Facial Bones- Orbits Procedures
1/4
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
5 Terms
Modified Waters - Pareitalacanthial
Recumbent or erect
Close eyes and hold them still for exposure
*Many facilities do the modified and regular waters
MSP centered
OML 50 degrees from cassette
*Even though 50 is a bigger number than the usual 37, it is actually less extension of the head
CR perpendicular to midorbits
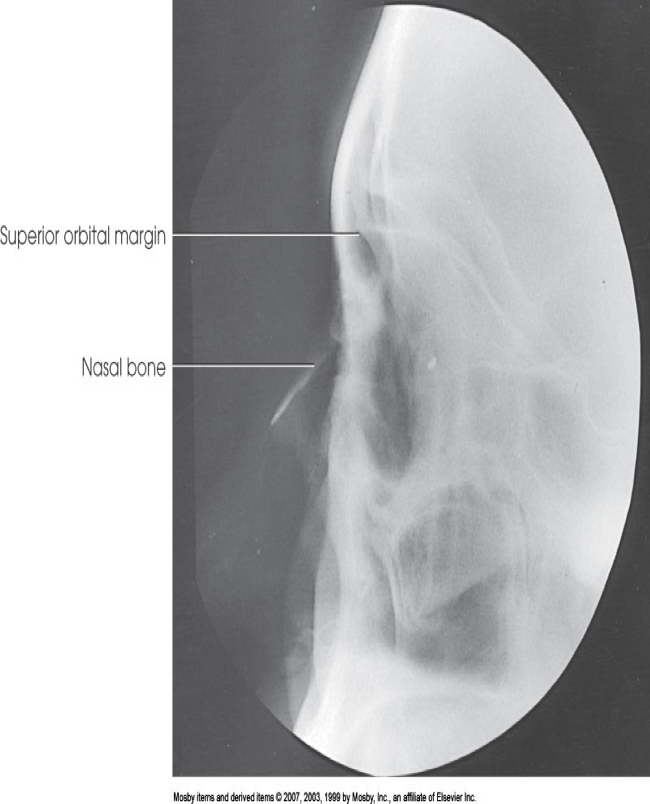
Lateral Orbits
Patient adjusted true lateral
Patient looks straight ahead for exposure
IOML, MSP, Interpupillary line
CR perpendicular to outer canthus
Evaluation Criteria:
Density and contrast optimal
Superimposed orbital roofs
No rotation
Collimate to just orbital region
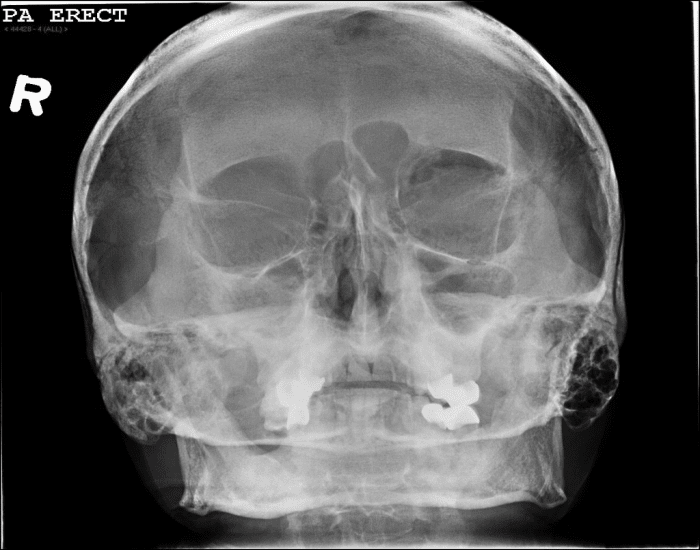
PA Axial - Exaggerated Caldwell
Pt. prone or seated
OML perpendicular to IR
MSP perpendicular to IR
For demonstration of orbital rims, in particular the orbital floors, CR to exit through orbits at an angle of 30 caudad
Evaluation Criteria:
Petrous pyramids lying below orbital shadows
What are some things that stay the same from skull and sinus imaging?
Radiation protection
Patient Prep
Room prep i.e. cleanliness
General body positioning
Techniques
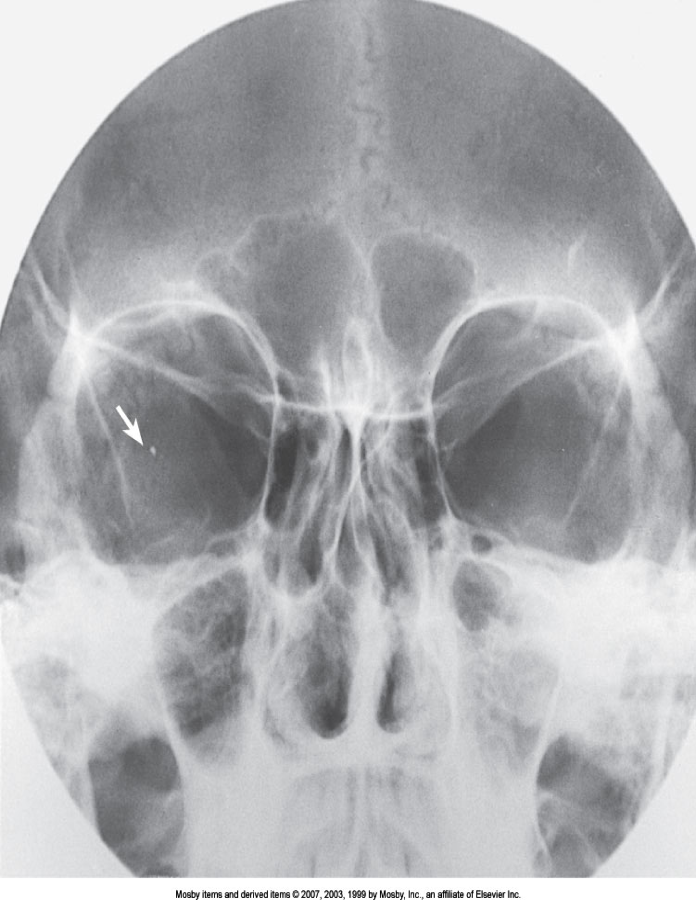
Why are orbits done?
Pressure directed to the eyeball forces it back into the orbit and may cause a “blow out” fracture of the delicate bony floor
In order to demonstrate bleeding into the sinus cavity, orbits must be done erect when possible
The injury must be diagnosed and treated accurately so that the person’s vision is not jeopardized
Also done for foreign body localization