Macroeconomic objectives and policies
1/21
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
22 Terms
The seven major objectives
Economic growth i.e increase in real incomes, or potential output
A reduction in unemployment
Control of inflation i.e preventing prices to rise too quickly
Restoration of equilibrium in the balance of payments, there should not be either a persistent and heavy outflow or inflow of income and wealth.
Fiscal balance
Protection of the environment
Making distribution of income more equal
Demand side policies
Any deliberate action taken by governments or monetary authorities to shift the AD curve
Two types of demand side policy
Monetary policy
Fiscal policy
Monetary variables
Money supply
Interest rates
Exchange rates
Monetary policy
The manipulation of monetary variables to achieve government objectives
Fiscal policy
The manipulation of government spending and taxation to shift AD
Interest rates
If aggregate demand needs to decrease, then interest rates are raised, this means C, I, and (X-M) tends to fall. The AD shifts left
If aggregate demand needs to increase, the interest rate is cut. This means that C, I, and (X - M) will tend to rise. The AD shifts right.
There are multiplier effects which increase the impact of the change
Who sets the interest rate
The Monetary policy committee of the Bank of England
Quantitative easing
A bank buys a large amount of financial assets (like government bonds) from the market
This increases demand for those bonds, raising their price
When bond prices goes up, their interest goes down
It has the same effect as lowering interest rates, makes borrowing cheaper and encourages spending/ investment
Fiscal deficit
When government spending is greater than government taxation revenue
Expands AD with multiplier effects
Fiscal surplus
When gov spending is lesser than government taxation revenue
Contracts AD, with multiplier effects
Direct and indirect taxes
A rise in direct taxes might mean people have reduced incentives to work hard and earn money
whilst if indirect taxes are raised, the cost of living increases, particularly for those on lower incomes
Strengths of demand side policies
According to Keynesian economics:
Demand side policies are the only way to get a country out of demand deficient unemployment and stagnation
If the multiplier is large, it can have a significant impact on growth
if there is spare capacity, the economy can grow quickly
If used to control demand-pull inflation, they can act quickly and solve the problem.
Weaknesses of demand side policies
Expansionary demand side policies only cause inflation in the long run
The multiplier might be so low they have little effect
If there is no spare capacity, supply side policies will be needed instead fir economic growth
The gov can end up running a huge deficit, adding to debt
Supply side policies
Government measures aimed at improving the productive capacity and efficiency of the economy
Types of supply side policies
Cutting corporation taxes
Removing regulations and restrictions preventing firms from growing
Encouraging investment by forcing banks to lend money, or quantitative easing
Increasing competition in markets
Privatising or subsidising industries
Improving labour market with improved education
Improving infrastructure
Conflict of inflation and unemployment
When the government tries to control inflation it is likely to try to dampen aggregate demand.
So, less spending means less upwards pressure on prices
The gov may increase taxes, or the MPC may increase interest rates
This may prevent inflation, but it reduces spending
Reduced spending means firms start laying off workers as they’re unable to sell all their products
As workers are laid off, incomes fall so the cycle continues
Conflict of unemployment and inflation
If the gov wants to reduce unemployment they may start spending more on training workers, or start subsidising firms to take on more workers.
The increased spending in the economy causes incomes to rise, pushing AD to the right.
If supply cant match this it causes an increase in prices as it is competitive
Philips curve
an economic model that suggests an inverse relationship between the rate of unemployment and the rate of inflation
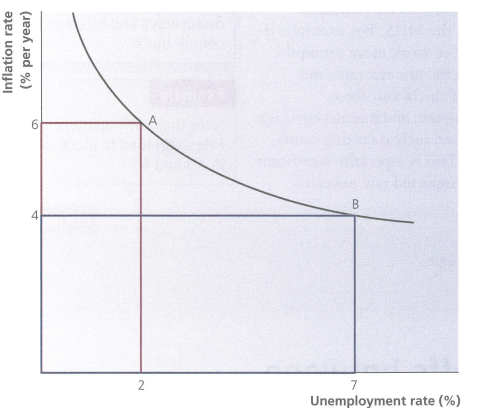
Conflict between economic growth and sustainability
When an economy grows, standards of living tends to improve
For standards of living to be sustainable, growth must not occur at the expense of future generations
There is a conflict between someone enjoying a resource today and in the future
Think of damage to the environment
If increased use of fuels increase global warming then it may not be as appealing
Sustainable growth
Sustainable growth is growth that does not compromise the welfare of future generations
Conflict between