Mid-Term Grade 9 SCIENCE
1/92
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
93 Terms
Q2: The metric unit you would use to measure the volume of a bottle of water.
Litres.
Q2: The metric unit you would use to measure the length of a house.
Metres.
Q2: The metric unit you would use to measure the weight of an apple?
Grams.
Q3: The symbol of meters.
m
Q3: The symbol of mega.
M
Q3: The symbol of millivolt.
mV
Q3: The symbol of centiwatt.
cW
Q3: The symbol of micro.
μ (upside down h)
Q4: The value of mega.
1 000 000
Q4: The value of kilo.
1000
Q4: The value of hecto.
100
Q4: The value of deca.
10
Q4: The value of base.
1
Q4: The value of deci.
0.1
Q4: The value of centi.
0.01
Q4: The value of milli.
0.001
Q4: The value of micro.
0.000 001
Q5: Qualitative observations.
The collected data based on observations using your five senses.
Q5: Quantitative observations.
The collected data based on observations reported in numbers.
Q6: List the correct order of the steps in scientific method.
1. Create an observation of something in nature. 2. Make a question/identify a problem. 3. Conduct background research.4. Form a hypothesis. 5. Design an experiment. 6. Preform experiment/collect data and analyze data. 7. Come to a conclusion. 8. Compare observations to hypothesis. 9. Communicate results.
Q7: A hypothesis.
A testable educated guess about how to solve a problem.
Q8: An independent variable.
The cause. The factor that’s adjusted to observe it’s effect the change will have on the other variable.
Q9: A dependent variable.
The effect. The factors that changes in response to a change on the other variable (the result of the experiment).
Q10: A controlled variable.
Any factor or condition that’s kept constant/alone throughout the experiment to ensure that it doesn’t influence the outcome.
Q11: To make a conclusion for an experiment…
decide whether the hypothesis was correct or not.
Q12: The highest level of scientfic proof.
Theory.
Q13: Matter.
Anything that takes up space and has mass. Matter is made up of atoms. This includes air and almost everything else.
Q14: The three states of matter.
Solid, liquid, and gas.
Q15: Liquid to solid (heat taken away or added).
Freezing and heat is being taken away.
Q15: Solid to liquid (heat taken away or added).
Melting and heat is being added.
Q15: Liquid to gas (heat taken away or added).
Evaporation and heat is being added.
Q15: Gas to liquid (heat taken away or added).
Condensation and heat is being taken away.
Q15: Gas to solid (heat taken away or added).
Deposition and heat is taken away.
Q15: Solid to gas (heat taken away or added).
Sublimation and heat is added.
Q16: Mixtures.
Made up of two or more types of particles that are not chemically bonded to each other.
Q17: The state of matter that has their atoms/molecules furthest apart.
gas.
Q18: The state of matter that has their atoms/molecules close together.
solid.
Q19: Pure substance.
Made up of one type of particle. It’s either a single type of atom, an element, or two or more types of atoms chemically bonded, a molecule.
Q20: Homogenous mixture.
A mixture that has evenly distributed parts/consists of true particles (atoms, molecules). They’re also known as a solution.
EX: Salt/sugar water, coffee, tea, juice, etc.
Q21: Heterogeneous mixture.
A mixture with differently distrubuted parts/consists of not true particles. They’re also known as a mechanical mixture. There’s no dissolving in a heterogeneous mixture, since the bits that made the mixture is larger than actual molecules.
EX: Salad, oil and water, soil, etc.
Q22: Solvent and solute.
A substance (the solute) is dissolved in another substance (the solvent).
Q23: Alloy.
A solid dissolved in a solid making homogeneous mixture of metals.
EX: Brass, bronze, sterilng silver, etc.
Q24: Colloid.
A heterogeneous and mechanical mixture. The bits are extremely small, but still larger than atoms or molecules. The bits in it will not settle due to gravity, but they can be separated by other methods (like spinning the colloid really fast).
EX: Butter, milk, smoke, etc.
Q25: Physical change.
When materials change but no new materials with no new properties are made.
Q26: Chemical change.
When materials change into new materials with new properties.
Q27: All matter is made of…
atoms.
Q28: Atoms are made of…
protons, neutrons, and electrons.
Q29: Protons and neutrons are located in an atom in the…
nucleus.
Q29: Electrons are located in an atom in the…
electron shell.
Q30: Forces that hold an atom together.
Electromagnetic forces.
Q31: The charge of a proton.
Positive.
Q31: The charge of a neutron.
Neutral (no charge).
Q31: The charge of a electron.
Negative.

Q32: Type of matter.
Compound
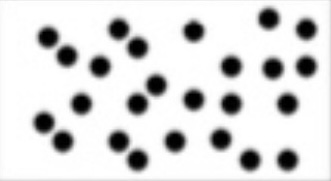
Q32: Type of matter.
Element.
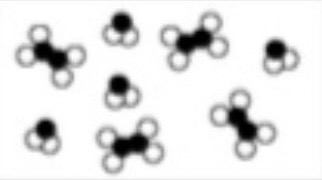
Q32: Type of matter.
Mixture.
Q33: Groups.
Vertical columns.
Q33: Periods.
Horizontal rows.
Q34: Metals location.
The left side of the periodic table separated by the zig-zag line.
Q35: The characteristics of metals.
Ductile, malleable, have cluster, are good conductors of heat and electricity, tend to be dense, and lose electrons when forming ionic bonds.
Q36: Examples of metals.
Gold (Au), calcium (Ca)
Q37: Non-metals location.
The right side of the periodic table separated by the zig-zag line.
Q38. The characteristics of non-metals.
Brittle, dull in appearance, insulators, lower in density, and gain electrons when forming ionic bonds.
Q39: Examples of a non-metal.
Sulfur (S), nitrogen (N), etc.
Q40: What is the highlighted part?
Atomic number.


Q40: What is the highlighted part?
Chemical symbol.


Q40: What is the highlighted part?
Element name.


Q40: What is the highlighted part?
Average atomic mass.


Q41: Identify the atomic number, atomic mass, chemical symbol, element name, amount of protons, neutrons, and electrons.
11, 22.98/23, Na, sodium, 11, 12, and 11.

Q42: This drawing of an atom according to…
Dalton.
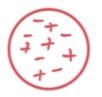
Q42: This drawing of an atom according to…
Thomson.

Q42: This drawing of an atom according to…
Rutherford.
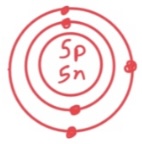
Q42: This drawing of an atom according to…
Bohr.
Q43: When elements as their smallest pieces form molecules instead of atoms.
Diatomic molecule.
Q44: Isotope.
Atoms of the same element with different numbers of neutrons. They have the same atomic number but different mass numbers.
Q45: How does an atom become charged both positively and negatively referring to the subatomic particles of the atom.
During chemical reactions, atoms become charged positively when they lose electrons. During ionic bonding, metals lose electrons, which now makes the atom have more positive charge. During chemical reactions, atoms become charged negatively when they gain electrons. During ionic bonding, non-metals gain electrons, which now makes the atom have more negative charge.
Q45: What is a neutral object?
A neutral object has the same amount of positive and negative charge, or the same amount of protons and neutrons. As a result neutral objects have no charge or are neutral.
Q46: The smallest piece of a compound is that retains the properties of that compound.
Molecule.
Q47: The order is for “filling” of electron shells in the Bohr model.
2 electrons in the first shell, then 8 electron in any other shell after the first shell.
Q50: Elements are categorized in families or groups because…
they have the same number of valence electrons.
Q51: The relationship between element reactivity and position on the periodic table.
The more left or right (excluding the noble gases, group 18) the more reactive the elements are. Also the higher up (lower period numbers) the more reactive the elements are.
Q52: The products on a chemical equation is on…
the right.
Q52: The reactants are on a chemical equation is on…
the left.
Q53: Coefficient.
The number placed before a chemical formula in a chemical equation used to balance the chemical equation.
Q56: Science.
The process that allows us to find out about the Universe.
Q57: Density.
The amount of mass per unit of volume. It is a characteristic property of substances.
Q58: Characteristic property.
A physical or chemical property that is unique to a specific substance and doesn't change with the amount of the substance. It’s used to help identify substances.
Q59: Covalent bonding.
A type of chemical bond where atoms share pairs of electrons to achieve a stable, full outer electron shell, primarily occurring between non-metal atoms.
Q60: Ionic bonding.
The bond typically between a metal and a non-metal formed between oppositely charged ions (cations and anions) that form when one atom completely transfers one or more valence electrons to another.
Q61: Charges that are the same.
Repel.
Q62: An element that in its smallest form is called when it is a molecule instead of an atom.
Diatomic. 02 is an example of this.
Q63: The formula for density.
mass ÷ volume
E= mc squared is the…
Special Theory of Relativity.