J Cards (Circulatory System) and K Cards (Heart Structure & Function) | Unit C
0.0(0)
Card Sorting
1/143
Last updated 5:49 AM on 5/23/23
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
144 Terms
1
New cards
artery
strong, thick walled. composed of inner endothelium, elastic tissue and smooth muscle, and outer connective tissue.
\
carries blood away from heart under high blood pressure
\
carries blood away from heart under high blood pressure
2
New cards
artiole
small vessels that branch off arteries. composed of thick layer of smooth muscle and less elastic tissue.
\
found only in organs, alters lumen diameter to control blood flow
constriction ↑BP
dilation **↓**BP
\
found only in organs, alters lumen diameter to control blood flow
constriction ↑BP
dilation **↓**BP
3
New cards
capillary-exchange area
walls one squamous empithelium cell thick (BEST EXCHANGE). less BP + velocity.
\
allows exchange of fluids, nutrients, and gasses between blood and cells
\
allows exchange of fluids, nutrients, and gasses between blood and cells
4
New cards
arteriovenous shunt
direct connection from arteriole to venule
5
New cards
venules
small veins. thin, distensible vessel. large lumen diameter.
carries deox blood from capillaries into veins. one-way waves from skeletal muscle contraction and respiratory movements prevent backflow
carries deox blood from capillaries into veins. one-way waves from skeletal muscle contraction and respiratory movements prevent backflow
6
New cards
one-way valves
from skeletal muscle contractions. increases BV
7
New cards
veins
thin, distensible vessel w/ large lumen. lacks skeletal muscles, NOT SMOOTH. little lumen to maintain pressure, BP lower.
\
carries deox blood from venules to heart. one-way waves from skeletal muscle contraction and respiratory movements prevent backflow (BV↑)
\
carries deox blood from venules to heart. one-way waves from skeletal muscle contraction and respiratory movements prevent backflow (BV↑)
8
New cards
hemorrhage
bleeding, constricts veins and venules, diverting blood to vital organs
9
New cards
right side of heart
pumps blood to lungs
10
New cards
left side of heart
pumps blood to all other body locations
11
New cards
pericardum
tough, fibrous, loose sac, surrounds heart. contains pericardial fluid
12
New cards
pericardial fluid
lubricating fluid found in pericardium. reduces friction
13
New cards
myocardium
contractile layer of cardiac muscle. only found in heart, fibers form junctions and an interconnected network that allows rapid transmission of electrical impulses through heart
14
New cards
atria (general)
thin walled, pulses together.
15
New cards
ventricles (general)
inferior to each atrium. thick muscular walls contract together.
16
New cards
septum
internal wall, divides heart into right and left side
17
New cards
atrioventricular valves (AV valves and cuspid valves) (general)
found between atria and ventricles. prevents backflow of blood. cusps held together by chordae tendinae
18
New cards
semilunar valves (general)
where major artery exits from ventricle. prevents backflow of blood
19
New cards
tricuspid valve
AV Valve, between RA and RV
20
New cards
bicuspid/mitral valve
AV valve, between left atrium and left ventricle
21
New cards
pulmonary semilunar valve
between right ventricle and pulmonary trunk
22
New cards
aortic semilunar valve
between left ventricle and ascending aorta
23
New cards
chordae tendinae
heartstrings, prevents valves from inverting
24
New cards
papillary muscles
elevated masses of muscle tissues in ventricles
25
New cards
superior/anterior vena cava
thick vein, drains deox blood from head, neck, arms, into RA
26
New cards
inferior/posterior vena cava
thick vein, drains deox blood from lower body regions
27
New cards
pulmonary trunk
RA → right and left pulmonary arteries
28
New cards
pulmonary arteries
left and right version. flows into lungs for oxygenation
29
New cards
pulmonary veins
2 from each lung. returns oxygenated blood to left atrium
30
New cards
pulmonary circulatory system
carries deox blood to lungs, ox blood back to heart
31
New cards
aorta
blood from LV → all other regions of the body except for lungs
32
New cards
coronary arteries
branches off aorta shortly after the exit from left ventricle. carries ox blood back to heart tissue
33
New cards
systemic circulatory system
includes vessels that carry blood to and from body cells
34
New cards
cardiac cycle
each heartbeat, end-to-end period of one contraction to another
35
New cards
systole
contraction
36
New cards
diastole
relaxation
37
New cards
atrial systole
happens first in cardiac cycle
38
New cards
ventricular systole
happens second in cardiac cycle
39
New cards
diastole
both ventricle and atria relax. happens third in cardiac cycle
40
New cards
“Lub” heartbeat
AV valves close, ventricles contracts
41
New cards
“-dup” heartbeat
semilunar valves close
42
New cards
pulse
expansion and recoil of artery walls due to blood pressure. cannot be found in a vein due to low blood pressure
43
New cards
initiation of heartbeat
comes from heart itself, not dependent on central nervous system
44
New cards
extrinsic control of heartbeat
medulla oblongata sends impulses down sympathetic/parasympathetic nerve to SA and AV node to increase/decrease heart rate
45
New cards
nodel tissues
specialized cardiac muscle tissues that stimulate heart to beat
46
New cards
sinoatrial (SA) node
found in wall of right atrium. pacemaker, sends out excitation impulse, causing atria to systole
47
New cards
atrioventricular (AV) node
found in base of right atrium near septum.
\
receives the wave of contraction down atria initiated by SA node → allows atria to fill ventricles → produces its own excitatory impulse, initiating ventricular contraction
\
receives the wave of contraction down atria initiated by SA node → allows atria to fill ventricles → produces its own excitatory impulse, initiating ventricular contraction
48
New cards
body of his
receives impulse transmitted by AV node. divides into right and left branch
49
New cards
purkinje fibers
located within ventricular walls
activated by body of his → rapidly transmits impulse to all parts of the ventricles → ventricles contract as a unit → max pressure exerted → blood forced throughout body
activated by body of his → rapidly transmits impulse to all parts of the ventricles → ventricles contract as a unit → max pressure exerted → blood forced throughout body
50
New cards
blood pressure
force exerted by blood against inner walls of blood vessels. caused by heart contractions. depends on cardiac output and resistance to blood flow imposed by blood vessels
51
New cards
systolic pressure
higher arterial pressure, produced by contraction of left ventricle (↑BP)
52
New cards
diastolic pressure
BP drops to lower number since left ventricle relaxes
53
New cards
pulse pressure
difference between systolic and diastolic pressure
54
New cards
hypertension
high BP. usually no symptoms, but heightened risk of heart attack, stroke, kidney, and eye damage (glaucoma)
\
* being overweight
* family history
* being Indigenous or African descent
* inactive lifestyle
* too much alcohol
* too much NaCl
* insufficient K, Ca, Mg
* using birth control pills, steroids, decongestants, anti-inflammatory drugs
* smoking
* high cholesterol diet
\
* being overweight
* family history
* being Indigenous or African descent
* inactive lifestyle
* too much alcohol
* too much NaCl
* insufficient K, Ca, Mg
* using birth control pills, steroids, decongestants, anti-inflammatory drugs
* smoking
* high cholesterol diet
55
New cards
hypotension
low BP. no symptoms, good health as less stress on heart and blood vessels.
\
symptoms:
* dizziness
* fainting
\
caused by:
* dehydration
* infection
* heart disease
* adrenal insufficiency
* bleeding out
* prolonged bed rest
* poisoning
* toxic shock syndrome
* blood transfusion reactions
\
drugs that can cause:
* BP drugs
* diuretics (water pills)
* heart medications
* depression medications
* alcohol
\
symptoms:
* dizziness
* fainting
\
caused by:
* dehydration
* infection
* heart disease
* adrenal insufficiency
* bleeding out
* prolonged bed rest
* poisoning
* toxic shock syndrome
* blood transfusion reactions
\
drugs that can cause:
* BP drugs
* diuretics (water pills)
* heart medications
* depression medications
* alcohol
56
New cards
cardiac output
volume of blood per minute left ventricle pumps into aorta. impacts BP and blood velocity
57
New cards
BP and BV are highest
near the heart
58
New cards
BP and BV decline rapidly
as blood enters arterioles → resistance to blood flow caused by friction between blood and arteriole inner walls
59
New cards
total cross-sectional area of capillaries
causes BP and BV to drop. total combined width is much greater, lowered BP and BV
60
New cards
far distance away from heart
BP and BV lower
61
New cards
gentle flow of blood for exchange of substances in capillary blood
BP and BV lower
62
New cards
bottle neck effect
decrease in total cross-sectional area in veins → BV increases
63
New cards
functions of blood
T ransport of O2, nutrients, hormones, CO2, other wastes
T hermoregulation by capillaries and blood surface
I mmunity via leukocytes (WBC)
C lotting by platelets and clotting proteins
A cid-base regulation (H+, HCO3-)
T hermoregulation by capillaries and blood surface
I mmunity via leukocytes (WBC)
C lotting by platelets and clotting proteins
A cid-base regulation (H+, HCO3-)
64
New cards
cellular components/formed elements
composes 45% of blood
\
* red blood cells
* white blood cells
* platelets
\
* red blood cells
* white blood cells
* platelets
65
New cards
liquid plasma
yellow, composed of water, dissolved or suspended molecules like glucose, electrolytes, amino acids, lactic acid, urea, minerals, hormones, enzymes, antibodies
66
New cards
plasma proteins
albumin, globulins, fibrinogens
67
New cards
albumins
maintains osmotic pressure, mostly made by liver
68
New cards
globulins
play roles in transportation, clotting, and immunity. formed by lymphocytes (WBC)
69
New cards
fibrinogens
play roles in transportation, clotting, and immunity. formed mostly by liver
70
New cards
protein content in blood
determines osmotic pressure, molecules too large to pass through capillary membranes
71
New cards
serum
blood - formed elements - protein
72
New cards
plasma electrolytes
ions like Na+, Cl-, K+, Ca+2, PO4-3, SO4-2, Mg+2, HO3-
73
New cards
red blood cells/erythrocytes
flexible, biconcave disks. lacks nuclei at maturity
\
carries hemoglobin
\
low O2 levels in arterial blood → kidneys stimulated to produce erythroprotein →stimulates erythroblast stem cells in red bone marrow → new made!
\
lives for 120 days → 4 heme groups sent to liver to be reused → each heme group binds to 4 O2 molecules → globin converted into bile (bilirubin and biliverdin) by liver
\
carries hemoglobin
\
low O2 levels in arterial blood → kidneys stimulated to produce erythroprotein →stimulates erythroblast stem cells in red bone marrow → new made!
\
lives for 120 days → 4 heme groups sent to liver to be reused → each heme group binds to 4 O2 molecules → globin converted into bile (bilirubin and biliverdin) by liver
74
New cards
anemia
produced by low RBC count and/or hemoglobin deficiency. inability of the blood to carry and deliver sufficient oxygen to body cells
75
New cards
white blood cells/leukocytes/lymphocytes
larger cells, translucent, have nuclei
\
produced in bone marrow, spleen, and lymphatic tissue (lymph nodes)
\
changes shape, slips through capillary walls into tissue, hunts bacteria, viruses, protists, fungi, and own cells
\
lives for 4-8 hours in blood, 4-5 days in tissue
\
produced in bone marrow, spleen, and lymphatic tissue (lymph nodes)
\
changes shape, slips through capillary walls into tissue, hunts bacteria, viruses, protists, fungi, and own cells
\
lives for 4-8 hours in blood, 4-5 days in tissue
76
New cards
leukemia
when one type of WBC produced excessively in bone marrow. causes insufficient room for RBC and platelets → anemia and clotting problems. WBC are abnormal and unable to function
77
New cards
neutrophils
phagocytosis to form pus
78
New cards
eosinophils
phagocytize antigen-antibody complex
79
New cards
basophils
releases histamine → capillaries become more permeable → more things able to go through to tissue to fight
80
New cards
monocytes/macrophage
phagocytosis & stimulates other WBC production
81
New cards
lymphocytes B-cells
produces antibodies, processed in bone marrow
82
New cards
lymphocytes T cells
destroys specific target cells directly. processed in thymus gland
83
New cards
platelets/thrombocytes
moves along blood vessel → attracted to rough texture on interior → plugs holes → initiates blood clotting
\
small cellular fragments from megakaryocytes
\
small cellular fragments from megakaryocytes
84
New cards
megakaryocytes
giant cells, pinches off bits of cytoplasm, releases into blood, forms platelets/thrombocytes
85
New cards
electrocardiogram/ECG/EKG
records myocardium’s potential difference (voltage, electrical impulses)
86
New cards
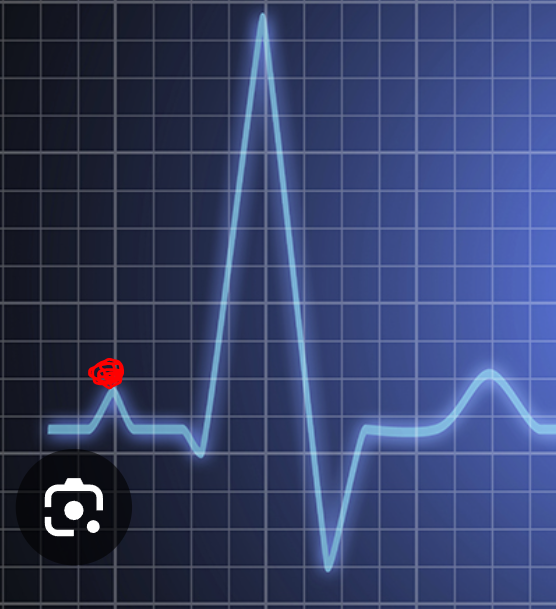
P Wave
depolarization (exchange of NA+ and K+) of atria → atrial systole
87
New cards
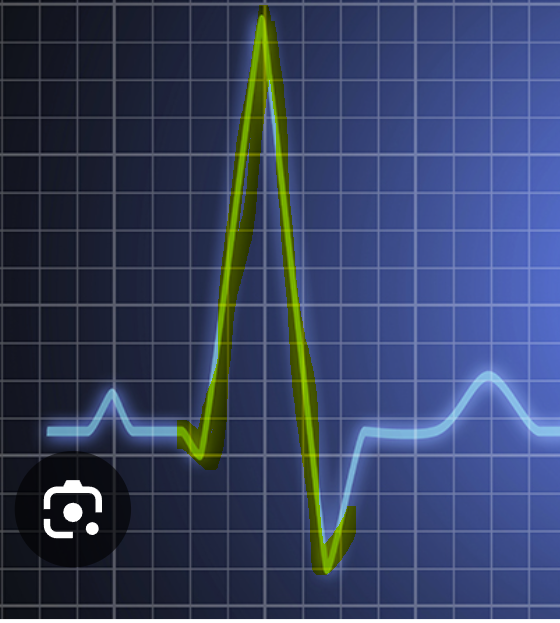
QRS complex
depolarization (exchange of NA+ and K+) of ventricles → ventricular systole
88
New cards
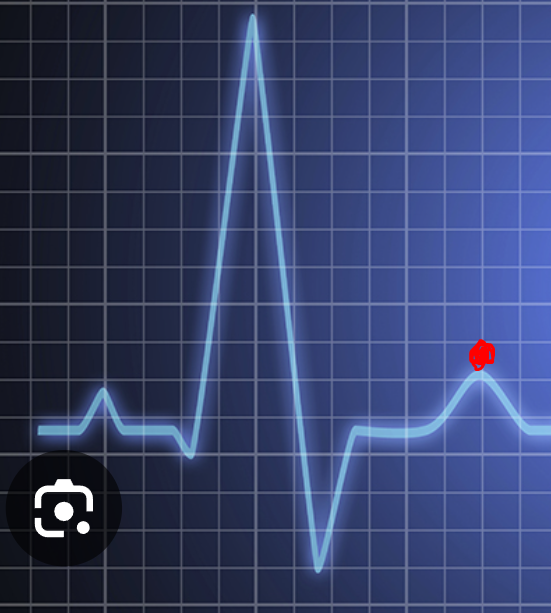
T wave
polarization of ventricles → ventricular diastole
89
New cards
why is diastole of atria not recorded
too small, can’t be detected
90
New cards
extracellular fluid/tissue fluid/intestinal fluid
surrounds cells, contains water, glucose, O2 to supply body cells
91
New cards
capillary fluid exchange BP>OP
arterial end of the capillaries. happens because closer to the heart and high total cross-sectional area. **ECF forced out into intracellular space**
92
New cards
capillary fluid exchange OP>BP
venous end of capillaries. happens because plasma proteins and salt make blood hypertonic, causing fluid to enter capillaries from tissue spaces via osmosis. **ECF returns back into capillaries**
93
New cards
edema
tissue swelling. starving individuals digest plasma proteins as last source of energy → decrease in osmotic pressure → less fluid enters back into capillaries → most fluid is outside in cells, → swelling
94
New cards
lymphatic system functions
1) transports lymph via lymph vessels back to blood
2) lacteals absorb fat at intestinal villi → transports back to bloodstream
3) protects the body from bacterial infection
2) lacteals absorb fat at intestinal villi → transports back to bloodstream
3) protects the body from bacterial infection
95
New cards
lymph
tissue fluid, transported in lymph vessels back to blood, contributes to blood plasma. contains more protein than ECF
96
New cards
lacteals
found in intestinal villi, absorbs fat, transports back to bloodsteam
97
New cards
lympatic organs
L ymph Nodes
S pleen
T hymus Gland
B one Marrow
T onsils
S pleen
T hymus Gland
B one Marrow
T onsils
98
New cards
lymph capillaries
microscopic vessels, takes up lymph not reabsorbed by systemic capillaries.
99
New cards
lymphatic vessels
collection of many lymph capillaries. parallels venules and veins. lymph flows through this via skeletal muscle contraction, intestinal peristalsis, and gravity. has valves that prevent backflow
100
New cards
right lymphatic duct
drains lymph from right arms and right halves of head and thorax. empties on right subclavian vein