Biopsychology
1/58
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
59 Terms
What is the nervous system and what does it consist of?
The nervous system is a network of cells and communicates using electrical signals
Collects, processes and responds to information in environment
Coordinates working of different organs and cells in body
Consists of brain and spinal cord
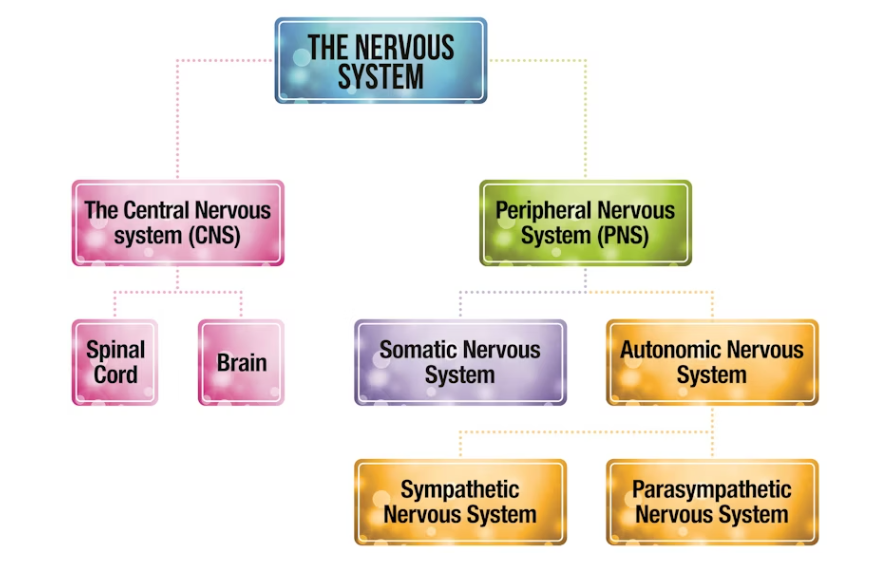
What is the nervous system divided into?
1.)Central nervous system
2.)Peripheral nervous system
What is the central nervous system responsible for?
Responsible for controlling our movements and thoughts
How many hemispheres does the brain have and what does it do?
2
Centre of all thought and conscious awareness
What does the spinal cord do?
Responsible for reflex actions i.e.pulling hand away from something hot
What is the peripheral nervous system and what is it divided into?
Transmits messages via neurons to and from CNS
Divided into autonomic nervous system(ANS)and somatic nervous system(SNS)
What does the ANS do?
Governs breathing, heart rate, digestion and stress
What does the SNS do?
Controls muscle movements and receives information from sensory receptors
What is the ANS further divided into?
The sympathetic nervous system and the parasympathetic nervous system
What is the function of the sympathetic nervous system?
Prepares body for intense, physical activity ‘fight or flight’ by increasing heart rate and blood pressure
What is the function of the parasympathetic nervous system?
Manages ‘rest and digest’ functions that calm the body after stress
Draw the divisions of the nervous system on a diagram
What does the endocrine system do?
Works alongside nervous system controlling vital functions in the body
Can have very powerful effects but works more slowly than nervous system at 2/3s compared to 0.25s response in nervous system
How does the endocrine system communicate?
Chemical signals (nervous system is electrical)
What does it instruct glands do?
To release hormones into bloodstream and carry them towards organs i.e. thyroid gland produces thyroxine increasing heart rate and therefore affecting growth rate.
What does the pituitary gland release?
Adrenocorticotrophic hormone(ACTH)/ oxytocin
What does the thyroid gland release?
Thyroxine
What does the adrenal gland release?
Adrenaline
What do the ovaries release?
Oestrogen
What do the testes release?
Testosterone
Why is the pituitary gland known as the ‘master gland’?
Controls release of hormones from other endocrine glands in body
One of first parts of brain to evolve
When do the endocrine system and the autonomic nervous system work together?
When there is a stressful event ‘fight of flight’ response
What happens to the ANS when there is an acute stressor?
Changes from parasympathetic to sympathetic
What does the pituitary gland release and what effect does this have on the adrenal gland?
ACTH and adrenal gland releases adrenaline into bloodstream
What changes happen in the body following the release of adrenaline?
Increased heart rate and breathing rate, pupils are dilated, digestion is inhibited
What happens when the threat has passed?
Parasympathetic nervous system returns body to resting state
Parasympathetic nervous system acts as a brake and reduces activities of body that were increased by actions of sympathetic branch-’rest and digest'
Give 3 evaluation points for ‘fight or flight’
1.)Gray(1988) suggests that first response to danger not to fight or flight but to avoid confrontation and ‘freeze’. Response not taken into account, does not provide explanation for why freeze may occur-doesn’t explain cognitive factors underpinning human response to danger.
2.)Taylor et al(2000) suggests women are more likely to protect offspring and form alliances with other women, rather than fight an adversary or flee-prompted more recent research which has provided an alternate explanation applicable to females.
3.)Modern day life rarely requires such an intense biological response and repeated activation of fight or flight response can have negative consequence on health i.e. raised blood pressure-activation of response can increase blood pressure can contribute to heart disease. Response is maladaptive in everyday life
What is the function of adrenaline in the ‘fight or flight’ response?
-Adrenaline secreted from adrenal medulla into bloodstream
-Heart rate increases to increase blood flow to organs and movement of adrenaline around body
-Pupils dilate to increase light entry to eyes and reduction in functioning of non-essential functions i.e.digestive system to increase energy supply to other essential functions
What are 2 ways of measuring stress?
1.)Checking size of adrenal gland which becomes enlarged under prolonged stress
2.)Checking levels of cortisol in urine
What does the sensory neuron do and what does it consist of?
Carries messages from PNS to CNS
Long dendrites and short axons
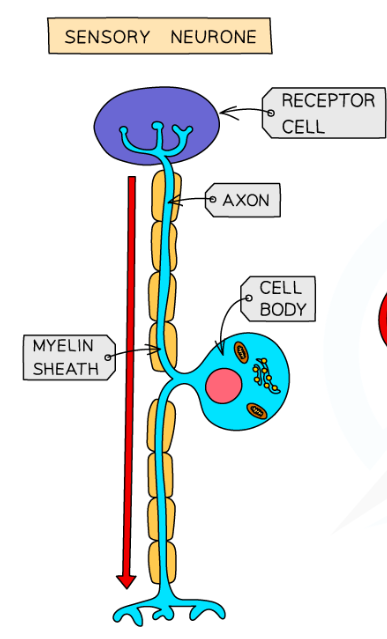
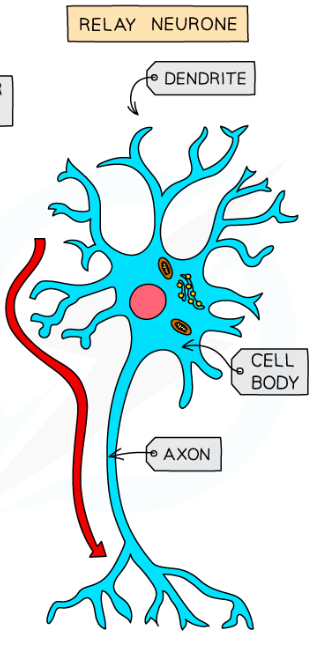
What does the relay neuron do and what does it consist of?
Connects sensory neurons to motor neurons
Short dendrites and short axons
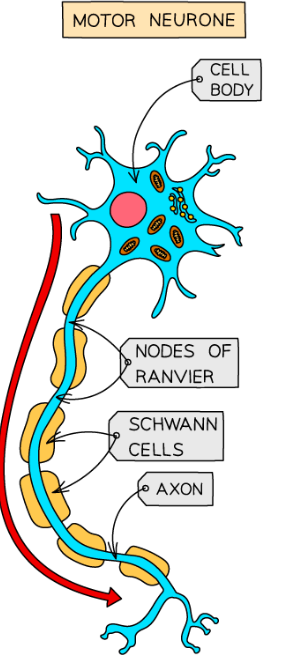
What does the motor neuron do and what does it consist of?
Connects CNS to muscles and glands
Short dendrites and long axons
What do neurons do?
Give nervous system means of communication-basis of nervous system
How do neurons transmit signals?
Electrically and chemically
Draw a neuron-basic structure
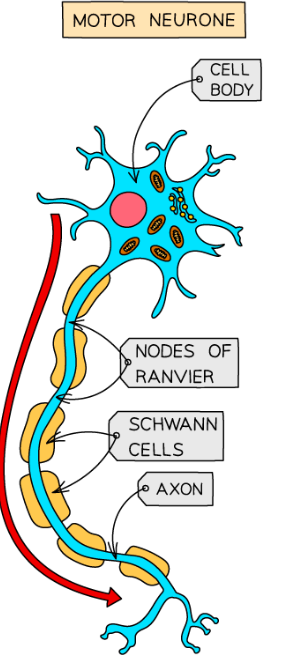
What are dendrites?
Branch like structures which protrude from cell bod
What is the cell body?
Includes nucleus, which contains genetic material of cell
What are axons?
Carry impulses away down neuron. Covered in a fatty layer of myelin sheath, speeds up electrical transmission of impulse
What are the nodes of ranvier?
Gaps in the sheath-speed process as impulse jumps across gap
What is synaptic transmission?
Process by which neurons communicate
Sends chemical messages across gap
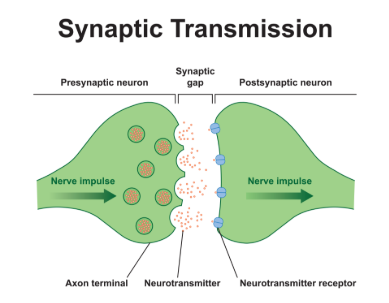
What are synapses and how do they work?
Small gaps that separate neurons-signals transmitted chemically
When electrical impulse reaches end of neuron (presynaptic terminal) it triggers release of neurotransmitter from sacs (synaptic vesicles)
What are neurotransmitters and how do they work?
Chemicals that diffuse across synapses between neuron and that have specialist functions i.e. acetylcholine is found at each point where a motor neuron meets a muscle.
Once it crosses gap, it is taken up by postsynaptic receptor site-dendrites of next neuron
What is excitation?
Adrenaline causes excitation of post synaptic neuron by increasing positive charge, making it more likely to fire and pass on electrical impulse
What is inhibition?
Seretonin neurotransmitter causes inhibition in receiving neuron-neuron becomes negatively charged and is less likely to fire.
What is a strength of increasing understanding of transmitters?
Has led to development of drugs i.e.prozac-slows down reuptake of seretonin
What are the 6 stages of synaptic transmission?
1.)Electrical signal arrives
2.)Neurotransmitter released
3.)Chemicals cross gap
4.)Signal received
5.)Next cell activated
6.)Signal is cleared
What is localisation of function in the brain theory?
The theory that specific functions/processes are localised in specific locations in the brain i.e. hippocampus strongly implicated in processing of memory
Challenges the idea that the brain is unimodal-holistic theory
How can LOF be measured?
Using brain imaging techniques
1.)fMRI
2.)MRI
3.)PET
What did Broca and Wernicke say?
Cortical specialisation-specific functions in specific locations of brain
How many hemispheres does the brain have and what is it covered by?
2 and a thin layer called the cerebral cortex
What are the different parts of the frontal lobe and their functions?
1.)Motor cortex-responsible for movement
2.)Prefrontal cortex-responsible for executive functioning
3.)Broca’s area-responsible for speech production
What are the different parts of the temporal lobe and their functions?
1.)Auditory area-responsible for auditory processing
2.)Wernicke’s area-responsible for language comprehension
3.)Hippocampus-responsible for memory and spatial navigation
What are the different parts of the parietal lobe and their functions?
1.)Somatosensory cortex-responsible for touch sensation
Governs body orientation and aids learning in practise of complex movements i.e.writing
What is the principal part of the occipital lobe and its function?
Visual area-responsible for processing visual information and distance perception
Label the different lobes of the brain
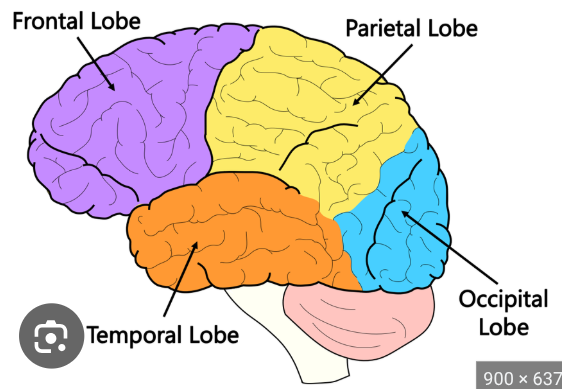
Give 3 strengths of localisation theory
1.)Support for theory-Petersen et al 1988 used brain scans to demonstrate how Wernicke’s area was active during a listening task and Broca’s area was active during reading task
Shows that these areas of the brain have different functions
2.)Support for theory-Tulving et al 1994-found semantic and episodic memories are in different parts of prefrontal cortex
3.)Neurosurgical evidence-Walter Freeman developed lobotomy meaning to cut connections in the brain to control aggression, still used for OCD and depression-success of procedures suggests disorders are localised
What is the central sulcus and where is it located in the brain?
-At the front of both parietal lobes is the somatosensory area which is separated from the motor area by central sulcus
-Prominent groove on lateral surface of cerebral hemisphere-separates frontal and parietal lobe
What did Broca and Wernicke identify about the language area?
Language located in the left side of the brain
Broca: Identified small area in left frontal lobe responsible for speech production
Wernicke: Identified an area in the left temporal lobe for understanding language
Give 2 limitations of localisation theory
1.)Lashley’s research-removed parts of cortex in rats-no area shown to be more necessary than another in the learning of a maze
Suggests that some higher cognitive functions are not localised but distributed in a holistic way- learning is too complex to be localised
2.)Dick and Tremblay 2016 found only 2% of modern researchers think that language is controlled by B’s and W’s areas
fMRI’s show function is distributed holistically in brain