FHS Bio - Living Earth - Unit 2 Vocab
1/37
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
38 Terms
Prokaryote
Unicellular organism that lacks a nucleus
Eukaryote
Organism with multiple cells that have a nucleus
Reactant
Elements or compounds that enter into a chemical reaction
Product
Elements or compounds produced by a chemical reaction
Radioactive Decay
Unstable atomic nucleus transforming into a stable one by emitting high energy waves
ATP
Compound used by cells to store and release energy
Photosynthesis
Process used by autotrophs to capture light energy and use it to power chemical reactions that convert carbon dioxide/water into oxygen and energy-rich carbs
Chlorophyll
Principal pigment of plants and photosynthetic organisms
Thylakoid
Sac-like photosynthetic membranes found in chloroplasts
Stroma
Fluid portion of the chloroplast; outside of the thylakoids
Stoma(ta)
Small opening in the epidermis that allows carbon dioxide, water, and oxygen to diffuse in/out of the leaf.
Guard Cell
Specialized cell in the epidermis of a plant that allows carbon dioxide, water, salts, proteins, and carbs.
Vacuole
Cell organelle that stores materials such as water, salts, proteins, and carbs.
Homeostasis
ADP - Adenosine Diphosphate
Compound that cells can turn into ATP by adding phosphate - “Rechargable battery that powers machinery of the cell”
Cellular respiration*
Process that releases energy by breaking down glucose and other food molecules in the presence of oxygen
Aerobic
Process that requires/uses oxygen
Anaerobic
Process that does not require oxygen
Glycolysis
1st set of reactions in cellular respiration in which a molecule of glucose is broken into two molecules of pyruvic acid
Kreb’s Cycle
2nd stage ot cellular respiration pyruvic acid is broken down into carbon dioxide in a series of energy-extracting reactions
Electron Transportation Chain
Series of electron carrier proteins that shuffle high-energy electrons during ATP generating reactions
Lactic Acid fermentation
A metabolic process in which glucose is converted into lactic acid in anaerobic conditions
Alcoholic Fermentation
An anaerobic process in which yeast turns sugar into alcohol
Mitochondria
Cell organelle that converts the chemical energy stored in food into compounds that are more convenient for cell use
Light Independent Cycle
Light-independent reactions of photosynthesis in which energy from ATP and NADPH is used to build high-energy compounds such as sugar
Calvin’s Cycle
Light-independent reactions of photosynthesis in which energy from ATP and NADPH is used to build high-energy compounds such as sugar
Light dependent cycle
Set of photosynthetic reactions that use energy from light to produce ATP/NADPH
Chloroplast
Organelle found in cells off plants and other organisms that use photosynthesis to produce energy
Radioactive decay
Unstable atomic nucleus transforms into stable by emitting high energy waves
Product
Elements of compounds produced by a chemical reaction
Reactant
Elements of compounds that enter a chemical reaction
Prokaryote
Organism that has multiple cells with nuclei
Eukaryote
Unicellular organism that lacks nuclei
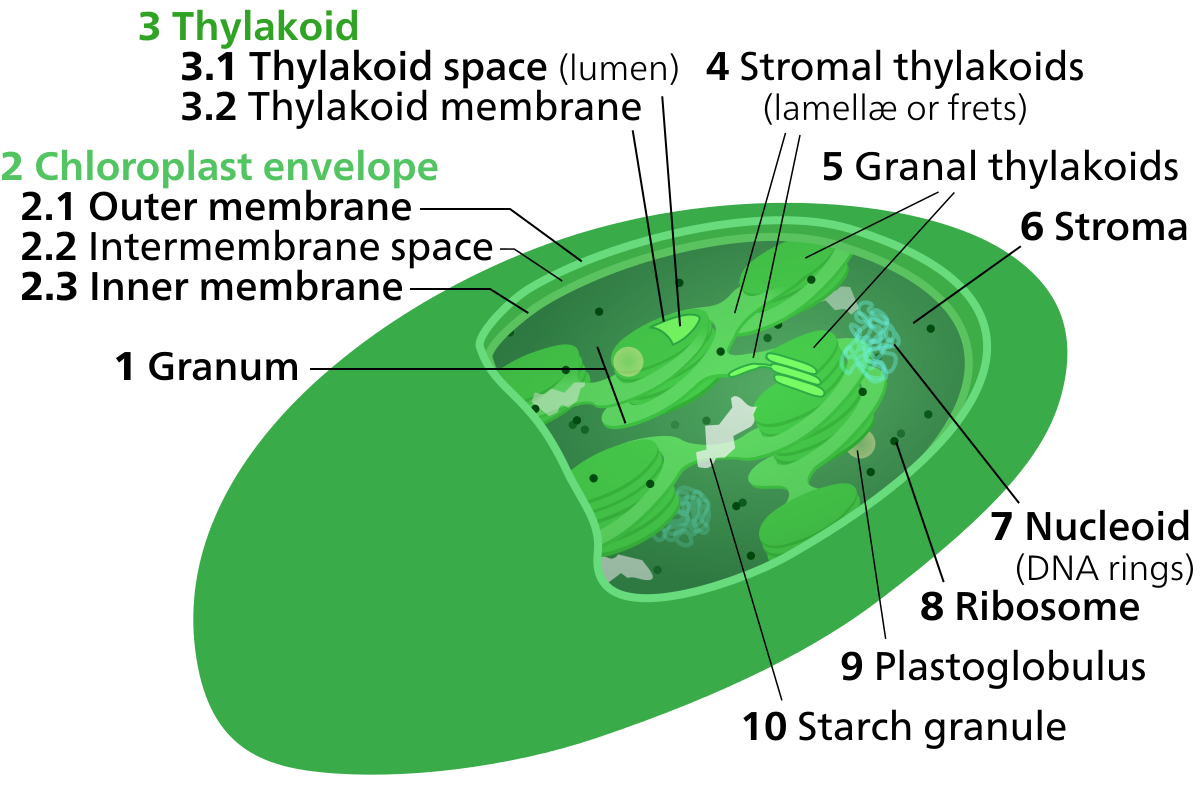
Thylakoid
Sac-like photosynthetic membrane found in chloroplasts
Stroma
Fluid portion of the chloroplast; outside the thylakoids
Glycolysis
First set of reactions in cellular respiration in which a molecule of glucose is broken into two molecules of pyruvic acid
Pyruvic acid
Key reactant in Kreb’s Cycle for producing energy