AP Environmental Science Unit 6 Exam
1/71
Earn XP
Description and Tags
lock the f in
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
72 Terms
Nonrenewable energy sources
Coal, oil, natural gas, and nuclear.
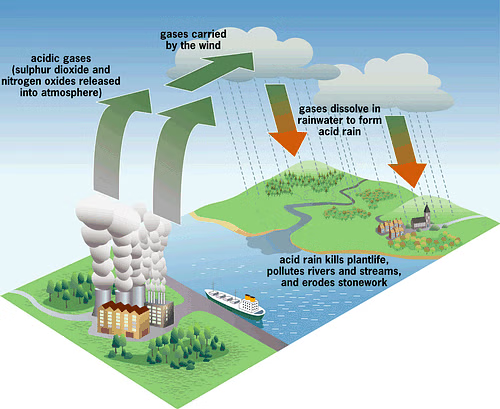
Sulfur emissions contribute to acid rain, soil and water acidification, respiratory problems in humans and animals, damage forests, harm aquatic ecosystems, corrode buildings.
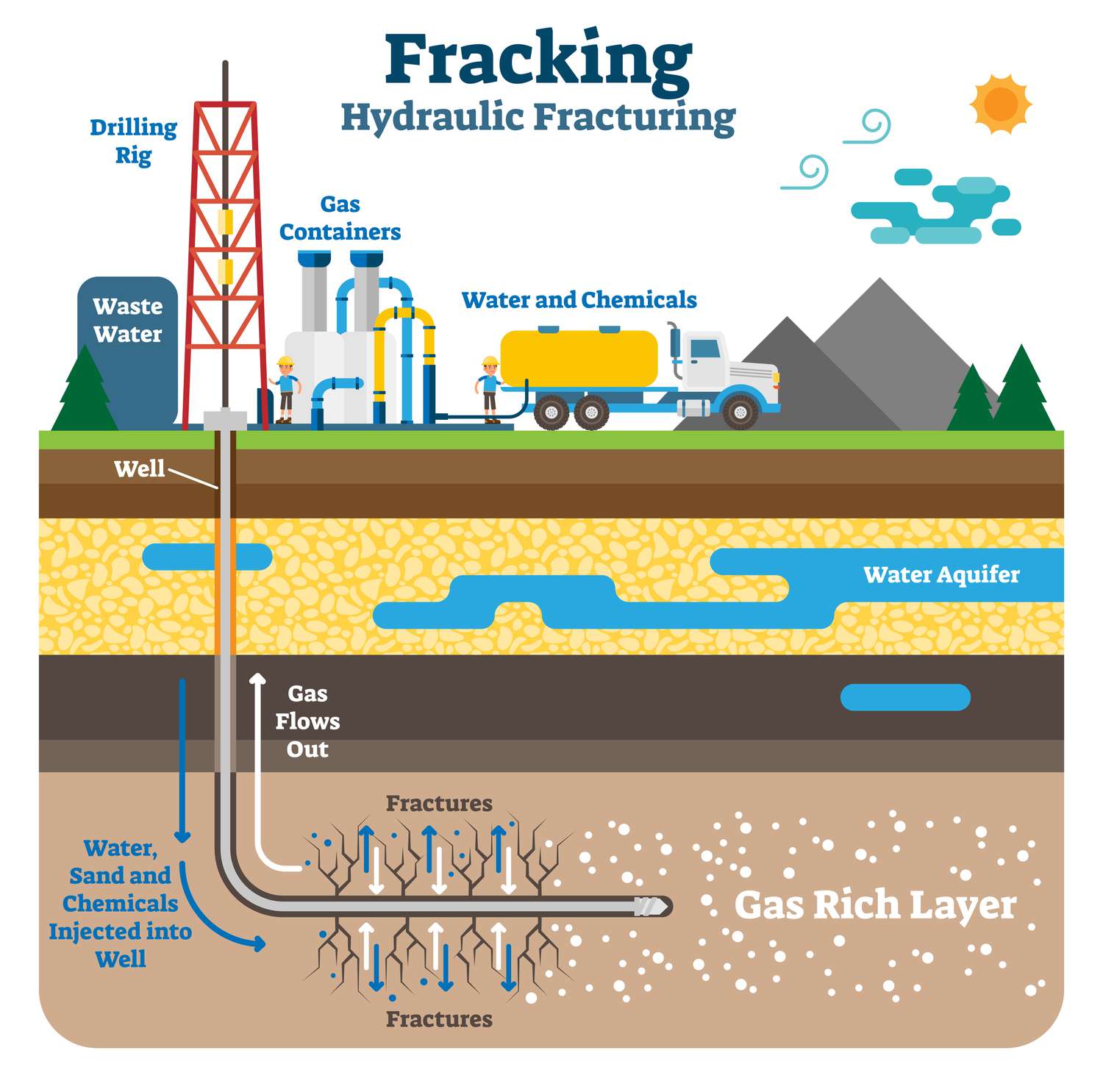
1) Seismic testing can disrupt wildlife behavior and migration.
2) Infrastructure development (roads, pipelines) can fragment habitats and increase the risk of oil spills.
1) Slow growth and recovery - Arctic ecosystems take a long time to recover from disturbances due to short growing seasons.
2) Permafrost dependency - Damage to permafrost from drilling or warming can release methane and CO₂, accelerating climate change.
1) Deforestation and habitat destruction - Large areas of land are cleared for tar sand mining.
2) Water pollution - Toxic waste from extraction contaminates local water sources.
Pro: Helps break down oil into smaller droplets, making it easier for microbes to degrade.
Con: Can be toxic to marine life and make oil sink to the ocean floor, harming ecosystems.
Economic: Loss of tourism and fishing industry revenue.
Environmental: Long-term damage to marine ecosystems and wildlife deaths from oil exposure.
1) Transportation (gasoline, diesel) - Use fuel-efficient vehicles or public transport.
2) Plastics production - Recycle and reduce plastic use.
Natural gas can offer life cycle greenhouse gas (GHG) emissions benefits over conventional fuels
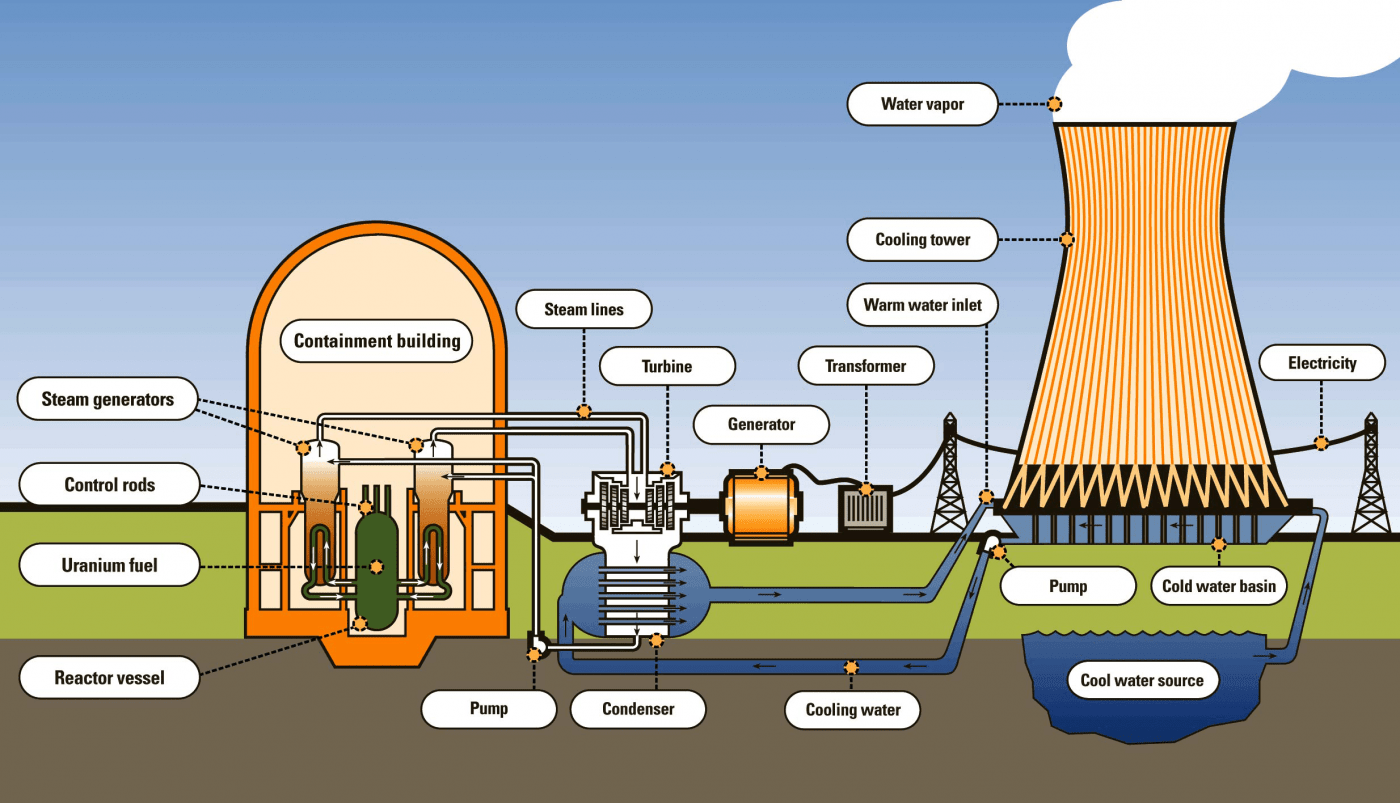
• Reactor core - Contains fuel rods where fission occurs.
• Control rods - Regulate the fission reaction.
• Coolant - Transfers heat away from the core.
• Turbine - Spins to generate electricity.
• Cooling tower - Releases excess heat.
Pros: Low greenhouse gas emissions, high energy output.
Cons: Radioactive waste, risk of meltdowns.
High-level waste - Used nuclear fuel from reactors.
Low-level waste - Medical equipment from radiation therapy.
1) Remote location to minimize human exposure.
2) Geological stability to prevent leaks.
3) Low water flow to reduce groundwater contamination.
1. Deep Borehole Disposal: Drilling boreholes 3-5 km deep into stable geological formations and sealing waste inside. Feasibility: Technologically possible but expensive; political and geological challenges exist.
2. Sub-Seabed Disposal: Burying waste beneath the ocean floor in geologically stable regions. Feasibility: Technically feasible, but international treaties prohibit ocean dumping.
• High-Level Waste: Comes from spent nuclear fuel and is highly radioactive. Example: Cesium-137 (Cs-137) (half-life ~30 years), a fission product emitting beta and gamma radiation.
• Low-Level Waste: Includes contaminated gloves, tools, and medical waste, with lower radiation levels. Example: Tritium (H-3) (half-life ~12 years), emitting low-energy beta radiation.
By analyzing a decay curve, identify the time at which the remaining quantity is half its original value. Repeat for additional half-lives to confirm consistency.
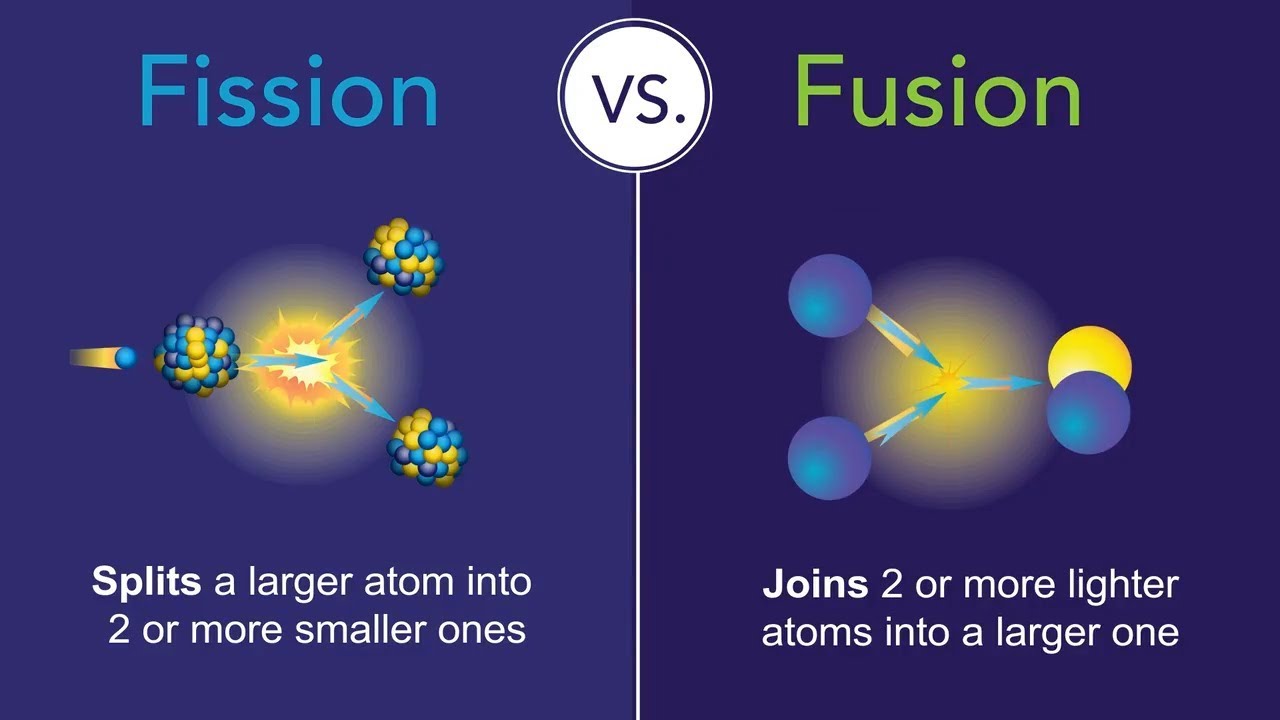
• Fission: Splitting heavy nuclei (e.g., uranium-235) into smaller fragments, releasing energy. Used in nuclear reactors.
• Fusion: Combining light nuclei (e.g., hydrogen isotopes) to form heavier nuclei, releasing more energy than fission. Requires extreme temperatures.
1) Increased food prices - Diverts corn from food to fuel production.
2) High water and land use - Requires large agricultural areas and irrigation.
1) Tax credits and rebates for homeowners and businesses that install photovoltaic (PV) solar panels.
2) Net metering policies that allow solar panel owners to sell excess electricity back to the grid, making solar power more financially attractive.
Pros: Renewable, low greenhouse gas emissions, provides flood control.
Cons: Disrupts aquatic ecosystems, displaces communities, sediment buildup reduces efficiency.
1) Provides irrigation for agriculture.
2) Creates recreational opportunities such as boating and fishing.
Geothermal hot spot
1) Reduces greenhouse gas emissions.
2) Lowers air pollution, improving public health.
Economic: Creates jobs in renewable energy industries.
Environmental: Does not require land, reducing habitat destruction.
1) Use energy-efficient appliances.
2) Install LED lighting to reduce electricity use.
1) Use low-flow toilets and showerheads.
2) Fix leaks to prevent water waste.
1) Lower CO₂ emissions.
2) Reduces air pollutants like nitrogen oxides and particulates.
1) Tax credits and subsidies for EV buyers.
2) Investment in charging station infrastructure.
Ecological: Absorb CO₂ and provide habitat for biodiversity.
Economic: Timber for construction and jobs in forestry.
Point source pollution comes from a single, identifiable location (e.g., factory discharge).
Non-point source pollution comes from diffuse sources (e.g., agricultural runoff).