(2.1.1g) Cell Ultrastructure
1/43
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
44 Terms
Cell ultrastructure (animal)
Nucleus
Nucleolus
Nuclear envelope
SER
RER
Golgi apparatus
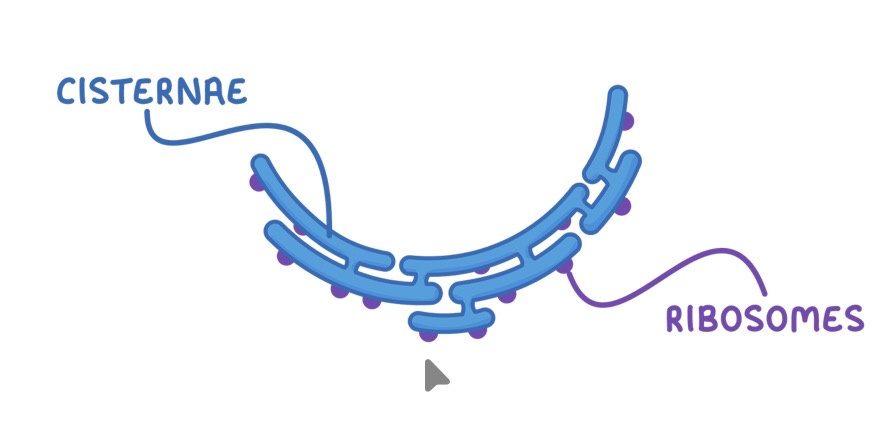
Ribosomes
Mitochondria
Vesicles (transport and secretory)
Lysosomes
Plasma membrane
Centrioles
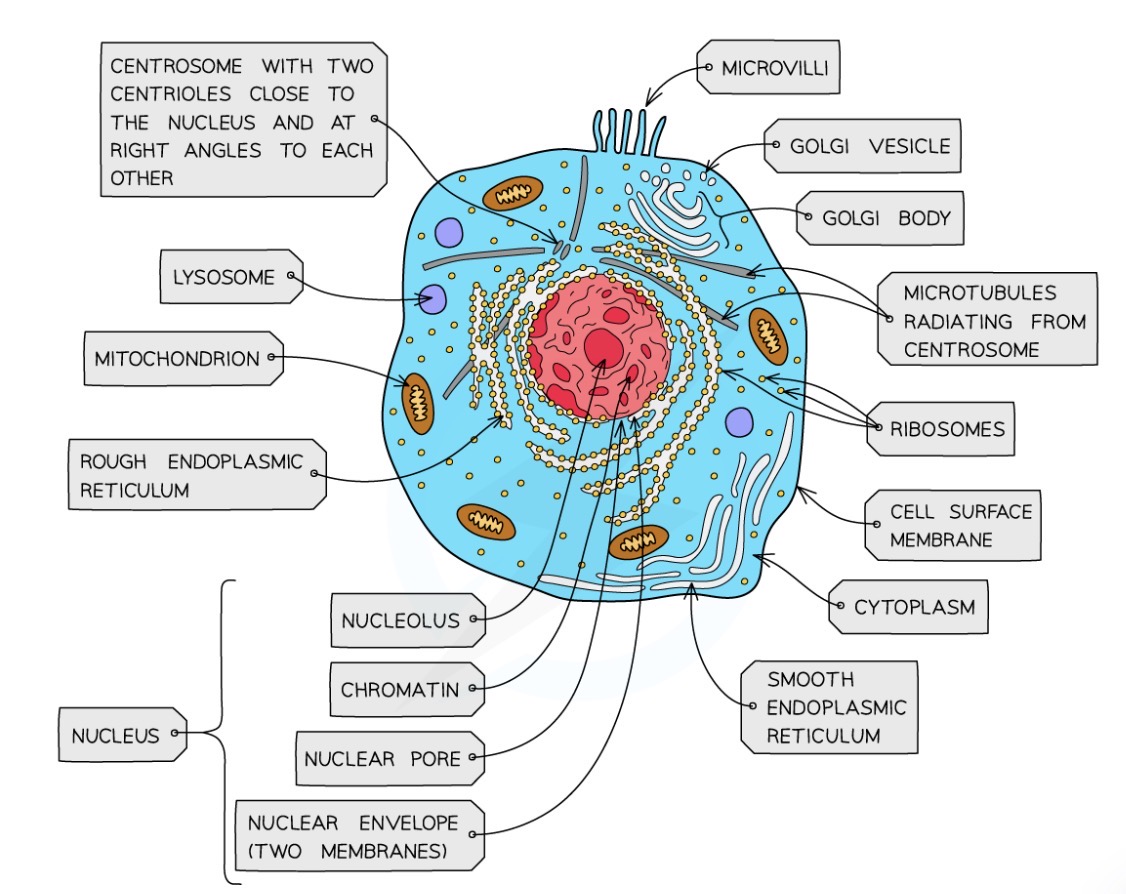
Which ones aren’t membrane bound
nucleolus
Ribosomes
Cytoplasm
Centrioles
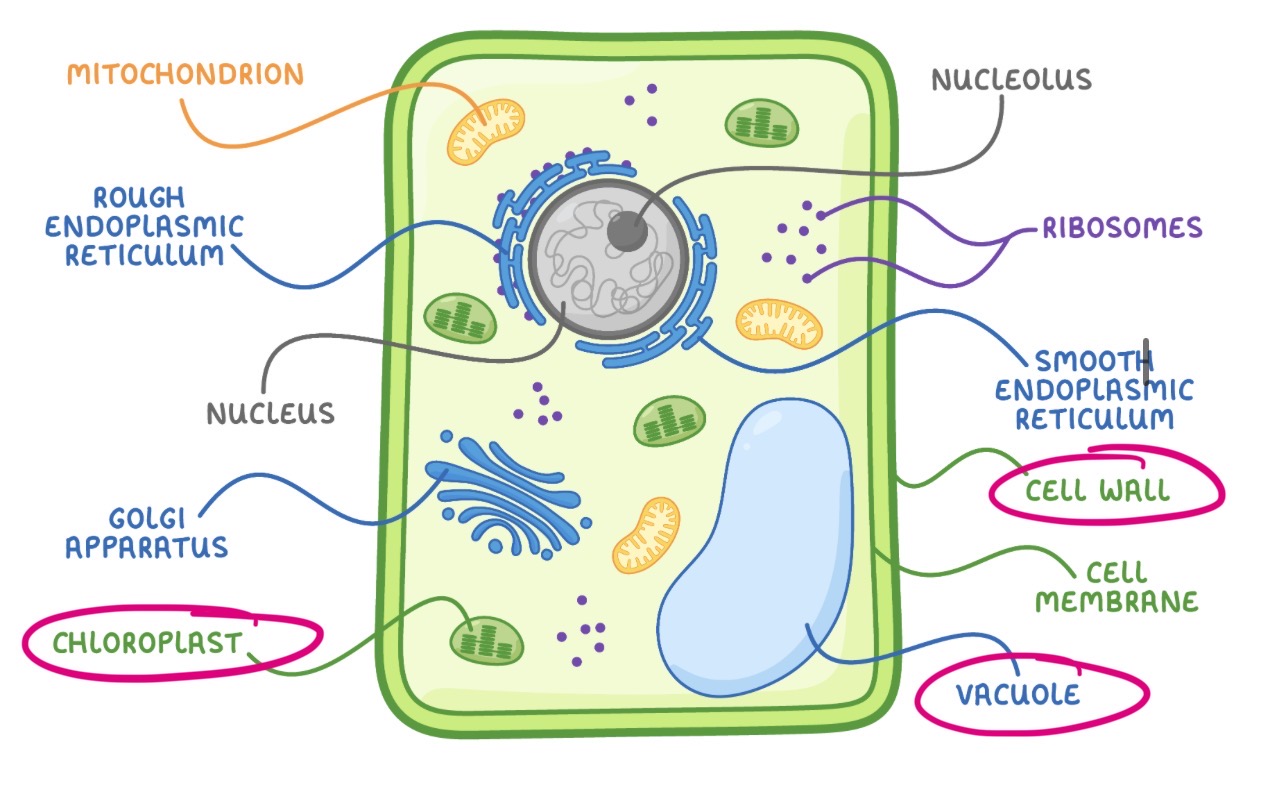
Cell ultrastructure (plants additions)
Vacuole
Chloroplasts
Cell wall
Nucleus function
Stores genetic material
Site of transcription
Makes ribosomes in nucleolus
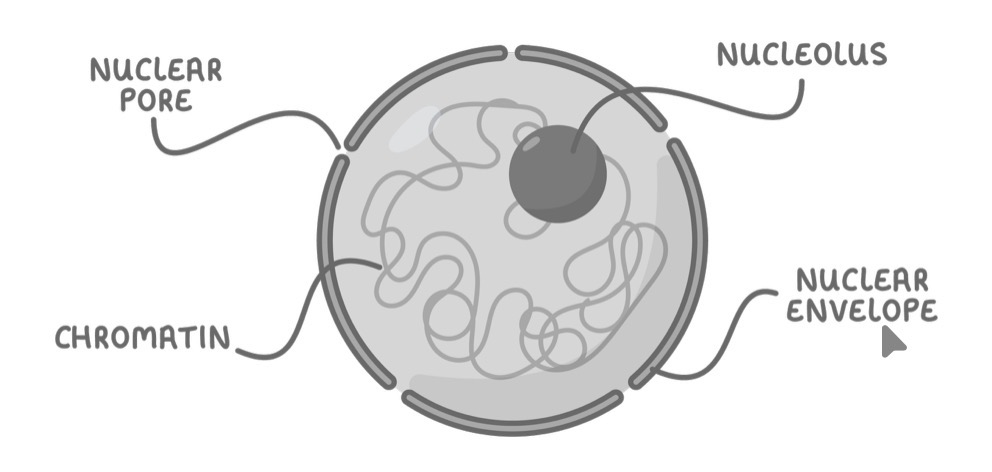
Nucleus ultrastructure
Nucleolus - composed of proteins and RNA (used to make rRNA) + not membrane bound
Nuclear pore
Nuclear envelope - double membrane that contains pres
Chromatin - DNA wound around histone proteins, condenses and coils tightly into chromosomes before cell division, otherwise more spread out
Nucleoplasm
Nucleus ultrastructure functions
Nucleolus - forms ribosomes necessary for protein synthesis
Nuclear pore - allows molecules to move in/ out of the cell
Nuclear envelope - protects nucleus from damage in the cytoplasm
Chromatin - condenses DNA
Nucleus size
10 micrometers
RER function
Synthesis and transport of proteins
Folds and processes proteins made in ribosomes
Destroys deformed proteins
Prepared proteins for transport to Golgi apparatus
RER structure
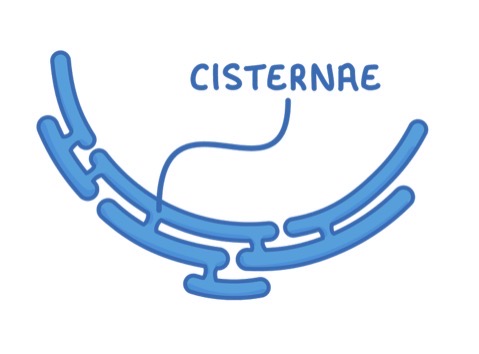
System of membranes containing fluid filled cavities (cisternae) that are continuous with the nuclear membrane
Coated with ribosomes
SER function
Responsible for lipid and carbohydrate synthesis, storage and transport
Synthesis of cholesterol, steroid hormones
Helps with detoxification
SER structure
System of cisternae that are continuous with the nuclear membrane
NO ribosomes
Golgi apparatus function
Modifying proteins and packaging them into vesicles (into lysosomes which stay in the cell or secretory vesicles which leave the cell)
forms lysosomes
Forms lipoproteins and glycoproteins
Golgi apparatus structure
Compact structure formed of cisternae
Contains smaller vesicles
Kinda looks like the WiFi signal
NO ribosomes

Ribosomes function
Site of protein synthesis
Ribosomes structure
Either free floating or attached to the RER
Made up of proteins and rRNA
consists of a large and small subunit
Eukaryotic: 80S ribosomes
Prokaryotic: 70S ribosomes
Mitochondria function
Site of the final stages of cellular respiration, where ATP is produced
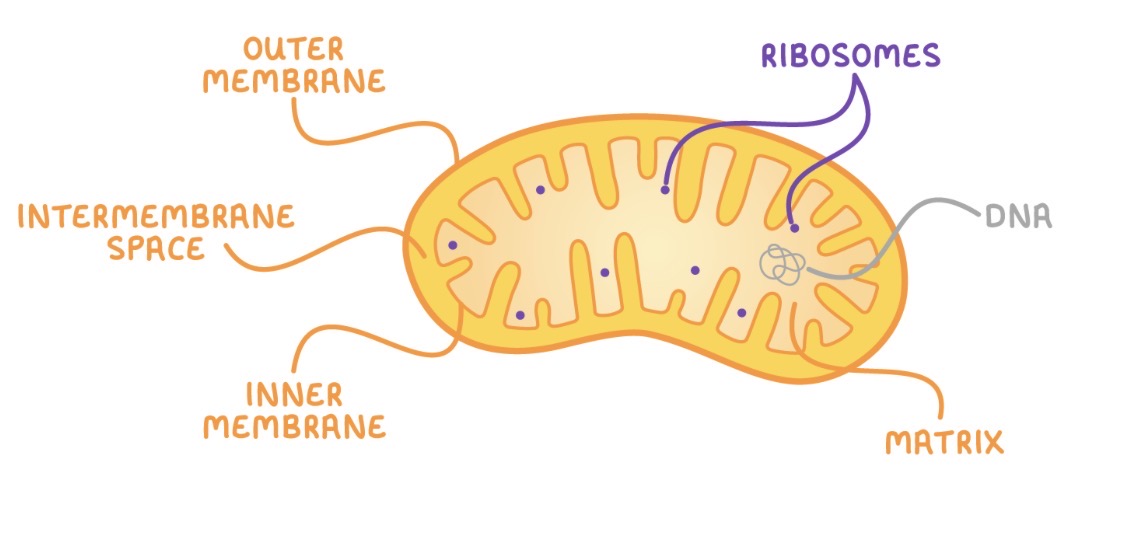
Mitochondria structure
Matrix - enzyme rich liquid
MtDNA - own DNA
Double membrane - inner highly folded to form cristae
Can produce own ribosomes and reproduce themselves
Lysosomes function
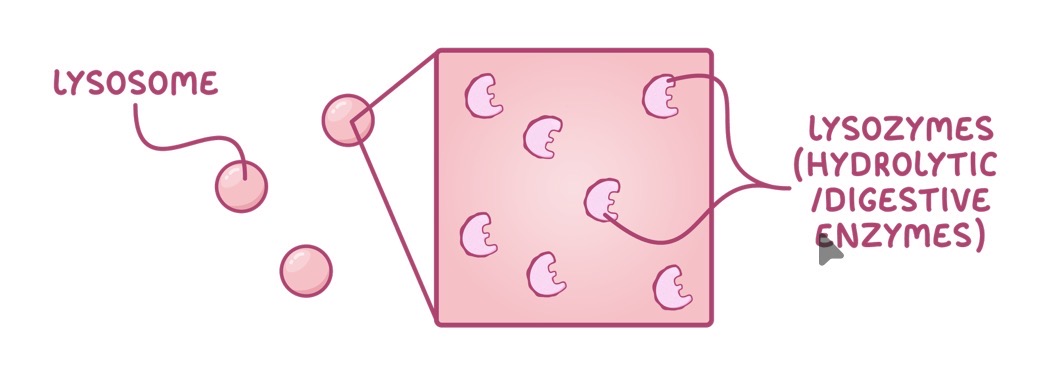
Contains hydrolytic enzymes to break down organelles and pathogens
Lysosomes structure
Round organelles
Contain hydrolytic enzymes
Surrounded by membrane to keep enzymes separate from cytoplasm of cell
Name 3 things that lysosomes engulf
Old organelles
Foreign matter
Bacteria
Vesicle function
Transport and store materials in and around cells
Vesicle structure
Membranous sacs
Single membrane that contains fluid inside
How do vesicles move from one organelle to another
Cytoskeleton provides pathways/ tracks for movement
Vesicle moves along microfilaments
Microtubules are broken down
ATP energy is used
Centrioles function
Involved in the assembly and organisation of the spindle fibres during cell division (centrosomes)
In organisms with flagella and cilia, centrioles are thought to play a role in the positioning of those structures
Centrioles structure
Component of cytoskeleton
Made of microtubules (hollow)
2 centrioles at right angles to each other form the centrosome
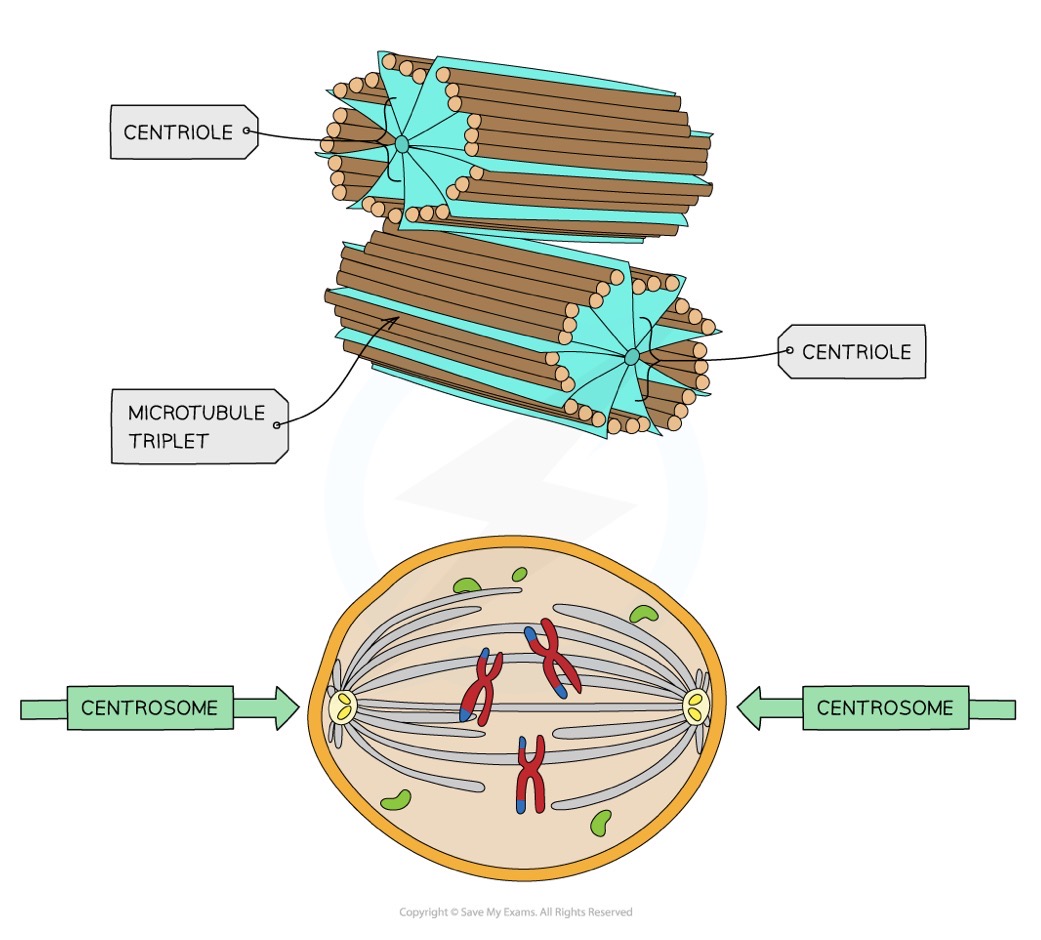
What eukaryotic organisms do not have centrioles
Not in flowering plants and most fungi
Cytoplasm function
Solvent
Reaction medium
Stable environment due to high SHC
Cell surface membrane function
Controls movement of substances into and out of cells
Cell signalling
Name 5 substances that need to travel through nuclear pores
mRNA
tRNA
Nucleotides
Steroid hormones
rRNA
Cell surface membrane structure
See other topic
Phospholipid bilayer
Chloroplast function
Site of photosynthesis - reactions to take place in grana and stoma
Chloroplast structure
Contains own DNA and ribosomes for replication
Surrounded by double membranes
Thykaloids - membrane bound containing chlorophyll
Thykaloids stack up to form grana
Grana are connected by lamellae (thin thykaloids)
Stroma - fluid
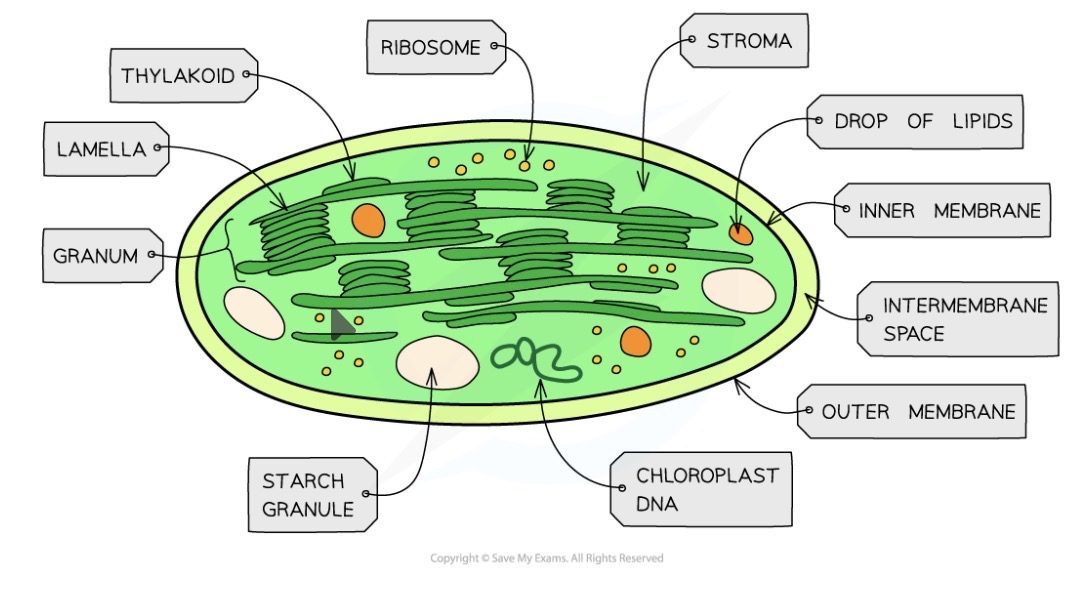
Where are chloroplasts found
The green part of plants (leaves and stems)
Chloroplast size
2-5 micrometres
Vacuole function
Storage of water, sugars and salts
Helps to maintain pressure within cells, which keeps the cells rigid and stops the plant from wilting
Vacuole structure
contains cell sap
Surrounded by tonoplast - selectively permeable membrane
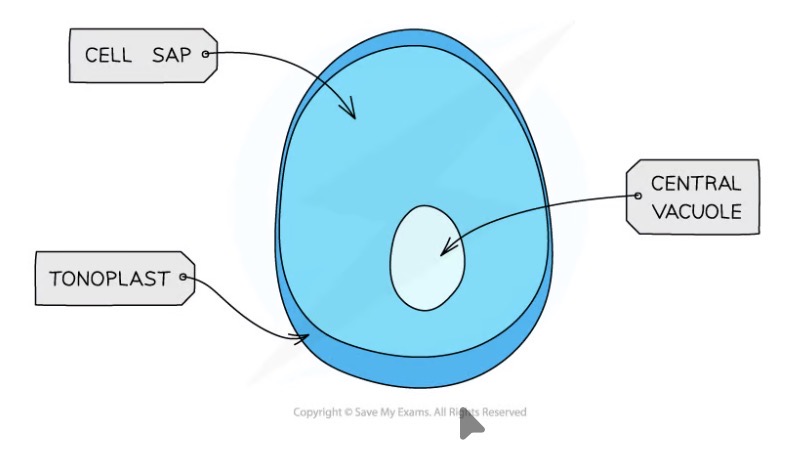
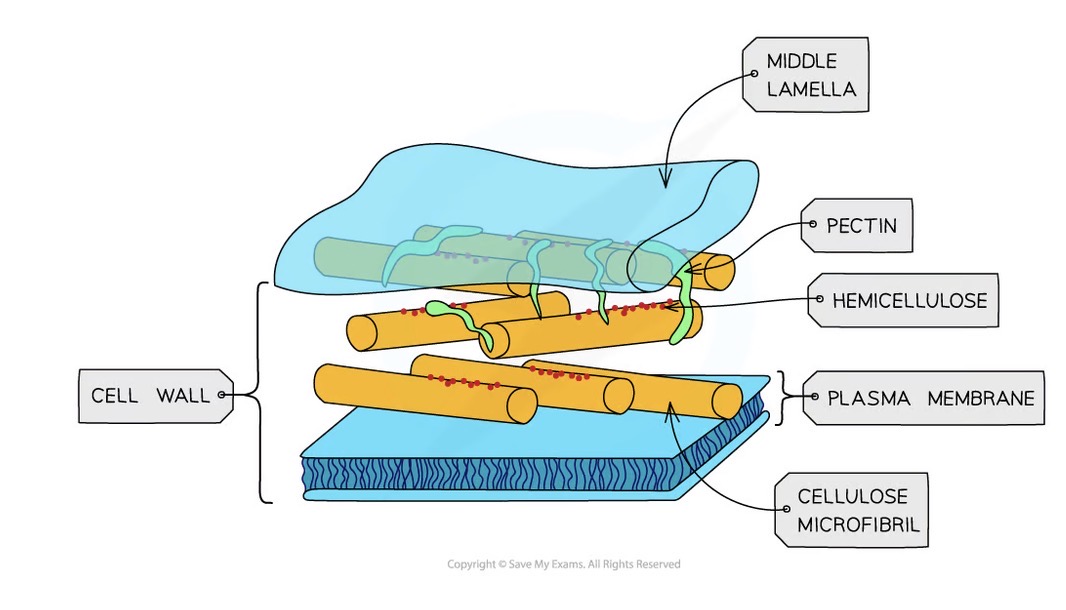
Cell wall function
Support cell
Prevents cell from bursting
Allows exchange of substances between cells
Cell wall structure
Made of cellulose in plants
Made of peptidoglycan in bacteria
Made of chitin in fungi
Freely permeable
Flagella function and structure
Enable cell motility (movement)
Made of long microtubules
E.g. sperm cell
Cilia function
Moves mucus out of lungs
Moves eggs into uterus
Made of microtubules (hair like projections)
Algae cells
Same as plant cells
Chloroplasts are different shapes
Fungi cells
contain most of the organelles found in plant cells
Do not contain chloroplasts
Cell wall made of chitin instead of cellulose
Name 3 organelles that have structures to increase surface area
Mitochondria - cristae on inner membrane
RER/ SER - cisternae
Chloroplast - grana
Where is DNA found
Nucleus
Mitochondria - mDNA
Chloroplasts - cpDNA