The Frontal Lobes
1/16
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
17 Terms
Frontal Lobe Function
1) Able to Plan and select relevant activities
2) Ignore distracting stimuli
3) have memory for what you’ve already done
4)executive functions
5) respond to internal and external cues
Fluid Intelligence
capacity to reason and solve problems independent of any knowledge in the past
Crystallized Intelligence
breadth of knowledge, vocabulary and the ability to reason using words and numbers
Salience Network
most active when behavioral change is needed; operates to modulate other networks’ activities
Default Network
active while participants are resting, thinking about one’s past, about the future or when mind wanders
Connectome
comprehensive map of structural connections of nervous system
Autonoetic Awareness
self knowledge
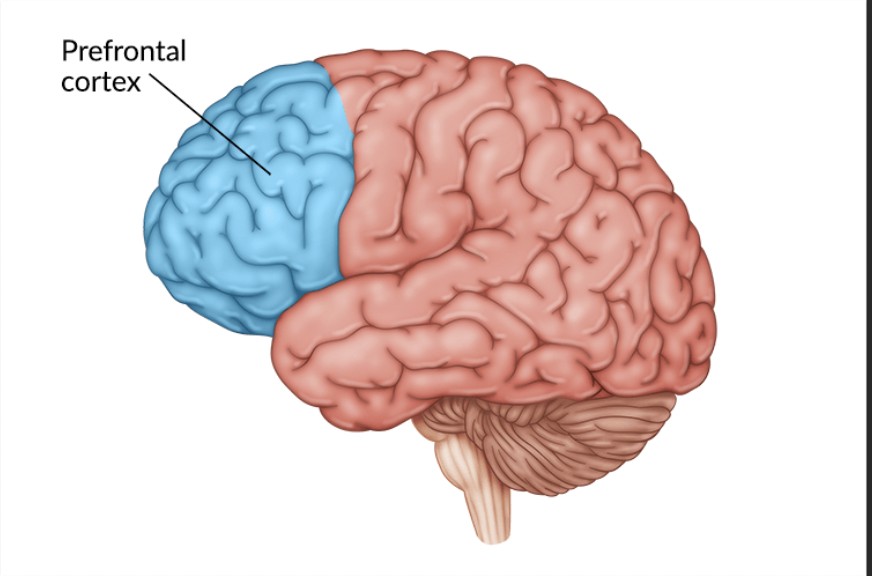
Prefrontal Cortex
1) controls cognitive processes so that appropriate movements are selected at the correct time
2)feedback about rewarding properties of stimuli
Dorsolateral Prefrontal Cortex
temporal memory (working memory)
Orbital Frontal Cortex
learning by association
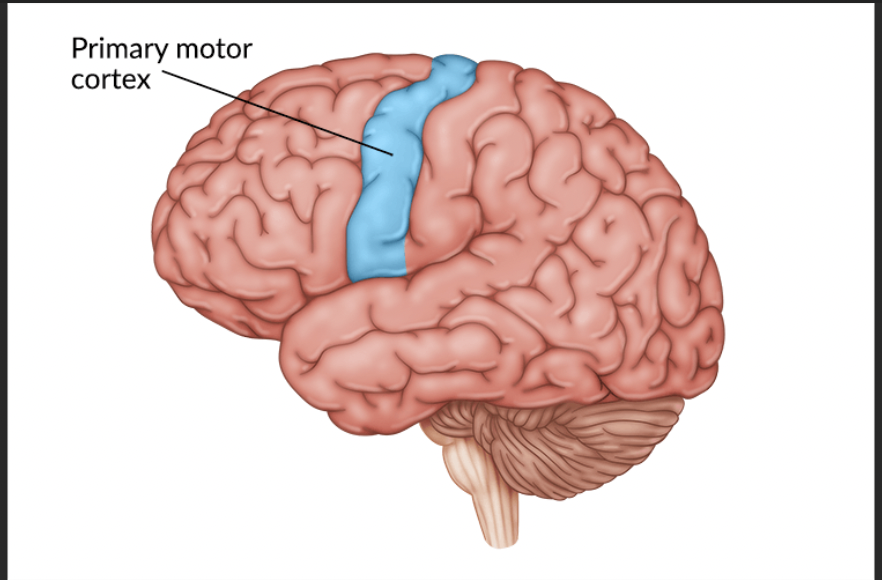
Role of Premotor Cortex
3 parts
1) dorsal premotor cortex
2) ventral premotor cortex
3) inferior frontal gyrus
Function
selects movement to be executed
increased activity when cues become associated with movement
Ventral Premotor Cortex
contains mirror neurons
receives projection from parietal regions and Dorsolateral Prefrontal Cortex
mirror neurons
a brain cell that reacts both when a particular action is performed and when it is only observed
Dorsal Premotor Cortex
chooses movement from movement lexicon
receives projection from parietal regions
What is the role of the Primary Motor Cortex
controls movement force and direction
projects to subcortical motor structures
basal ganglia
red nucleus
cranial nerves VII, IX, X, XII
spinal cord
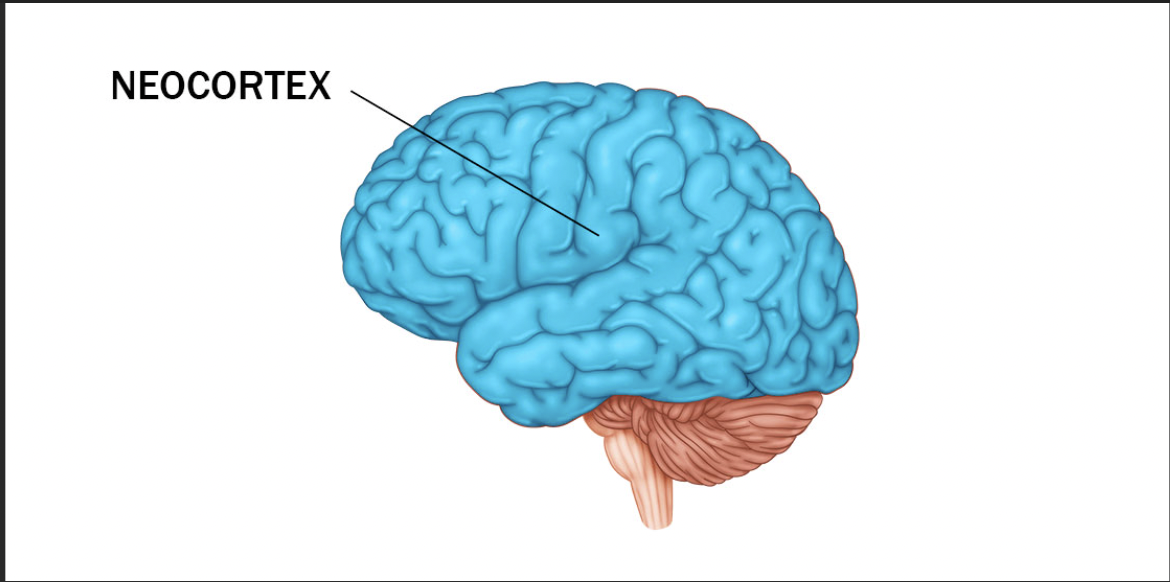
What % of the neocortex is made of the frontal lobe
30-35 %
Inferior Frontal Gyrus
Brocas area