Module 2.1.3 Nucleotides and nucleic acids
1/65
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
66 Terms
what are chromosomes made up of?
DNA
DNA carries the...
genetic code
What does the genetic code tell the cell?
The order of amino acids to make certain proteins
gene
section of DNA coding for a single protein
locus
location of a gene on a chromosome
how many alleles are there per gene?
2 - provides genetic variation
structure of monomer of nucleic acids
phosphate group - pentose sugar - organic nitrogenous groups
what are the two pentose sugars
ribose and deoxyribose
what do different nucleic acids have?
different nucleotides, sugars and bases
structure of monomer of DNA
phosphate group - deoxyribose - base (AGCT)
structure of monomer of RNA
phosphate group - ribose - base (AGCU)
How are nucleotides formed?
-sugar and base join by a condensation reaction
-create a nucleoside + 1 molecule of water
-phosphoric acid joins the nuclear side, forming a phosphoester bond between the OH group of an acid and the OH group of the carbon 5 of the sugar.
-this creates a nucleotide + another molecule of water.
pyrimidine bases
cytosine, uracil and thymine
purine bases
guanine and adenine
cytosine structure
3 bonds, single ring
adenine structure
2 rings, 2 bonds
uracil structure
single ring, 2 bonds
thymine structure
single ring, 2 bonds
guanine structure
2 rings, 3 bonds
ATP and ADP
nucleotides become phosphorylated when they contain more than one group
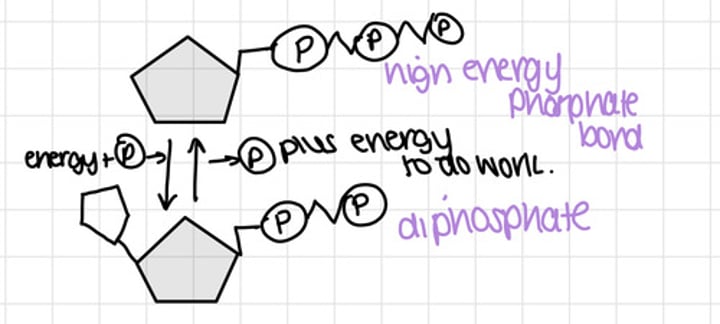
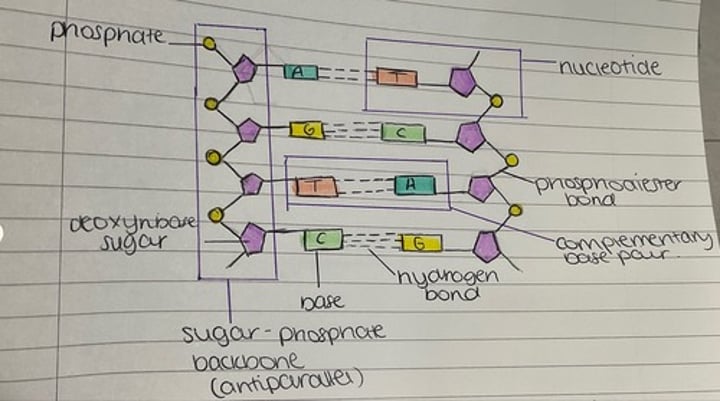
formation and structure of polynucleotides
-2 nucleotides join in a condensation reaction creates a phophodiester bond between the OH group on the phosphate group of 1 nucleotide, and the OH group on C3 of the other nucleotide
-each chain has a 5’ end and a 3’ end
-additional nucleotides join by further phosphodiester bonds, eventually creating a polynucleotide chain
-the nucleic acid DNA contains a second, anti parallel chain that runs in the opposite direction (3’ to 5’) to the first one.
-the bases in both ends are complementary to each other
-A + T (2 H+ bonds)
-G + C (3 H+ bonds)
structure of DNA
two chains of nucleotides lined up side by side, anti parallel, linked by H+ bonds
one complete turn of the helix
10 base pairs
width of each strand in DNA
2nm
enzyme used to unzip DNA
DNA helicase
when in mitosis does DNA replication take place?
interphase
Why is complementary base pairing important in DNA structure?
-conserves genetic information (ensures same sequence of nucleotides is produced)
-prevents occurrence of random/spontaneous mutations
Why is it called semi-conservative replication?
-theres one strand from the original DNA and one newly formed strand
-each original strand acts as a template for a new strand
Evidence for semi-conservative replication
-all bases in DNA contain nitrogen
-nitrogen has 2 forms - light (14N) and heavy (15N)
-bacteria will incorporate nitrogen from their growing medium into any new DNA they make
Replication fork
The point at high the 2 strands are separated
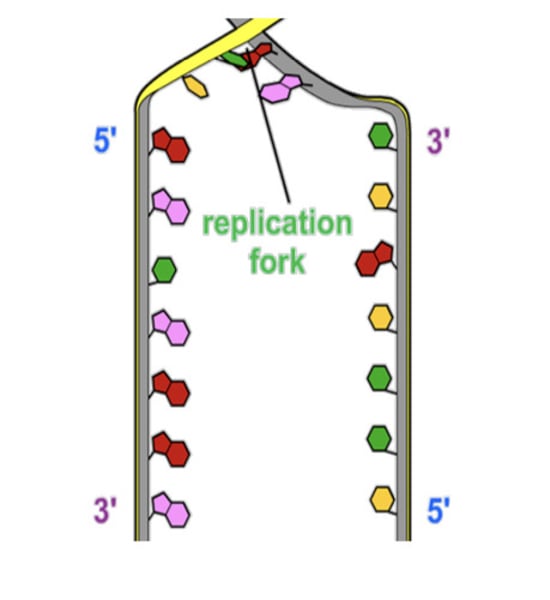
Steps 1-4 of semi-conservative replication
-Helicase enzymes separate the 2 strands at the replication fork.
-Each strand of the DNA molecule are kept apart during replication by single grand binding proteins
-The formation of new strands is catalysed by DNA polymerase. It uses each parent strand as a template, 'reading' the sequence of bases and adding complementary bases to form new strands
-DNA polymerase reads the parent strands in a 3' to 5' direction, and builds the leading strand in a 5' to 3' direction towards the replication fork.
Stages 5-9 of the semi conservative replication
-In contrast, the lagging strand is built in a 3' to 5' direction away from the replication fork. It grows discontinuously in small sections (Okazaki fragments).
-The Okazaki fragments are joined together by DNA lignes.
-The DNA helix continues to unwind and separate. The leading strand grows continuously toward the replication fork. At the same time, the lagging strand grows continuously away from the replication fork.
-There are multiple replication forks along a single DNA molecule, which speeds up replication. Replication occurs in both directions in replication bubbles
-Eventually, all individual segments of the strands meet up and are joined together, creating 2 new DNA molecules, each one identical to the parent molecule
Steps 1-4 of evidence for semi-conservative replication
-The bacteria E.coli are grown in a medium containing 15N - a heavy isotope - for several generations.
-The 15N isotope will be incorporated into the bases, and therefore into new DNA. After many generations all DNA is a 'heavy' type containing 15N.
-A sample of E. Coli is grown purely in 15N and saved for later
-E. Coli are transferred to a medium containing 14N, the normal, 'light' isotope. All new DNA will synthesise with this isotope rather than 15N.
Step 5-9 of evidence for semi-conservative replication
-The E. Coli are left to grow and divide. After the time it has taken for the E. Coli to divide once (50 mins at 36°C), a sample is taken
-After the E. Coli have divided the second time (another 50 mins at 36°C), a second sample is taken
-The tubes are spun at high speeds in a centrifuge. In each tube, the DNA collects in a band. The higher the DNA, the lower the tube the band will form.
-Comparing the position of the bands from the different E. Coli samples provides strong evidence for the semi-conservative method of DNA replication
SCR results: 1st gen: 15N only
The heavy DNA from E. Coli grown exclusively in 15N forms a band hear the bottom of the tube.
SCR results: 1st gen: 15N - 14N only
DNA from E. Coli grown for one generation in 14N forms a band midway between the 'heavy' and 'light' bands. This 'intermediate' DNA contains one strand of 14N and one strand of 15N
SCR results: 2nd gen: 15N-14N
DNA from E.Coli grown for 2 generations in 14N forms 2 bands. 'Intermediate' DNA is first generation 'light' DNA is the second generation
SCR results: 14N only
The 'light' DNA from the E. Coli grown exclusively in 14N form a band near the top of the tube
How is RNA different to DNA?
-contains ribose sugar
-single stranded
-uracil base attaches to adenine rather than thymine
-3 types
what are the 3 types of RNA?
messenger RNA (mRNA)
ribosomal RNA (rRNA)
transfer RNA (tRNA)
How does DNA code for proteins?
-3 nucleotides make up a triplet code.
-each triplet code codes for a different amino acid
-the sequence of triplets in a section of DNA codes for a polypeptide
how many triplets make a polypeptide?
3 triplets
What can the genetic code be described as?
universal, non-overlapping, degenerate
universal
almost all living organisms, amino acids are made from the same triplet of DNA bases and codes
non-overlapping
reads from a fixed point in groups of 3 bases (reads it in 3s)
degenerate
for almost all amino acids, there is more than one base triplet code
What is the genetic code?
-Sequence of bases along the DNA
-Contains thousands of sections called genes/cistrons
-Each gene codes for a specific polypeptide
-All polypeptides are made from amino acids, so the sequence of bases in a gene must code for amino acids
-Genetic code is almost universal
The triplet code
A set of three-nucleotide-long words that specify the amino acids for polypeptide chains.
How many amino acids are possible if one base is used?
4
How many amino acids are possible if 2 bases are used?
16
How many amino acids are possible if 3 bases are used?
64
protein synthesis
involves production of a chain of amino acids that forms the primary structure of a proteins
The stages of protein synthesis
-transcription of the gene in the nucleus (an mRNA strand is formed)
-processing the mRNA
-translation of the mRNA in a ribosome (a polypeptide chain is formed)
-modification of the protein
messenger RNA
-made in nucleus
-nucleic acid
-makes a copy of the gene
-moves out of the nucleus, through the nuclear pore and into the cytoplasm
-each set of 3 bases are called a codon
-single stranded
-contains ribose
-contains uracil
how is mRNA related to protein synthesis?
-when a polypeptide is required, the triplet code of its gene is converted into a molecule of mRNA
-this process is called transcription and is the first stage of protein synthesis
ribosomal RNA
-the ribsomes are made up of rRNA
-moves along the mRNA strand during protein synthesis
-catalyses the formation of polypeptide bonds between amino acids
transfer RNA
-carries amino acids to the ribosomes where they are used to make proteins
-a single polynucleotide chain but its folded up into a clover shaped molecules
-held into its shape by hydrogen bonds between base pairs
-at one end, of the tRNA molecule there is a specific sequence of 3 bases called an anticodon
-at the other end is an amino acid binding site
-tRNA carries amino acids to the ribosomes where they are used to make proteins
-each tRNA is specific for one amino acid
-as anticodons
anticodons
-each tRNA molecule has a sequence of 3 bases (anticodon)
-complementary to codons on the mRNA molecule
what happens in transcription (including codons)
-During transcription, the mRNA is built up by complementary base pairing, using the DNA as a template
-the DNA base triplets are converted into mRNA codons
-the genetic code is non-overlapping : each base is only part of one triplet/codon, and each triplet/codon codes for just one amino acid
transcription
-during transcription,a section of DNA is transcribed/copied into molecules of another nucleic acid called mRNA. At the start, DNA is a double helix.
-Helicase breaks the hydrogen bonds between the bases in a specific region of double-stranded DNA in the nucleus. This causes the 2 strands to separate
-RNA polymerase binds to a base sequence called the promoter region. RNA polymerase moves along the DNA strand in the 5’ to 3’ direction. As it passes over the DNA bases, it forms a complementary mRNA strand from free RNA nucleotides in the nucleus.
-As the mRNA strand is produced the 2 strands of DNA start to recoil behind it.
-When a terminator region is reached, the DNA is no longer copied. The mRNA is now ready for the next stage of protein synthesis
what is translation
the formation of polypeptides from the mRNA base sequence. Each codon codes for one amino acid.
process of translation
-the mRNA strand formed in the nucleus attaches to a ribosome in the cytoplasm. The mRNA is attached at the start codon, at the 3’ end of the strand.
-transfer RNA molecules contain a sequence of 3 bases called an anticodon. The tRNA molecule will bond with. complementary codon on the mRNA strand.
-As the ribosome moves along the mRNA, another tRNA moves in carrying the corresponding amino acids. The 2 amino acids are joined together with a peptide bond by an enzyme.
-Another tRNA moves into the ribosome, adding another amino acid to the chain the first tRNA molecule is released, and is free to collect another amino acid from the cytoplasm
-This process continues until a stop codon is reached on the mRNA strand. As there is not a corresponding tRNA for this sequence, the polypeptide chain is released.
-The polypeptide chain will then undergo post-translational modifications before it is able to function.
why is salt added to the DNA purification process?
it helps to remove DNA bound proteins
why is detergent added to the DNA purification process?
it helps disrupt cell membranes
why are protease enzymes added to the DNA purification process?
hydrolyse the proteins
why is ethanol added to the DNA purification process?
causes DNA to precipitate