🦃 Guest Lecture 3
1/11
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
12 Terms
About Us
5 species-specific business units
1 region-specific business units
Global operations in 25 countries
Geneticist Job - 17th Century
Selective breeding for:
More milk, more meat, more eggs
Different feather/skin/egg colors
Mate the best to the best
Led to the formation of different purebreds
Geneticist Job - 18 - 19th Century
Scientific breeding - Systematic approach
Keep records (pedigree, perform)
Maintains bloodlines, consistency, and quality
Select individuals based on the performance of ancestors
Inbreeding to stabilize characteristics
Emphasis on productivity traits
Meat yield, milk production, work efficiency
Key livestock breeds developed

Geneticist Job - 20th Century
Modern genetics and breeding prgoram
Discobery of DNA for more precise genetic selection
Marker-assisted selection: Specific genes linked to desirable traits
Genomic selection: Using thousands of DNA markers to evaluate animals’ breeding value
Artifcial insemination (AI) for higher breednig efficiency
Crossbreeding
Heterosis: Superior qualities of crossbred offspring compared to purebred parents
Breed complimentary: Combining desirable traits
How Does This Apply to the Turkey Industry?
Players in the turkey industry:
Breeding companies
Hybrid, Aviagem
Selection, assign mating
Multiply
Crossbreeding
Customers
Multiplier breeder
Commercial product grower
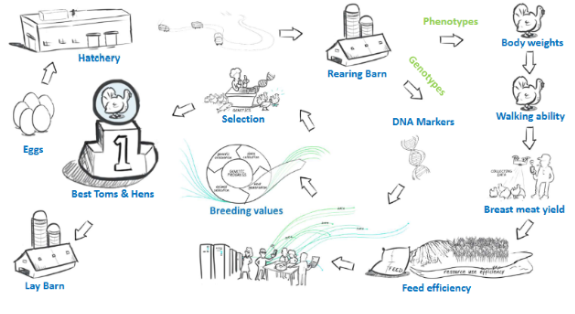
How You Do Selection
Eggs
Hatchery
Rearing barn
Phenotypes 4. Genotypes
Body weights 5. DNA markers
Walking ability 6. Breeding values
Breast meat yield 7. Selection
Feed efficiency 8. Best toms and hens
9. Lay barn
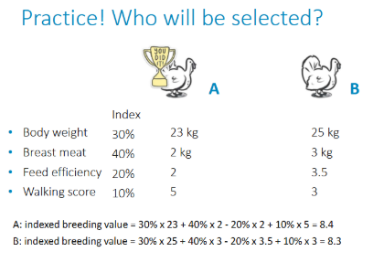
Breeding Direction
Desirable traits
Productivity traits
Body weight
Breast meat yield
Feed efficiency
Egg production
Data Collection - 21st Century
RFID (Radio Frequency Identification)
Animal weight system
CT scan for breast meat yield
Feed station for feed efficiency
Animal Welfare and Health
Leg health and walking ability
Group housing behavior
Balanced Breeding
Product quality
Production efficiency
Health and welfare
Better Breeding Today
Multi-species advantages
Combined research team
IT breeding
Innovative technologies
R&D (Research and Development) network
Investment capacity
Brighter Life Tomorrow
Economically sound sector
Animal welfare
Lower stress
Housing
Environmentally friendly
Socially accepted