Semester 1 Exam 2025 - Homeostasis + Waves vocabulary
1/47
Earn XP
Description and Tags
Homeostasis, nervous system, endocrine system, lenses, brain, eyes, light, sound, colour, types of waves, electromagnetic spectrum, reflection and refraction,
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
48 Terms
transverse wave
the medium vibrates perpendicular to the direction of movement
longitudinal wave
the particles in the medium vibrate horizontally. the wave moves parallel to the particles
medium
a substance or material which a pulse moves. carries the pulse, does not create the pulse.
crest
peak of a wave
trough
lowest point of a wave
wavelength
distance between crest to a crest, or a trough to a trough; length of a complete wave cycle, often linked with frequency
sound: longer = lower pitch, vv
light: longer = lower energy/brightness, vv
amplitude
height of the wave
sound: higher = louder, vv
light: higher = brighter, vv
frequency
the rate at which the wave moves; number of wave cycles per second, often linked with wavelength
sound: higher = higher pitch, vv
light: higher = higher energy/brightness, vv
compression
sections where particles are closest together in a particle model
rarefaction
sections where particles are furthest apart in a particle model
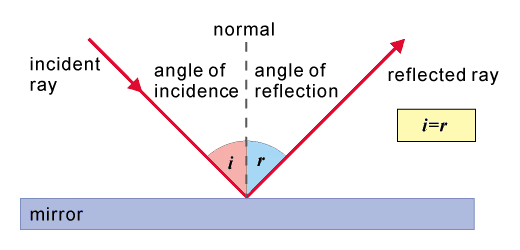
reflection: law of reflection
when something bounces back off a surface. the law of reflection suggests that the angle of reflection is always equal to the angle of incidence.
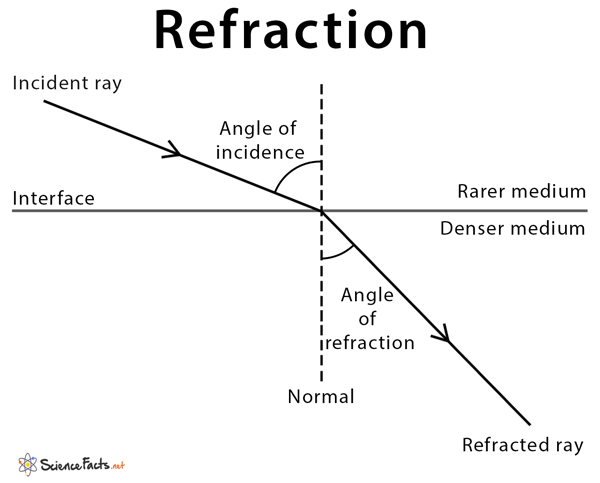
refraction
bending of light or sound as it passes through something (e.g. glass or water). The bending is caused due to the change in density or speed.
lower to higher density = bends towards the normal line
higher to lower density = bends away from the normal line
transmission
the transfer of energy between or through materials
how is sound transmitted to another medium?
sound particles in the air vibrate, which cause the next particle to vibrate, until it eventually reaches the target medium. (e.g. eardrum, then you can hear the sound)
lens
a piece of glass that is curved on at least 1 side used to refract light for different purposes
e.g. magnify objects, correct vision problems, etc.
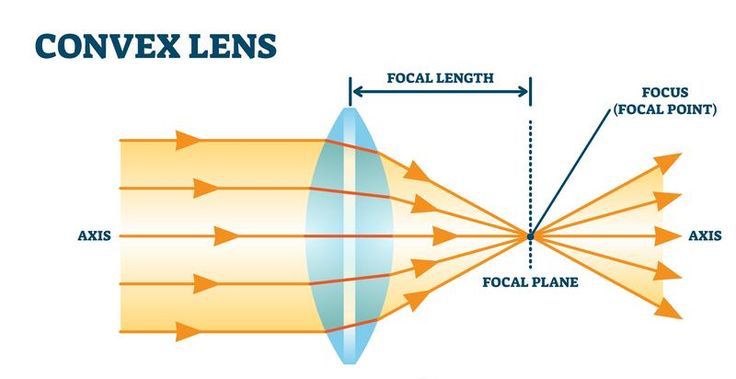
convex lens
make light rays converge, thicker in the middle
can make the image larger or smaller.
larger images are formed when the object is located between the lens and focal point
smaller images are formed when the object is >2 focal lengths from the lens
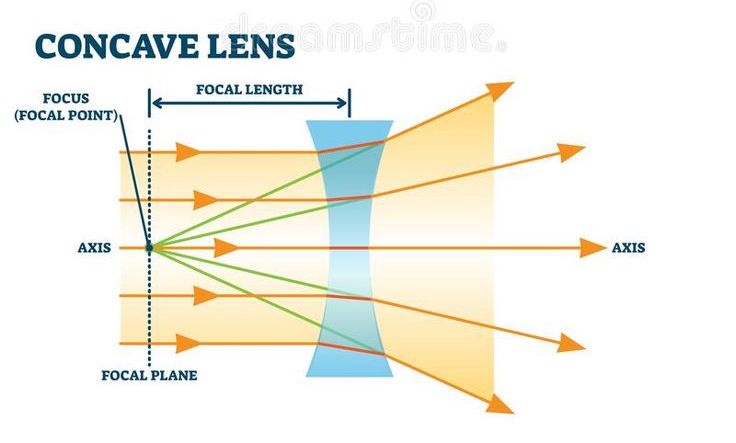
concave lens
make light rays diverge, thinner in the middle
always make images seem smaller than reality.
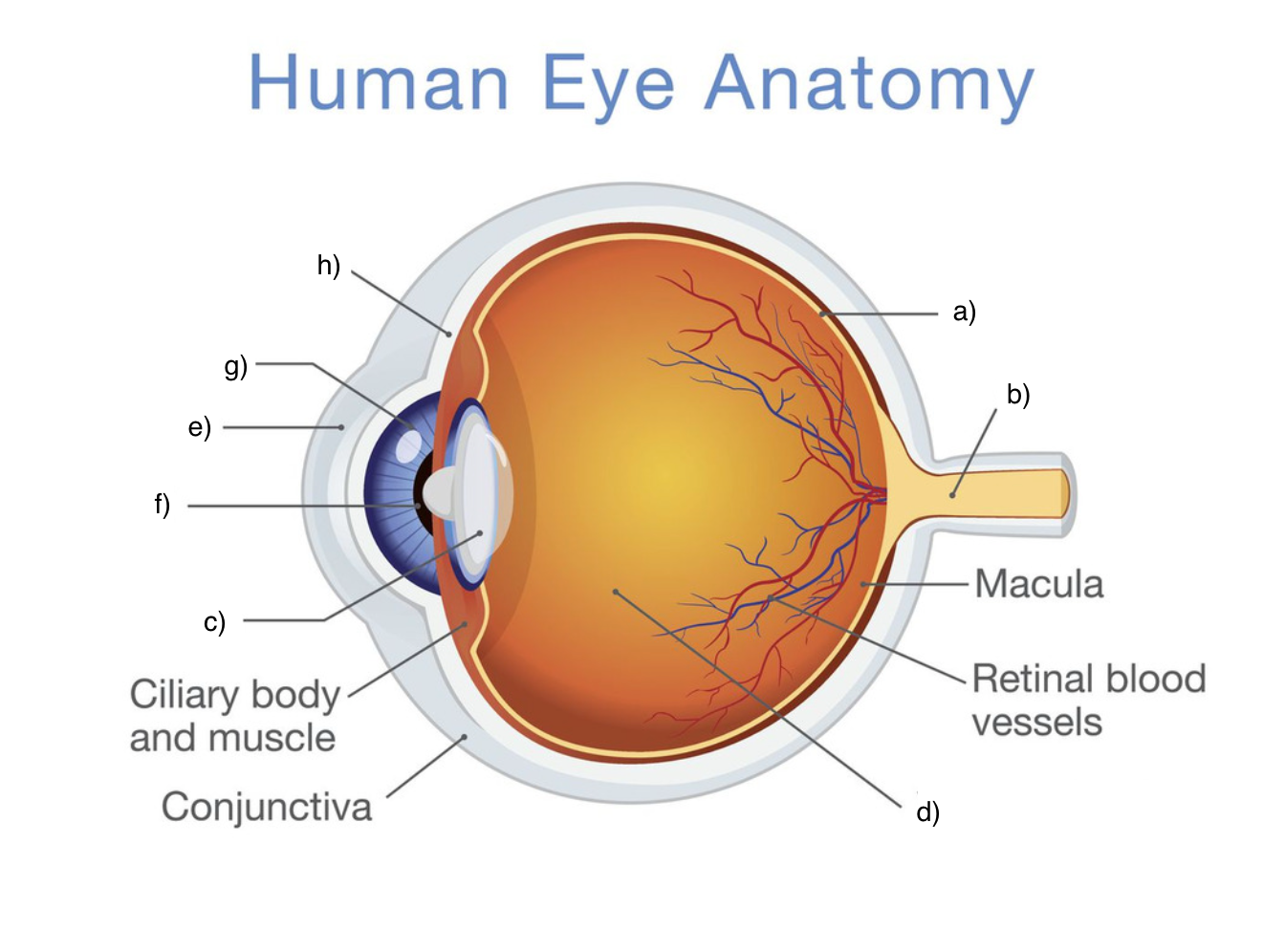
label the eye
(sclera, cornea, iris, pupil, lens, vitreous humour, retina, optic nerve)
a) retina: thin layer of nerve tissue that detects light and converts into electrical signals
b) optic nerve: a nerve extending out of the eyeball that transmits information from the retina to the brain to be processed
c) lens: a flexible and transparent structure that focuses light onto the retina for clearer vision
d) vitreous humour: a gel-like substance that fills the inside of the eye and transmits light onto the retina
e) cornea: transparent and dome-shaped that refracts and focuses light entering the eye - acts as a protective barrier
f) pupil: opening in iris that regulates the amount of light entering the eye by contracting and expanding
g) iris: coloured part of the eye that controls the size of the pupil by adjusting to different lighting conditions
h) sclera: a tough, white outer layer that provides protection and structure to the eye
explain the double-slit light experiment
When two waves overlap, they interact. If their crests meet, their amplitudes add together, resulting in a brighter light (constructive interference). If a crest meets with a trough, their amplitudes cancel out, resulting in a dimmer light (destructive interference).
what happens to white light when it is refracted? why does this happen?
White light is composed of all colours of the rainbow. When refracted, each colour is refracted a different amount because of their difference in wavelengths and frequencies. Red has the lowest frequency, therefore refracts less, while violet has the highest frequency, therefore refracts more.
absorption
The transfer of light energy into an object which is then transformed into heat energy.
radio waves
do not harm living things or the environment
can pass through dense materials (i.e. concrete, buildings)
have a low frequency, long wavelength
stimulus
a change in the internal or external environment that causes a response
receptor
a type of sense organs that detect stimuli
mechanical: related to senses touch and hearing
chemical: related to senses smell and taste - sensitive to chemicals in mouth and nose
electromagnetic: related to light (photoreceptor) and temperature (thermoreceptor)
effector
a part of the body that receives responses. becomes active in response to a stimulus.
response
the action taken as a result of a stimulus
negative feedback
counteracts the stimulus (stimulus ‘disappears’)
e.g. sweating in response to the rise in temperature
positive feedback
increases the stimulus (stimulus worsens)
e.g. contractions in childbirth cause worse contractions
central nervous system
brain and spinal cord. registers messages it receives from sense organs and coordinates responses to send to the muscles and glands
peripheral nervous system
nerves send messages between sense organs, CNS, the muscles and glands. spread entirely through the body.
somatic and autonomic nervous system
both found in the PNS
somatic: controls voluntary movements
autonomic: controls involuntary movements
sympathetic and parasympathetic divisions
both part of the autonomic nervous system
sympathetic division: fight or flight, prepares body for action
parasympathetic divions: rest and digest, calms body after action
motor neuron
sends response information away from the CNS to the muscles (efferent neuron)
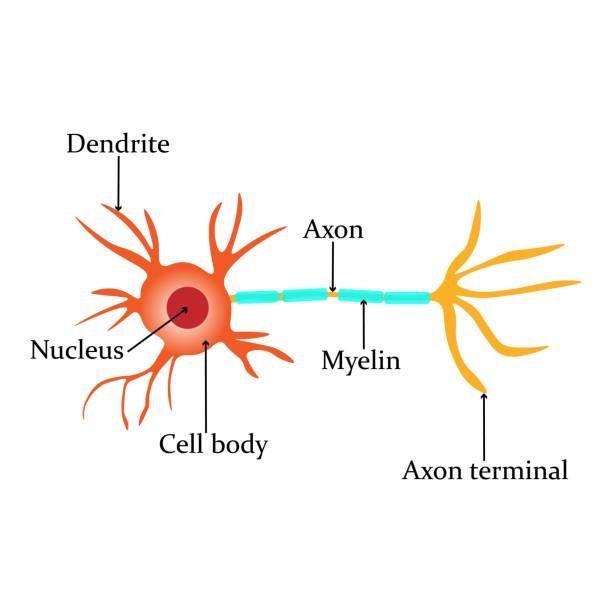
sensory neuron
sends sensory information towards CNS (afferent neuron)

interneuron
sends messages between motor and sensory neurons. only found in the CNS (lacks the myelin sheath, axons are shorter)
synapse
gap between neurons that transfers neurotransmitters (chemical signals) from one neuron to another
left side of brain
analysis and logic, maths and language, reasoning
right side of brain
creativity, intuition, feelings and sight, arts, music and emotions
frontal lobe
decision-making, problem-solving and reasoning, planning, voluntary movement, personality, emotional regulation
parietal lobe
sensory perception (touch, temp., pain), spatial awareness, attention
occipital lobe
visual processing (the visual cortex), object recognition, colour perception, spatial vision (comprehending size, shape, etc)
temporal lobe
sound processing, memory formation and retrieval, language comprehension
cerebellum
coordination of movement, balance, muscle tone, motor learning
brain stem
receives sensory information from the peripheral nervous system and sends motor commands to the body
hypothalamus
maintains internal homeostasis. an endocrine gland that releases hormones that regulate the pituitary gland.
and:
regulates the autonomic NS
regulates the circadian rhythm (sleep-wake cycles)
controls emotions
regulates sexual behaviour and reproduction
diencephalon
controls sensations, weight regulation, energy and instinctual behaviours
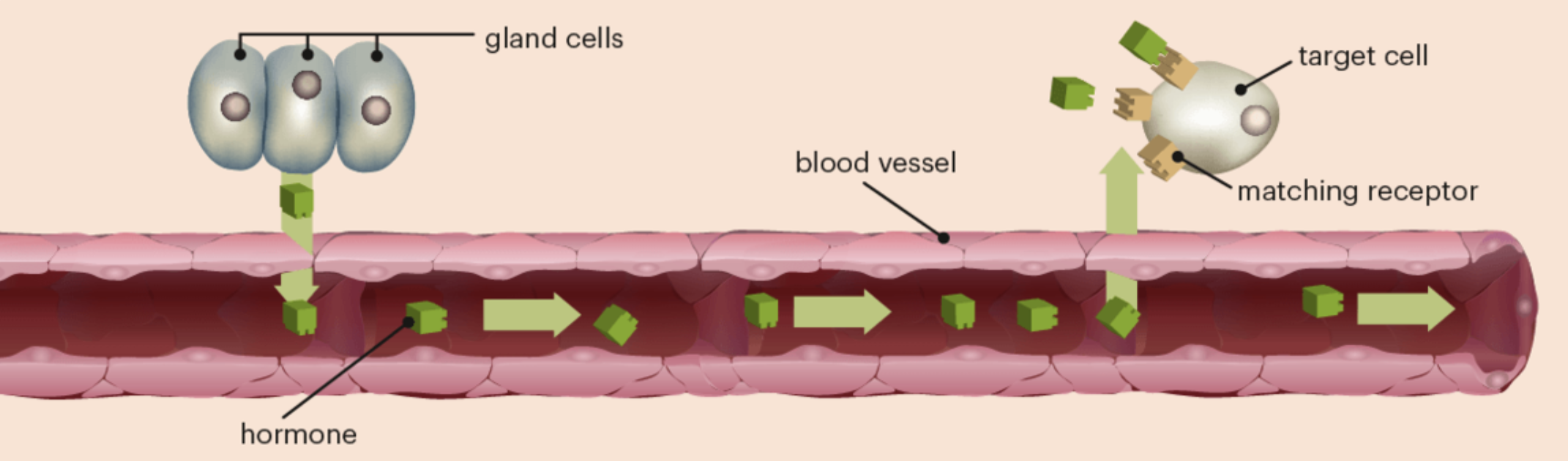
endocrine system
produces and releases hormones to maintain homeostasis. regulates mood, growth, development, metabolism, reproduction, etc.
hormone receptors
target cells have specific receptors that recognise and bind into the hormone to be detected