AP Chem Unit 3 Stuff
1/29
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
30 Terms
What is the Auf Bau Principle?
Fill the lowest energy levels first
What is Hunds Rule?
Fill each orbital before doubling up electrons
What is the Pauli Exclusion Principle?
No two electrons can have the same configuration
Exceptions to “normal” electron configurations (Au, Ag, Cu exception, and Cr, Mo exception?
These exceptions occur because a completely full or half-full d subshell is more stable than a partially filled one.
How to determine electron configuration for atoms?
If the element has fewer electrons (Ex. Fe2+) than write out the original configuration and then remove 2 electrons from the highest energy level. Do the same if it has more electrons, but this time add those electrons to the highest energy level.
What does the quantum number “n”
mean?
Describes the main energy level, It can be any positive integer, 1, 2, 3…
What does the quantum number “l”
mean?
Describes the shape of the electron's orbital and corresponds to subshells. Its value depends on “n”
and can range from 0 to n−1
What does the quantum number “m”
mean?
Describes the specific orbital within a subshell and its orientation in space. Its possible values range from −𝑙 to +𝑙, including 0.
What does the quantum number “s”
mean?
Describes the spin of the electron. It can have only two possible values: +1/2 or −1/2
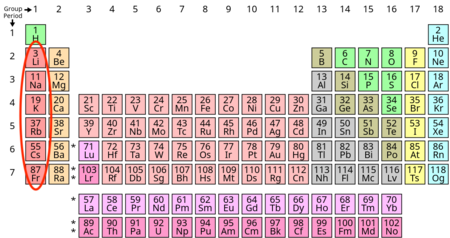
Which group/family is this?
Alkali Metals
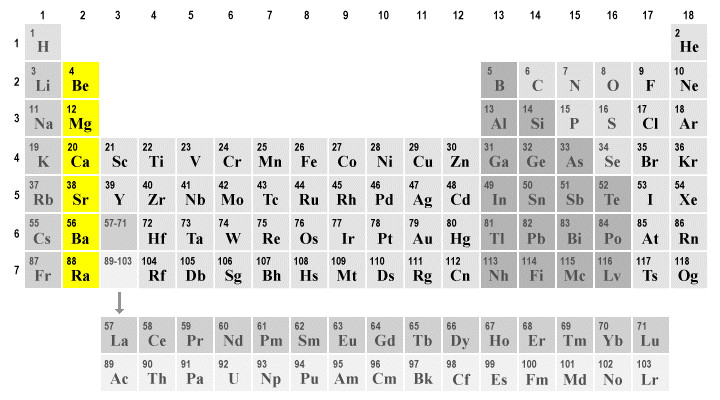
Which group/family is this?
Alkaline Earth Metals
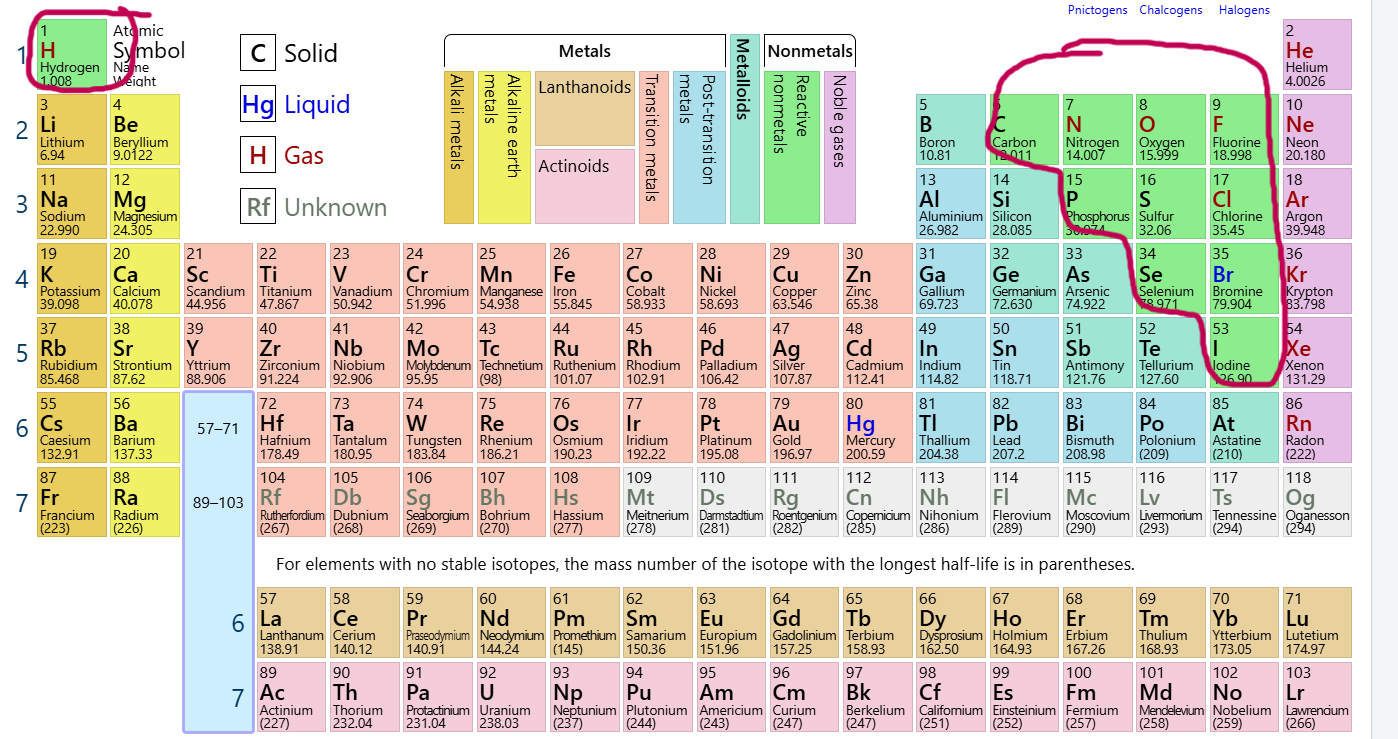
Which group/family is this?
Reactive Nonmetals
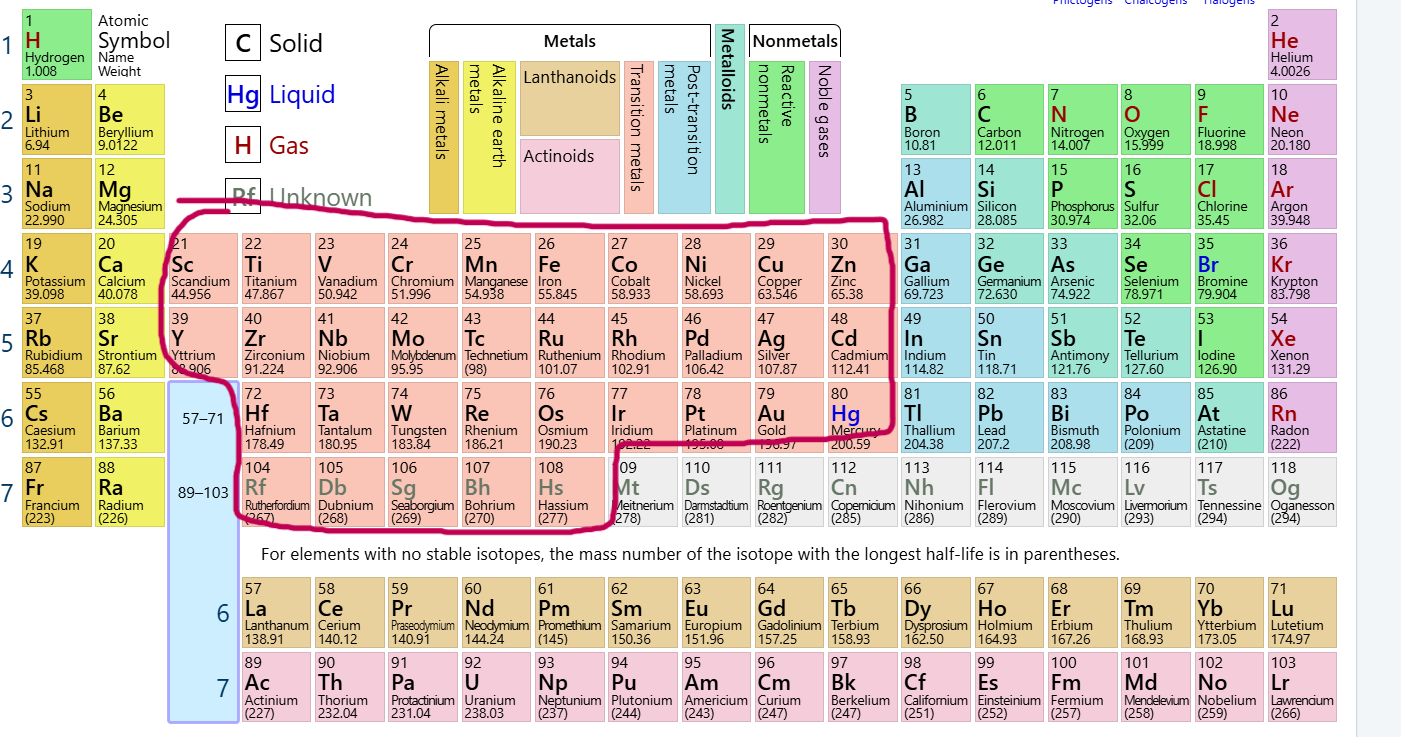
Which group/family is this?
Transition Metals
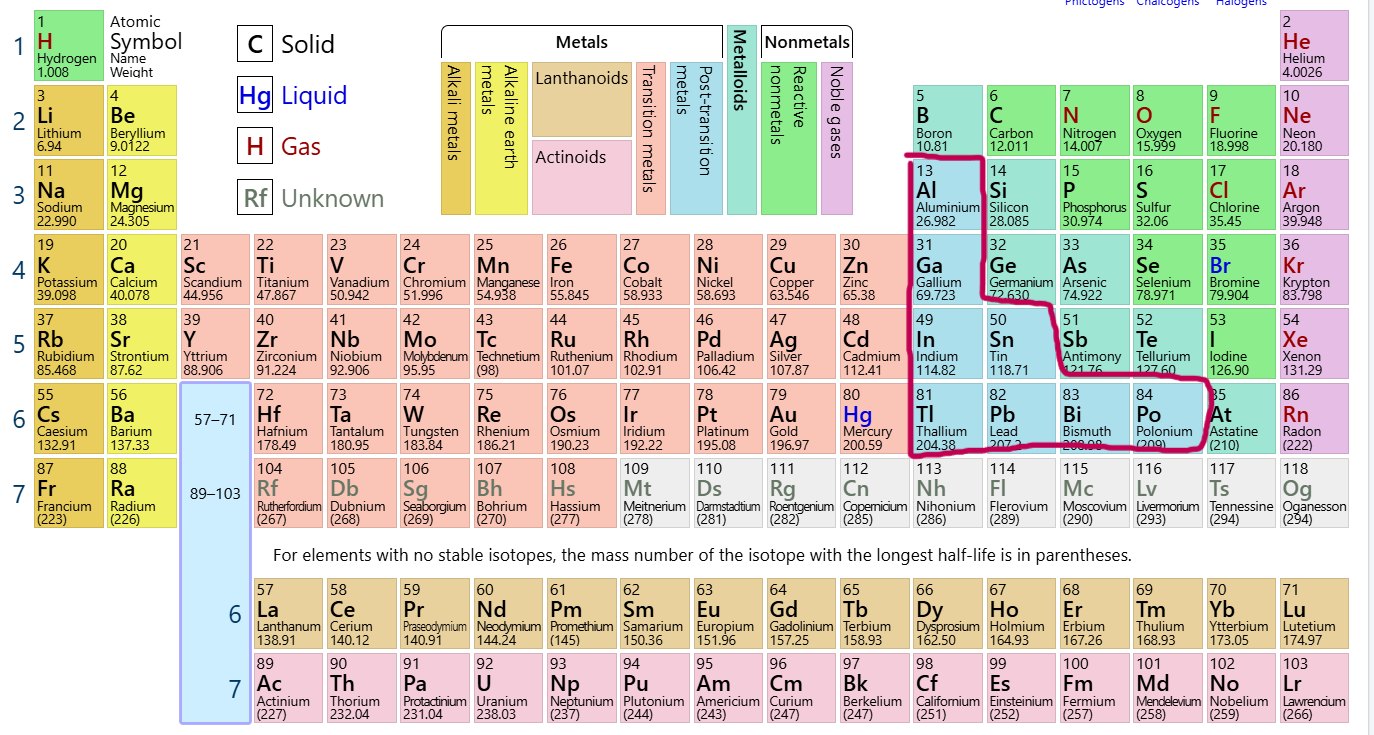
Which group/family is this?
Post-Transition Metals
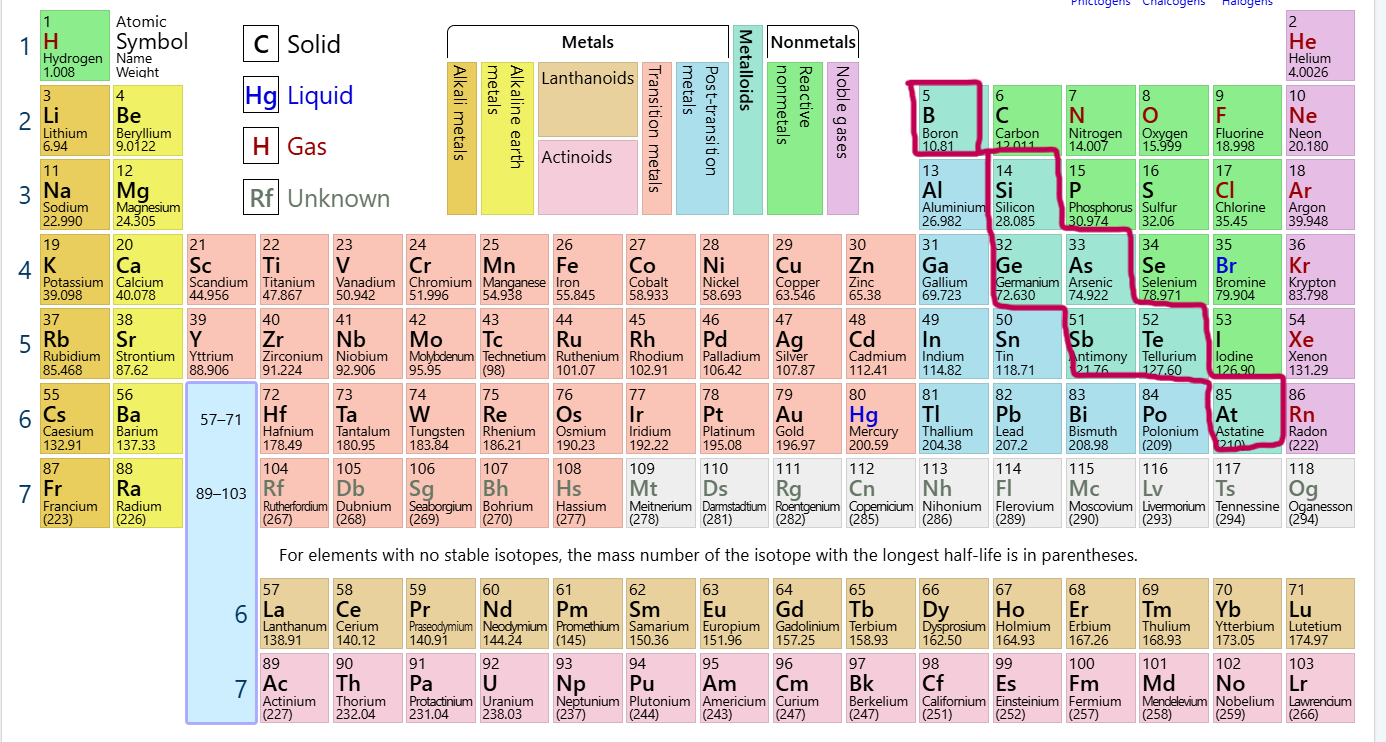
Which group/family is this?
Metalloids
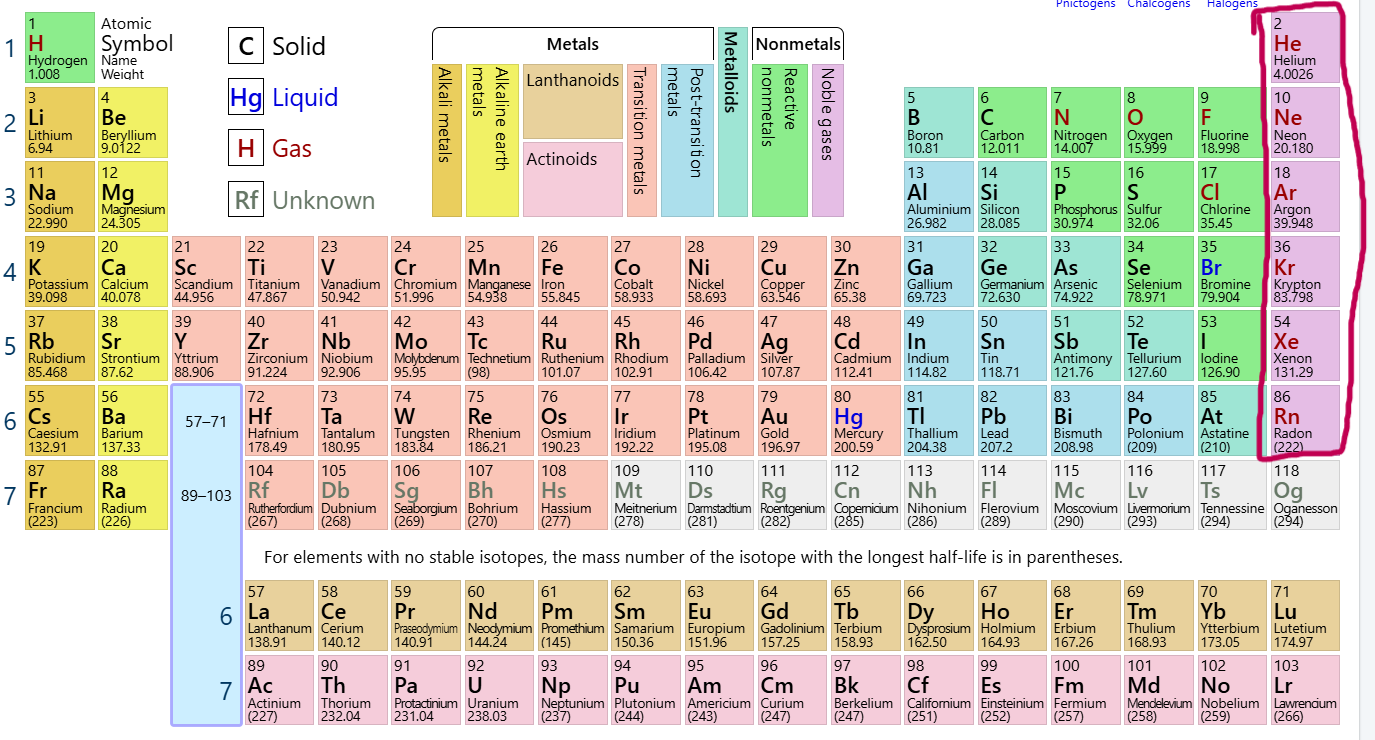
Which group/family is this?
Noble Gases
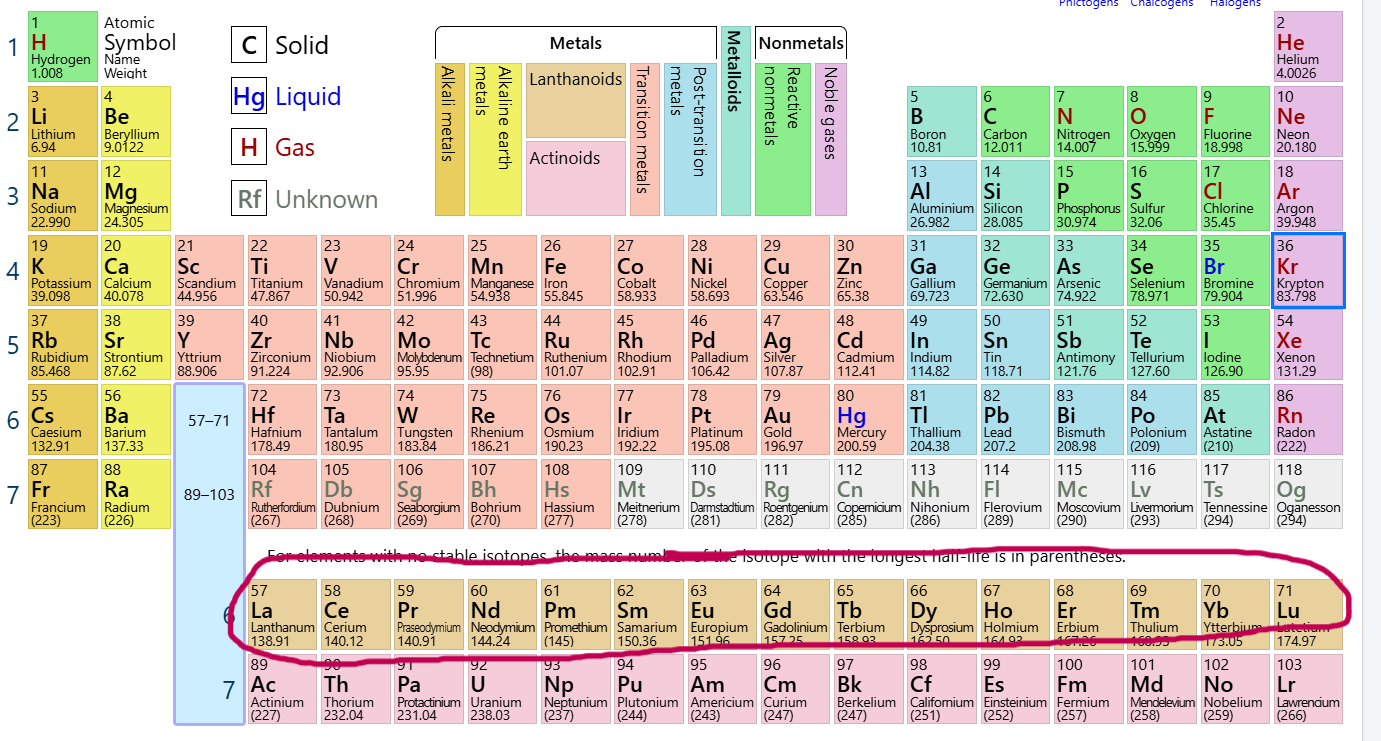
Which group/family is this?
Lanthanoids
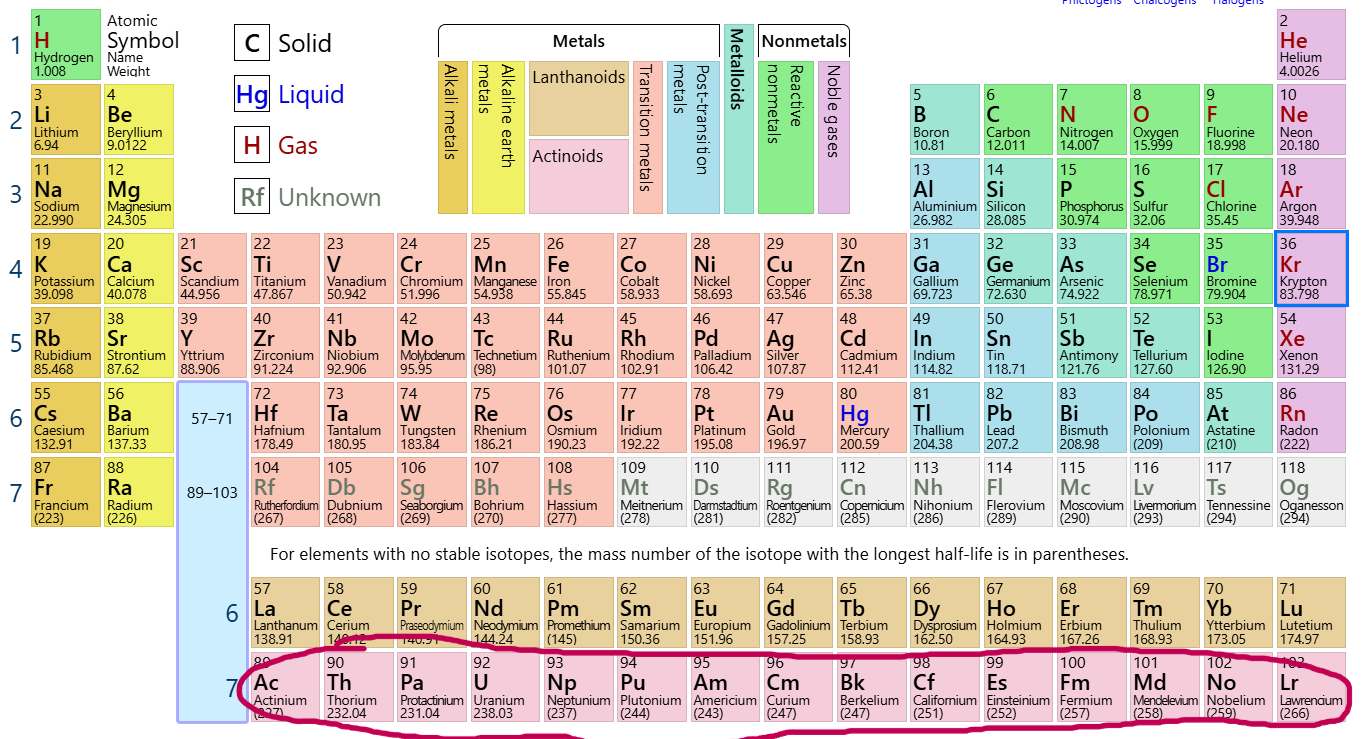
Which group/family is this?
Actinoids
What are periods?
Periods are the rows that go across the table and can determine energy level
What are columns?
Columns are the rows that go up and down the table and elements in the same column or column have the same amount of valence electrons.
How to determine valence electrons on the periodic table?
Count each column, 1, 2, 3, 4, 5, 6, 7, 8. Skip the Transition metals
What is electronegativity?
Tendency of one atom in a bond to pull electrons away from the other atom
What is Ionization Energy? (Ei)
Energy required to take 1 electron away from an atom
What is Effective Nuclear Charge? (Zeff)
The net positive charge experienced by an electron in a multi-electron atom.
What is Atomic Mass?
The weighted average mass of an element's atoms, considering all of its naturally occurring isotopes
What is Atomic Number?
The number of protons in the nucleus of an atom and uniquely identifies a chemical element
What is the Atomic Radius?
Average distance from the nucleus to the outermost part of the electron cloud
What is Reactivity of Metals?
Metals tend to lose electrons to form positive ions, and their reactivity increases as you move down and to the left on the periodic table.
What is Reactivity of Non-metals?
Non-metals tend to gain electrons to form negative ions, and their reactivity increases as you move up and to the right.
What is Electron Affinity?
The energy change that occurs when a neutral atom in the gaseous state gains an electron to form a negative ion