(MOCKS BIOLOGY) "EOY BIOLOGY, Bio - topic 7, Bio Topic 6"
1/272
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
273 Terms
RIBOSOME
PLANTS, ANIMALS, AND BACTERIAL CELLS
Makes proteins by reading mRNA
MITOCHONDRIA
PLANTS AND ANIMALS
involved in respiration
cells that need more energy have more of these
NUCLEUS
PLANTS AND ANIMALS
contains chromosomes -> that carry genes
controls activities of the cell
VACUOLE
PLANT CELLS ONLY
filled with cell sap -> which stores dissolved mineral ions and sugars
helps cell keep shape
NUCLEOID OR CIRCULAR DNA
BACTERIAL CELLS ONLY
tangle of double stranded DNA
contains chromosomes
free floating
PLASMID
BACTERIAL CELLS ONLY
circular loop of DNA
small number of non-essential genes
copied independently
can be transferred
free floating
RESOLVING POWER OR RESOLUTION
the ability to distinguish between two points
CONCENTRATION GRADIENT
difference in the concentration of a substance from one location to another
OSMOSIS* (ALWAYS about water, water like 99% always osmosis)
the NET movement of WATER molecules from a region of HIGH WATER POTENTIAL to a region of LOW WATER POTENTIAL, DOWN A CONCENTRATION (of water) GRADIENT, through a SEMIPERMEABLE MEMBRANE.
(water, passive) (root hair cells absorbing water from the soil)
DIFFUSION
the NET movement of particles DOWN A CONCENTRATION GRADIENT, from an area of HIGH CONCENTRATION to an area of LOW CONCENTRATION, which is a result of their RANDOM movement
(fluids, passive) (ex. oxygen diffusing across the lungs)
FACTORS that affect DIFFUSION
limited to:
- surface area
- temperature
- concentration gradients
- distance
PLASMOLYZED
bro has shrunk from osmosis (little free water/too much minerals leading to low water potential outisde of the cell, the cell shrivels up from losing water)
CELL MEMBRANE
PLANTS, ANIMALS, AND BACTERIAL CELLS
semi-permeable membrane (controls what enters/exits)
CYTOPLASM
PLANTS, ANIMALS, AND BACTERIAL CELLS
site of chemical reactions
jelly-like, contains the organelles
CELL WALL
PLANT AND BACTERIAL CELLS
helps cell keep shape
cellulose
permeable
CHLOROPLAST
PLANT CELLS ONLY
chlorophyll (green pigment, absorbs light energy)
site of photosynthesis
CELL CAPSULE
BACTERIAL CELLS
outermost wall of the cell
FLAGELLUM (plural FLAGELLA)
BACTERIAL CELLS, a long, hair-like structure that extends from the cell membrane and is used for quick movement (looks like a twisting turbine thing when there is two)
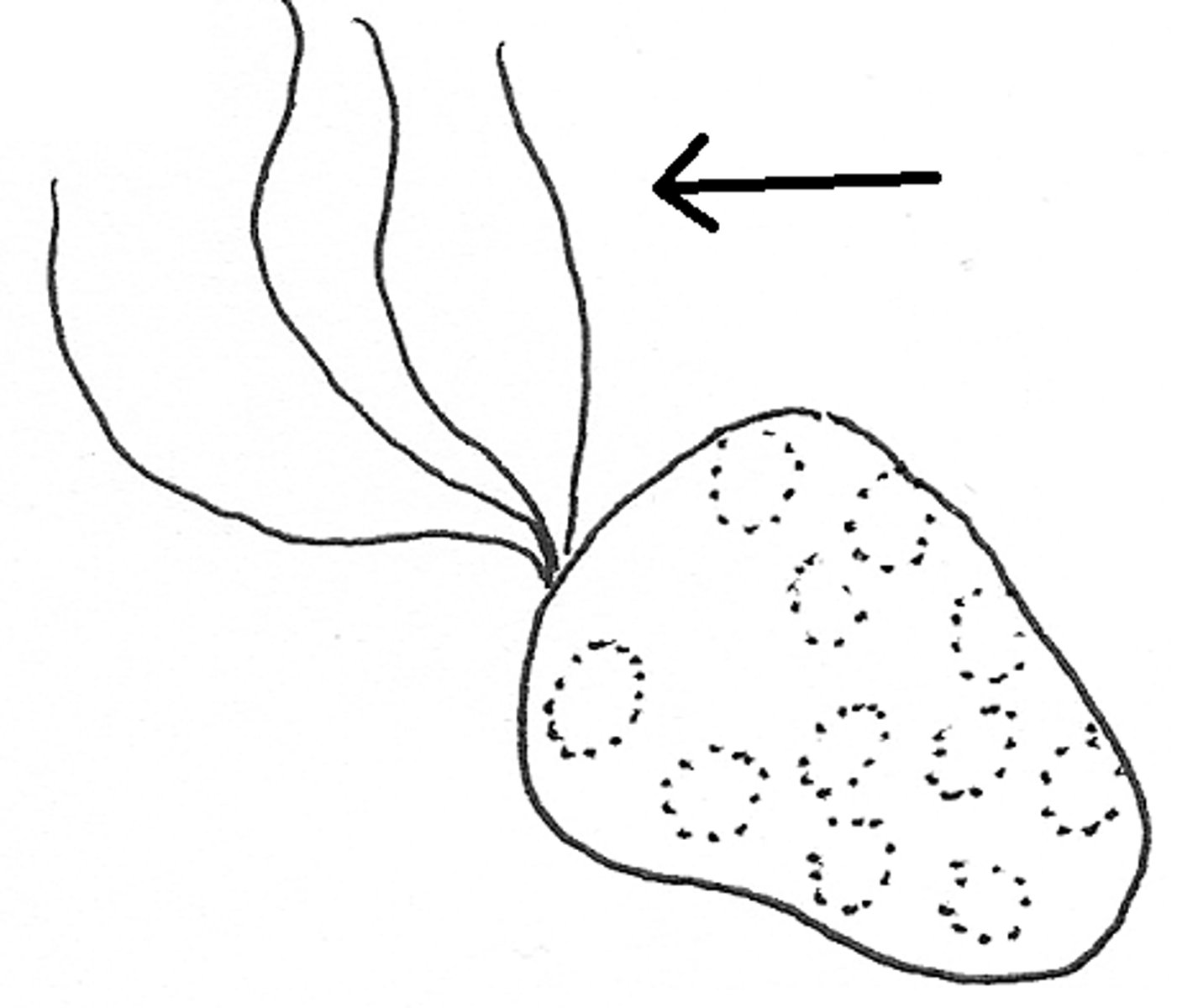
CILIA
BACTIERAL CELLS, hairlike projections that extend from the plasma membrane and are used for movement
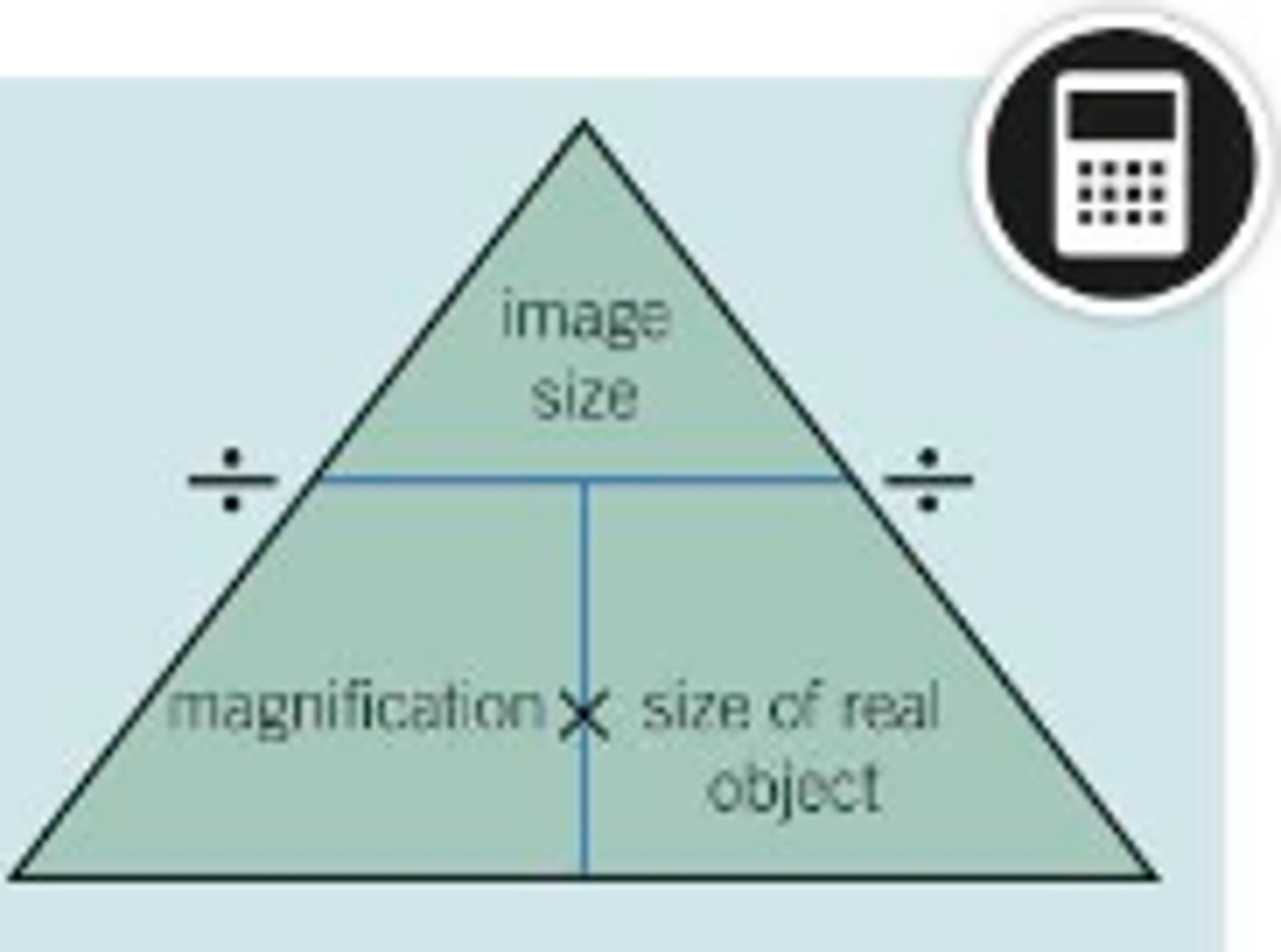
EYEPIECE
magnification of x10
TOTAL MAGNIFICATION
x10 * objective lens
MAGNIFICATION FORMULA
triangle IAM with I on top
ADAPTATION
how an organism or species became better suited to its environment/job
SPERM CELLS
LONG TAIL to swim
head contains ENZYMES to allow it to digest into an egg cell
designed to fertilize eggs
found in the testes
EGG CELL
large and BULKY
contains YOLK -> that has a large food store for the new cell being formed
found in the ovaries, designed to be fertilized
PALISADE CELL
tall and LARGE SURFACE AREA to absorb water and minerals
packed with CHLOROPLASTS
designed for photosynthesis, found on the top of a leaf
CILIATED CELL
HAIRS sweep MUCUS with trapped dust and bacteria back up the throat
tiny hairs called CILIA
line all the air passages of the lungs
designed to stop lung damage
ROOT HAIR CELL
THIN CELL WALL so that minerals can easily pass through
LARGE SURFACE AREA to absorb water and minerals easily
found in the plant's roots
designed for absorbing water and minerals
NERVE CELL (NEURONE)
LONG
CONNECTIONS AT EACH END
carry electrical signals
carry nerve impulses to different parts of the body
found all over the body
RED BLOOD CELL
NO NUCLEUS
LARGE SURFACE AREA for OXYGEN to pass through
contains HEMOGLOBIN which joins with oxygen
found in blood
designed to carry oxygen
FLACCID
cell starts to lose water (due to lack of water/water potential in the environment around the cell)
TURGID
when a plant cells has lots of water and its cytoplasm is pressed against the cell wall. Plant stands up straight (healthy plant! water is going into the cell)
TURGOR PRESSURE
Pressure inside the cell exerted by water molecules causes by the cell membrane pushing agains the cell wall
PLASMOLYSIS
when the cell loses turgor pressure, SHRINKING
ACTIVE TRANSPORT
the movement of particles against a concentration gradient across a cell membrane, from an area of low concentration to an area of high concentration, which requires energy (ex. plant roots absorbing mineral ions)
CELL
smallest level of organization
TISSUE
between cell and organ
ORGAN
between tissue and organ system
ORGAN SYSTEM
between organ system and organism
ORGANISM
highest level of organization
how to describe levels of organization?
a bunch of _____ working together
microscope question
1. place the slide on stage
2. put the objective lens to the lowest power
3. adjust the mirror/switch on the light
4. adjust the coarse focus
5. then adjust the fine focus
6. change to the desired lens (x10 x20 etc)
7. refocus using the coarse then fine focus
calculating percentages? avoiding uncertaincies or inconsistencies in experiment
a student calculated the percentage of change in mass rather than the change in mass itself since the object may have varying masses or sizes (READ QUESTION CAREFULLY)
concentration gradient x intercept
** Y AXIS IS CHANGE IN MASS
** X AXIS IS CONCENTRATION (mol/dm^3)
the point wherein the line of best fit intersects with the x axis means there is 0 change in mass, therefore that is when equilibrium is reached
osmosis vs diffusion
osmosis: WATER only, SEMIPERMEABLE membrane is required
diffusion: FLUIDS (gas and liquids), NO OBSTACLES
low water potential
high solute concentration
lysis
The bursting of an animal cell due to being placed in a hypotonic (lots of free water, low concentration) solution
do not say zoom...
say magnified or (x10) times 10, times 20, times 100!
do not say explodes...
bursts!
shrinks
when a red blood cell is placed in a concentrated salt solution
What is found in a plant cell but not an animal cell?
Cell wall
chloroplast
vacuole
What is found in both plant and animal cells?
Cell membrane
cytoplasm
mitochondria
nucleus
ribosomes
carbohydrates
provides energy; cereal, bread, pasta, rice
a balanced diet
one that gives your body the nutrients in the correct proportions in order for it to function correctly and for health to be mantained
protein
growth and repair; fish, meat, eggs, beans, dairy
water
needed for cell cytoplasm and bodily fluids; fruit juice, milk, water
iron
hemoglobin in rbcs; red meat and liver
calcium
strong teeth and bones; dairy products
fat
provides energy, stores energy, insulates the body; butter, oil, nuts
vitamin c
maintains the cell membrane; citrus fruits
vitamin d
helps with the absorption of calcium; sunlight and fatty fish
fiber
keeps food moving through the digestive system; vegetables and bran
unbalanced diet
explains bad nutrition; nutrients may be lacking/excessive/unbalanced (not in the right proportions)
scurvy causes
lack of vitamin c; lack of eating fruits and vegetables;
symptoms include: bleeding gums, loosening teeth, bleeding under skin, fatigue
rickets causes
lack of vitamin d; lack of calcium; lack of phosphorous
symptoms include: pains in the bones, bone fractures, muscle cramps, teeth or skeletal deformities
enzymes' 5 properties
1. made of protein (amino acids
2. catalyze reactions (speed them up)
3. specific shape
4. affected by temperature and
5. pH
substrate
what enzymes react with
enzyme words to use!
specific
active site
binds
shape
denatured
collisions
substrate + enzyme =
enzyme-substrate complex
active site
the part of the enzyme which the reactant binds to; it is specific to its substrate
temperature's effects on enzymes
higher temperature increases kinetic energy of the enzymes allowing them to move around more and causes more collisions;
however, once the temperature reaches beyond the optimum, the enzyme's is denatured, destroying its shape/active site
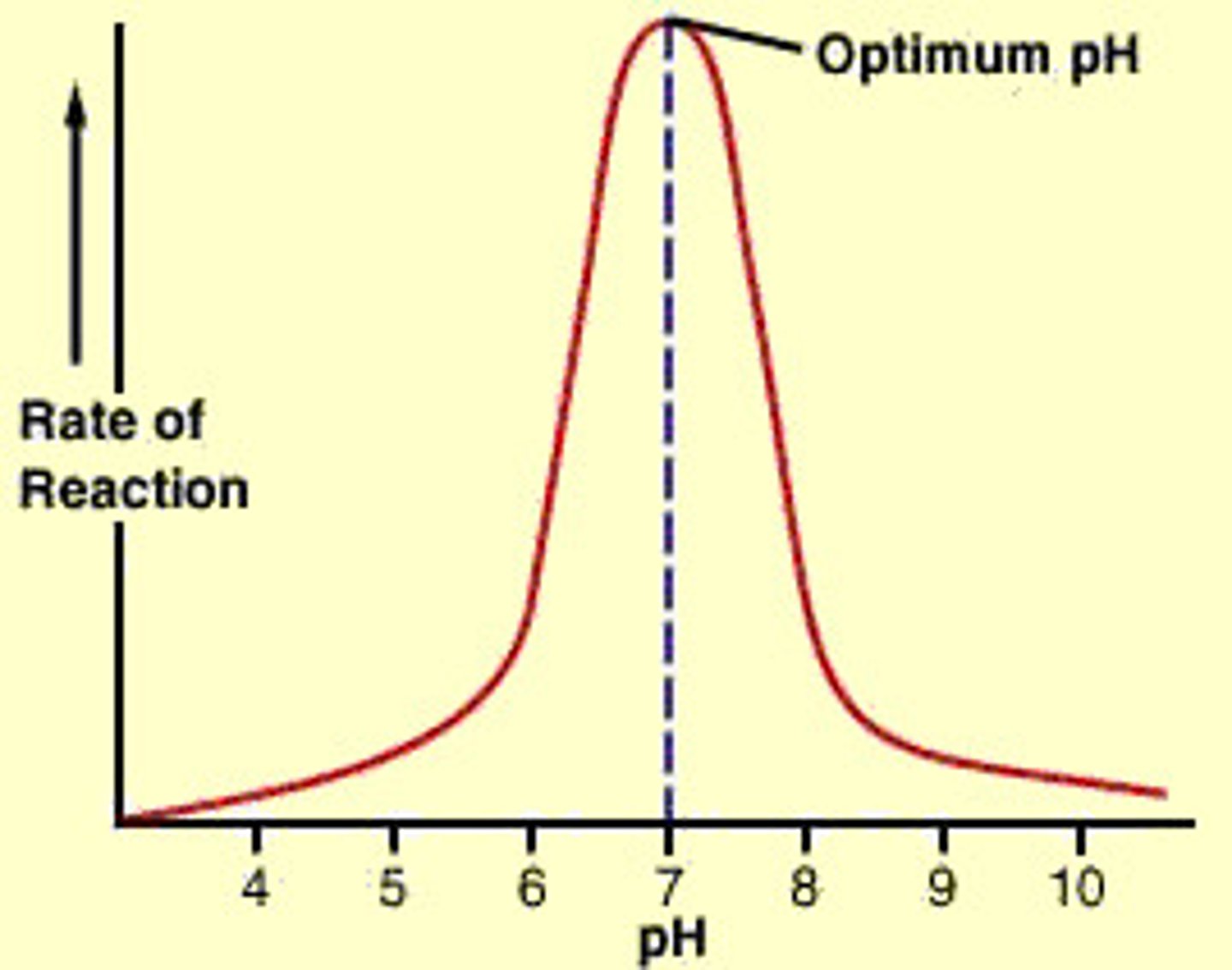
pH's effects on enzymes
there is an optimum pH for enzymes to work;
a too high or too low pH can cause the enzyme to be denatured and its shape/active site will be destroyed
pH enzyme graph
steep increase, steep decrease
temperature enzyme graph
gradual increase, steep decrease
enzyme-substrate complex
what is formed when enzyme binds to a substrate when they collide
amylase
secreted from the SALIVARY GLANDS and PANCREAS
works in the MOUTH, SALIVA, AND SMALL INTESTINES
breaks down starch into small reducing sugars :D
protease
secreted from the STOMACH and PANCREAS
works in the STOMACH and SMALL INTESTINES
breaks down protein into amino acids
lipase
secreted from the PANCREAS
works in the SMALL INTESTINES
breaks down fats&oils OR lipids into fatty acids AND glycerol
lipase amylase and protease optimum temperature
37-40 degrees
mouth
physical digestion (+ chemical from saliva)
esophagus
peristalsis occurs here
stomach
chemical + physical digestion, has gastric juices or HCl, has goblet cells that protect itself from the acidity
HCl role
kills harmful microorganisms in food; providing an acidic pH for optimum conditions for protease
small intestine + duodenum + ileum
absorption + chemical digestion
large intestine + colon + rectum + anus
absorption + egestion
salivary glands
chemical digestion, secretes amylase
pancreas
chemical digestion, secretes enzyes
liver
makes bile for chemical digestion
gall bladder
stores bile for chemical digestion
bile
neutralizes the acidity of the HCl, increases the surface area of the fats by emulsifying them (separating them), big globules -> small droplets
ingestion
the taking of substances, ex. food and drink, into the body
physical digestion
the break down of food into smaller pieces; increases surface area
absorption
the movement of nutrients from the intestines into the blood
chemical digestion
the breakdown of food from large insoluble molecules into small soluble molecules that the body can absorb
assimilation
the uptake and use of nutrients by cells
egestion
the removal of undigested food from the body as feces
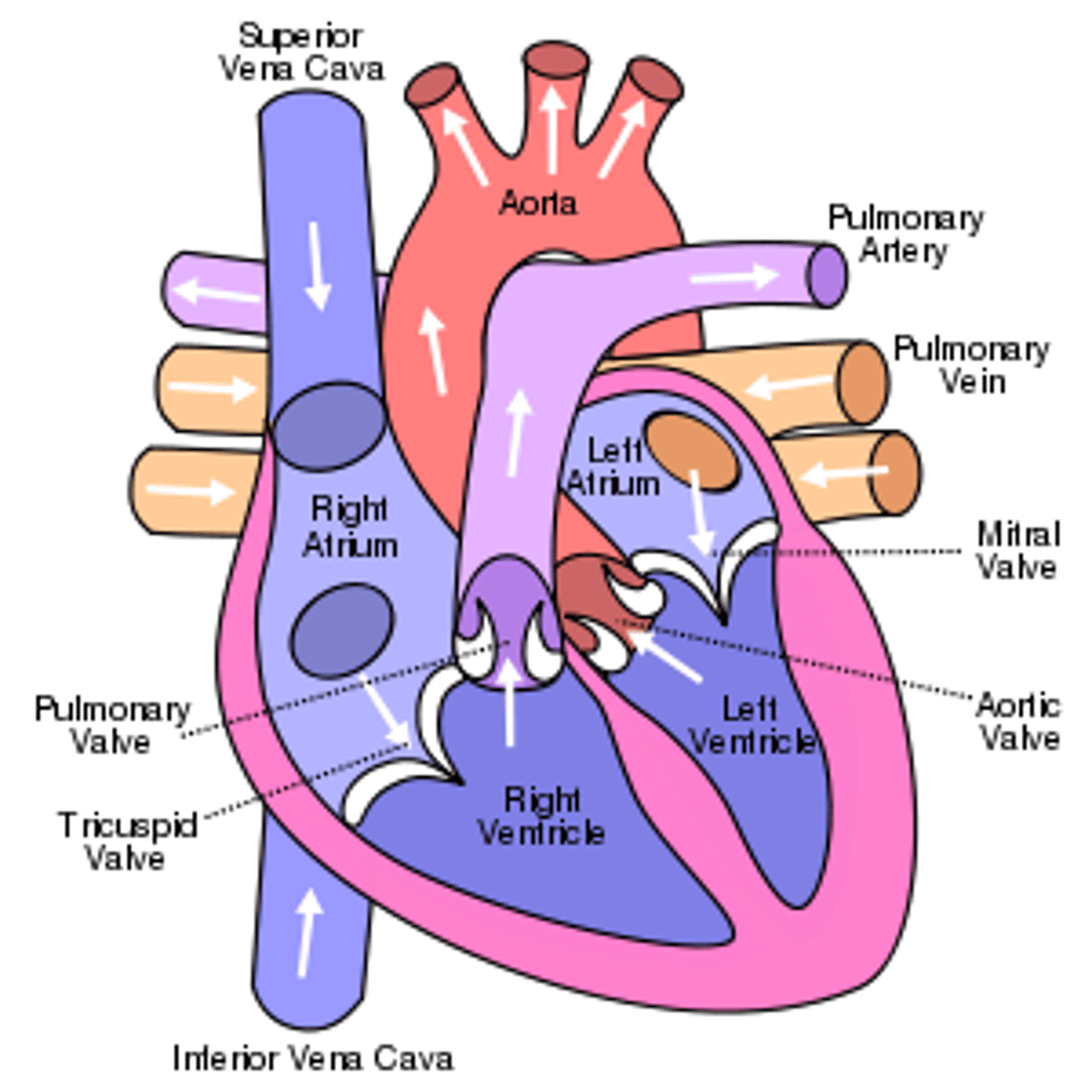
circulatory system
a system of blood vessels with a pump (the heart) and valves to ensure the one-way flow of blood
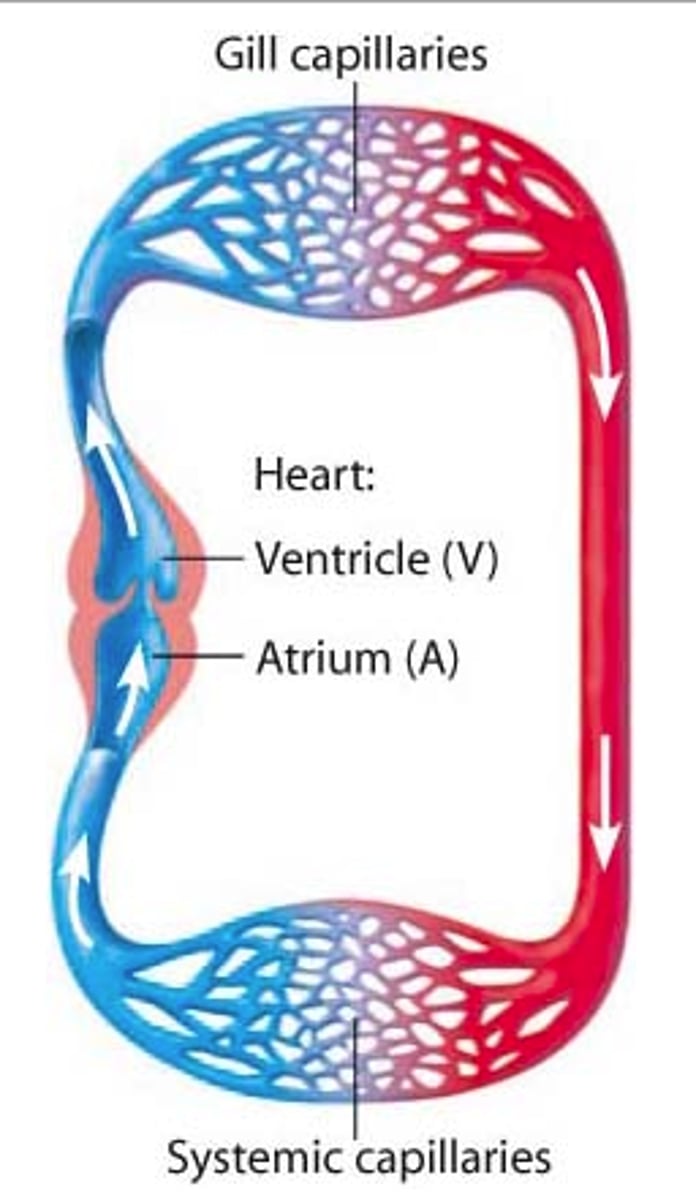
single circulatory system
only have DEOXYGENATED blood flowing into the heart (or just flowing in general), hearts have TWO chambers, blood gets pumped into the heart ONCE
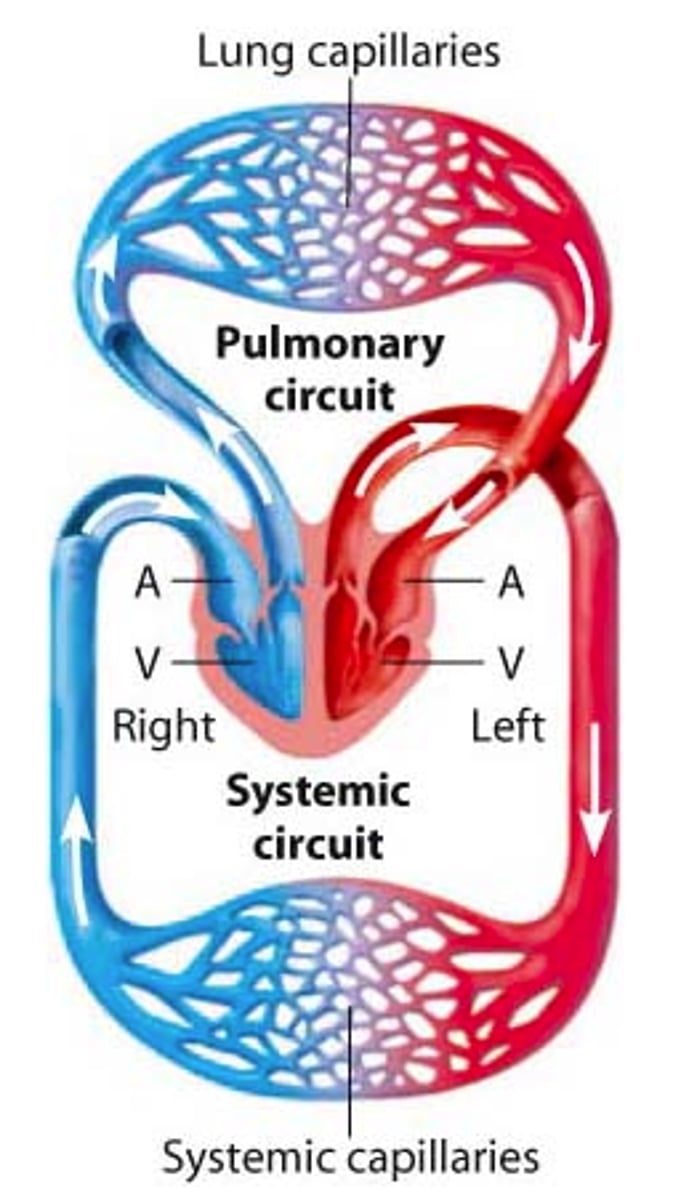
double circulatory system
have both OXYGENATED AND DEOXYGENATED blood flowing into the heart (or just flowing in general), have FOUR chambers, blood gets pumped into the heart TWICE,
heart
pump, has 1-2 pumps, contraction of muscles pumps blood