Chemistry 4-6
1/32
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
33 Terms
atom
the smallest particle of an element that retains all the properties of that element; is electrically neutral, spherically shaped, composed of electrons, protons, neutrons
atomic mass
the weighted average mass of the isotopes of that element
atomic mass unit
One- twelfth the mass of carbon 12 atom
atomic number
the number of protons in an atom
electrons
A negatively charged, fast moving particle with an extremely small mass that is found in all forms of matter and moves through the empty space surrounding an atom's nucleus
isotope
Atoms of the same element with different numbers of neutrons
mass number
the number after an elements name, representing the sum of its protons and neutrons
neutrons
A neutral subatomic particle in an atom's nucleus that has a mass nearly equal to that of a proton
nucleus
the extremely small, positively charged dense center of an atom that contains positively charged protons and neutral neutrons
proton
a subatomic particle in an atom's nucleus that has a positive charge of 1+
Daltons
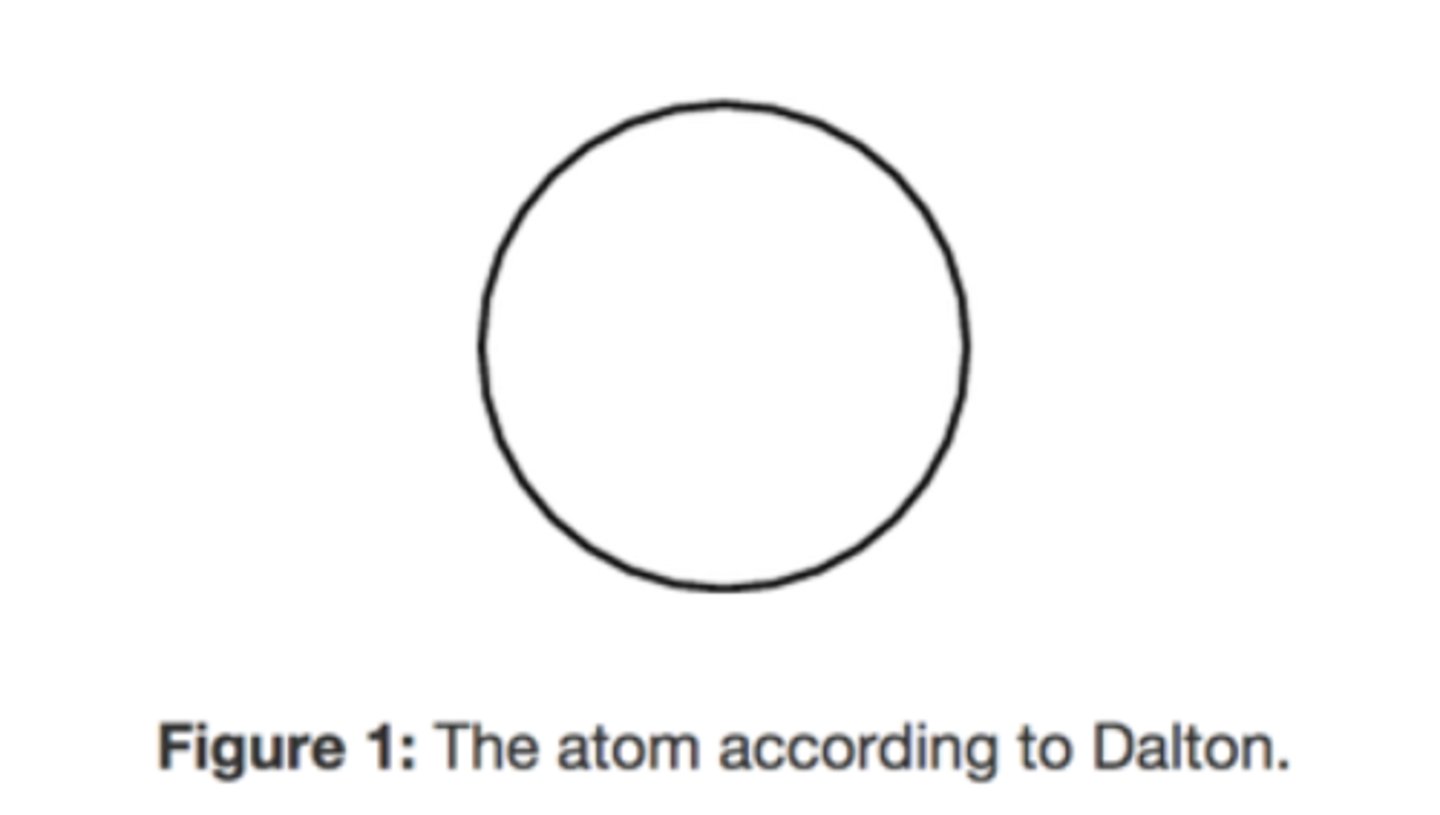
did not account for the existence of subatomic particles
What's wrong with Dalton's model
JJ Thompson Plum Pudding Model
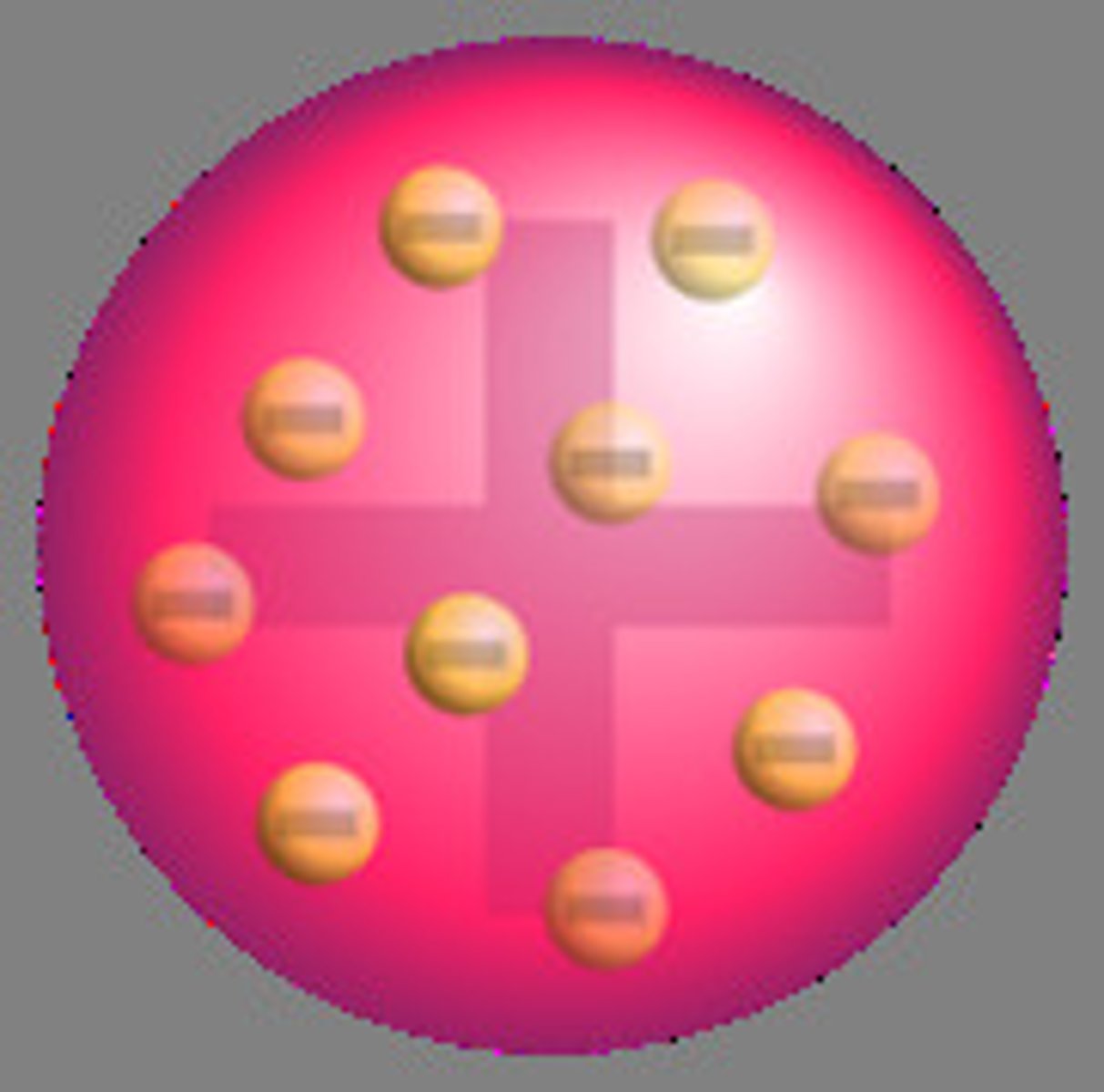
the atom is mostly empty space
Whats wrong with the plum pudding model
Rutherford
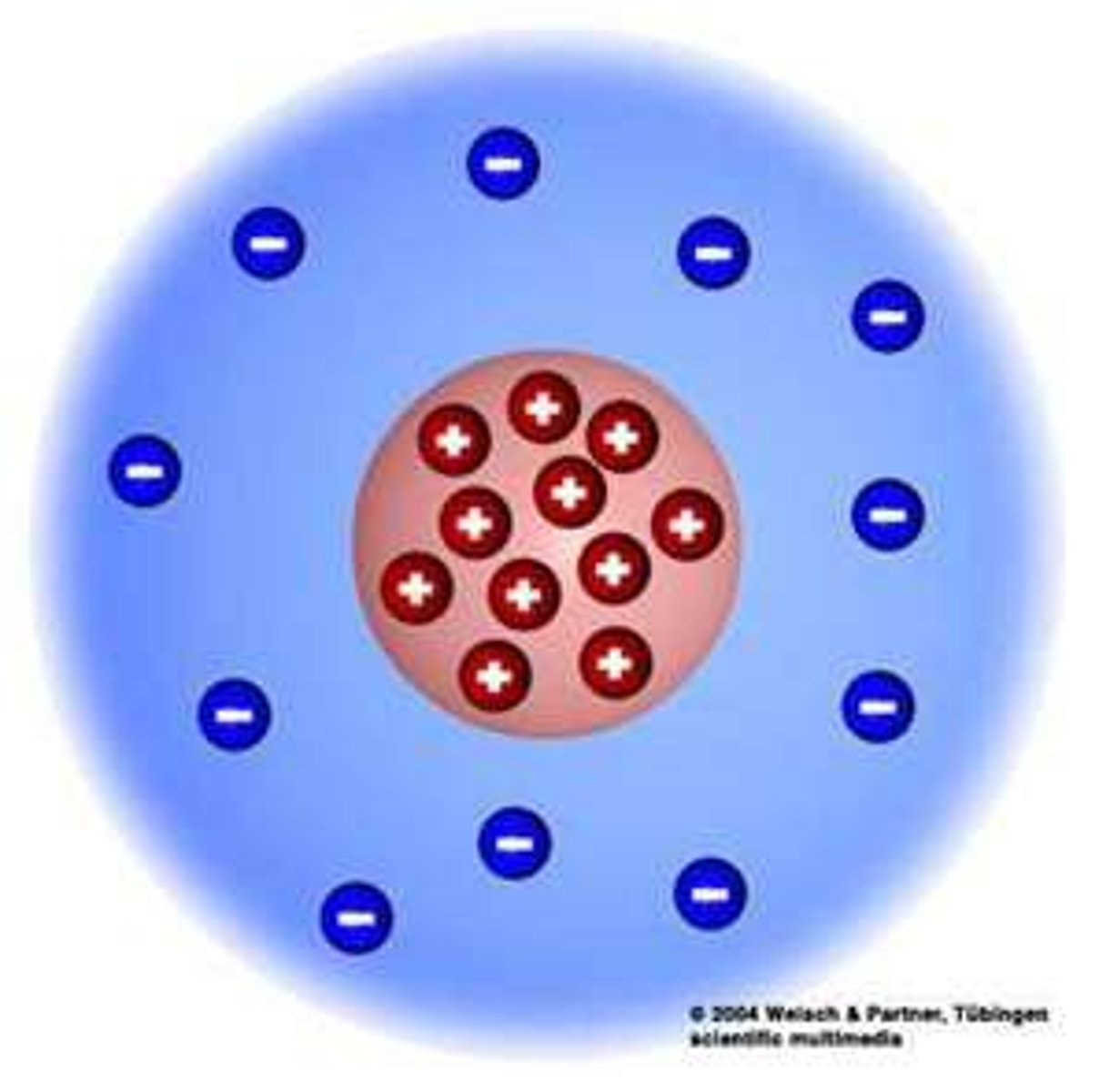
the negative electron will collapse into the positive proton
what was wrong with Rutherford's model
Bohr's
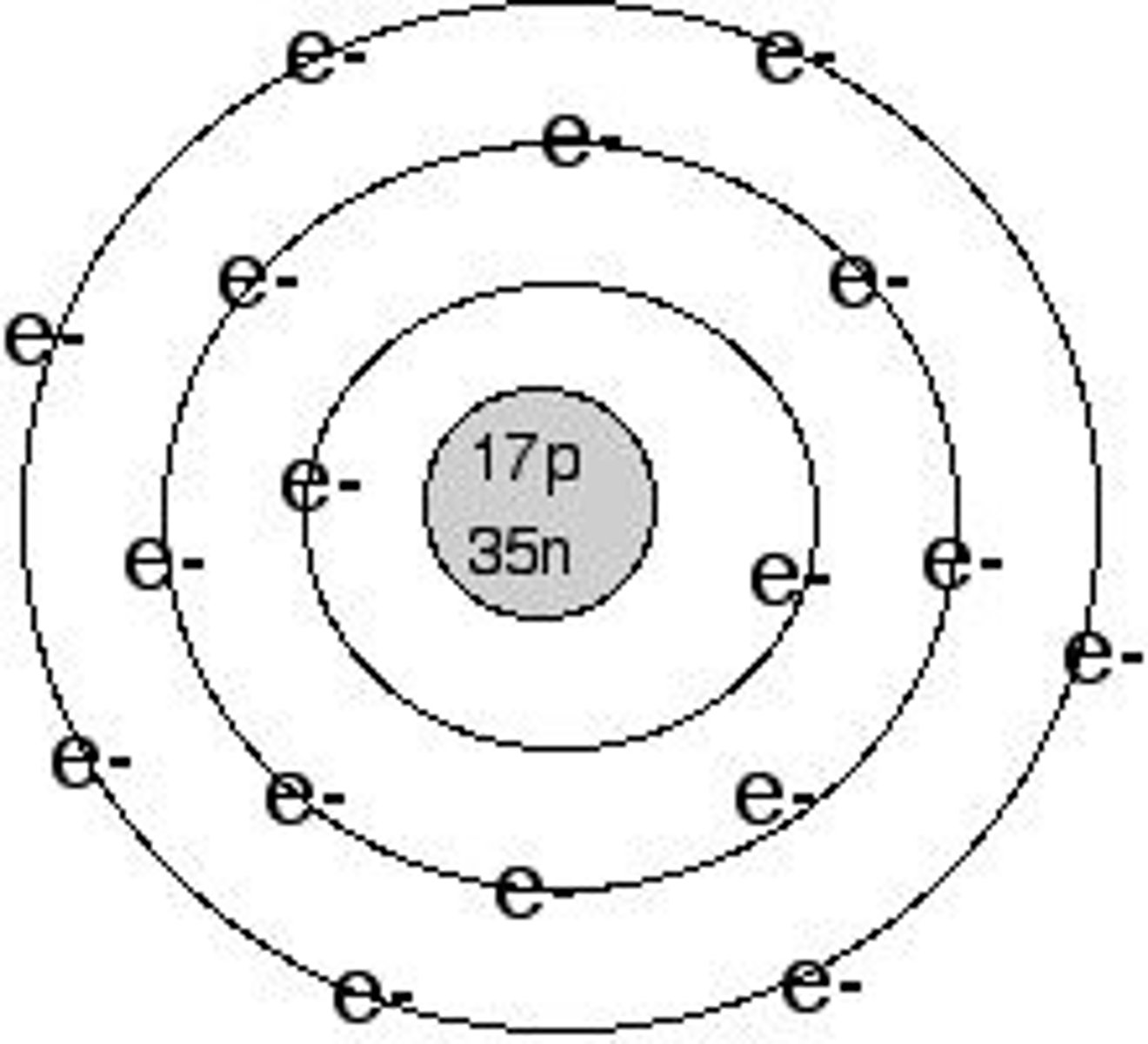
the toms move too fast to be given a rigid location
what was wrong with Bohr's model
quantum mechanical model
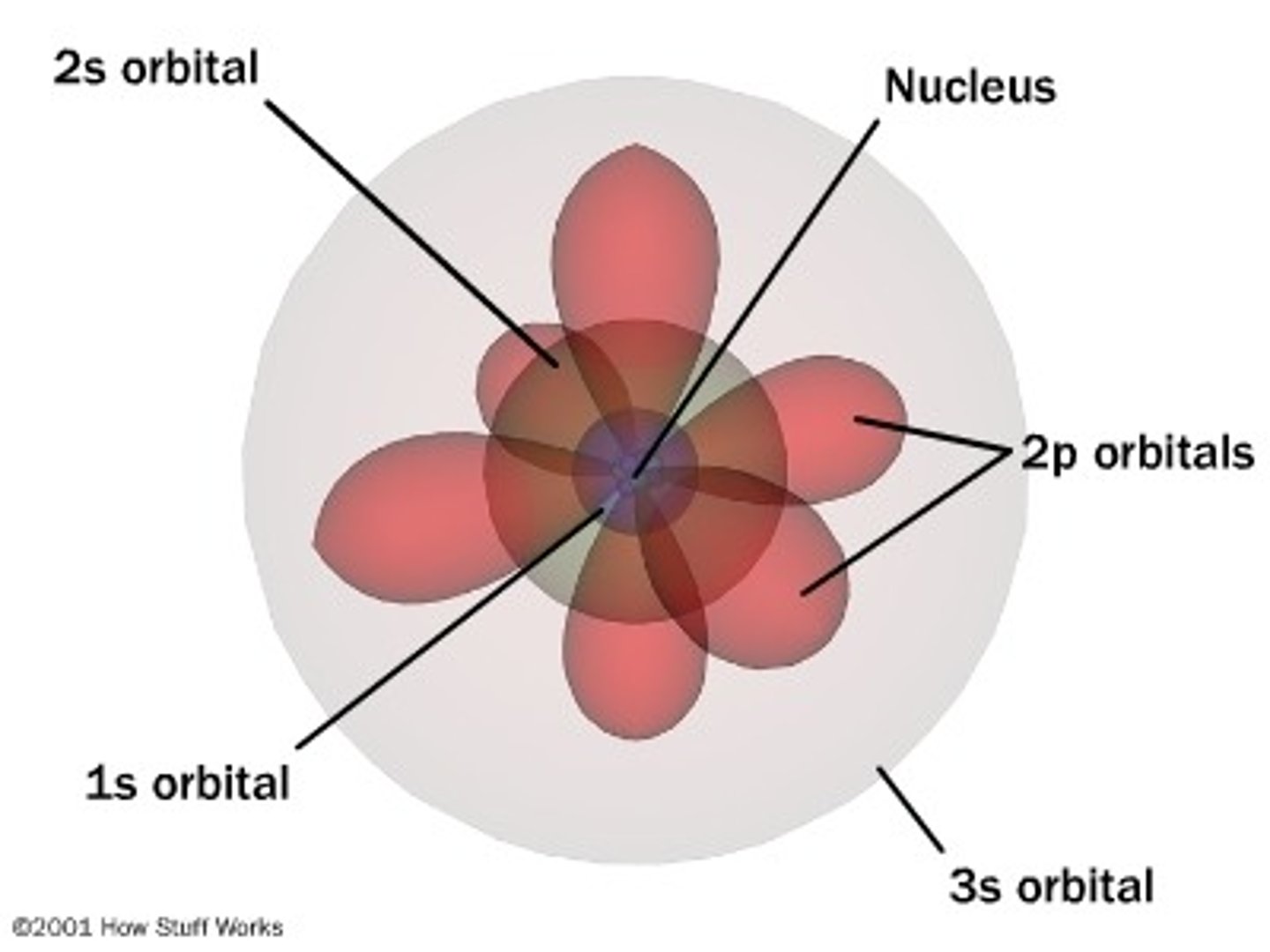
still more to discover
What was wrong with the quantum mechanical model
S-block
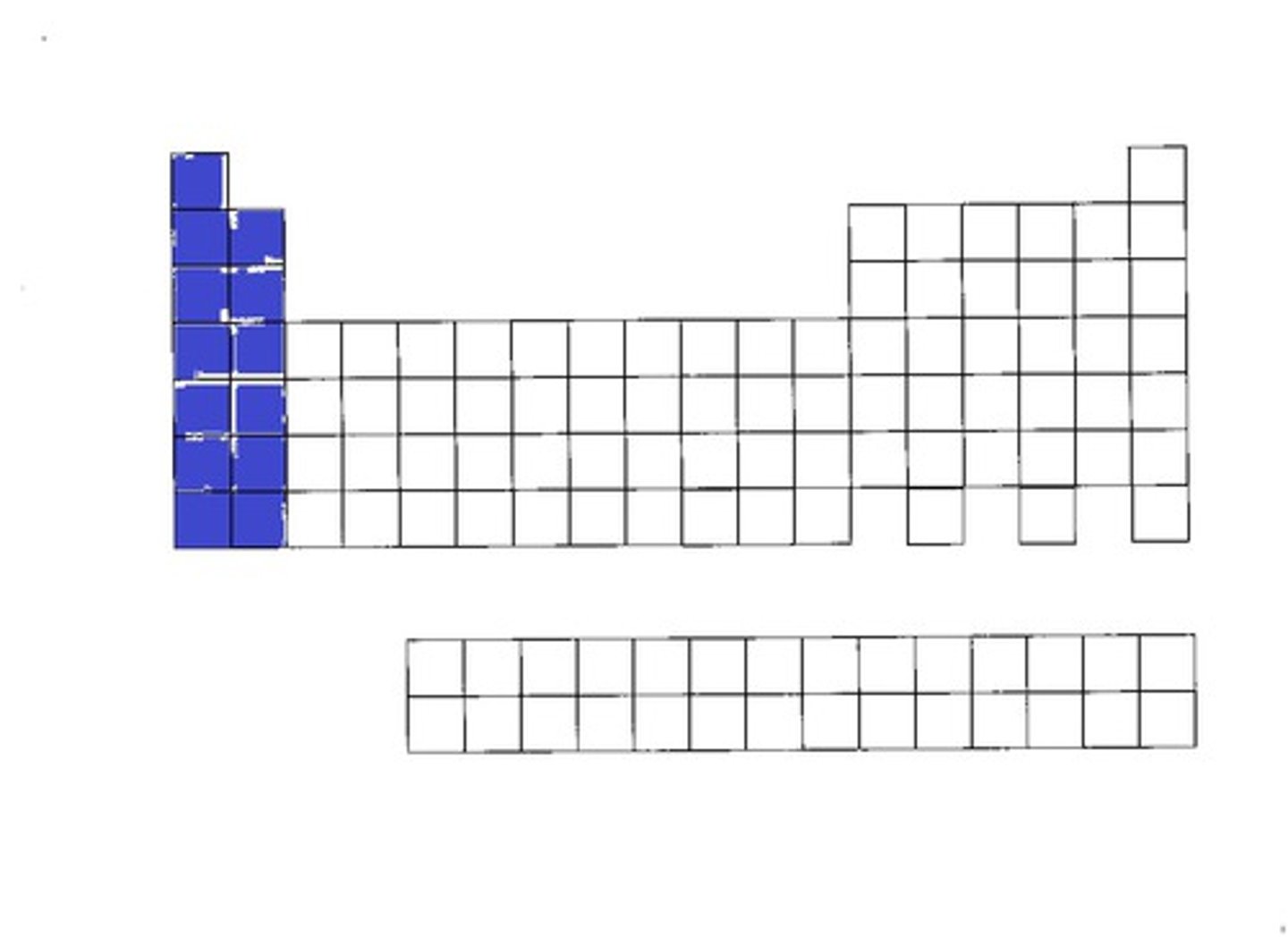
p-block
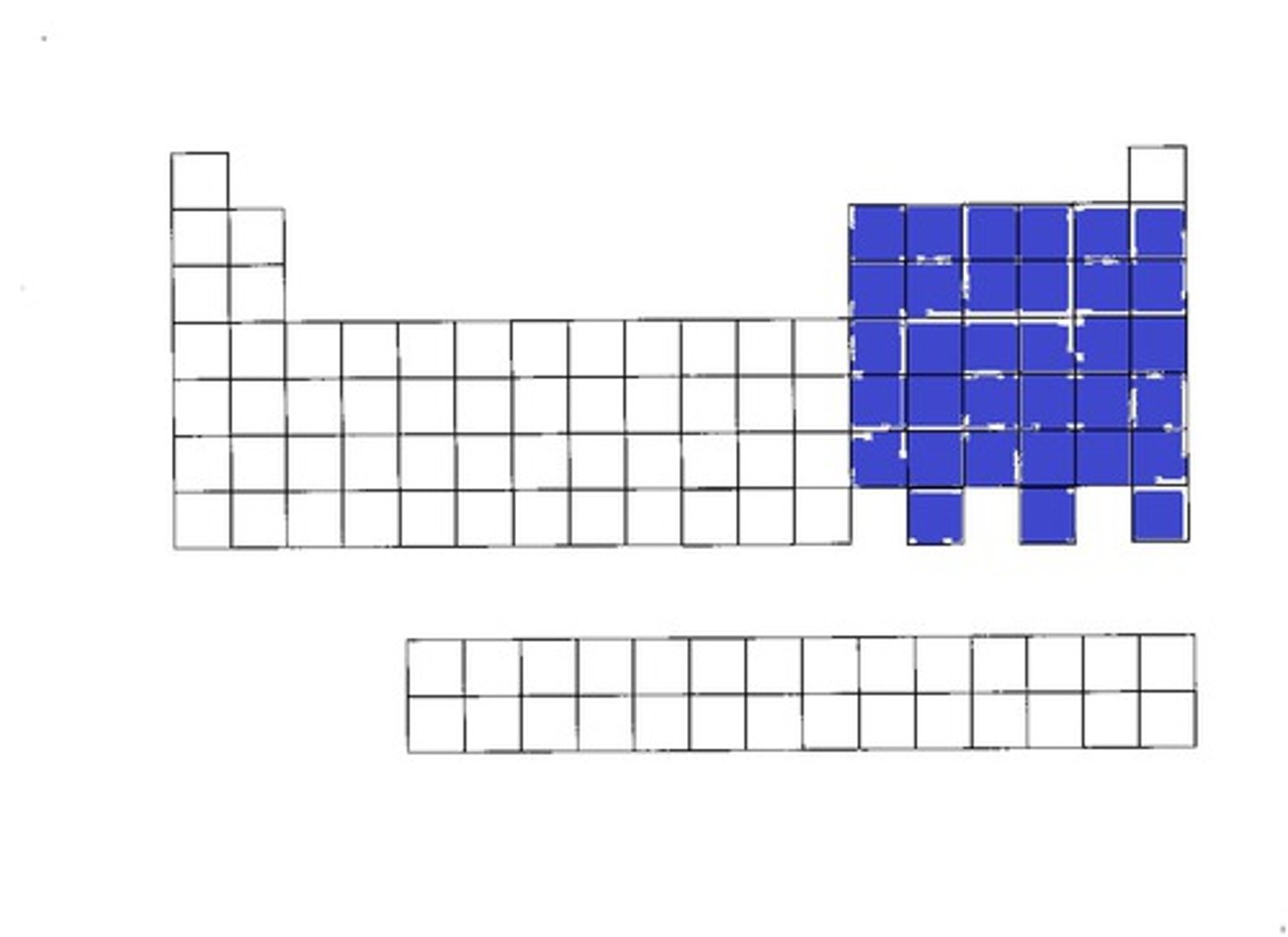
d-block
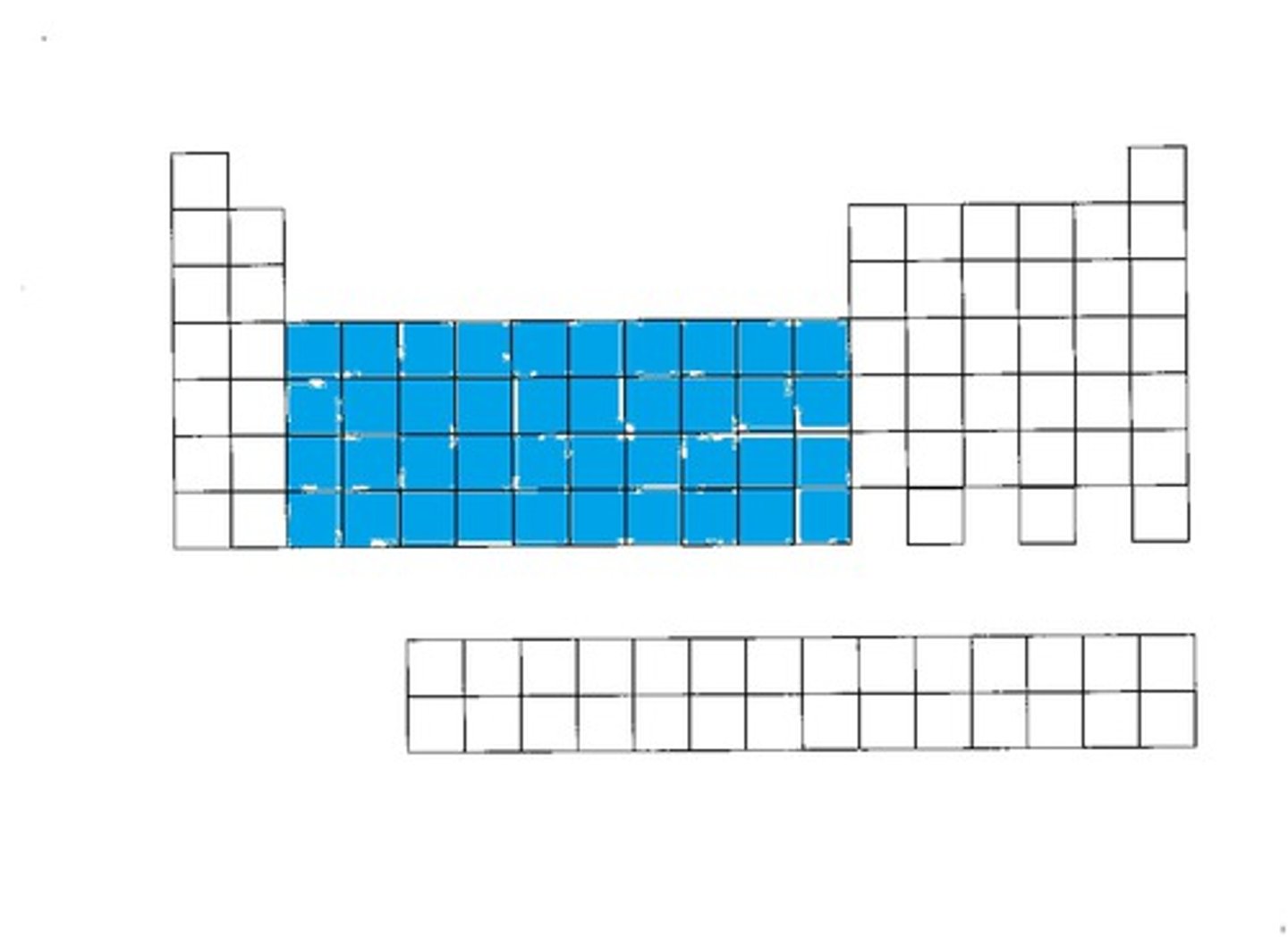
f-block
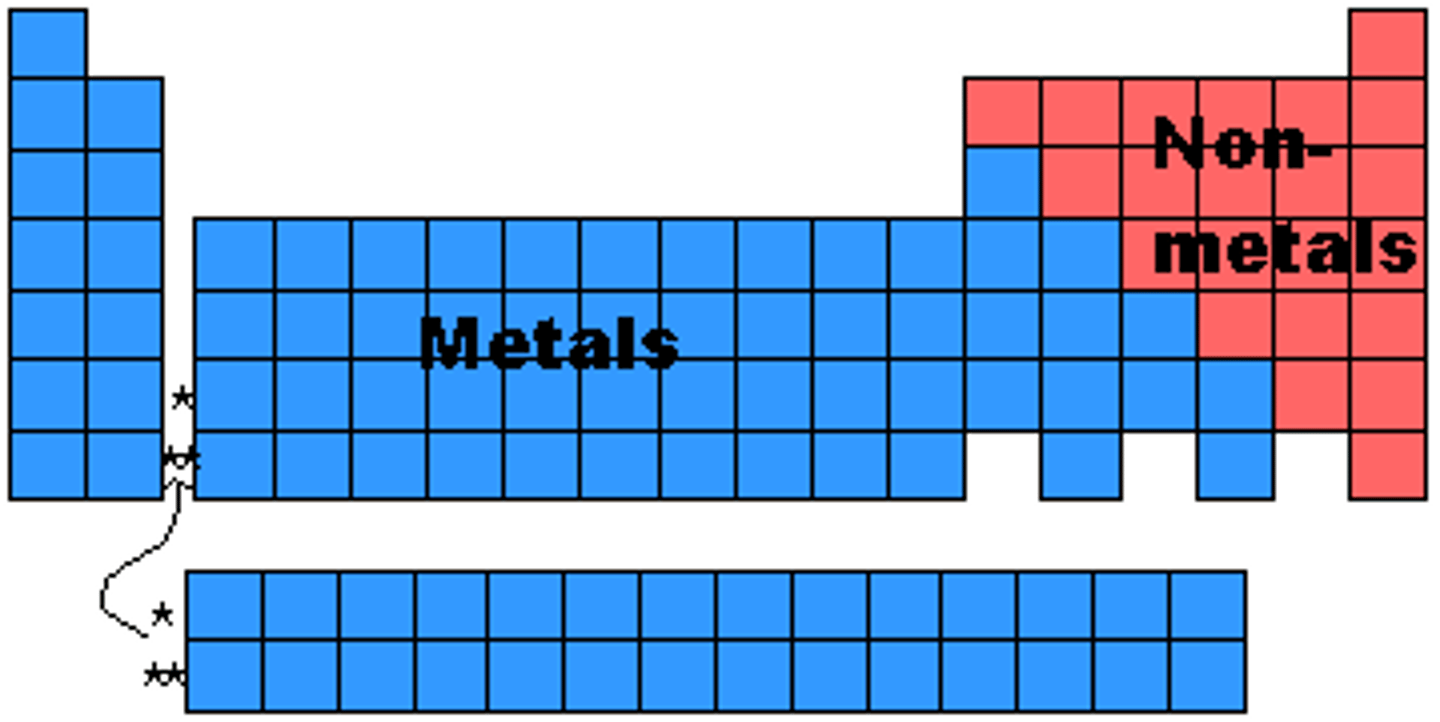
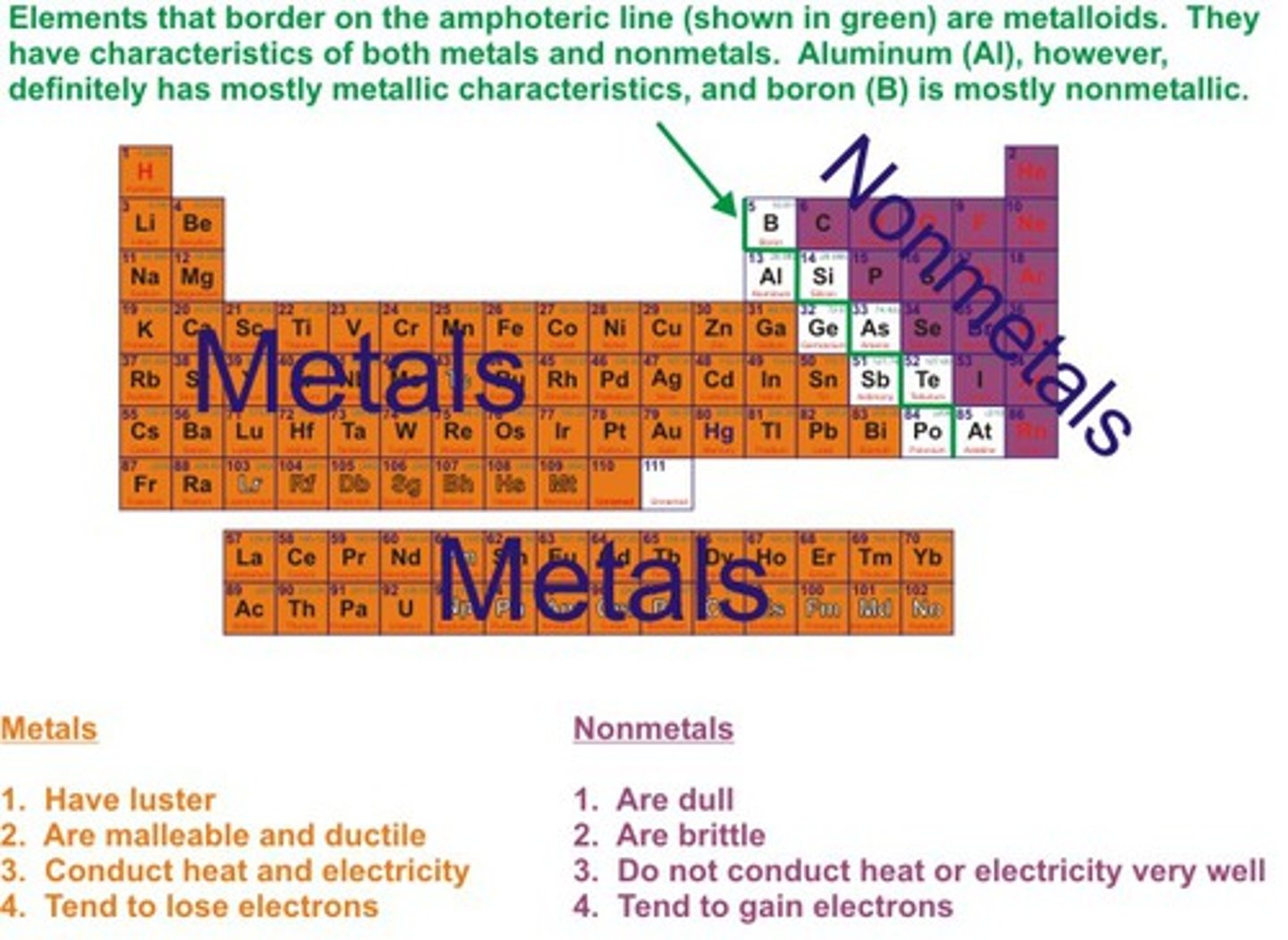
metals period table
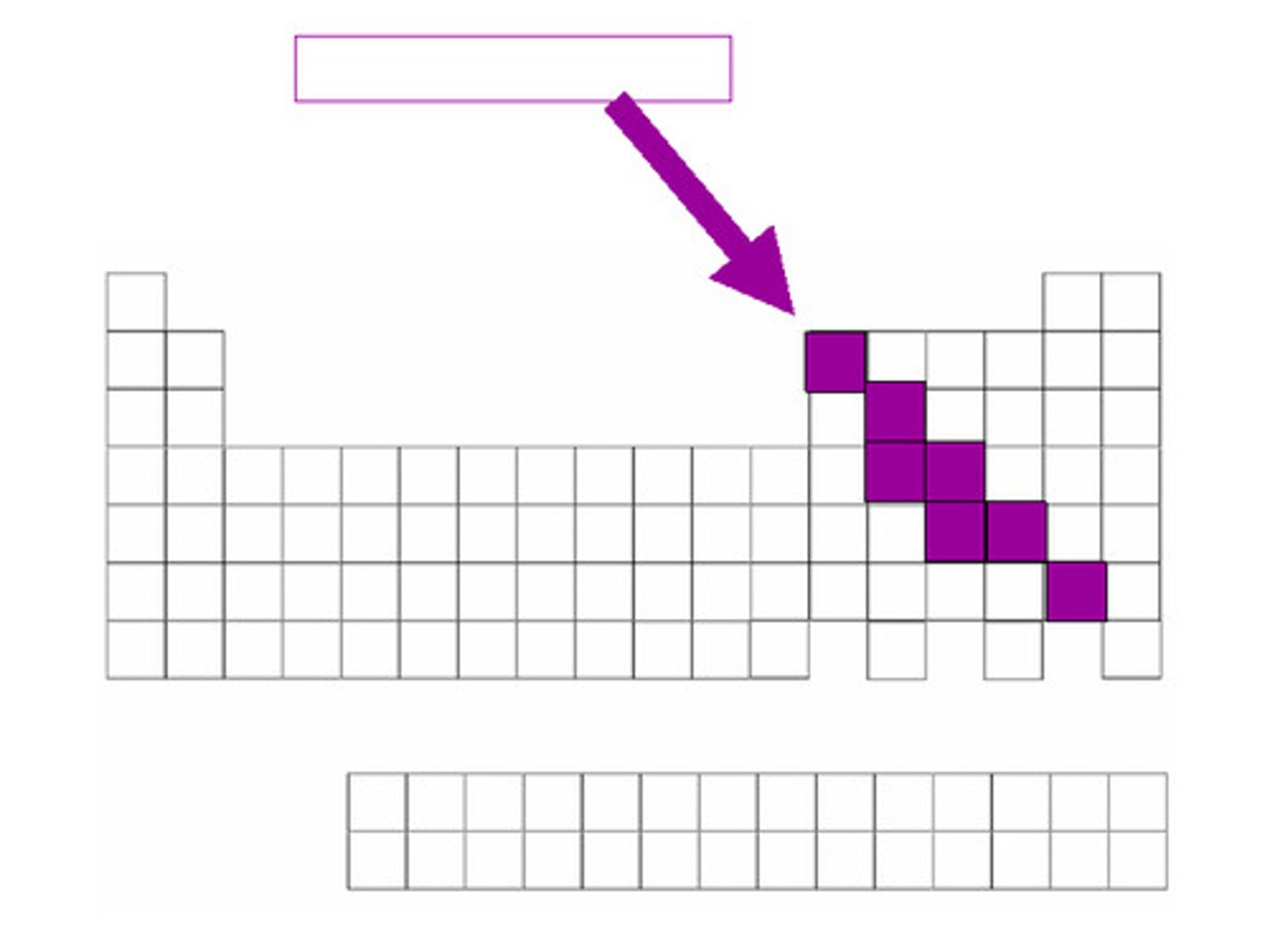
metalloids
non-metals
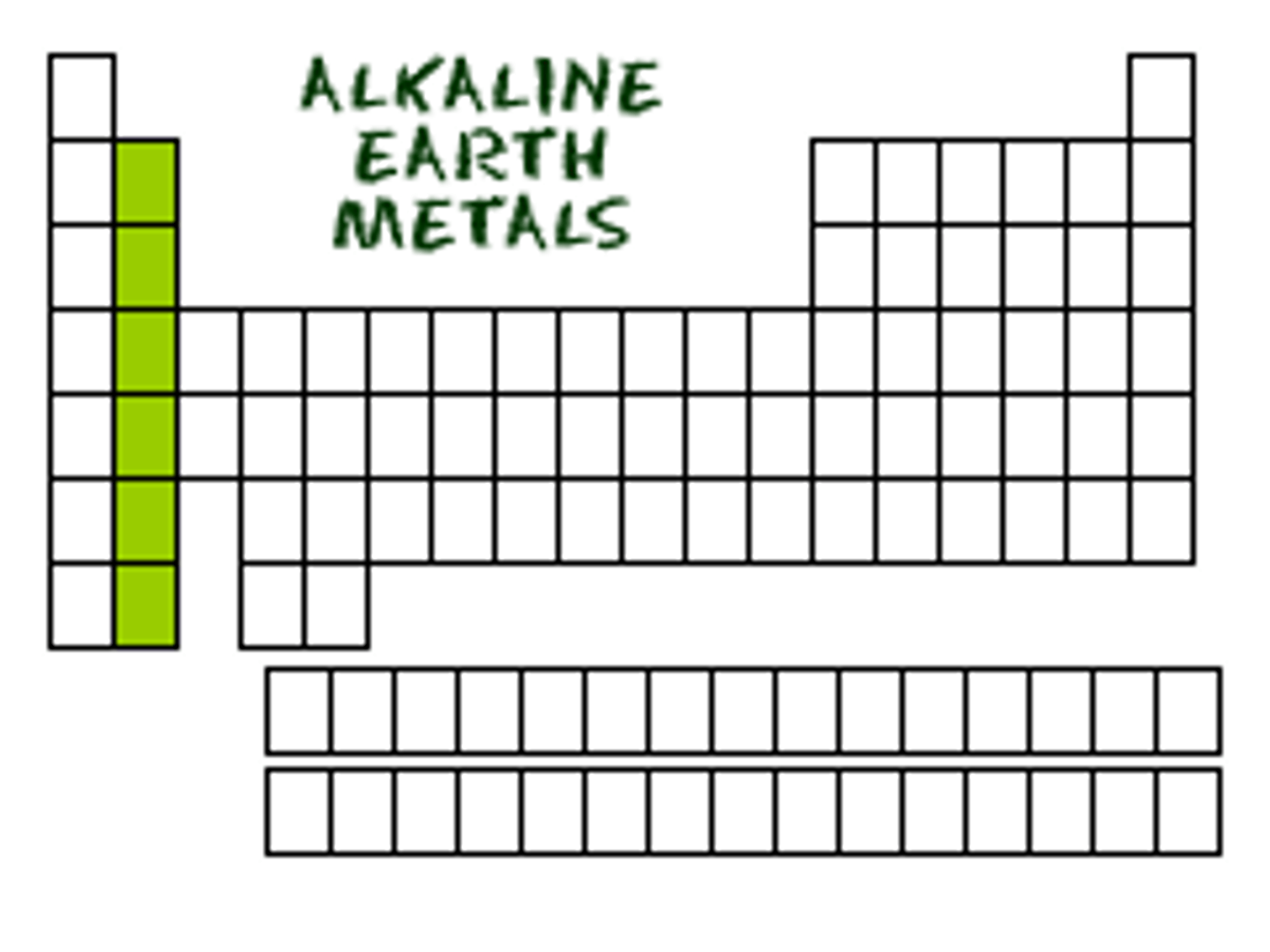
alkaline metals
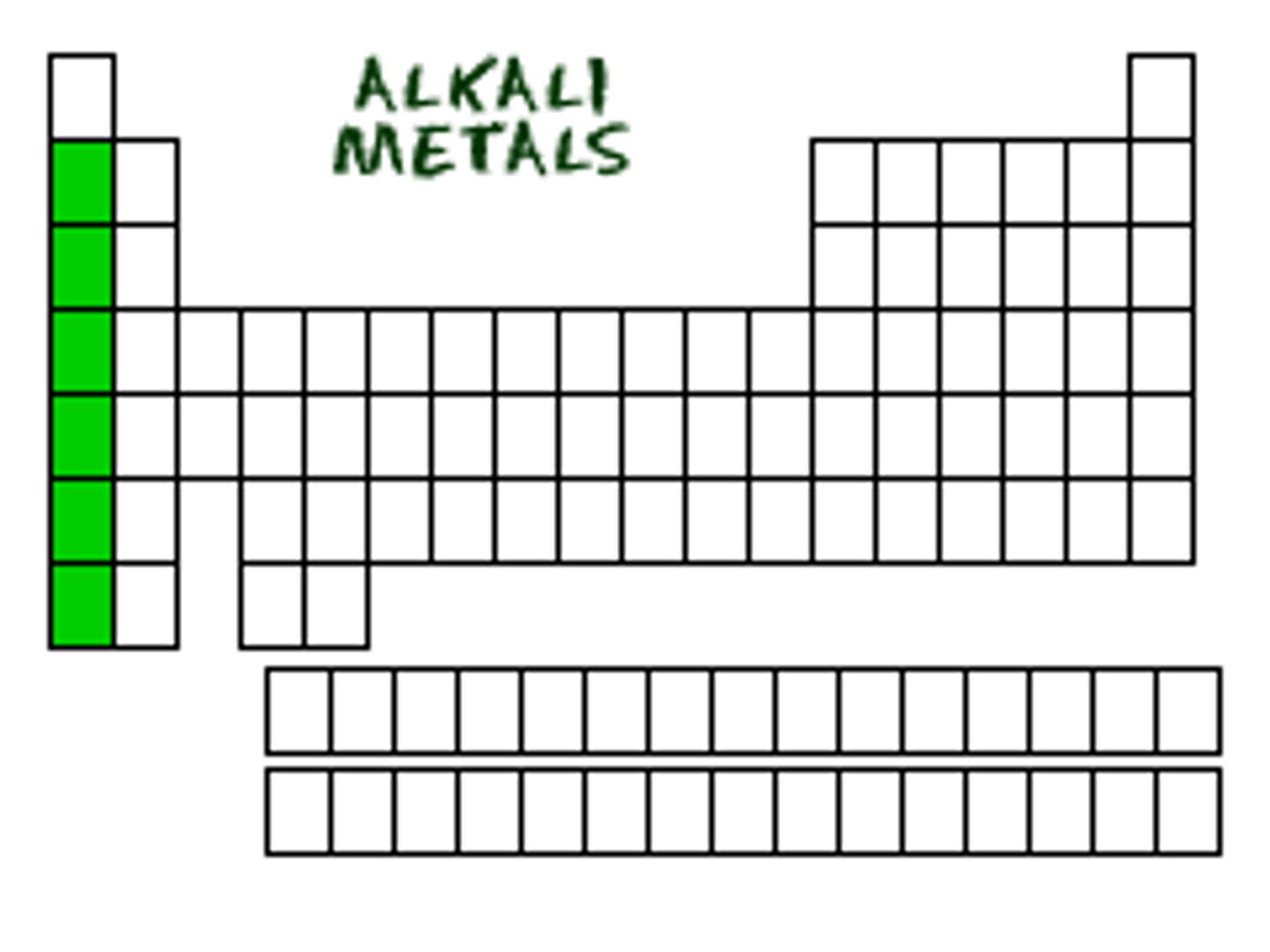
alkali metals
halogens

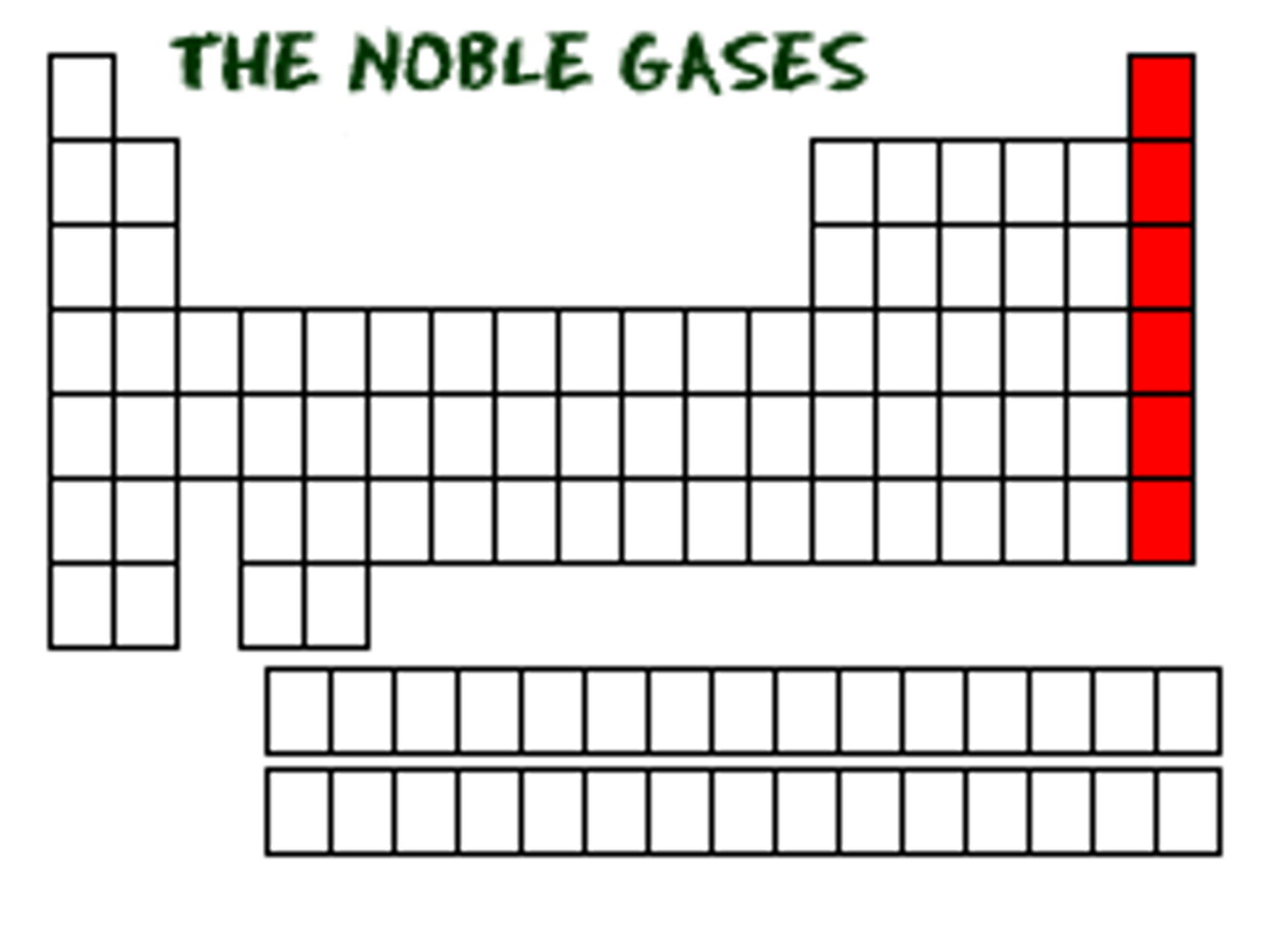
noble gases
transition elements
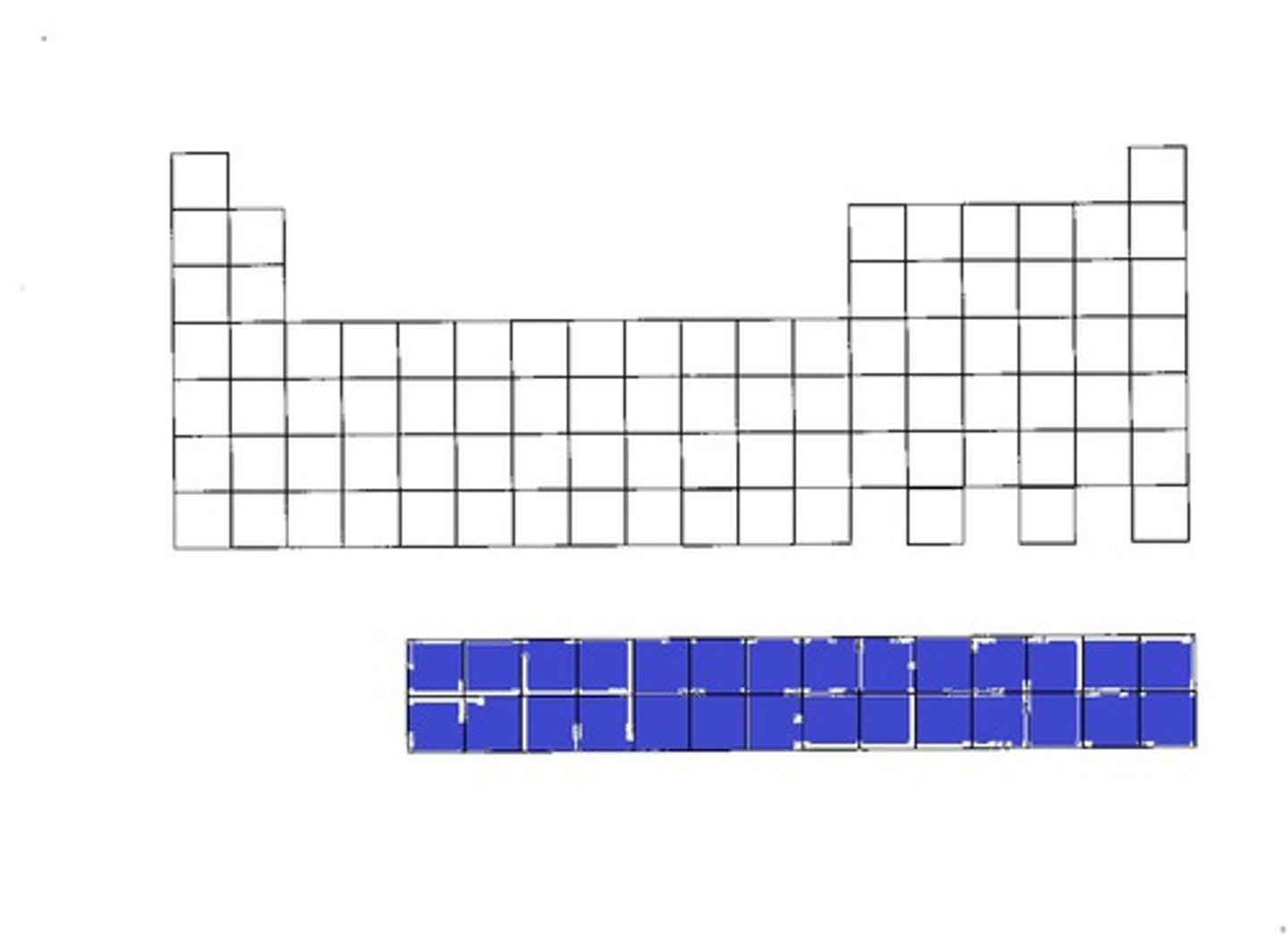
inner transition elements