Psych Unit 2: Intelligence and Achievement (copy)
1/33
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
34 Terms
factor analysis
a statistical method used to identify clusters of related variables (factors) within a set of data; reduces large amts of data into smaller sets; often used for personality traits (determining correlations between various traits)
fluid intelligence (Gf)
the ability to solve new problems and reason abstractly without having to rely on previously learned knowledge (prior knowledge isn’t applicable)
crystallized intelligence (Gc)
the ability to use previously learned knowledge to solve problems
stanford-binet
a standardized test used to measure an individual’s cognitive abilities and intelligence (measures fluid reasoning, knowledge, quantitative reasoning, visuospatial processing, and working memory)
criticized for only looking at analytical skills rather than issues of performance as well
Wechsler-adult intelligence scale (wais)
intelligence test for adults that measures cognitive ability in vocabulary, math, comprehension, and reasoning skills
psychometrics
a field of study within psychology that focuses on the theory and technique of measurement (testing, measurement, assessments on human abilities, attitudes, and traits)
normal curve
all data points are clustered around the mean value, creating a symmetrical bell shape (mean, median, and mode are all equal)
cross-sectional study
research design in which data is collected from a group of ppl at a single point in time (allows researchers to focus on a specific variable, like age, without following the same individual over time)
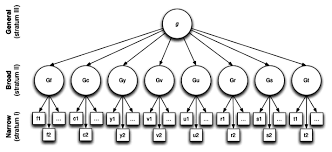
cattell-horn-carroll theory (CHC)
a model for classifying and describing human cognitive abilities; it merges a hierarchical model of intelligence (some abilities having a broader scope than others) and the concept of crystallized intelligence (using learning) an fluid intelligence (using cognitive abilities)
savant syndrome
a condition in which someone with a developmental disorder or intellectual disability has an extraordinary ability in a specific area
grit
characterized by perseverance, passion, and maintaining effort; a non-cognitive trait that helps people overcome obstacles and drive themselves to achieve long-term goals
emotional intelligence
the ability to perceive, understand, and handle your emotions as well as others (self-awareness, self-regulation, motivation, empathy, and social skills)
longitudinal study
a research design in which a group of individuals are repeatedly observed and assessed over a long period of time, allowing researchers to see changes in behaviors, thoughts, or emotions (has an observational nature)
cohort
a group of people who share a common set of demographic characteristics and experiences (such as age → ppl are influenced by the same cultural events in similar stage of life)
content validity
a measure of the degree to which an instrument (like a test) covers all relevant parts of the construct in aims to measure
general intelligence (g)
a level of intelligence all people have
can be measured empirically
supports special abilities
2 types: crystallized and fluid
intelligence
ability to learn and adapt to new situations and apply that knowledge to reach a desired outcome
defined differently throughout the decades
combination of several skills: problem-solving, abstract thinking, critical thinking, reasoning, communication, social skills, and more
umbrella for many different types of it
intelligence quotient (IQ)
score yielded from the Stanford Binet and Weschler tests that compares mental age with chronical age
the average score is 100
modern-day test combines verbal and performance
mental age
a person’s mental ability expressed at an age the at which an average person reaches the same ability
standardization
the process of ensuring that all psychological tests are administered and scored the same way for all test takers
multiple intelligences
a proposition (by howard gardner) that there are many aspects to intelligence
linguistic, logical-mathematical, musical, spatial, bodily-kinesthetic, interpersonal, intrapersonal, naturalistic, naturalistic, existential
achievement test
a measurement tool that assesses a person’s knowledge or skills in a specific subject/area
tests academic abilities
aptitude test
a way to measure a person’s natural ability and potential to learn or perform tasks in a given environment
measures inborn talents, not talents that are learned
valid
test assess what it’s designed to measure
Flynn Effect
IQ scores increases 3pts by decade likely due to better nutrition, more stimulating surroundings, and increased schooling
construct validity
a test measures the construct or idea its designed to measure
predictive validity
a test accurately predicts the level of someone's future performance
reliability
test provides consistent results over time
test-retest reliability
there is a correlation between the scores of the same test taken multiple times
split-half reliability
scores in the first half of the test equal the scores in the second half (can be tested by comparing even and odd number questions)
stereotype threat
test takers who are stereotypes to do worse may do worse because of the stereotype and not their capabilities
stereotype lift
test takers who are not part of a group expected to do poorly may do better because of this validation
fixed mindset
the belief that intelligence, abilities, and talents are set in stone and cannot be changed
growth mindset
the belief that intelligence, abilities, and talents can be improved with practice, effort, and persistence