Chapter 9: Nucleic Acids
1/81
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
82 Terms
Primary structure
order of bases in the polynucleotide sequence
Secondary structure
three-dimensional conformation of the backbone
Tertiary structure
super coiling of the molecule
Quaternary structure
interaction with other macromolecules
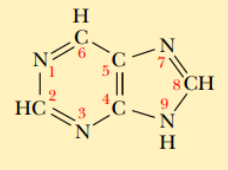
Nucleic acid bases
Nitrogen-containing aromatic compounds that make up the coding portion nucleic acids
Pyrimidine bases
Compounds that contain a six-membered ring
Parent compounds of several nucleobases
Cytosine, Thymine, Uracil
Purine bases
Compounds that contain a six-membered ring fused to a five-membered ring
Parent compounds of adenine and guanine
Nucleoside
Purine or pyrimidine base bonded to a sugar (ribose or deoxyribose)
Lacks phosphate group
Forms a glycosidic linkage with the sugar
Nucleotide
Monomers of nucleic acids
3 parts: nitrogenous base, sugar, phosphoric acid residue
Naming: parent nucleoside, with the suffix -monophosphate added
3’, 5’-phosphodiester bond
Covalent linkage in which phosphoric acid is esterified to the 3′ hydroxyl of one nucleoside and the 5′ hydroxyl of another nucleoside
Dr. Rosalind Franklin
Created the famous Photo 51, an X-ray diffraction work demonstrating the double helix structure of DNA (the molecule containing the genetic instructions for the development of all living organisms
DNA Double Helix
Two polynucleotide chains wrapped around each other; the fundamental structural motif of DNA
DNA
Biopolymer that consists of a backbone of alternating units of 2-deoxy-D-ribose and phosphate
Phosphodiester bond
3′ —OH of one 2-deoxy-D-ribose is joined to the 5′ —OH of the next 2-deoxy-D-ribose by a _____
5’ end to 3’ end
Nucleotide residues of nucleic acids are numbered from the _____
Base pairing
Complementary joining of two nucleic acid bases making the two chains of the double helix as complementary strands
Sugar moieties
Vertical lines show the positions of the _____ to which the individual bases are attached
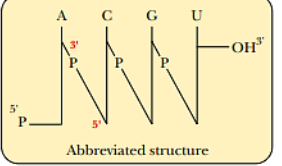
Phosphodiester bond
Diagonal lines through the letter P represents a _____
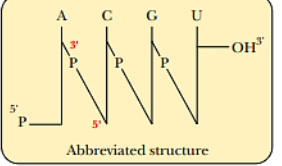
Deoxyribonucleotide residue
Letter “d” is added to indicate a _____
A-DNA
DNA Conformation
Not found in in vivo techniques
Right-handed helix (helix winds upward) but thicker than B-DNA
11 base pairs per turn of the helix
Base pairs are not perpendicular to the helix axis; lie at an angle of about 20º to the perpendicular
Originally found in dehydrated DNA samples
DNA:RNA and RNA:RNA
Hybrids that may be found in the A-DNA form
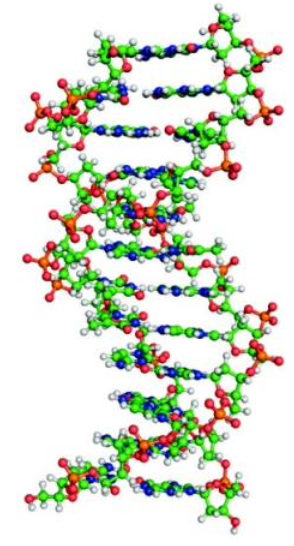
B-DNA
DNA Conformation
Normal, physiological DNA form
Right-handed helix
10 base pairs per turn of the helix
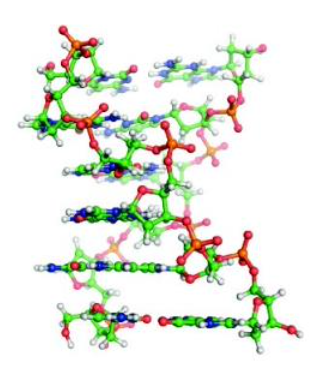
Z-DNA
DNA Conformation
Usually consists of alternating purine-pyrimidine bases; regulation of gene expression
Left-handed double helix
Derivative of the B form
Produced by flipping one side of the backbone 180 ̊ without disturbing the backbone covalent bonds or hydrogen bonds
Zigzag look of the phosphodiester backbone when viewed from the side
hydrophobic
Bases are (hydrophobic/hydrophilic)?
Base stacking
The ring portions of the DNA bases interact with each other via hydrophobic bonding (van der Waals) of their pi-cloud electrons
In standard B-DNA, each base pair is rotated 32º with respect to the preceding one (optimal for maximal base pairing but not optimal for maximal overlap of bases)
B-DNA
In standard _____, each base pair is rotated 32º with respect to the preceding one
Minor groove
Bases that are exposed to the _____ must come in contact with water
Propeller twist
Base-pairing distances are less optimal, base stacking is more optimal, and water is eliminated from minor-groove contacts with bases
H-bonds between bases are distorted by this motion, yet remain intact
Bases slide sideways
Step
The dinucleotide with its complementary pairs is called a _____ in the nomenclature of DNA structure
Prokaryotic DNA
Circular and forms supercoils
Extra twists (over and above those of the double helix) in closed circular DNA
Circular DNA
The 5′ and 3′ ends of each strand are joined by phosphodiester bonds
Negative supercoils
Circular DNA with fewer than normal number of turns of the helix (underwound)
Positive supercoils
Circular DNA with more than normal number of turns of the helix (overwound)
Replication
Naturally occurring circular DNA is negatively supercoiled except during _____
Topoisomerases
Enzymes that relax supercoiling in closed circular DNA
Class I topoisomerases
Cut the phosphodiester backbone of one strand, pass the other end through, and reseal
Class II topoisomerases
Cut both strands, pass some of the remaining DNA helix between the cut ends, and reseal
DNA gyrase
(Class II topoisomerase) Bacterial topoisomerase that introduces negative supercoils into DNA
tetramer
cuts both strands of DNA
Class II
Which class of topoisomerase is gyrase?
chromatin
Supercoiling in eukaryotic DNA results in _____
Chromatin
Complex of DNA and protein found in eukaryotic nuclei
Resembles beads (nucleosome) on a string
String portions are called spacer regions
Structure and spacing of nucleosomes is important in its function
Spacer regions
Consist of DNA complexed to some H1 histone and nonhistone proteins
30 to 50 base pairs long
Further coiling of this region produces the compact form of chromatin found in the cell
Spacer regions
Further coiling of the _____ produces the compact form of chromatin found in the cell
Ubiquitin
A protein involved in the degradation of other proteins
histone-protein
Topological changes induced by supercoiling must be accommodated by _____ component of chromatin
Histones
Principal proteins in chromatin
Basic proteins found complexed to eukaryotic DNA
Main types - H1, H2A, H2B, H3, and H4
Rich in the basic amino acid residues, lysine and arginine
DNA Denaturation
Energy must be added to a sample of DNA to break the hydrogen bonds and to disrupt the stacking interactions
Carried out by heating the DNA in a solution
Melting: heat denaturation of DNA
Slow cooling: renaturation is possible
Slow cooling
DNA renaturation is possible through _____
260nm
Bases absorb light in the _____ wavelength region
does not change, increases
As the DNA is heated and the strands separate, the wavelength of absorption _____ change, but the amount of light absorbed _____
Hyperchromicity
As the DNA is heated and the strands separate, the wavelength of absorption does not change, but the amount of light absorbed increases
G—C
Melting temperature (Tm), midpoint of the melting curve, is higher when the percentage of _____ is higher
3.4 Å / 0.34 mm
Individual base pairs are _____ apart
RNA
Single-stranded
Consists of long, unbranched chains of nucleotides joined by phosphodiester bonds between the 3′ —OH of one pentose and the 5′ —OH of the next
Pyrimidine bases are uracil and cytosine
β-D-ribose
Pentose unit of RNA
2-deoxy-D-ribose
Pentose unit of DNA
Replication
Yields 2 DNA molecules identical to the original one, ensuring transmission of genetic information to daughter cells with exceptional fidelity
Transcription
The process by which the order of bases is passed from DNA to RNA
The sequence of bases in DNA is recorded as a sequence of complementary bases in a single-stranded mRNA molecule
Translation
The process by which the order of bases in mRNA specifies the order of amino acids in the growing protein
3-base codons on the mRNA corresponding to specific amino acids direct the sequence of building a protein
These codons are recognized by tRNAs carrying the appropriate amino acids
Splicing
The process of intron removal and exon joining
Transfer RNA (tRNA)
RNA Type
Small, transports amino acids to site of protein synthesis
Single-stranded polynucleotide chain between 73 and 94 nucleotide residues long
Carries an amino acid at its 3′ end
Where intrachain hydrogen bonding occurs
Cloverleaf structure
Stems: H-bonded portion
Loops: Non-H-bonded portion (contain modified bases)
tRNA and mRNA
Both _____ and _____ bound to the ribosome ensures the correct order of the amino acids in the growing polypeptide chain
L-shaped conformation
tRNA folds into this conformation to produce the specific tertiary structure needed for tRNA to interact with the enzyme that attaches the amino acid
Ribosomal RNA (rRNA)
Combines with proteins to form ribosomes
Accounts for 60% to 65% of the total weight of a ribosome and the protein portion constitutes 35% to 40% of the weight
Both prokaryotes and eukaryotes have ribosomes with two subunits (one larger than the other)
Analytical ultracentrifugation
Used to monitor the dissociation and reassociation of ribosomes
Motion of particles is characterized by a sedimentation coefficient, expressed in Svedberg units (S)
Messenger RNA (mRNA)
Least abundant type of RNA
Directs amino acid sequence of proteins
Initially formed as a larger precursor molecule called heterogeneous nuclear RNA (hnRNA)
Carries coded genetic information from DNA to
ribosomes for the synthesis of proteins
Present in cells in relatively small amounts and is short-lived
Heterogenous nuclear RNA (hnRNA)
Precursor molecule of mRNA
3’
Complementary strand of mRNA is synthesized along one strand of an unwound DNA, starting from the _____ end
Introns
IxEntervening sequences that do not encode a protein
Exons
Protein-coding regions
Small nuclear RNA (snRNA)
Recently discovered
Found in nucleus of eukaryotic cells
About 100 to 200 nucleotides long
Complexes with proteins and forms small nuclear ribonucleoprotein particles (snRNPs)
Small nuclear ribonucleoprotein particles (snRNPs)
Protein–RNA complexes found in the nucleus that aid in processing RNA molecules for export to the cytosol
Help with processing (splicing) of the initial mRNA transcribed from DNA into a mature form
Have a sedimentation coefficient of 10s
Cytosol
Most protein synthesis occurs in the _____
Small interfering RNAs (siRNAs)
Short stretches of RNA have been found to have an enormous control over gene expression
Used to eliminate expression of an undesirable gene
Used in the study of gene expression
Micro RNAs (miRNAs)
Control the production of many gene products
Can lead to inhibition or activation depending on which mRNA is being bound
Bind to mRNA and prevent its translation
Used in the treatment of hepatitis C
Hepatitis C
Leading cause of liver cancer and liver failure that kills 350,000 people annually in the US
Miravirsen
RNA drug that binds to a liver miRNA (miR-122) designed to attack another miRNA
Small interfering RNAs (siRNAs)
Bind to mRNA but lead to the cleavage of the RNA in question
Used in the treatment of Ebola virus
Long noncoding RNA (lncRNA)
Promising and controversial model for study for future therapies
Ubiquitous in the cell
Disruption of many of them lead to nonviable offspring in mouse models, and alterations in lncRNA are found in many cancer types
CRISPR (Cas)
Clustered regularly interspaced short palindromic repeats
Repetitive stretches of DNA found in bacteria and archaea
Used to develop treatments for cystic fibrosis and sickle-cell anemia
Epigenetics
Refers to changes in DNA that are not reflected in the actual base sequence
Acetylation, methylation
_____ generally switches on gene expression, while _____ usually silences the expression