Cholinergic Vs Adrenergic (Video)
1/30
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
31 Terms
What type of postganglionic nerve fiber secretes norepinephrine?
Sympathetic Nerve Fiber (Adrenergic)
What type of postganglionic nerve fiber secretes acetylcholine?
Parasympathetic
T/F: The preganglionic receptors secrete a mixture of Acetylcholine and Norepinepherine
False, pre-ganglionic receptors only secrete Acetylcholine
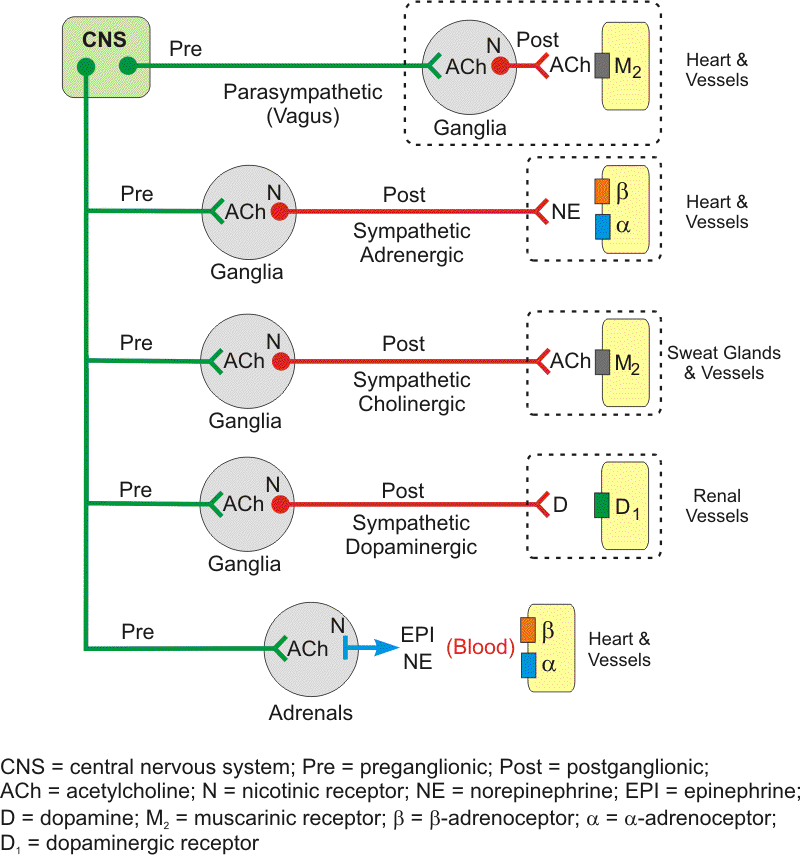
T/F: All pre-ganglionic nerve fibers are autonomic
False, most are autonomic, but some are somatic (one that releases onto skeletal muscle) (NM)
2 organs are supplied by a sympathetic muscarinic fiber, what type of neurotransmitter do they secrete? Which organs are they?
Acetylcholine
This is the exception to the “sympathetic fibers secrete norepinephrine“ rule
Sweat Glands and blood vessels of skeletal muscle
What are the clinical signs of a cholinergic crisis? Hint think D.U.M.B.E.L.L.S
Diarrhea
Urination
Miosis
Constricted/Pinpoint pupils
Bradycardia
Emesis
Nausea/Vomiting
Lacrimation
Lethargy
Salivation
Don’t forget that cholinergic fibers are a part of the PNS which is “rest and digest“, everything on this list would be from the body relaxing too much
In an adrenergic nerve fiber, what type of neurotransmitter is secreted?
What are the 2 structures that the neurotransmitter can bind too?
Lastly, what are the 3 ways that the neurotransmitter is removed from the synapse?
Norepinephrine (NE)
Alpha-1 and Beta-1
3 ways
Re-uptake
Broken down
Binds to Alpha-2 as a negative feedback loop to prevent the release of more NE
To which type of nervous system does each of the following belong?
Nicotinic
Muscarinic
Cholinergic
Adrenergic
PaNS
PaNS
PaNS
SNS
If a NN nicotinic receptor binds to the heart, what receptor on the heart is it binding to?
A muscarinic receptor (Not sure about this)
A sympathetic pre-ganglionic nerve fiber that is binding to its ganglion bind to what type of receptor? Would it change if the preganglionic receptor was parasympathetic?
NN
No
T/F: Ganglions are nicotinic receptors
True
A cholinergic pre-ganglionic nerve fiber binds to the adrenal medulla. What type of receptor does it bind to? (subtype of muscarinic or nicotinic)
NN
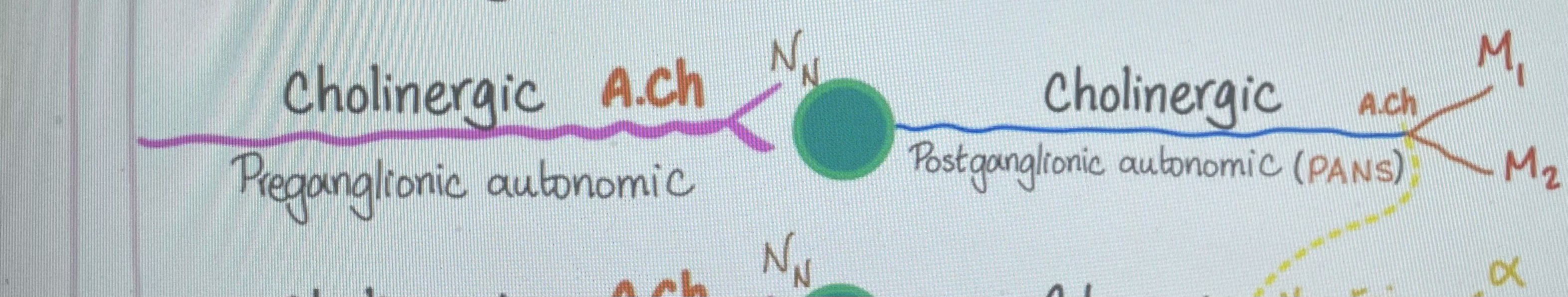
Why is the first receptor nictotinic (NN) and the 2nd is Muscarinic (M) even though both are stimulated by Ach?
The determinant is what the Ach binds to, in the first receptor, the Ach binds to a nicotinic receptor and induces a the release of nicotine
In the second receptor, the Ach stimulates a muscarinic receptor which releases a muscarinic
What are the effects of Nicitonic NM Antagonists?
It blocks the NMJ
Causing paralysis
The NMJ is where a motor neuron binds to skeletal muscle
So these drugs prevent cognizant movement of muscles
Both nicotinic and muscarinic receptors are stimulated by….
Acetylcholine
T/F: Nicotinic Receptors, both NN and NM are usually Pre-Ganglionic Receptors
True
T/F: Adrenergic fibers can releases adrenaline as well as nor-adrenaline
False, they only release nor-adrenaline (nor-epinepherine)
Which receptor subtypes, cholinergic or adrenergic, cause the contraction of smooth muscle?
M1,M3, and Alpha-1
Which receptors are Gq coupled?
M1,M3, and Alpha-1
All Beta-receptors (of the adrenergic receptor) are G_ coupled
Gs
They increase adenyl cyclase which increases cyclic-AMP (cAMP)
Why does the heart and bronchi “love“ cyclic-AMP (cAMP) which is produced by Gs receptors?
It increases cardiac properties such as
Ca2+
Contractility
Lungs bc it dilates them
Alpha receptors are usually _____, while Beta receptors are normally ______, are there any exceptions?
Excitatory
Inhibitory
Yes
Beta receptors are inhibitory for everything, but excitatory for these 3 things
Heart
Hormone
Metabolism
Why does N.E need 2 different receptors that essentially accomplish the same thing (alpha/beta)?
When an animal is running from a predator, its body will trigger fight/flight and produce N.E, that neurotransmitter will perform a variety of tasks, but one example would preventing urination
To prevent urination it has to relax the bladder wall (beta receptor) and also constrict the urethral sphincter (alpha receptor) by working in tandem this will prevent urination
T/F: Alpha-1 and Alpha-2 work together to stimulate a stronger SNS response
False, they are antagonists
Alpha-1 is pro-sympathetic (Gq)
Alpha-2 is anti-sympathetic (Gi)
Why is the Alpha-2 receptor inhibitory?
It is a negative-feedback mechanism that prevent prolonged response of a synapse from N.E
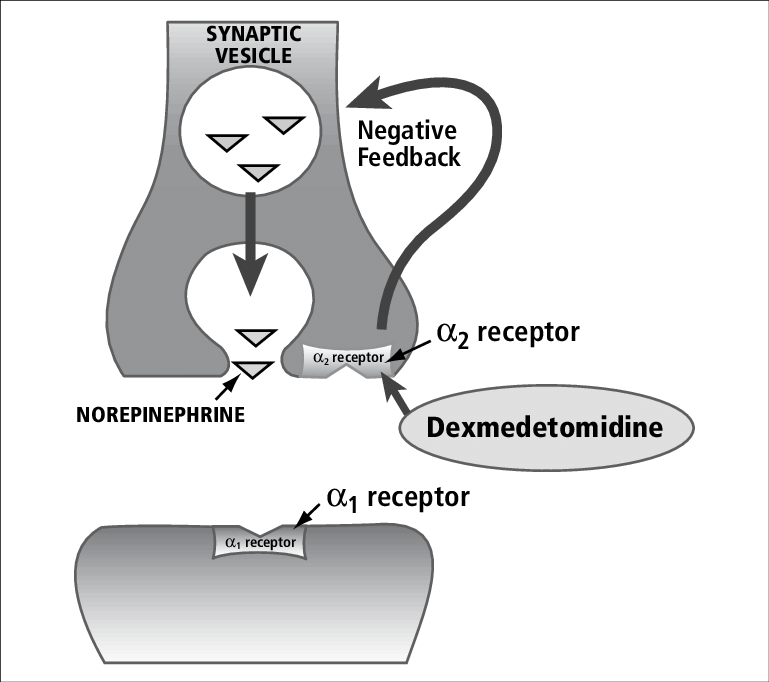
Where is Beta-1 receptor located? Beta-2?
The heart
The Lungs
Alpha and Beta receptors are types of _______ receptors
Adrenergic
What effect would Alpha-agonists have on the animal?
They would promote SNS function (fight/flight)
Which of these agonists and blockers perform similar functions?
Alpha Agonist
Alpha Antagonist
Beta Agonist
Beta Antagonist
Beta Agonists and Alpha Antagonists
Beta Antagonists and Alpha Agonists
T/F: Ganglionic Blockers (NN blockers) can inhibit some of both cholinergic/adrenergic receptors
True! If those receptors are attached to a ganglion and then NN is inhibited/blocked then it can stop everything downstream