ANAT 200 - Muscular System
0.0(0)
Card Sorting
1/168
Earn XP
Last updated 5:45 PM on 2/8/23
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
169 Terms
1
New cards
axial musculature
associated with the axial skeleton (skull, vertebral column, and ribs)
2
New cards
What are the main characteristics of axial musculature?
* innervation by cranial nerves (CNs) or spinal nerves
* attachments on axial skeleton, associated organs (e.g. eyeball), or soft tissue (skin of face)
* attachments on axial skeleton, associated organs (e.g. eyeball), or soft tissue (skin of face)
3
New cards
What are the major functions of the axial skeleton?
* vision, mastication, facial expression, and swallowing
* upright posture and movement of the back
* support of abdominal and pelvic viscera
* respiration
* urination, defecation, and partuition
* upright posture and movement of the back
* support of abdominal and pelvic viscera
* respiration
* urination, defecation, and partuition
4
New cards
What are the major groups of the axial skeleton?
* muscles of the head and neck (face, oral, cavity, pharynx, and larynx)
* muscles of the back
* muscles of the thorax and abdominopelvic cavities
* muscles of the pelvis and perineum
* muscles of the back
* muscles of the thorax and abdominopelvic cavities
* muscles of the pelvis and perineum
5
New cards
appendicular musculature
associated with the appendicular skeleton (limb bones, including should and pelvic girdles)
6
New cards
What are 6 head and neck muscles?
* extraocular muscles
* muscles of mastication
* muscles of facial expression
* pharyngeal muscles
* tongue msucles
* neck muscles
* muscles of mastication
* muscles of facial expression
* pharyngeal muscles
* tongue msucles
* neck muscles
7
New cards
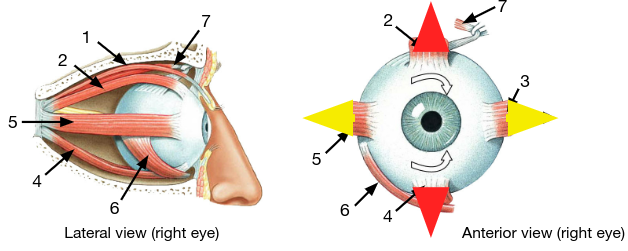
extraocular muscles
innervated by oculomotor (CN III), trochlear (CN IV), and abducens nn. (CN VI)
8
New cards
What are 7 extraocular muscles?
* levator palpebras superioris
* superior rectus
* medial rectus
* inferior rectus
* lateral rectus
* inferior oblique
* superior oblique
* superior rectus
* medial rectus
* inferior rectus
* lateral rectus
* inferior oblique
* superior oblique
9
New cards
Levator palpebras superioris
CN III; pulls eyelid up; attches to eyelid
10
New cards
Superior rectus
CN III; look up
11
New cards
Medial rectus
CN III; side to side
12
New cards
Inferior rectus
CN III; look down
13
New cards
Lateral restus
CN VI; side to side
14
New cards
Inferior oblique
CN III; look up
15
New cards
Superior oblique
CN IV; look down
16
New cards
CN VI palsy
lateral rectus is paralyzed on right side fo the patient
17
New cards
muscles of mastication
innervated by trigeminal n. (CN V**3**)
18
New cards
What are 4 muscles of mastication?
* temporalis
* masseter
* lateral pterygoid muscle
* medial pterygoid muscle
* masseter
* lateral pterygoid muscle
* medial pterygoid muscle
19
New cards
Temporalis
attaches on frontal bone, parietal bone, temporal bone and through zygomatic arch to the coronoid process of the mandible; elevator of mandible when chewing on food and closing mouth
20
New cards
Masseter
attaches on zygomatic arch and ramus of mandible; elevator of mandible when chewing on food and clsoign mouth
21
New cards
Lateral pterygoid muscle
attach on pterygoid plate of sphenoid bone; depressor of mandible to open mouth; can also move mandible side
22
New cards
Medial pterygoid muscle
attach on pterygoid plate of sphenoid bone; elevator of mandible when chewing on food and closing mouth
23
New cards
What are the biomechanics of chewing?
24
New cards
muscles of facial expression
innervated by facial n. (CN VII)
25
New cards
What are 5 muscles of facial expression?
* orbicularis oculi
* orbicularis oris
* platysma
* occipitofrontalis (frontal belly)
* buccinato
* orbicularis oris
* platysma
* occipitofrontalis (frontal belly)
* buccinato
26
New cards
Orbicularis oculi
closes eyelids
27
New cards
Orbicularis oris
purses lips; kissing
28
New cards
Platysma
tenses skin of neck
29
New cards
Occipitofrontalis (frontal belly)
raises eyebrows, wrinkles forehead
30
New cards
Buccinato
tenses cheeks, suction
31
New cards
Bell’s palsy
damage to facial nerve (CN VII); right side of the face sags
32
New cards
pharyngeal muscles
innervated mostly by vagus n. (CN X); involved in swallowing
33
New cards
What are 4 pharyngeal muscles
* tensor and levator veli palatini
* superior constrictor
* middle constrictor
* inferior constrictor
* superior constrictor
* middle constrictor
* inferior constrictor
34
New cards
Tensor and levator veli palatini
tenses and elevates soft palate
35
New cards
Superior constrictor
constriction of pharynx
36
New cards
Middle constrictor
constriction of pharynx
37
New cards
Inferior constrictor
constriction of pharynx
38
New cards
tongue muscles
innervated mostly by hypoglossal n. (CN XII); glossus in name = tongue muscle
39
New cards
What are the 4 tongue muscles
* palatoglossus
* styloglossus
* hyoglossus
* genioglossus
* styloglossus
* hyoglossus
* genioglossus
40
New cards
What do the 4 tongue muscles do?
control position of tongue
41
New cards
Which tongue muscle has an attachment on the hyoid bone?
hyoglossus
42
New cards
neck muscles
innervated by CNs or cervical nn.
43
New cards
What are the 6 muscles of the neck?
* mylohyoid
* diagastric
* infrahyoid mm,
* sternocleidomastoid
* longus colli
* scalene mm.
* diagastric
* infrahyoid mm,
* sternocleidomastoid
* longus colli
* scalene mm.
44
New cards
Mylohyoid
tenses floor of mouth during swallowing
45
New cards
Diagastric
has 2 bellies; assists in depression of mandible to open mouth wide; attach to hyoid
46
New cards
Infrahyoid mm.
there are 4; pull down hyoid bone
47
New cards
Sternocleidomastoid
turns head to opposite side of contraction; attaches to sternum, clavicle, and mastoid process
48
New cards
Longus capitis
flexor of neck and head
49
New cards
Longus colli
flexor of neck
50
New cards
Scalene mm.
lateral flexor of neck; elevators of ribs 1 and 2
51
New cards
What are the biomechanics of swallowing?
1. contraction of mylohyoid and tongue muscles to move tongue up and back
2. contraction of tensor and levator veli palatini muscles - elevates and stretches soft palate so nothing enters nasal cavity
3. elevation of larynx by many muscles so the food does not go into airway
4. sequential contraction from top the top of constrictor muscles - bring food down neck
52
New cards
What are 2 back muscles?
* transverospinal group
* erector spinae
* erector spinae
53
New cards
transverospinal group
delicate adjustments at zygapophyseal joints of vertebrae; can be source of back pain
54
New cards
erector spinae
extensors of back; allows trunk to remain in vertical position
55
New cards
What are the 3 erector spinae muscles?
* longissimus
* spinalis
* iliocostalis
* spinalis
* iliocostalis
56
New cards
What are 4 muscles of the trunk?
* intercostal muscles mm.
* rectus abdominis
* abdominal mm.
* diaphragm
* rectus abdominis
* abdominal mm.
* diaphragm
57
New cards
intercostal muscles mm.
3 different layers; most superficial are elevators of ribs during respiration (inhalation phase)
58
New cards
intercostal contraction during respiration
contraction of intercostal mm. produces elevation of ribs; increases volume of thoracic cavity
59
New cards
rectus abdominis
flexors of trunk
60
New cards
What are the 3 layers of the abdominal mm.
* 2 obliques
* 1 transverse
* 1 transverse
61
New cards
external and internal abdominal obliques
flexors, lateral flexors, and rotators of trunk
62
New cards
transversus abdominis
deepest muscle on the side; used to compress
63
New cards
What can all abdominal mm. do?
increase intra-abdominal pressure (during defecation, urination, parturition, loud singing, etc)
64
New cards
diaphragm
separates thoracic and abdominal cavities; chief muscle of respiration; innervated by phranic n. (C3-C5 levels of spinal cord)
65
New cards
What are the 3 parts of the diaphragm
* central tendon
* muscle fibers
* crura
* muscle fibers
* crura
66
New cards
central tendon
brought down each time you breath in
67
New cards
muscle fibers
attach to sternum, ribs, central tendon; in back for cris or crura in back
68
New cards
crura
legs of diaphragm
69
New cards
What 3 things does the diaphragm have an opening for?
* inferior vena cava
* esophagus
* aort
* esophagus
* aort
70
New cards
Inferior vena cava
brings blood from the lower extremities and abdomen to heart
71
New cards
Esophagus
brings food to stomach
72
New cards
Aort
blood from the heart to support body
73
New cards
Contraction
relaxation of diaphragm during exhalation phase of respiration; contraction of diaphragm during inhalation phase of respiration; brings central tendon down to increase volume of thoracic cavity
74
New cards
What are 2 muscles of the pelvis?
* coccygeus
* levator ani
* levator ani
75
New cards
What do the 2 pelvic muscles do?
form the pelvic diaphragm (pelvic floor); provide support to pelvic viscera such as urinary bladder, rectum, uterus (female), prostate gland (male)
76
New cards
What are 4 perineal muscles?
* external anal sphincter
* external urethral sphincter
* bulbospongiosus
* ischiocavernosus
* external urethral sphincter
* bulbospongiosus
* ischiocavernosus
77
New cards
External anal sphincter
regulates anal opening (fecal continence); under voluntary control; innervated by pudendal n.
78
New cards
External urethral sphincter
regulates urethral opening (urinary continence); more developed in males; innervated by pudendal n.
79
New cards
What so the bulbospongiosus and ischiocavernosus do?
contraction increases blood flow into erectile tissues of genitalia; innervated by pudendal n.
80
New cards
What are the major characteristics of the appendicular musculature?
* innervation by spinal nerves forming plexuses (with exception of trapezius - CN XI)
* attachments on axial and appendicular skeleton
* movements - muscle contraction causes a limb segment to move in a specific plane at a given joint (e.g. contraction of quadriceps femoris extends the leg at the knee joint)
* attachments on axial and appendicular skeleton
* movements - muscle contraction causes a limb segment to move in a specific plane at a given joint (e.g. contraction of quadriceps femoris extends the leg at the knee joint)
81
New cards
How are limb muscles organized?
in compartments (each muscle compartment is innervated by a specific nerve branch of a plexus)
82
New cards
What are major characteristics of upper limb musculature?
* innervated by branches of brachial plexus (levels C5 to T1 of psinal cord), except trapezius (CN XI)
* four major muscle groups crossing upper limb joints: shoulder (pectorial girdle), arm, forearm, and hand
* four major muscle groups crossing upper limb joints: shoulder (pectorial girdle), arm, forearm, and hand
83
New cards
What are major functions of upper limb musculature?
Upper limb joints are designed for mobility (rather than stability); reaching, throwing, grasping, and manipulating are all important functional roles of the upper limb
* Muscles positioning the pectoral girdle
* Muscles moving the arm
* Muscles moving the forearm and hand
* Muscles moving the hand and digits
* Muscles positioning the pectoral girdle
* Muscles moving the arm
* Muscles moving the forearm and hand
* Muscles moving the hand and digits
84
New cards
What 9 muscles move the pectoral girdle?
* trapezius
* levator scapulae
* rhomboids
* serratus anterior
* deltoideus
* pectoralic major
* latissimus dorsi
* rotator cuff muscles
* teres major
* levator scapulae
* rhomboids
* serratus anterior
* deltoideus
* pectoralic major
* latissimus dorsi
* rotator cuff muscles
* teres major
85
New cards
Trapezius
multiple actions depending on the fibre orientation (elevator, retractor, and depressor of scapula)
86
New cards
Upper fibers
when contracts pulls the scapula up
87
New cards
Lowers fibers
when contracts pull it down and to the side
88
New cards
Levator scapulae
elevator of scapula; attaches to vertebral column of neck and superior medial border of scapula
89
New cards
Rhomboids
retractors of scapula; attaches to
90
New cards
Serratus anterior
protractor of scapula; bulk of muscle goes from ribs to anterior aspect of the scapula; attaches along medial vertebral border of scapula; pulls scapula down
91
New cards
Force couple
muscles working together to do something they could not otherwise do (e.g. trapexius and serratus anterior)
92
New cards
Deltoideus
major arm abductor; arm flexor and medial rotator (anterior part) on posterior side arm extensor and lateral rotator (posterior part)
93
New cards
Pectoralix major
arm abductor, flexor, and medial rotator
94
New cards
Latissimus dorsi
powerful arm retractor; arm extensor, adductor, and medial rotator; attaches to; crosses shoulder joint underneath
95
New cards
Rotator cuff muscles:
tendons of SITS muscles reinforce should joint capsule and hold the humeral head against glenoid fossa (preventing dislocation of the shoulder joint)
96
New cards
What are the 4 rotator cuff mucles?
* supraspinatus
* infraspinatis
* subscapularis
* teres minor
* infraspinatis
* subscapularis
* teres minor
97
New cards
Supraspinatus
arm abductor (assists deltoid)
98
New cards
Infraspinatis
arm lateral rotator
99
New cards
Subscapularis
arm medial rotator; on anterior aspect of scapula in subscapular fossa; one of 4 muscles known as the rotator cuff
100
New cards
Teres minor
arm lateral rotator