3 - Electrons in Atoms
1/84
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
85 Terms
In Bohr's model of the atom, where are the electrons and protons located?
The electrons move around the protons, which are at the center of the atom.
What is the maximum number of electrons in the third principal energy level?
18
The shape (not the size) of an electron cloud is determined by the electron's ____.
energy sublevel
If the spin of one electron in an orbital is clockwise, what is the spin of the other electron in that orbital?
counterclockwise
What types of atomic orbitals are in the second principal energy level
s and p
What is the next atomic orbital in the series 1s, 2s, 2p, 3s, 3p?
4s
Define the Aufbau Principle
Electrons fill atomic orbitals in order of increasing energy, from the lowest energy level to the highest
Define the Pauli Exclusion Principle
no two electrons in the same atom can have the same four quantum numbers
In the Bohr model of the atom, an electron in an orbit has a fixed ____.
energy
Define Hund's Rule
electrons will fill orbitals of equal energy (degenerate) singly with parallel spins before they start pairing up.
If three electrons are available to fill three empty 2p atomic orbitals, how will the electrons be distributed in the three orbitals?
one electron in each orbital
How many half-filled orbitals are in a bromine atom?
1
The most stable electron configurations are likely to contain
filled energy sublevels
How does the speed of visible light compare with the speed of radio waves, when both speeds are measured in a vacuum?
the speeds are the same
Which color of visible light has the shortest wavelength?
violet
How does the energy of an electron change when the electron moves further from the nucleus?
it increases
How are the frequency and wavelength of light related?
they are inversely proportional to eachother
What is the wavelength of an electromagnetic wave that travels at 3.00 x 10^8 m/s and has a frequency of 60 MHz? (1 MHz = 1,000,000 Hz)
300,000,000 m/s/60,000,000 Hz
Emission of light from an atom occurs when an electron
drops from a higher to lower energy level
The atomic emission spectra of a helium atom on Earth and of a helium atom in the sun would be
the same
What is the approximate energy of a photon having a frequency of 4.10 x 10^7 Hz? (h = 6.626 x 10^-34 J•s)
2.72 x 10^-26 J
The principal quantum number indicates what property of an electron?
energy level
What is the shape of the 3p atomic orbital?
dumbbell
What is the maximum number of p orbitals in a principal energy level?
3
Define valence electrons
the electrons in the outermost shell of an atom
Which variable is directly proportional to frequency?
energy
What are quanta of light called?
photons
When an electron moves from a lower to a higher energy level, the electron
absorbs a quantum of energy
What is the number of electrons in the outermost energy level of an oxygen atom?
6
What is the electron configuration of potassium?
1s2 2s2 2p6 3s2 3p6 4s1
How many unpaired electrons are in a sulfur atom, which has the atomic number 16?
2
What is the basis for exceptions to the aufbau diagram?
Filled and half-filled energy sublevels are more stable than partially-filled energy sublevels.
Which electron configuration is most stable
One with a full valence shell, and full subshells
Which of the following electromagnetic waves have the highest frequencies?
gamma rays
As changes in energy levels of electrons increase, the frequencies of atomic line spectra they emit
increase
How many energy sublevels are in the second principal energy level?
2
What is the maximum number of f orbitals in any single energy level in an atom?
7
What is the maximum number of orbitals in the p sublevel?
3
What is the approximate frequency of a photon having an energy 5.50 10^-24 J? (h = 6.626 10^-34 J•s)
8.30 x 10^9 Hz
How do the energy differences between the higher energy levels of an atom compare with the energy differences between the lower energy levels of the atom?
they are smaller in magnitude than those between lower energy levels
Bohr's model could only explain the spectra of which type of atoms?
single atoms with one electron
The quantum mechanical model of the atom
involves the probability of finding an electron in a certain position
Who predicted that all matter can behave as waves as well as particles?
Louis de Broglie
According to the Heisenberg uncertainty principle, if the position of a tiny moving particle is known, the
velocity of the particle cannot be determined
The wavelike properties of electrons are useful in
magnifying objects
How many electrons are in the highest occupied energy level of a neutral strontium atom?
2
Which type of electromagnetic radiation includes the wavelength 10^-7 m?
visible light
In an s orbital, the probability of finding an electron a particular distance from the nucleus can best be determined by the
quantum mechanical model
Give the electron configuration for a neutral atom of chlorine.
1s2 2s2 2p6 3s2 3p5
What is the frequency of violet light with wavelength 4.25 x 10^-7 m? (c = 3.00 x 10^8 m/s)
7.06 x 10^14 Hz
What is the wavelength of gamma ray radiation with a frequency of 2.97 x 10^20 Hz? (c = 3.00 x 10^8 m/s)
1.01 x 10^-12 m
How many electrons are in the highest occupied energy level of a neutral phosphorous atom?
5
What is the electron configuration for sodium
1s2 2s2 2p6 3s1
What is the electron configuration for iron
1s2 2s2 2p6 3s2 3p6 4s2 3d6
What is the electon configuration for bromine
1s2 2s2 2p6 3s2 3p6 3d10 4s2 4p5
What are the seven noble gases
Krypton (Kr), Helium (He), Neon (Ne), Argon (Ar), Xenon (Xe), Oganesson (Og), Radon (Rn)
What is the abbreviated electron configuration of cobalt
[Ar] 4s2 3d7
What is the abbreviated electron configuration of tellurium
[Kr] 4d10 5s2 5p4
What is the order of atomic orbitals
1s 2s 2p 3s 3p 4s 3d 4p 5s 4d 5p 6s 4f 5d 6p 7s 5f 6d
Electron configuration is
the arrangement of electrons in an atom
How many electrons in each box of atomic orbital?
2
How many electrons max per s orbital?
2
How many electrons max per p orbital?
6
How many electrons max per d orbital?
10
How many electrons max per f orbital?
14
Define atomic orbital
region of high probability of finding an electron
Define ground state
lowest electron energy level
How does the energy of an atom change when the electron moves closer to the nucleus?
it decreases
How many unpaired electrons are in a germanium atom which has the atomic number 32?
2
The light given off by an electric discharge through sodium vapor is
an emission spectrum

Which principle of electron configuration is violated by the configuration in the image shown?
aufbau principle
The letter “p” in the symbol 4p³ indicates the
orbital shape
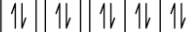
For which of the following would the electron configuration in the image shown not be valid? -
Mg²+
Ne
Na
F-
Na
What is the number of electrons in the outermost energy level of a carbon atom?
4
Identify the element with the following electron configuration: [Xe] 6s² 4f^4
Nd
What is the frequency of ultraviolet light with wavelength 1.93 × 10^-8 m?
1.55 × 10^16 Hz
What is the energy of a microwave photon that has a frequency of 1.18 × 10^12 Hz?
7.82 × 10^-22 J
How many electrons are in the highest occupied energy level of a neutral phosphorous atom?
5
How many electrons are in the highest occupied energy level of a neutral magnesium atom?
2
How many electrons are in the highest occupied energy level of the bromine ion, Br^1-?
8
How many unpaired electrons are in an atom of arsenic?
3
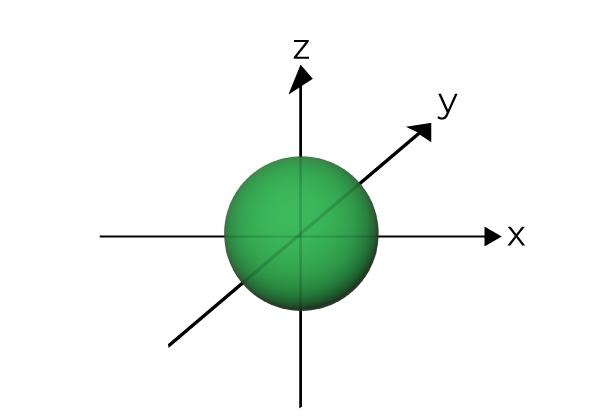
What orbital is the shape shown?
p
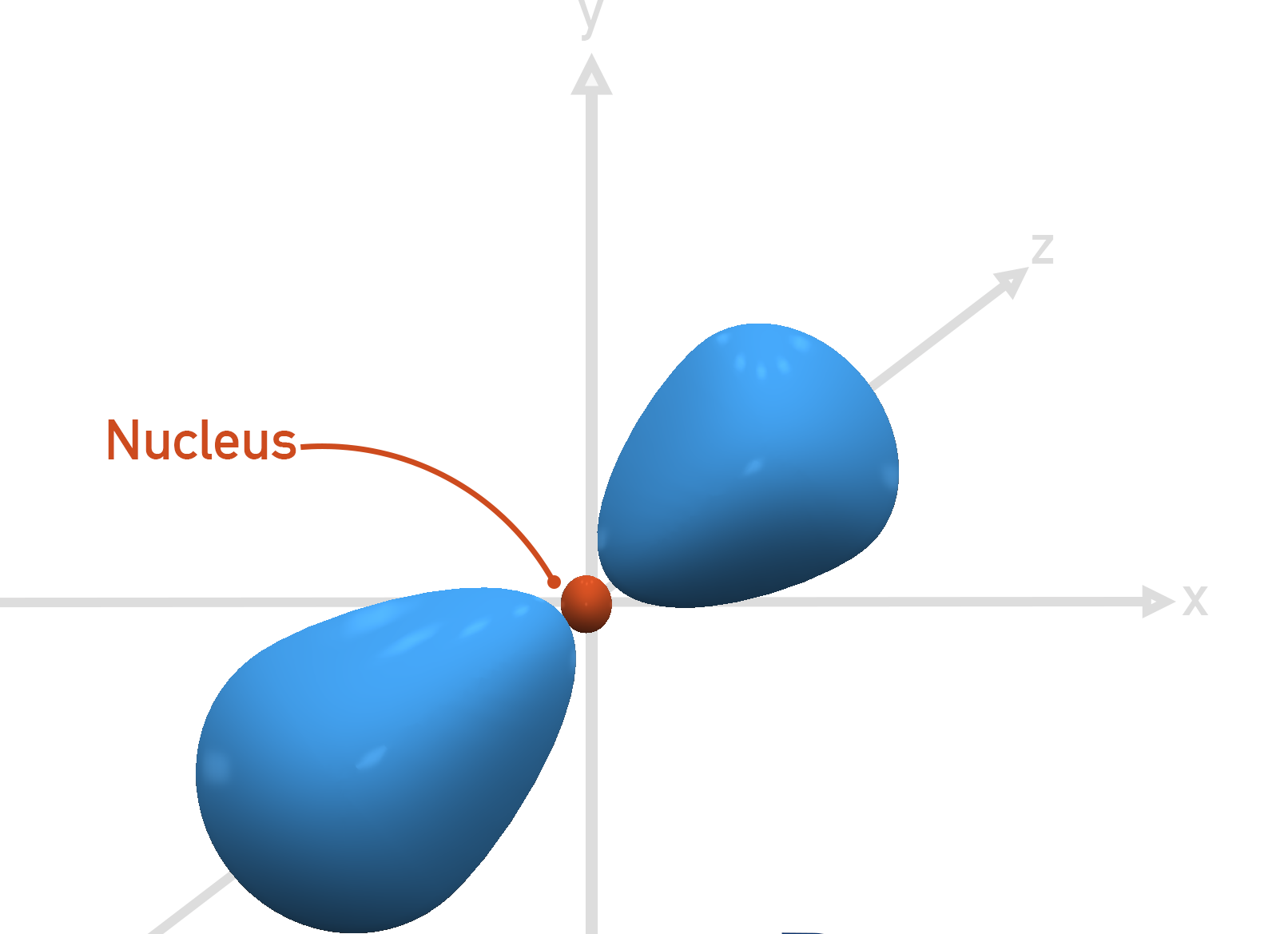
What orbital is the shape shown?
s
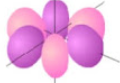
What orbital is the shape shown?
f
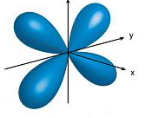
What orbital is the shape shown?
d