Neuro L3
1/91
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
92 Terms
what forms the outermost layer of the brain?
gray matter
what makes up the sulci and gyri?
gray matter
what makes the central aspect of the spinal cord and looks like a horn shape structure?
gray amtter
the gray matter receives information from _____ matter
white
what forms the central aspect of the brain?
white matter
what forms the peripheral aspect of the spinal cord (ascending and descending pathways)?
white matter
white matter is mostly made up of what?
axons coated with myelin
the spinal cord receives sensory info via _____ pathways from the extremities
ascending
relays info to the brain
afferent neurons
extends from skin receptors and runs to dorsal root ganglion into posteior horn of gray matter in spinal cord
first order neuron
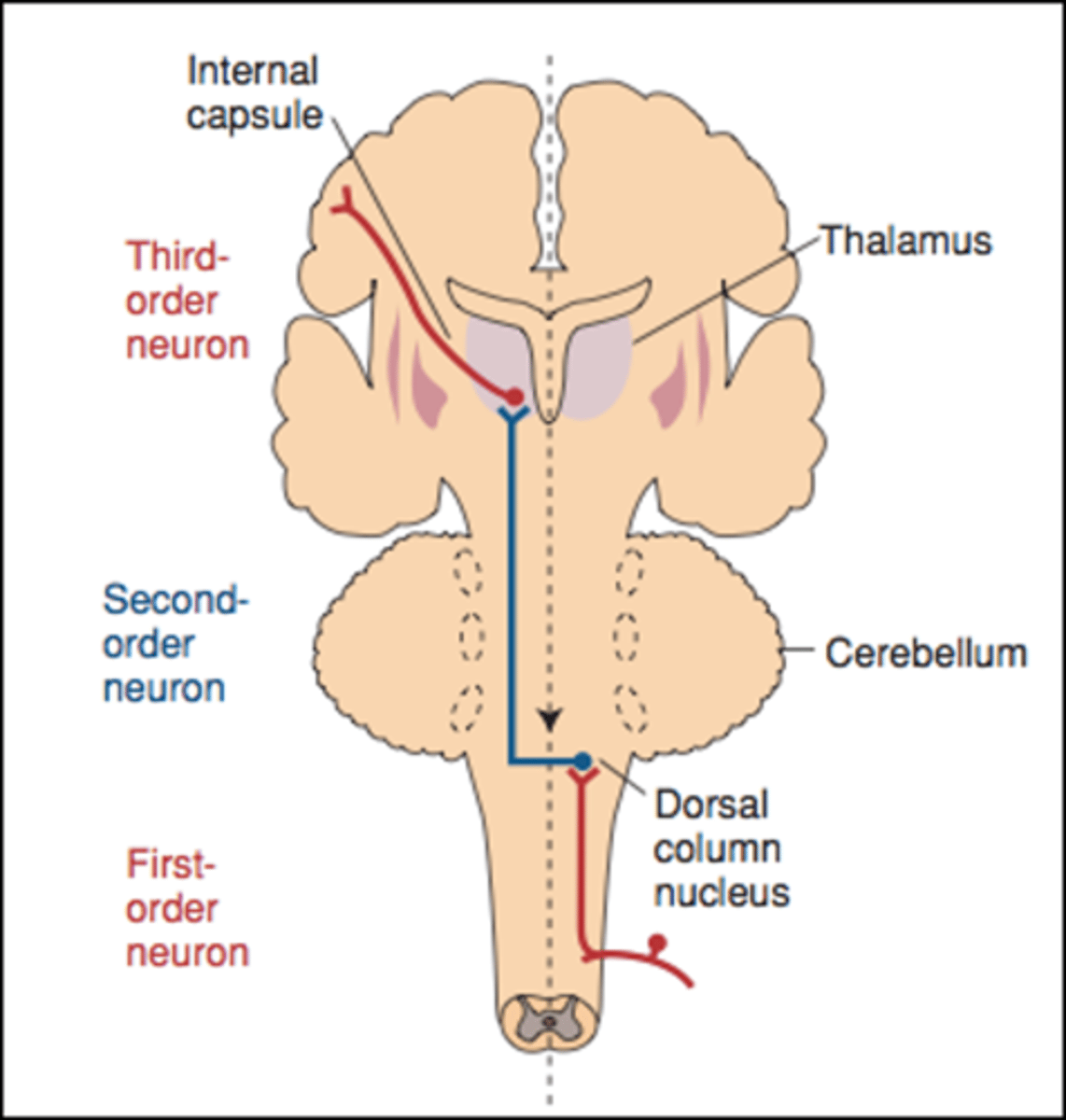
carries sensory impulses to subcortical areas in thalamus
second order neuron
carries impulses to cerebral cortex
third order neuron
how many ascending pathways do we have?
10
match the ascending pathway to the description: spinothalamic tract
-pain and temp
-light touch
match the ascending pathway to the description: posterior column
-proprioception and stereognosis
-light touch
-vibration
match the ascending pathway to the description: spinocerebellar tract
-unconscious proprioception
What is the spinothalamic tract order from when someone receives input and up to the brain?
1. dorsal root ganglion
2. substantia gelationosa (dorsal horn of spinal cord) (cross over)
3. contralateral spinal cord
4. brain stem
5. thalamus
6. postcentral gyrus
injury to the sPinoThaLamic tract what happens?
loss of PAIN and TEMP sensation contralaterally and some loss of LIGHT TOUCH
What can cause spinothalamic tract injury?
-trauma
-syringomyelia
-anterior spinal artery syndrome
-thalamic pain syndrome
what is syringomyelia?
cystic enlargement of central canal of spinal cord = loss of normal flow of CSF
what type of birth defect can cause syringomyelia?
chiari malformation type 1
syringomyelia can cause loss of sensation in what type of distribution?
cape-like
what is anterior spinal artery syndrome?
infarction or hyperflexion injury
what are the sx of anterior spinal artery syndrome?
-sudden onset
-loss of pain and sensation B/L
-flaccid and areflexic paraplegia
-urinary incontinence
-vibration and proprioception are PRESERVED (posterior column)
what is thalamic pain syndrome?
post stroke pain syndrome can cause burning/gnawing pain to contralateral side (first will lose all sensation to contralateral side)
posterior column crosses at the ____
brain stem (medullary tegmentum)
injury to the posterior column tends to cause______ sx
ipsilateral
spinothalamic tract crosses over at the _____
dorsal root (spinal cord)
the posterior column is involved in what functions?
-fine touch
-two point discrimination
-conscious proprioception
-pressure and vibration
what are some common posterior column injuries?
-tabes dorsalis
-vit B12 deficiency
-brown sequard syndrome
what is tabes dorsalis?
Demyelination of posterior columns (from syphilis)
What disease causes these sx:
-delay sensory input
-loss of reflexes
-dec in vibration
-charcot joints
-argyll robertson pupils
tabes dorsalis
severe b12 def causes what sx?
-compromised nerve transmission
-paresthesias
-loss of vibration senses
c spine injury that involves only ONE side of the spinal cord
brown-sequard syndrome
what are the classic sx of brown-sequard syndrome?
-loss of pain and temp (contralateral)
-hemiparesis (ipsilateral)
-loss of vibration and proprioception (ipsilateral)
what controls unconscious proprioception?
spinocerebellar tract
spinocerebellar tract: no crossover of _____ portion but crossover of the ____ portion
1. posterior
2. anterior
list the spinocerebellar tract pathway:
1. golgi tendon organs/muscle spindles
2. dorsal root ganglion (clark's nucleus)
3. cerebellum
what are some injuries to the spinocerebellar tract injury?
-tabes dorsalis
-b12 def
-vit E def
-friedreich's ataxia
-brown-sequard syndrome
what is friedreich ataxia?
Degenerative disorder of the cerebellum and spinal cord (ataxia, loss of proprioception, spastic paralysis, loss of DTR)
what chromosome is affected in friedreich ataxia?
autosomal recessive disorder on chromosome 9
what are the 2 tracts in the descending pathway?
-pyrimidal tract
-extrapyrimidal tract
descending pathway: 1st order neuron-upper motor neuron
-cerebral cortex and brain stem
-spinal cord to anterior gray horn
descending pathway: 2nd order neuron-lower motor neuron
spinal cord to skeletal muscles
the pyramidal tract is aka
corticospinal tract
the pyramidal tract functions...
-controls limb and trunk movement
-controls head, neck, and face movement
-motor cortex to LMN of cranial nerves
if you get an injury of the pyramidal tract and it is above the medulla then the sx will be
contralateral
if you get an injury of the pyramidal tract and it is below the medulla then the sx will be
ipsilateral
where is the extrapyramidal tract located?
brain stem
the extrapyramidal tract controls what?
-muscle tone
-balance
-posture
-modulator of motor response
what are the sx of an extrapyramidal tract injury?
-hypokinetic sx (slow movement, loss of pendulation with walking)
-hyperkinetic sx (athetosis, chorea, myoclonus, tremors)
what is athetosis?
writhing movements
upper or lower motor neuron injury?
-spastic paralysis
-limited muscle atrophy
-NO fasiculations
-hyperreflexia
-babinski reflex may be present
upper
upper or lower motor neuron injury?
-flaccid paralysis
-significant atrophy
-YES fasiculations
-hyporeflexia
-babinski NOT present
lower
Wernicke's area is in what cerebrum lobe?
temporal lobe
the "senses" area is in what cerebrum lobe?
parietal lobe
cerebellar injuries cause what kind of signs/sx?
-ataxia (gait distrubances)
-balance issues
-weakness
-coordination issues
-tremor
What is Amyotrophic Lateral Sclerosis (ALS)?
Also known an Lou Gherig's disease, ALS is a motor neuron disease which can lead to paralysis.
ALS includes mixed upper and lower neurons sx, which tracts in UMN and LMN might we see sx from?
UMN: corticospinal tracts
LMN: anterior horns and grey matter
ALS is fatal within how many years?
3-5years
how is ALS fatal?
pulm infx MCC of death
in ALS, there is difficulty with swallowing, chewing, coughing, talking, due to ______ involvement
bulbar (CN 9, 10, 11, 12)
what is dysarthria?
slurred speech
what dz has these sx?:
-drooping palate
-depressed gag reflex
-weak cough
-pooling of saliva in pharynx
ALS
What is the key tx of ALS?
noninvasive ventilation 4hrs/d (start with maximal inspiratory pressure less than 60cm h2o)
how do we control drooling in ALS?
-decongestants
-anticholinergics
what rx do we give for pseudobulbar effect in ALS?
dextromorphan/quinidine
what is absolutely necessary that the pt receives if they get dx with ALS?
refer to palliative care
what are the typical EMG findings in ALS?
denervation and reninnervation...
-changes in cervical, thoracic, and lumbar region
-2 spinal regions and bulbar musculature
what are the 2 types of reactions with tertiary syphilis?
-hyperproliferative gummatous reaction
-diffuse inflam that involves CNS, large arteries
gummatous lesion
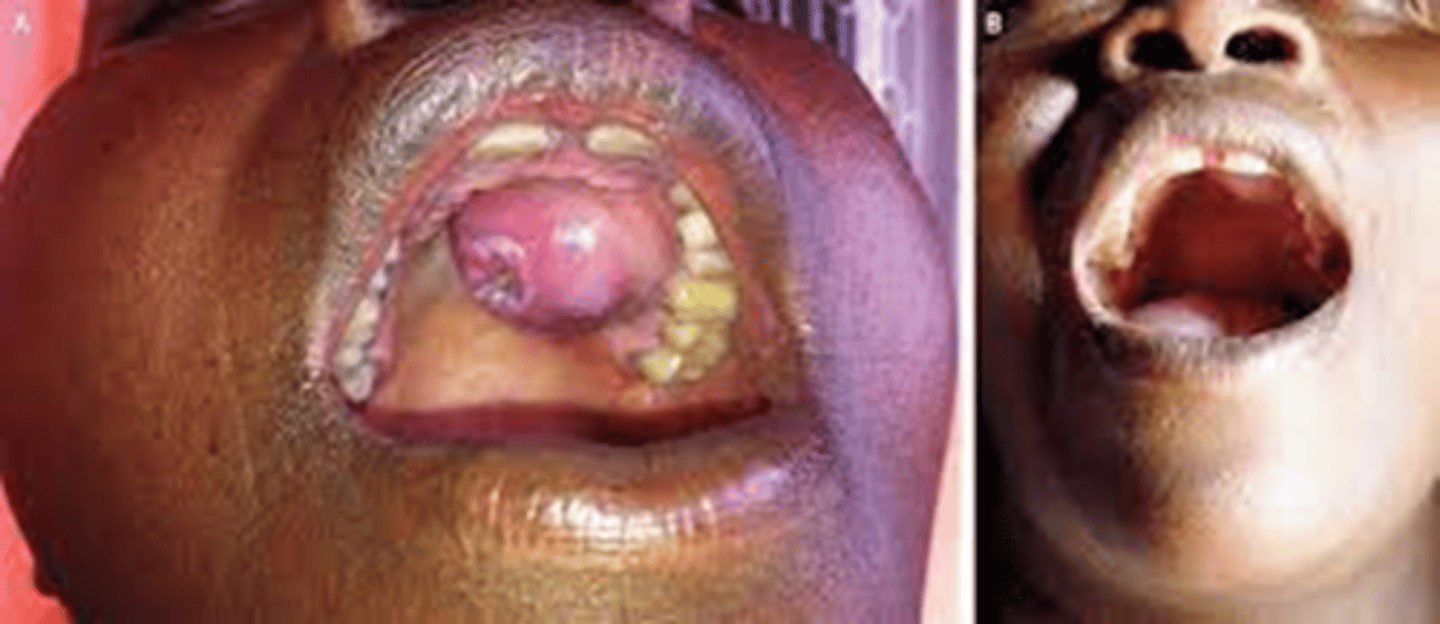
CSF findings: + spinal fluid serology, lymphocytic pleocytosis, inc protein
tertiary syphilis
tertiary syphilis causes what dz?
tabes dorsalis
what tests are done to confirm syphilis?
VDRL
RPR
what is used to tx syphilis?
penicillin or ceftriaxone (if pcn allergy)
what is the Argyll Robertson pupil?
sign of tertiary syphilis - constricts with accommodation but is not reactive to light
what causes guillain barre syndrome?
Campylobacter jejuni from undercooked or raw poultry
in GBS, where does weakness start?
in the extremities and makes its way to the muscles of respiration
how to tx with GBS?
plasmapheresis or IVIG and respiratory toileting
elevated MMA and homocysteine levels, what dz?
pernicious anemia
tx for pernicious anemia?
parenteral b12 (preferred over oral)
in poliomyelitis, we see involvement of what neuro areas?
anterior horn involvement
LMN involvement
polio is highly contagious through what route?
fecal-oral
abortive/nonparalytic/paralytic polio?
-fever
-HA
-vomit
-diarrhea/constipation
-sore throat
abortive
abortive/nonparalytic/paralytic polio?
-abortive sx +
-meningeal irritation
-muscle spasms
-absence of paralysis
nonparalytic
abortive/nonparalytic/paralytic polio?
-flaccid assymetric paralysis
-bulbar involement (CN 9 and 10)
paralytic
what type of labs would we do if someone has polio?
-throat washing
-stool studies
-CSF (inc opening pressure)
which US president had polio?
Franklin D. Roosevelt
decorticate posturing
characterized by upper extremities flexed at the elbows and held closely to the body and lower extremities that are extended
(this is a sx, not a dx)
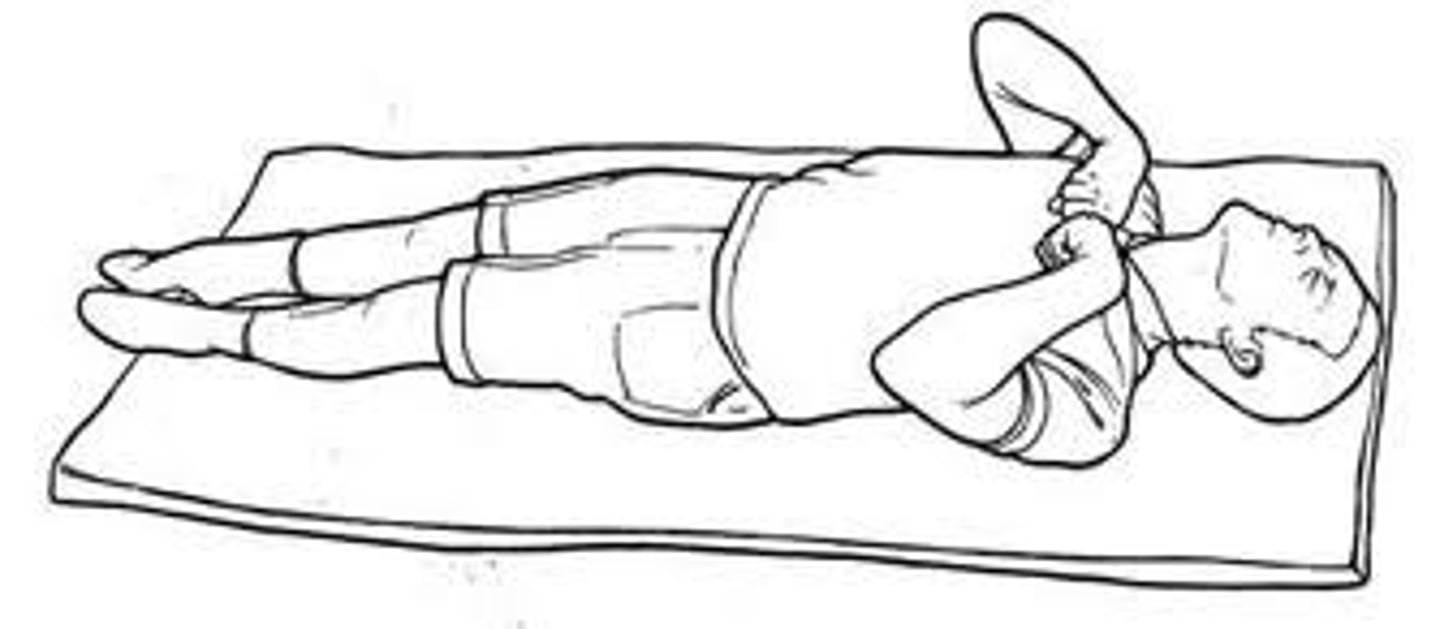
what is a pathologic response to noxious stimuli?
decorticate/decerebrate posturing
decerebrate posturing
-adduction and internal rotation at the shoulder
-extension of elbows with flexed wrist/fingers
-extension at the knees with plantar flexion of the ankle and extension of the toes
(this is a sx, not a dx)
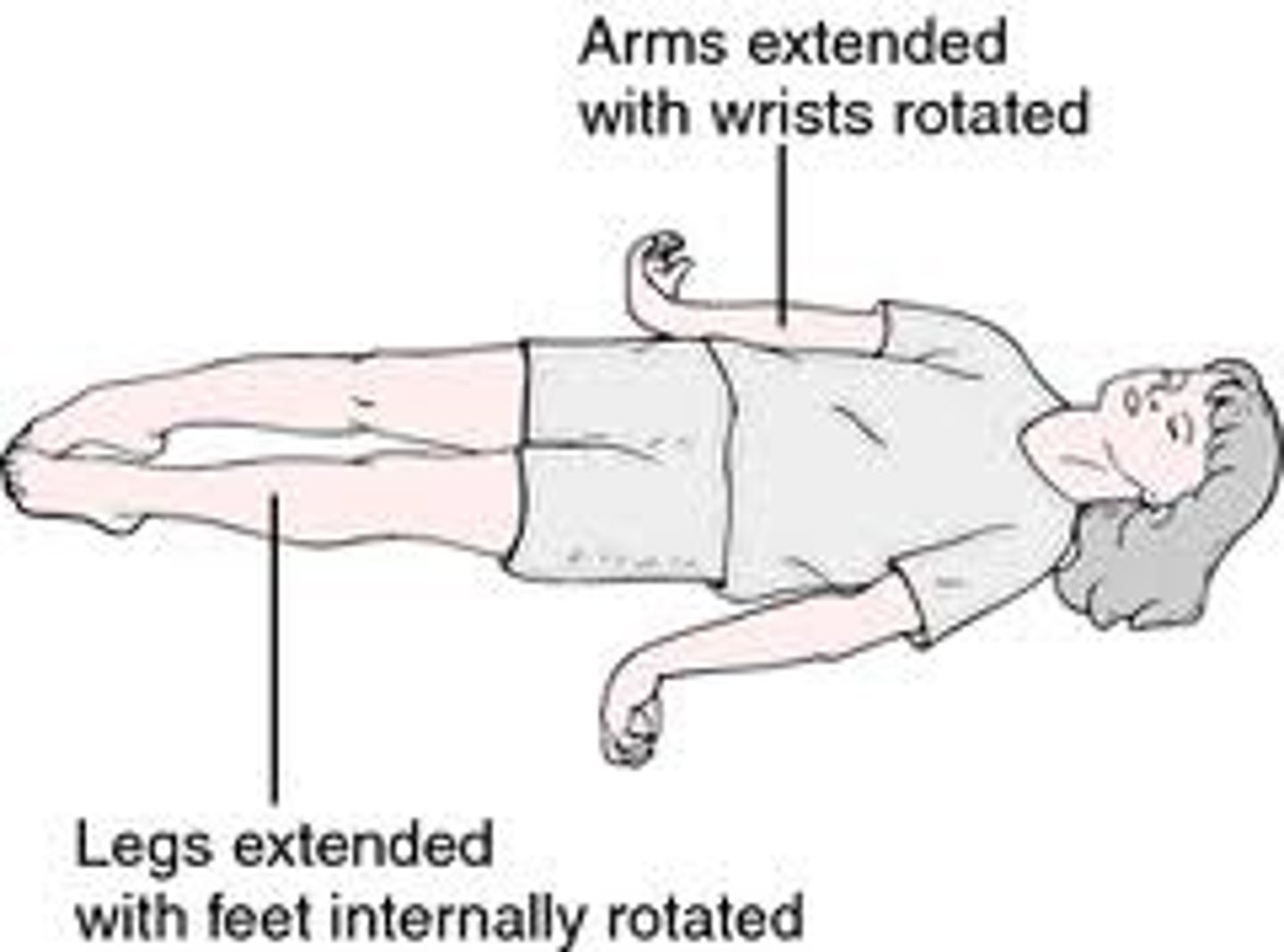
what is a more severe presentation? decerebrate or decorticate?
decerebrate