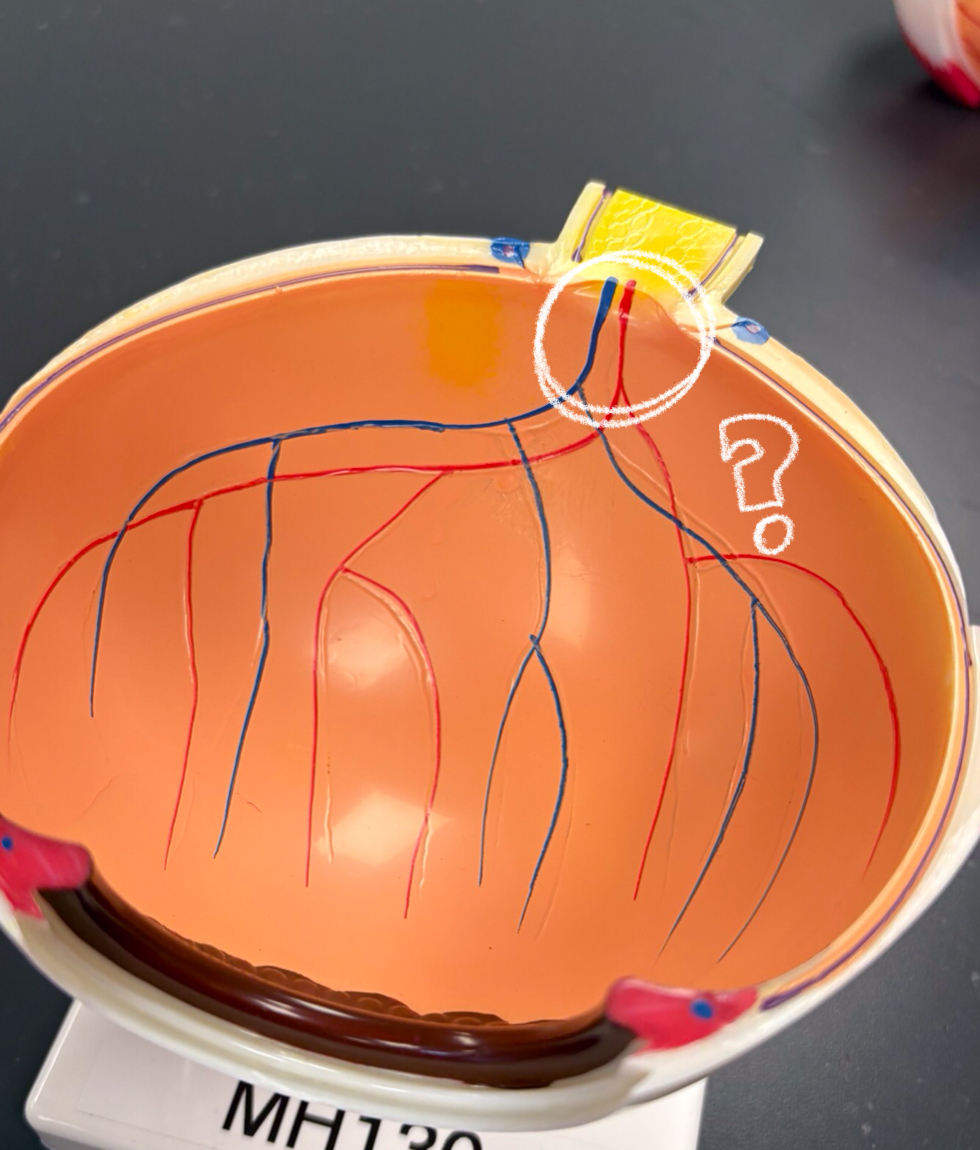
lens model
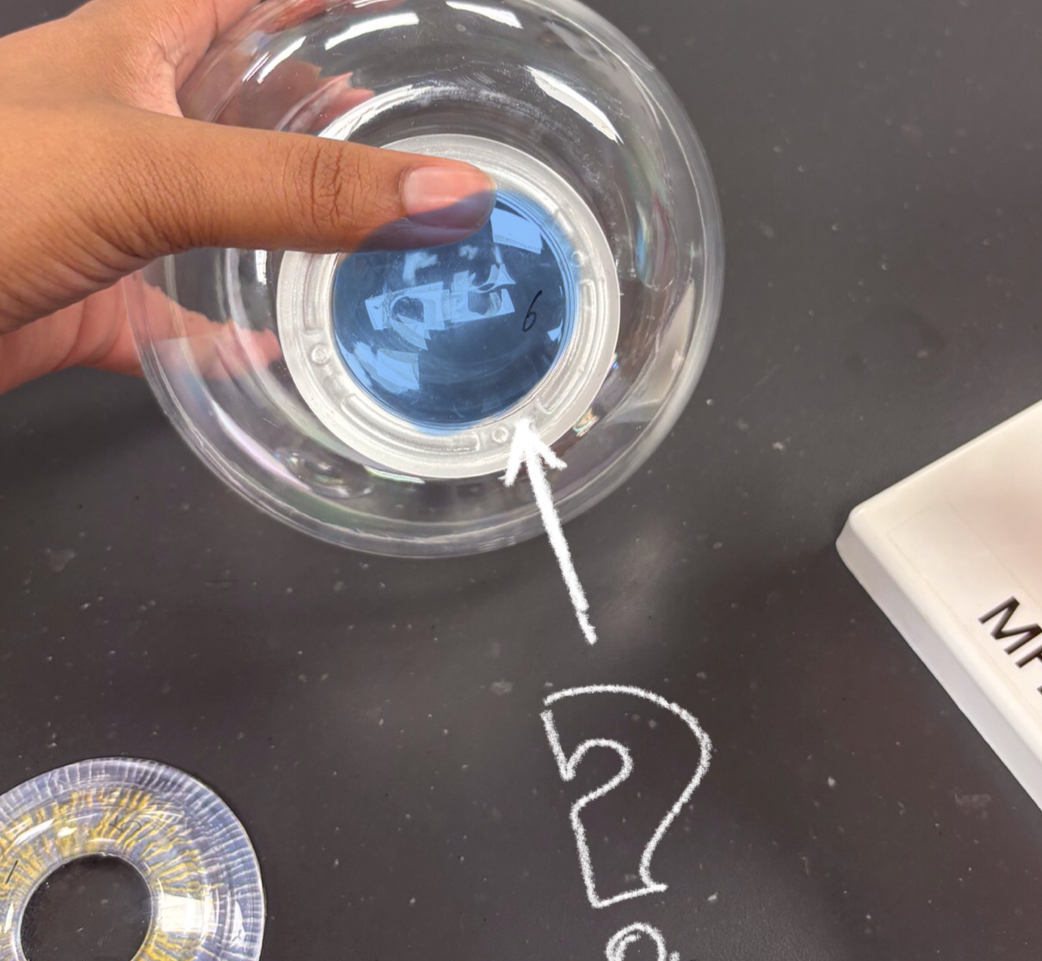

vitrous humor model

ciliary body model
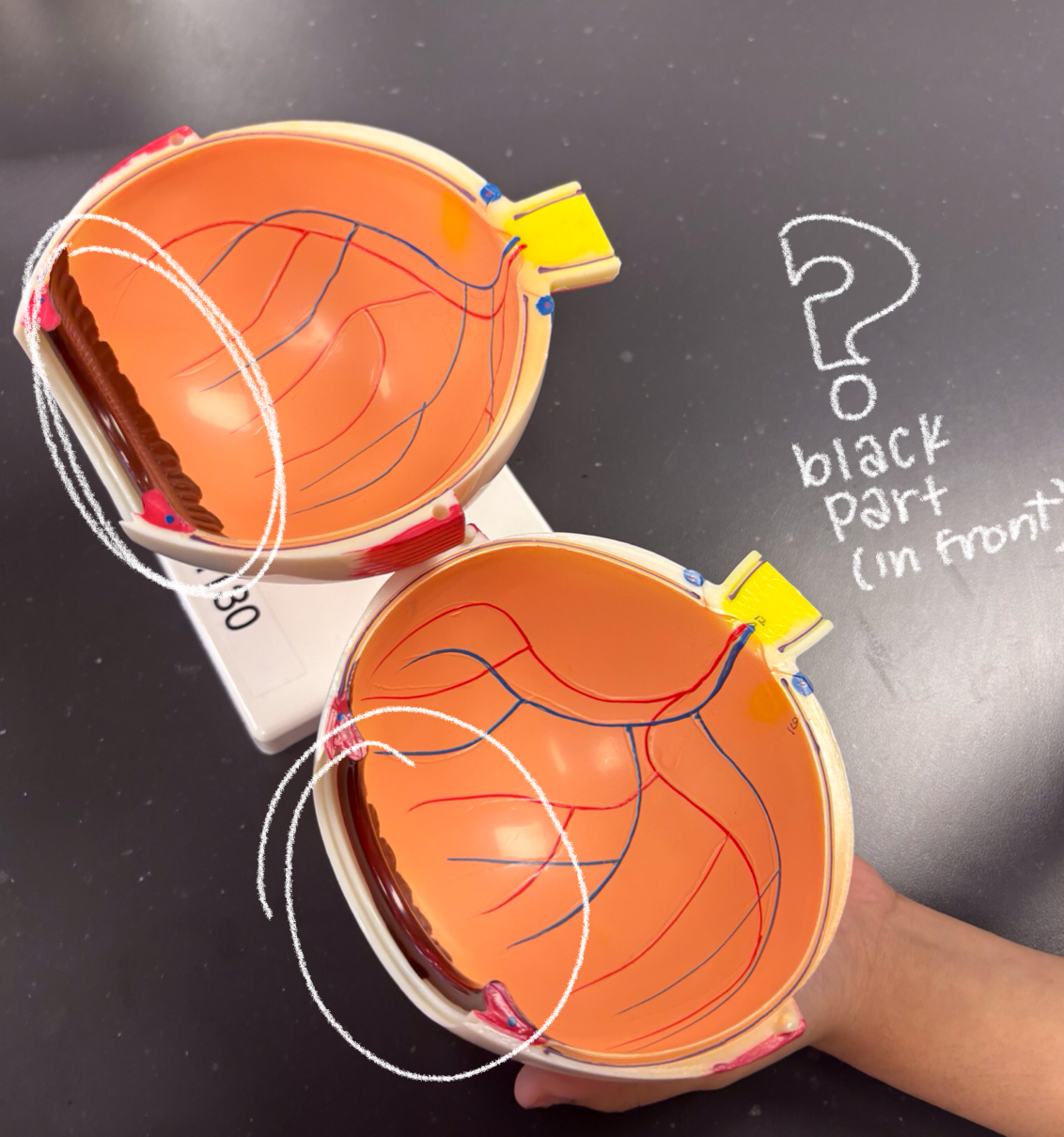
light reaches photoreceptors cells → activates rods/cones → receptors send signals forward thru bipolar cells to ganglion cells → gang cells send action potential down axons → axons from gang cells extend towards optic disc → then it exits thru posterior of eye → combines to form optic nerve
signal pathway