CELL JUNCTIONS AND BASEMENT MEMBRANE
1/35
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
36 Terms
What is epithelial tissue?
A body tissue that covers the body surface, lines hollow organs, cavities and ducts and forms the glands of the body
What are the key functions of epithelial tissues?
Selective barriers (limit or aid transfer)
Secretory (onto a free surface)
Protective (especially from abrasion)
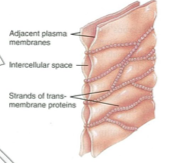
What type of cell junction is this?
Tight
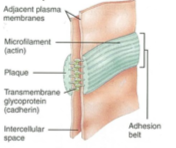
What type of cell junction is this?
Adherens
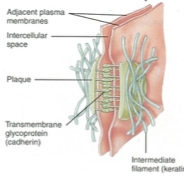
What type of cell junction is this?
Desmosome
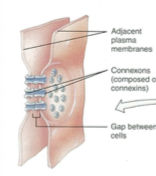
What type of cell junction is this?
Gap
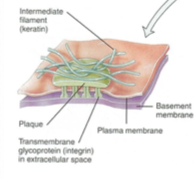
What type of cell junction is this?
Hemidesmosome
What is the function of a tight junction?
Holds membranes of cells together tightly
Prevents ions and other molecules pass down between the cells in an uncontrolled way
Where are the tight junctions located on the cell?
Near the apical section
What are the proteins that bind and sew the membranes together tightly?
Claudins and occludins
What does the orientation of tight junctions allow?
Allows polarity - cell can have different functions at top vs bottom as the environment is controlled
Describe the structure of adherens junction
Plaque of proteins forms linear structure that traverses around the cell and provides belt like interaction between the 2 cells
Protein structure spans the gap
Where are adherens junctions located?
more basal than tight junctions
What is the protein bridge in adherens junctions?
cadherins
What protein does the cadherins protein bridge link to in adherens junctions?
catenin
What does catenin do in adherins junctions?
locks cadherin to actin (microfillaments)
What is the function of adherens junction?
Locks cells cytoskeletons together - keeps structure and resists tension
What is the function of demosome junction?
Where are desmosome junctions located
What is the structure of desmosome?
plaque of proteins like adherens junctions
isolated points of contact between the cells (more discrete)
What proteins spans the gap in desmosome junctions?
cadherin
What does cadherin bind to in desmosome junctions?
desmoplakin
What does desmoplakin lock into in desmosome junctions?
keratin (intermediate filaments)
What is the function of desmosome junctions?
Security of cell
What is the function of the gap junction?
coordinated communication between cells
allows ions, RNA etc to pass between cells
What are gap junctions made of?
6 proteins - each called a connexin (6 together = connexon/hemichannel)
2 hemichannels make up a gap junction
Describe how gap junctions form
hemichannels will form in cell membranes
they migrate around the membrane until they find another on a different cell
dock together on a chemical level
forms an opening between the cells - has special molecules that control what goes between cells (RNA, ions)
What is the function of hemidesmosome?
connect epithelial cells to basement membrane
locks cytoskeleton of cells onto basement membrane
Where are hemidesmosome located?
basal layer of cell/bottom
What protein spans the gap of hemidesmosome junctions?
integrin
What does the protein spanning the gap of hemidesmosomes bind to?
laminin in basement mebrane
What is the basement membrane made of?
Basal lamina and reticular lamina
What is the basal lamina secreted by?
epithelial cells
What is the reticular laminar made by?
cells of underlying connective tissues known as fibroblasts
Where is the basement membrane located?
between epithelial and connective tissue
What is the function of basement membrane?
diffusion - allows oxygen and nutrients to diffuse through it to epithelia.
supports epithelium
provides a surface along which epithelial cells migrate during growth and wound healing