unit 4 peds F & E
0.0(0)
Card Sorting
1/114
Earn XP
Description and Tags
Last updated 10:41 PM on 9/13/23
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
115 Terms
1
New cards
What if we have a patient admitted that is dehydrated but their electrolytes are low?
Nurse will give IVF with electrolytes, such as Potassium Chloride (k+).
2
New cards
What is important to note when give IVF with the electrolyte Potassium?
do not exceed 20 mEq/kcl
3
New cards
What if a patient is admitted due to dehydration but has kidneys that do not function well?
The nurse gives IVF of NS without the potassium (kcl)
4
New cards
What organ must we make sure is working before we administer fluids with potassium?
Kidneys; nurse must assess function by asking the patient to urine & then assess urine
5
New cards
What does the nurse need to do to assess kidney function if the patient is dehydrated?
ask the patient to drink a glass of water (hydrate)
6
New cards
If a patient comes in with severe vomiting or severe diarrhea, what if the nurses priority?
oral dehydration/IVF
7
New cards
Hypotonic swells the cell. This is best to use when cellular dehydration that occurs in ____.
DKA
8
New cards
Hypertonic dehydrates the cell. This is best to treat what?
hyponatremia to help fluid move out of the cell
9
New cards
What physiological differences in infants and young child increases their insensible fluid loss?
Kids breathe faster (faster fluid loss)
BSA- they are made of more water
metabolic rate creates more waste (urine) due to immature kidneys
fever accompanies sickness so more fluid loss
BSA- they are made of more water
metabolic rate creates more waste (urine) due to immature kidneys
fever accompanies sickness so more fluid loss
10
New cards
What does mild dehydration look like?
looks normal with slight thirst, and slight longer capillary refill (>2 seconds)
11
New cards
What does moderate dehydration look like?
increased capillary refill (2-4 seconds) with pale and dry oral mucosa that is lethargic
12
New cards
What does severe dehydration look like?
capillary refill >4 seconds with sunken anterior fontanels, tented skin, sunken eyeballs, oliguria/anuria, tachycardia/tachypnea but hypotension
13
New cards
A patient comes into the ER with a weak, thread pulse. The vital signs are a RR of 20 with a BP of 50/88. The nurse inspects his mucous membranes and they appear dry and the capillary refill is more than 3 seconds. How would the nurse expect the patient to act?
the patient is irritable with sunken fontanels along with a high-pitched cry with no tears
14
New cards
A ___ is directly affected by dehydration.
child’s weight
15
New cards
How much weight loss does a patient who is MILDLY dehydrated lose?
3-5%
16
New cards
How much weight loss does a patient who is MODERATELY dehydrated lose?
6-9%
17
New cards
How much weight loss does a patient who is SEVERELY dehydrated lose?
>10%
18
New cards
What is the best way to monitor status for infants and young children?
count the number of wet diapers per day
19
New cards
What is the normal Potassium leb values?
3\.5-5 mEq/L
20
New cards
What is the normal value for urine specific gravity?
1\.005-1.030
21
New cards
What is the normal pH value?
7\.35-7.45 mEq/L
22
New cards
What is the normal CO2 value?
21-28 mEq/L
23
New cards
Oral rehydration therapy is _____.
50-100 mL/kg every 4 hours.
24
New cards
What is the normal urine output?
1-3 ml/kg/hr
25
New cards
A pH that is higher than ___ accompanied by a high CO2 indicates metabolic alkalosis.
greater/higher than 7.45
26
New cards
A pH that is lower than ___ accompanied by a low CO2 indicates metabolic acidosis.
lower than 7.35
27
New cards
_____ causes inflammation of the stomach and intestines.
Gastroenteritis
28
New cards
What are the hallmarks symptoms of gastroenteritis?
diarrhea and vomiting
29
New cards
What precautions is required for gastroenteritis & how is it prevented?
contact with gown and gloves; good washing
30
New cards
A _____ is an olive shaped mass in the epigastrium or slight toward the RUQ.
hypertrophic pyloric stenosis
31
New cards
Hypertrophic pyloric stenosis causes _____ which leads to severe dehydration, electrolytes imbalances, and metabolic alkalosis.
projectile vomiting which causes failure to gain weight
32
New cards
How is a pyloric stenosis diagnosed?
ultrasound revealing an olive-shaped mass
33
New cards
A child with a diagnosis of pyloric stenosis has projectile vomiting. The child is always hungry. How can the nurse meet the nutritional needs of the child?
Have MD order a thickened formula 5 mL of rice cereal/ounce of formula.
34
New cards
What is the nurses priority after feeding a patient with a pyloric stenosis?
Sit the patient upright after feeding to protect from aspiration & keep bulb syringe close by to remove any vomit from the airway.
35
New cards
_____ is the incomplete fusion of the oral cavity, resulting in an opening through the upper lip towards the nose. Repair done via cheiloplasty at 2-3 months.
Cleft lip
36
New cards
What is the nurses role post-op from a cleft lip repair surgery?
keep the incision clean and apply elbow restraints to protect repair site
37
New cards
Prior to cleft lip surgery, what is the nurses role for the nutrition of the child?
use a wide-based nipple and squeeze infant’s cheeks together during feeding
38
New cards
What is the nursing care after a palate surgery?
Protect incision site by not allowing any pointy objects in the mouth (including pacifiers)
39
New cards
How is the nutritional needs of a child with a cleft palate met?
Sit the child upright during feeding & burp often to prevent choking. The consistency (soft, thick) may help with keeping the food in.
40
New cards
What are the long term complications of cleft lip/palate that a nurse may have to refer specialist?
Hearing deficits
Speech
Sinus issues (chronic)
Dental - may need braces
Speech
Sinus issues (chronic)
Dental - may need braces
41
New cards
Tracheoesophageal Fistula (TEF) is a fistula or connection between the trachea and the esophagus. What is the nurses priority?
aspiration
42
New cards
What are the s/s of a Tracheoesophageal Fistula (TEF)?
Prenatal polyhydramnios
Excessive salivation or drooling, choking, coughing, sneezing
Fluids may be expelled from mouth and nose during feeding.
Excessive salivation or drooling, choking, coughing, sneezing
Fluids may be expelled from mouth and nose during feeding.
43
New cards
A hallmark symptoms of an TEF is abdominal distention. What does the nurse expect the MD to order?
A gt-tube immediately after surgery to drain the stomach via a cannister to help with nausea as well.
44
New cards
A patient was placed on an NG-tube following a TEF surgery whom suddenly became nauseated. What should the nurses first intervention be?
Assess the tube for kinking/clogging. If present, flush the tubing or change it.
45
New cards
A _____ is when a portion of the intestine invaginates or telescopes into itself; commonly occurs at the ileocecal valve, leading to intestinal obstruction. It is a palpable sausage shaped mass in URQ or right mid-abdomen.
intussusception
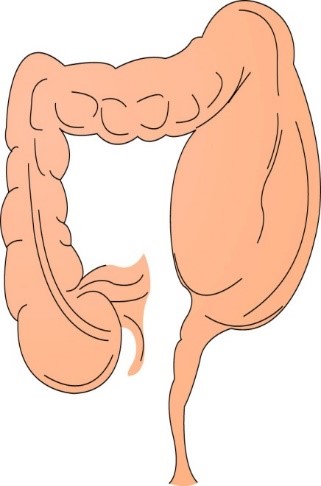
46
New cards
An infant’s mother states acute pain in the child upon palpating the URQ in the abdomen. The mother says the child cries out due to the pain and draws their knees up on the abdomen. What is this acute pain an indicator of?
intussusception
47
New cards
A nurse expects a ____ stool in a patient with an intussusception called ____.
brown to bloody red; mucoid (a currant jelly character)
48
New cards
The nurse expects the HCP to order what therapeutic procedure for a patient with an intussusception?
air enema/barium enema
49
New cards
______ is an obstruction (megacolon) due to inadequate motility due to poor nerve formation/function (aganglionic) in the sigmoid colon to the rectum. The nurse knows this is congenital, or born with it.
Hirschsprung Disease
50
New cards
What is the hallmark symptom for Hirschsprung Disease in newborns?
**No meconium passed within 48 hours after birth.**
\
\
51
New cards
What is the hallmark symptoms for Hirschsprung Disease in older children?
History of ribbon stools
Failure to gain weight (FTT)
Vomiting bile.
Abdominal distention.
Failure to gain weight (FTT)
Vomiting bile.
Abdominal distention.
52
New cards
What patient education is priority to a family caring for a child with Hirschsprung Disease?
Provide a high-calorie, high-protein, low fiber diet.
53
New cards
What is the hallmark symptom of appendicitis?
RLQ abdominal pain (McBurney’s point)
54
New cards
What is the major concern in children with appendicitis?
children can have spontaneous ruptures
55
New cards
_____ is a chronic malabsorption syndrome associated with intolerance of gluten, a protein in wheat, rye, barley, and oats. The nurse must educate the patient to avoid these foods to avoid further complications.
Celiac Disease
56
New cards
Celiac disease causes a deficiency in what vitamins?
fat soluble (A DEK in that fat ass) such as Vitamin A, D, E, & K
57
New cards
What stools does the nurse expect to see in a patient with celiac dx?
fatty, frothy, foul-smelling stool called steatorrhea
58
New cards
What are the hallmark symptoms of celiac disease?
steatorrhea, reduced fat absorption, weight loss, and abdominal distention
59
New cards
What foods can be eaten by a patient with celiac disease?
dairy, rice, corn, potatoes, eggs, fruits, veggies
60
New cards
What does the nurse expect the MD to order with a patient with extracellular fluid volume excess?
diuretics & IVF
61
New cards
What is the nurse’s priority assessment in a child who is receiving fluids via pumps?
to assess to IV site for signs of infiltration
62
New cards
A patient who has a history of group A beta-hemolytic streptococal infection has to have what assessed?
urine due to the increased risk of glomerulonephritis, especially if it occurred 1 month prior and it lasted 10 days
63
New cards
A child with a history of group A infection has been diagnosed with acute glomerulonephritis. The nurse expects to see what colored urine?
cloudy, tea colored urine accompanied by facial edema
64
New cards
Glomerulonephritis causes ____, which indicates something is wrong with kidneys.
hypertension
65
New cards
What labs does the nurse expect to see in a patient with glomerulonephritis?
proteinuria and hematuria
66
New cards
Nephrotic syndrome is also known as “leaky kidney.” This allows protein (albumin) to pass in the urine. What are the hallmark symptoms of this syndrome?
weight gain due to facial/peripheral edema & proteinuria with foamy urine
67
New cards
What labs are seen in patients with nephrotic syndrome?
hypoalbuminemia, hypertension, proteinuria (>2+), hematuria
68
New cards
In nephrotic syndrome, the increased protein (albumin) results in decreased serum osmotic pressure (hypoalbuminemia). What interventions is needed to treat this problem?
Restore the patient’s albumin by giving 25% albumin IV infusion and give corticosteroids (prednisone)
69
New cards
Why are corticosteroids given in a patient with nephrotic syndrome?
they decrease glomerular permeability and decrease edema
70
New cards
A first-degree burn is also known as superficial. What are the chaeracteristics?
no blisters or open lesions present with a sunburn effect (red/pink) or red surface blanches
71
New cards
A second-degree burn is also known as superficial-partial thickness. What are the characteristics?
red/pink surface with blisters and serous drainage
72
New cards
A third-degree burn is also known as a deep-partial thickness. What are the characteristics?
red/white color with blisters but does not blanch that involves both epidermis and subcutaneous tissue
73
New cards
A fourth-degree burn is also known as a deep-full thickness. What are the characteristics?
involves the muscle, fat, and bone with a dry/leathery appearance
74
New cards
What is the best diet choice for burn patients?
Grilled chicken, broccoli, butter beans (protein filled!!!)
75
New cards
This chart is known as:
the rule of 9s
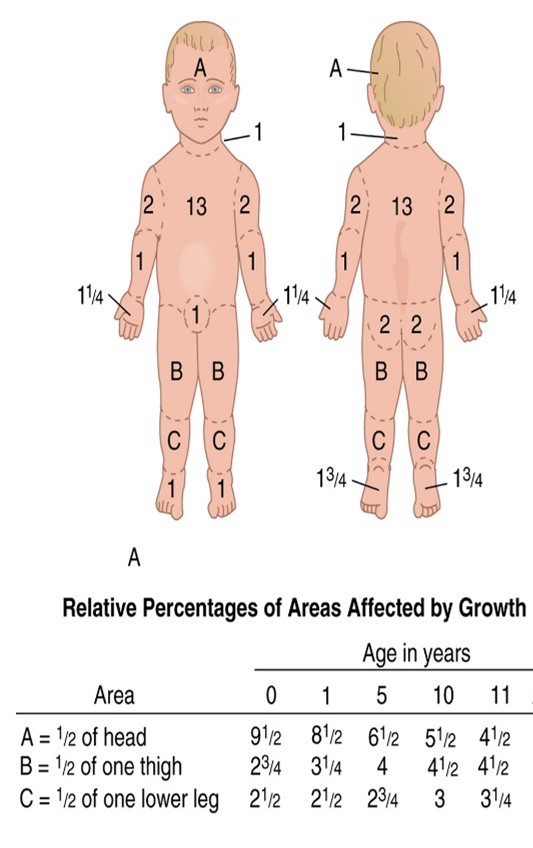
76
New cards
What is some patient education regarding the prevention of burns in kids?
Turn pot handles towards the back of the stove.
Water heater temperature.
Water heater temperature.
77
New cards
_______ is a condition in which urine from the bladder is able to flow back up into the ureter and kidney.
Vesicoureteral reflux (VUR)
78
New cards
What does the nurse need to take into consideration when dealing with vesicoureteral reflux?
the key is to prevent UTIs to avoid further complications that can lead to pyelonephritis (and subsequent renal scarring) which can contribute to hypertension later in life
\
\
79
New cards
VUR may require surgical intervention is it gets to what grade?
grade 3-5 and also if the child has recurrent UTIs
80
New cards
How does the nurse educate a child who has VUR to prevent future infections such as UTIs?
Educate to empty the bladder completely.
Wipe front to back.
Teach parents to finish the full course of antibiotics.
\
Wipe front to back.
Teach parents to finish the full course of antibiotics.
\
81
New cards
Urologic surgery after recurrent UTIs require what interventions post-op?
Nurses must avoid manipulating F/C.
Administer analgesics & antispasmodics PRN for pain/bladder spasms.
**PUSH FLUIDS!!! HIGH URINARY OUTPUT IS WANTED!!!**
Encourage ambulation/advancement of diet.
Administer analgesics & antispasmodics PRN for pain/bladder spasms.
**PUSH FLUIDS!!! HIGH URINARY OUTPUT IS WANTED!!!**
Encourage ambulation/advancement of diet.
82
New cards
A child has been admitted to the acute care facility for the management of dehydration. The nurse is preparing to administer IV fluid replacement to the child. Which fluid(s) is suitable for use? Select all that apply.
lactated Ringer's & normal saline
83
New cards
Which finding would lead the nurse to suspect that a child is experiencing moderate dehydration?
sunken fontanels (fontanelles)
\
\
84
New cards
A 9-month-old girl is brought to the emergency room with what appears to be bouts of intense abdominal pain 15 minutes apart in which she draws up her legs and cries, often accompanied by vomiting. In between the bouts, the child recovers and appears to be without symptoms. Blood is found in the stool. What condition should the nurse suspect in this case?
Intussusception
85
New cards
What occurs in the gastrointestinal system of the child with Hirschsprung disease?
There is a partial or complete mechanical obstruction in the intestine.
\
\
86
New cards
\
The labor and delivery nurse is caring for a mother who has demonstrated polyhydramnios upon delivery. The newborn displays copious, frothy bubbles of mucus in the mouth and nose, as well as drooling. The nurse is concerned that the infant has what disorder?
\
The labor and delivery nurse is caring for a mother who has demonstrated polyhydramnios upon delivery. The newborn displays copious, frothy bubbles of mucus in the mouth and nose, as well as drooling. The nurse is concerned that the infant has what disorder?
\
esophageal atresia
87
New cards
A group of students are reviewing information about fluid balance and losses in children in comparison to adults. The students demonstrate a need for additional review when they state that:
the infant's immature kidneys have a tendency to overconcentrate urine.
88
New cards
The parents of a 6-week-old boy come to the clinic for evaluation because the infant has been vomiting. The parents report that the vomiting has been increasing in frequency and forcefulness over the last week. The mother says, “Sometimes, it seems like it just bursts out of his mouth.” A diagnosis of hypertrophic pyloric stenosis is suspected. When performing the physical examination, what would the nurse most likely find?
Hard, moveable, olive-shaped mass in the right upper quadrant
89
New cards
The caregiver of a child diagnosed with celiac disease tells the nurse that the child has large amounts of bulky stools and what looks like fat in the stools. The clinical manifestation this caregiver is describing is:
steatorrhea.
90
New cards
The nurse is talking with a woman in her second trimester of pregnancy who has been diagnosed with polyhydramnios. The physician has ordered an ultrasound be performed to check for the presence of esophageal atresia. Which statement by the woman indicates an understanding of the relationship between these conditions?
"Babies with esophageal atresia have an inability to swallow amniotic fluid causing the excess buildup."
91
New cards
The nurse is caring for a 2-year-old child with a gastrointestinal infection resulting in 4 to 5 liquid stools per day over the past 3 days. Based on this information, which important concern(s) will the nurse address in the child's care? Select all that apply.
fluid deficiency risk: dehydration
diarrhea and loss of electrolytes
the risk for skin maceration in the perineum
diarrhea and loss of electrolytes
the risk for skin maceration in the perineum
92
New cards
A nurse is providing education to parents of a child diagnosed with vesicoureteral reflux (VUR). Which would be included in the parental education?
This occurs when there is backflow of urine into the bladder and sometimes the kidneys.
93
New cards
A 2-year-old child is brought to the urgent care center for treatment of burns on both hands. The parent reports that the child pulled the coffee pot over and the hot liquid splashed on to the child’s hands. The nurse examines the child and notes that the backs of the hands are reddened with a well-defined line of demarcation at the wrists. Several medium to large blisters are also present. What initial action should the nurse take?
Make arrangements to transfer the child to the hospital.
94
New cards
A child diagnosed with acute glomerulonephritis will most likely have a history of:
recent illness such as strep throat.
\
\
95
New cards
\
The nurse is providing discharge teaching regarding oral fluid rehydration to a mother who brought her child to the clinic because of vomiting over the past 2 days. The child is mildly dehydrated. Which comments by the mother indicated learning occurred?
\
\
The nurse is providing discharge teaching regarding oral fluid rehydration to a mother who brought her child to the clinic because of vomiting over the past 2 days. The child is mildly dehydrated. Which comments by the mother indicated learning occurred?
\
\
"I should not give my child any fluids for 1 to 2 hours after an episode of vomiting.”
"Oral rehydration solutions (ORS) are good sources of fluids for rehydration."
"I should be sure my child receives 50 to 100 ml/kg of oral rehydration solution (ORS) over 4 hours."
"Oral rehydration solutions (ORS) are good sources of fluids for rehydration."
"I should be sure my child receives 50 to 100 ml/kg of oral rehydration solution (ORS) over 4 hours."
96
New cards
\
The nurse is teaching an in-service program to a group of nurses on the topic of gastrointestinal disorders. The nurses in the group make the following statements. Which statement is most accurate related to the diagnosis of congenital aganglionic megacolon?
\
The nurse is teaching an in-service program to a group of nurses on the topic of gastrointestinal disorders. The nurses in the group make the following statements. Which statement is most accurate related to the diagnosis of congenital aganglionic megacolon?
\
A partial or complete intestinal obstruction occurs.
97
New cards
The newborn was diagnosed with esophageal atresia and a nasogastric tube was inserted. Which findings are most consistent with this condition? Select all that apply.
The newborn coughed excessively during attempts to feed.
Coarse crackles were auscultated throughout all lung fields.
X-ray revealed that the nasogastric tube was coiled in the upper esophagus.
Coarse crackles were auscultated throughout all lung fields.
X-ray revealed that the nasogastric tube was coiled in the upper esophagus.
98
New cards
A nurse taking a health history of a newborn notes that there is a maternal history of polyhydramnios. What GI condition might this history precipitate?
esophageal atresia (EA)
99
New cards
\
The nurse is planning an educational program on burn prevention at home. Which information should be included? Select all that apply.
\
\
The nurse is planning an educational program on burn prevention at home. Which information should be included? Select all that apply.
\
\
Keep pot handles turned in on a stove.
Test bath water temperature before bathing children.
\
Test bath water temperature before bathing children.
\
100
New cards
An 8-year-old client presents with sudden onset of abdominal pain and reddish-brown urine. A urinalysis shows 4+ protein. On taking the child's health history, the nurse learns that the child had strep throat 9 days ago. Which condition does the nurse suspect?
acute glomerulonephritis