ch17.1 - Long term potentiation (LTP)
1/42
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
43 Terms
LTP meaning
long term potentiation
LTP is a
increase in activity of synapses from a specific stimulation
long term potentiation means that the ______ lasts longer
excitatory effect
what happens if you stimulate axons with a low frequency (1Hz)
stable response size in neurons
what happens if you stimulate axons with a high frequency for a brief moment (100Hz)?
higher response that remains for minutes/hours afterwards
LTP was first observed in the ___ but is fundamental to neurons in the entire ____
hippocampus/ CNS
3 hippocampal pathways that display LTP
perforant pathway
mossy fiber
schaffer collaterals
LTP is a physiological mechanism of learning that requires the ____ (which gives it plasticity)
hypothalamus
time of LTP =
time of learning
early stage LTP
short term memory; NO protein synthesis
late stage LTP
long term memory (⬆CREB, makes proteins, ⬆gene expression, stronger synapses)
when you sleep you ___ so that when you wake up you can ____
make proteins/ remember
diagram of LTP stages
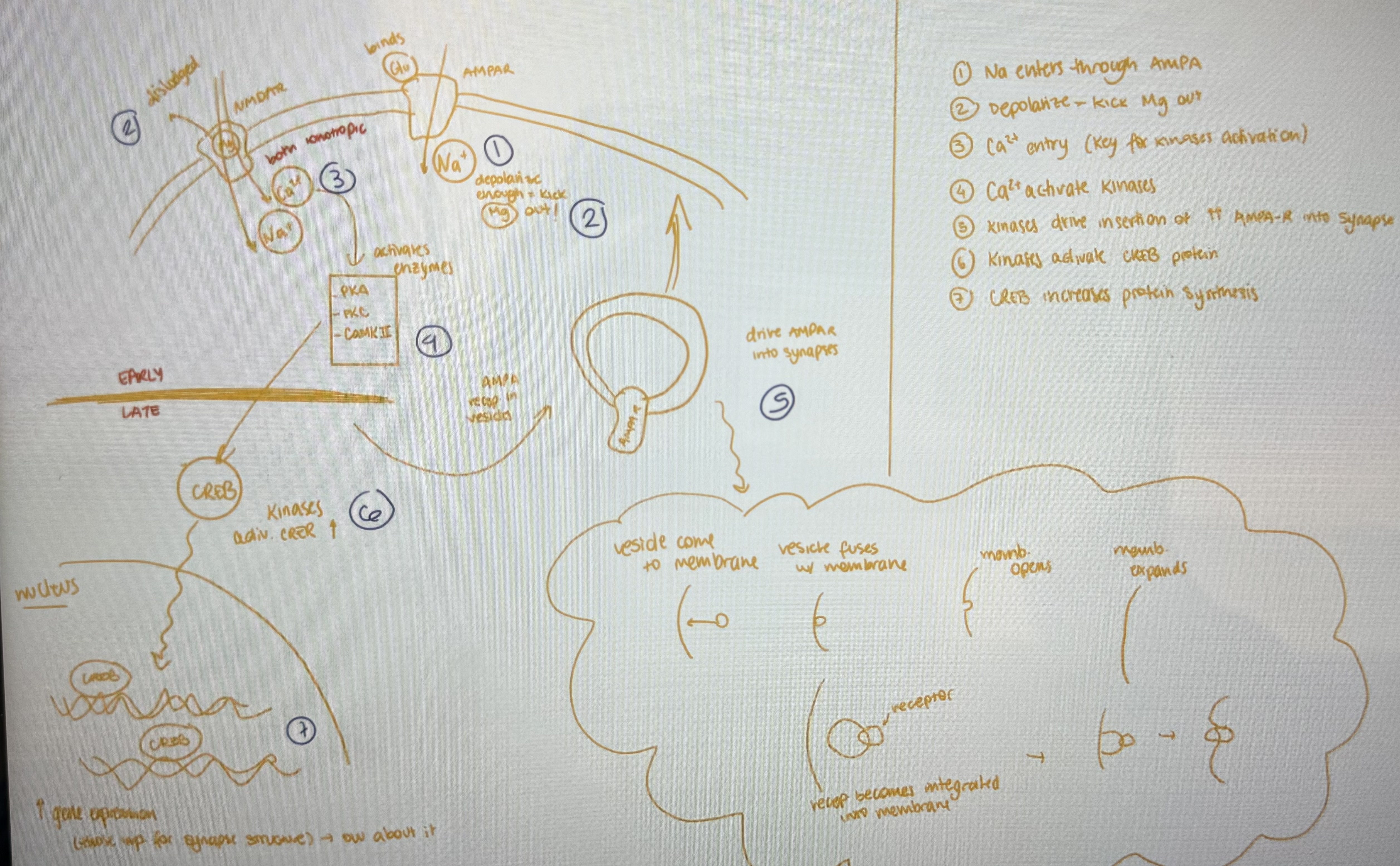
step 1 LTP
Na enters through AMPA-R
step 2 LTP
depolarize cell enough that Mg gets kicked out
step 3 LTP
Ca2+ entry (key for kinases activation)
step 4 LTP
Ca2+ activate kinases
step 5 LTP
kinases drive insertion of AMPA-R into synapse
step 6 LTP
kinases activate CREB protein
step 7 LTP
CREB increases protein synthesis
AMPA-R
ionotropic Glu receptors that control excitatory NT
NMDA-R
ionotropic Glu receptor that controls EPSP
why is NMDA unique and VERY important?
permeable both to Na and ALSO CA2+!!! this is huge because Ca2+ basically drives the whole process of LTP
what does driving AMPA-R into synapses do?
the more AMPA-R on post-syn, the more sensitive to glutamate it is!
why is it important for a cell to be sensitive to glutamate?
because it’s the primary excitatory NT, essential for rapid communication, learning and memory!!!
retrograde signals
enhance Glu release in presynaptic terminals
3 kinases
PKA
PKC
CAMKII
what are kinases
enzymes that add phosphate groups to molecules using ATP; drive growth and metabolism; on and off switch
adding phosphate to proteins is a way of
storing energy
kinases will trigger the synthesis of
proteins
CREB
key protein that alters gene expression during LTP
CREB’s journey in LTP stages
gets phosphorylated by kinases, goes into nucleus, binds to DNA and turns genes important for strengthening synapses
early stage takes approximately
1 hour
hippocampal neurogenesis
another mechanism of learning; neurons are generated in dentate gyrus
cells that survive in dentate gyrus after being neurogenerated will become
granule neurons in granule cell layer
3 things that increase neurogenesis
exercise
experience in environment
spatial learning tasks
new neurons are more ___ and have ____ LTP than older ones
plastic/ stronger
learning will _____ survival of neurons generated in hippocampus
enhance!
key term in synaptic strengthening?
plasticity
plasticity may be ___ or ___
functional/ structural
functional plasticity
more NTS, more receptors (reorganization)
structural plasticity
more synapses, more neurons (physical changes to brains wiring)
plasticity ONLY occurs in brian regions that are..
essential for the storage of a certain type of memory