Myelin Sheath
1/15
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
16 Terms
What are myelin sheaths?
Insulating structures that are composed of lipoprotein myelin
Which axons are myelinated?
Surround thicker axons of the body
Therefore which axons and unmyelinated?
Thin axons
Difference between myelinated and unmyelinated axons?
Structure
Layers
Nodes of Ranvier
Speed of impulse transmission
Location
Structure:
MY:
Have concentric layers of plasma membrane
Have nodes of Ranvier
UN:
Schwann cells do surround axon, but not in layers
Nodes of Ranvier are absent
Speed of impulse transmission
MY: Fast
UN: Slow
Location:
MY: In most cells
UN:
Autonomic nervous system
Sensory fibers
Dendrities that only carry graded potentials
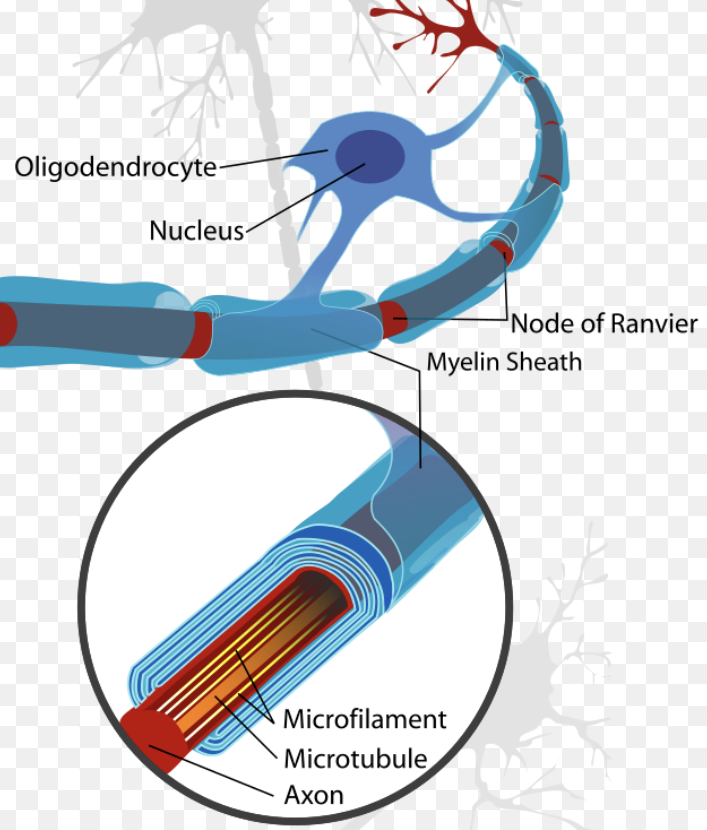
What is the structure of myelin?
Each segment consist of plasma membrane of a supporting cells rolled in concentric layers around axon
What are the functions of myelin sheaths?
Form an insulating layer that
Prevents leakage of electrical current from axon
Increases speed of impulse conduction
Makes impluse propagation more energy efficient
Why are they good electrical insulators?
Because plasma membrane of myelinated cells have less protein
What is consist in the external material and what is it called?
Called the neurilemma and consist of:
Nucleus
Most of cytoplasm
How does myelin sheath make electrical impulses quicker?
Produces Nodes of Ranvier because myelin sheath do not touch each other, forming gaps
Allows electrical impulses to jump between Nodes of Ranvier
Myelin sheath produced by in:
CNS
PNS
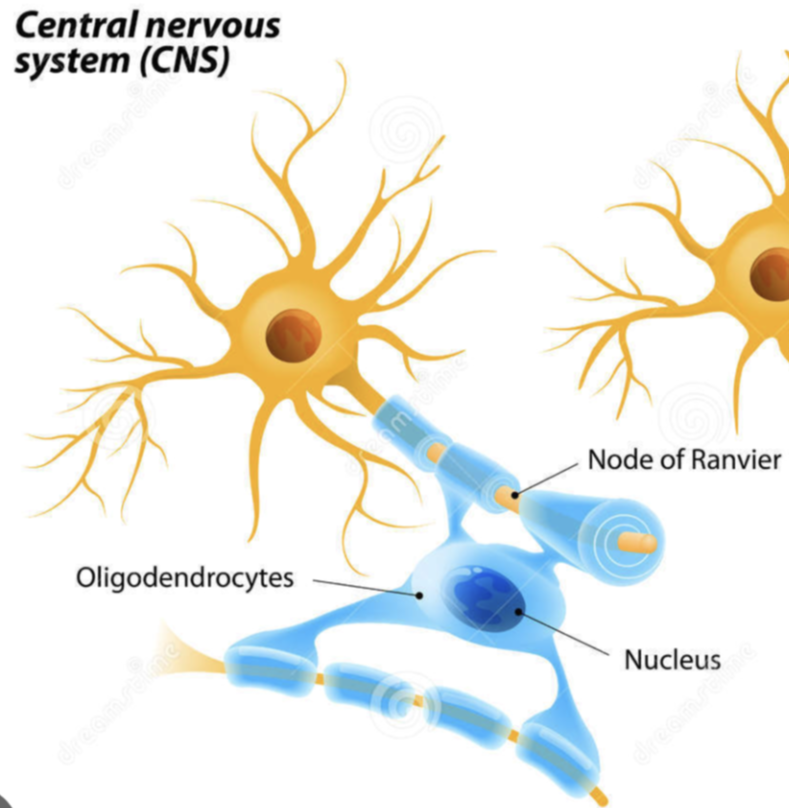
In CNS, MS produced by: Oligodendrocytes
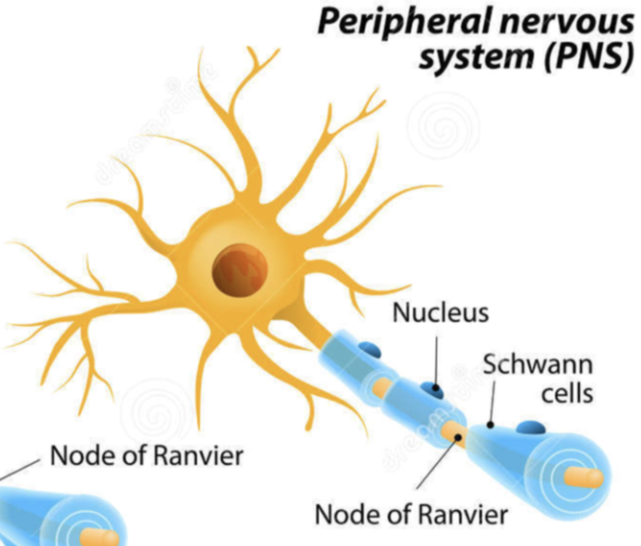
In PNS, MS produced by: Schwann cells
Myelin Sheath in PNS
Developed during
Structure
Developed during: Fetal peirod and 1 year of postnatal life
Structure: Concentric layers of Schwann cell plasma membrane wrap the axon in packed coil of membranes
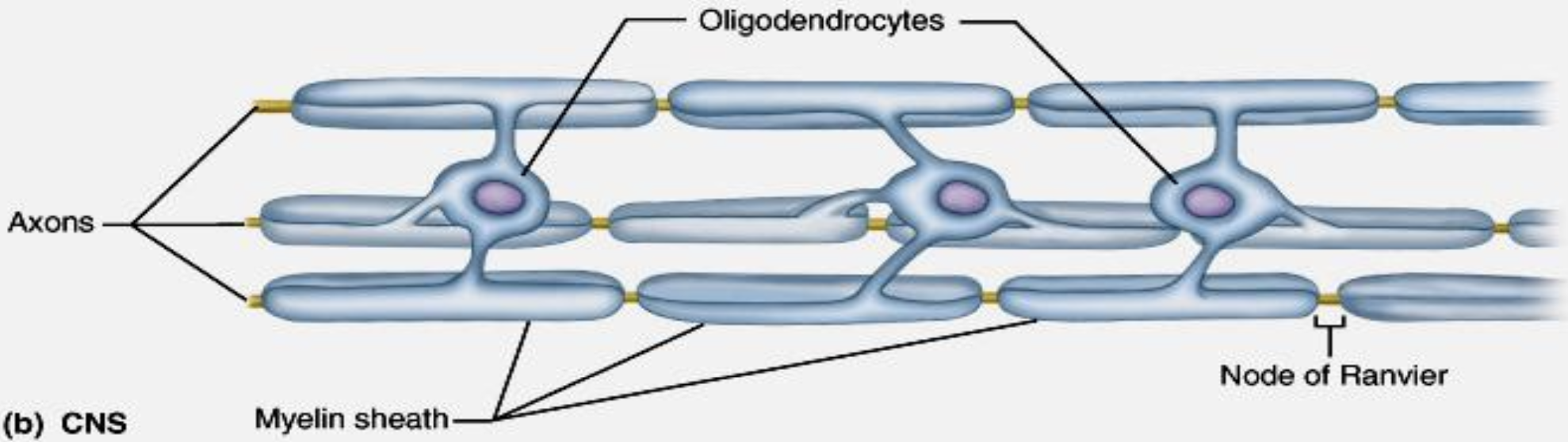
Myelin Sheath in CNS
Structure
Structure: Each oligodendrocyte has multiple processes that coil around several different axons
Structural differences between myelin sheath in CNS and PNS
Which one forms faster
Which one has nodes that are spaced more
Faster formation: CNS
Nodes are spaced more: PNS
What is neurolemma?
Outer nucleated cytoplasmic layer which encloses myelin sheath
What is white matter?
Regions of the brain that contain dense collections of myelinated fibers
What is grey matter?
Regions of the brain that contain mostly nerve bodies and unmyelinated fibers