CH 101 piece of shit class
1/304
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
305 Terms
giga
10'9
mega
10'6
kilo
10'3
deci
10'-1
centi
10'-2
milli
10'-3
micro
10'-6
nano
10'-9
pico
10'-12
resonance structure
same sequence, diff bond and lone pair placement
best resonance structures have:
full octets
minimized formal charge diffs
formal charges add up to total chg
- formal charge is on most EN atom
e delocalization throughout = stability
more res structure = more stabile
valence bond theory
predicts overlap of valence electrons
VSEPR - valence shell electron pair repulsion
explain discrepancies in bond angles and geo hybridsixzation, how e config
sp2 hybrid orbital :
1s+2p=sp2
1 p left unbonded
surround unhybrid p in center
33%s, 66% p
sp hybrid orbital
s+p=sp
2 unhybridized p orbital
sp3 hybrid orbital
25% s 75% p
s+3p=sp3
AX4 = 4 atom bond, tetra
AX3E, 3 atom, tri py
AX2E2, 2 atom, bent
AXE3, 1 atom, lin
morphine mocks what
endorphins (shape received by receptors)
octet exceptions
odd elec/free radical
incomplete octet
expanded octet
odd elec: ex Cl, NO2, NO
incomplete: B and Al 6/8, H 2/8, Be 4/8
expanded: elements in period 3+ ( low lying d orb accomadates extra electrons)
spdf are wave functions, so
new waves =
absence of waves =
new = bonding molc orb
absence = nodes/anti molc orb
rotation : pi and sigma
pi restricted (double bond rotation breaks pi orb interaction), sigma free (internuc axis)
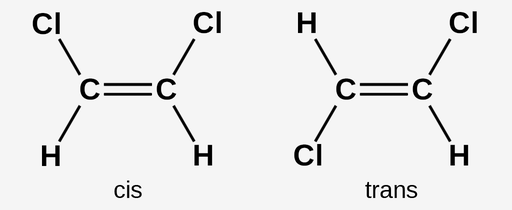
isomers
const:
stereo:
same molc form, diff struct form
const: same molc form, diff sequence
stereo: same molc form, seq, diff spatial arc
cis - same side of double bond
trans - opposite sides
perturbation theory
complex system = simple system that is sl;ighty altered
greater orbital overlap =
lower e, stronger bond , typically hybrid
more likely to be hybridized
central and interior (more bonds formed)
MO theory “trial function”
best possible orbital = lowest energy orbital (more stable)
bonding orbital has intrinsic ….
electron density

diatomic homonucelar mo diagram
diatomic homonuclear mo diagram
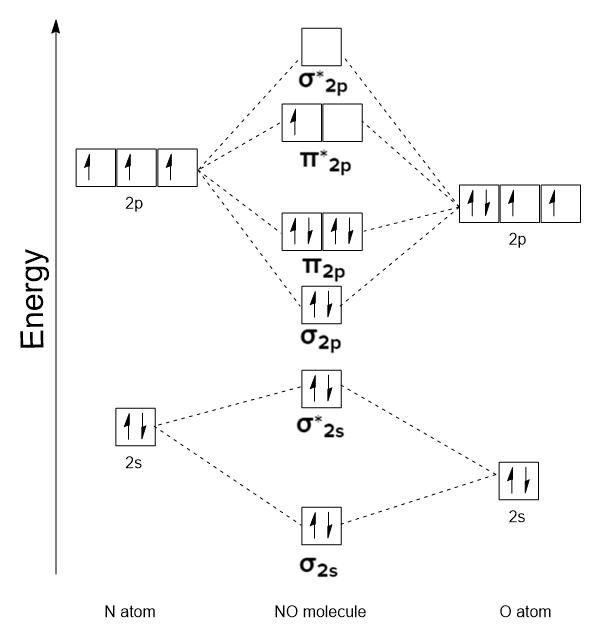
diatoimic hetero nuclear mo diagram
diatomic hetero nuclear mo diagram
NH4+
ammonium
CN-
cyanide
CH3CO2-
acetate
CO3²-
carbonate
HCO3-
hydrocarbonate/bicarbonate
NO2-
nitrite
NO3-
nitrate
PO43-
phosphate
HPO42-
hydrogen phosphate
H2PO4-
dihydrogen phosphate
OH-
hydroxide
SO32-
sulfite
SO42-
sulfate
HSO4-
hydrogen sulfate/bisulfate
ClO-
hypochlorite
ClO2-
chlorite
ClO3-
chlorate
ClO4-
perchlorate
Cr4O2-
chromate
Cr2O72-
dichromate
MnO4-
permanganate
methane
CH4
ethane
C2H6
propane
C3H8
butane
C4H10
salient chem prop is
tendency to undergo oxidation/lose e
tendency to undergo reduction/gain e
potential energy is attrib to ?
low = ?
high = ?
sys pos, comp, state
low = stable
high = unstable
only predictible trans metals
Zn
Ag
Cd
Zn2+
Ag+
Cd2+
ex. [cation] (x) [anion]
higher x =
lower x =
higher x: -ic
lower x: -ous
S2-, Br- , PO43-are always charged liek this
S2-, Br- , PO43-are always charged liek this
nomenclature of main group ionic comps
[cation] [anion]-ide (no prefixes)
nomenclature of binary ionic comp
[cation] ([cation charge]) [anion]-ide
(find cation charge by cx+d*([anion charge])=0)
nomenclature for poly atomics: oxoanions
exclusions
XO4n- per…ate
XO3n- …ate
XO2n- …ite
XOn- hypo…ite
exc: Cr As P S
XO4n- …ate
XO3n- …ite
acid nomenclature (anion endings)
ate → ic
ite → ous
ide → hydro…ic
acid nomenclature
HnXO4 per…ic acid
HnXO3 …ic acid
HnXO2 …ous acid
HXO hypo…ous acid
HX hydro…ic acid
Hydrate nomenclature
[[ionic name]] [# prefix]-hydrate
hydrate prefixes (#)
1 mon
2 di
3 tri
4 tetr
5 pent
6 hex
7 hepta
8 oct
9 non
10 dec
molecular comp nomenclature rules
element with lower group # is always listed 1st
same group - higher period # listed 1st
[lower group #] (prefix)[higher group#]-ide
mol to atom
multiply by avogardro
atom to mol
divide by avogadro
organic compounds are made of CHNOPS
key element?
simplest form?
compose common what?
carbon ( can form 4 bonds)
hydrocarbons
fuels
common hydrocarbons
methane CH (natural gas)
propane C3H8 (LP gas/grills gas)
n-butane C4H10 (lighter fuel)
n-pentane C5H12 (gasoline)
ethene C2H4 (fruit ripening agent)
ethlyne C2H2 (fuel for wielding sm sm)
n= straight chain
degenerate orbitals
orbitals of same n value
hydrogen energy state depends solely on
n value
multielectron atoms
energy levels split into subshells with own energy
as n inc, some sublevels overlap as energy levels come closer together
aufbaus
fill lowest energy orbital first
hunds rule
electrons must be added singly, and all singly/unpaired orbitals are same spin to maximize spin
pauli exclusion
orbital can have a max of 2 e with opposite spins +/-
Z (at num) guides # of electron being addes
f and d are diff by what numbers
f = row # - 2
d = row # - 1
steps to find config
write row #
write letter of corres. subshell
count across until filled
trans metal exceptions for stability
Cr & Mo:
Cu & Ag & Au:
Pd:
how?
Cr & Mo: ns1(n-1)d5 (partially filled)
Cu & Ag & Au: ns1(n-1)d10 (completely filled)
Pd: (n-2)d10(completely filled)
They steal the nearest electrons (lowest level)
cation monatomic
pos charge, e deficient
typically metal
subtract 1 electron from valence shell per positive charge
anion monatomic
neg charge, e gain
typically nm
add 1 electron to valence shell per negative charge
special case of transition metal cations
comp form involve e of highest energy
after Z=20 energy of 4s orbital exceeds energy of 3d, e in s orb is more likely to change than d
innner/core electrons are represented by what
nearest noble gas
complete trans series d10 and f14
outer electrons are rep by
highest n values in atom
furthest from nuc
valence electrons are rep by
bonding
main group group #
periodic law (mendeleeve and meyer)
properties recur periodically if organized by mass number
mendeleeve accounted for blank spaces
alkali traits
loiw melting point
high molar vol
+1 state
moseley x ray spectra
inner ejected, outer drop down to fill
energies depend on nuc charge and xray freq = v
v=A(Z-b)²
periodic patterns
metallic left and down
radius left and down
IE, EA, and EN right and up
if sheild is constant,
z inc, and zeff inc
ionization energy exclusions
IEAl<IEMg
IEP>IES
newtons second law
force = m(kg) * a (m/s²)
1 newton =
1 kg m/s²
density
mass/volume
volume
mass/density
F to C
(F-32)/1.8
C to K
C + 273.15
percent mass
mass/comp mass
work
force*distance (in J)