Kinetics and Equilibrium - Honors Chemistry
1/45
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
46 Terms
kinetics
study of the rate of chemical reactions
reaction rate
speed at which reactants become products
chemical reactions are balanced in
mass charge and energy
chemical reactions have what type of energy
potential energy stored in chemical bonds
chemical reactions start with
certain amount of energy and products end with different amount of energy (endo vs. exo)
heat of reaction (∆H)
net energy absorbed or released in a chemical reaction; change in enthalpy of a system (∆H = H products - H reactants)
nature and chemistry favors
low energy - stability
entropy
measure of randomness or disorder of a system
nature and chemistry favors
high entropy - chaos (phase change S→ L → aq → G)
spontaneous reactions
favor lower enthalpy and higher entropy; if both factors present in reaction then it’s spontaneous
Gibbs Free Energy formula
∆G = ∆H - T∆S
∆G is
kJ/mol - Gibbs free energy
∆H is
kJ/mol - enthalpy
T is
k - temperature
∆S is
kJ/mol * k - entropy
natural processes proceed in
direction that lowers free energy
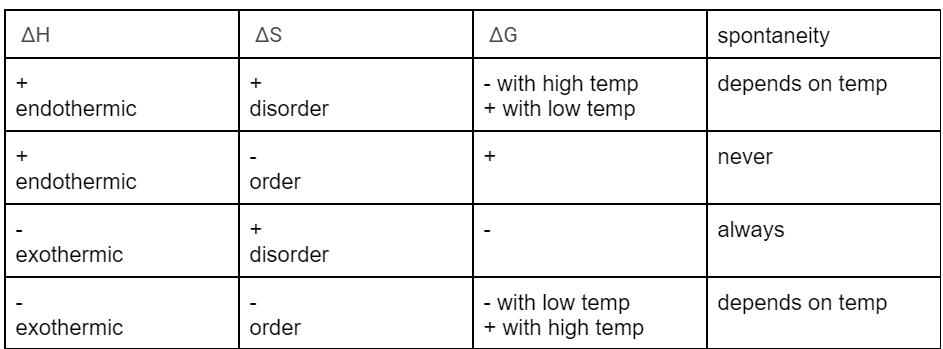
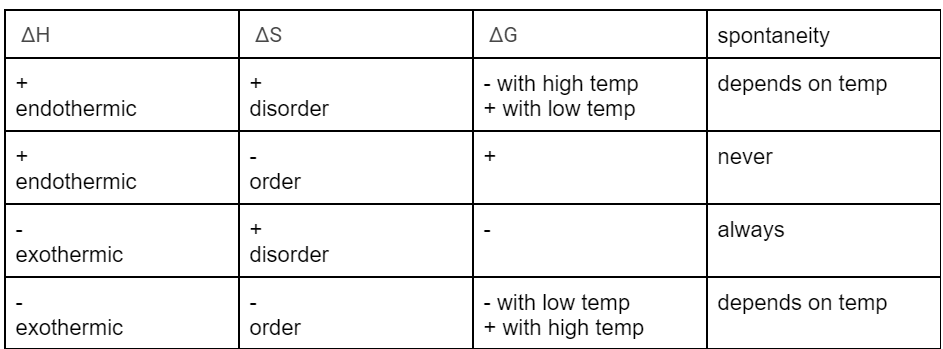
describe how (-) exothermic and (+) disorder would look like in Gibbs Free Energy equation
∆G = ∆H - T∆S; if ∆H is negative and subtracting positive T (kelvin can’t have negative numbers) multiplied by positive ∆S then it’s ∆H(-) - T∆S (+) so ∆G is always negative
collision theory
in order for reactions to occur molecules and atoms must collide with each other
for reactions to occur they need
enough energy and proper orientation
do you want factors to increase or decrease to make reactions occur faster
factors that increase energy and orientation
effective collisions
reactants become products
ineffective collisions
reactants remain unchanged
sufficient kinetic energy
brings reactants together but potential energy brings them apart
proper orientation
orientation which mot likely breaks the bond is most effective or if given what product is supposed to look like then orientation that will give product
how do you increase reaction rate
increasing number of collisions
factors that affect reaction rate
temperature, concentration, surface area, pressure, nature of reactants, catalyst
how does temp affect reaction rate
higher temp = more collisions
how does concentration affect reaction rate
higher concentration = more collisions
how does surface area affect reaction rate
greater surface area = more collisions
how does nature of reactants affect reaction rate
ionic substances generally react faster than molecules and dissolving speeds up reactions
how does a catalyst affect reaction rate
substances that speeds up reaction by giving new path with lower activation energy - facilitate reaction but not part of it so always in reactant and product without changing
reaction mechanism
steps or pathway by which reacting particles rearrange themselves to form productsne
net reaction
chemical equation that shows the reactants and products onlyac
activated complex
temporary arrangement of particles of chemical reactions
activation energy
minimal amount of energy needed to form an activated complex and have chemical reaction occur
kinetic energy diagram
higher temp increases number of particles that can have effective collisions by increasing their kinetic energy
thermodynamics
study of energy in chemical reactions
enthalpy
heat of content in a system
endothermic reaction has heat of reaction that’s
positive; ex. dissolving potassium nitrate
heat is on which side for it to be endothermic
on reactant side being absorbed
exothermic reaction has heat of reaction that’s
negative; ex. combustion of propane
Table I
net energy of equation is heat of reaction at 101.3 kJ and 298K; endo ∆H = (+) and exo ∆H = (-)
in Table I energy is proportional to
moles
if reaction reverses in Table I then
sign reverses; ex. opposite of endo (+) is exo (-)
why is most of Table I exothermic
nature wants lower energy so there’s more reactions where heat is released
How many kJ of energy are absorbed for 1 mole of nitrogen dioxide?
33.2 kJ