Lecture 28 - the adrenal glands and gonads
1/11
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
12 Terms
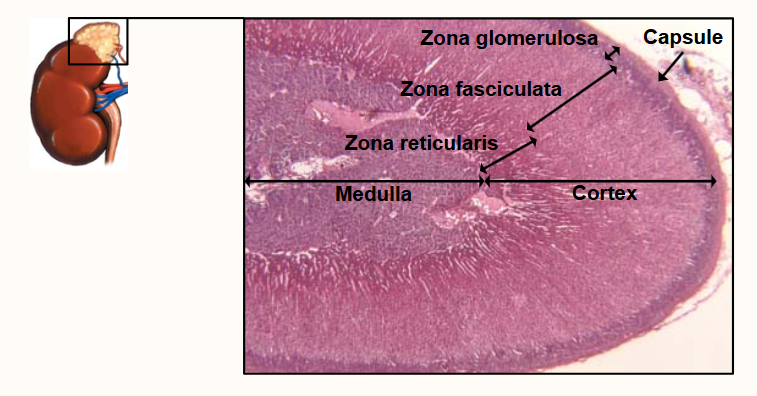
Describe the basic structure of the adrenal glands
Sit above the kidneys
Composed of Cortex:
Comprises 80-90% of adrenal weight and has 3 distinct zones:
• Zona glomerulosa (outer)
• Zona fasciculata (middle)
• Zona reticularis (inner)
Medulla:
• Comprises 10-12% of adrenal weight:
• Major product is epinephrine
• Highly specialised part of the sympathetic nervous system
Key features of the zona glomerulosa
About 15% cortical volume
Produces aldosterone
What does the zona glomerulosa lack?
17 a-hydroxylase
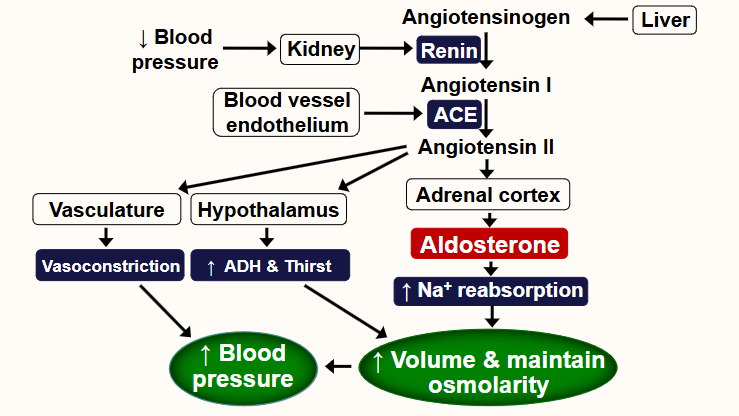
What is aldosterone and its key features?
• Major mineralocorticoid
• 50-70% bound to albumin in plasma
• Half-life 15-20 minutes
• Primary action on kidney, colon and salivary glands to maintain normal Na+
concentration and extracellular fluid volume
• Binds to mineralocorticoid receptors within principal cells
• Upregulates ENaC
• Upregulates & activates Na+/K+ ATPase
• Na+ reabsorption: with aldosterone >99.6% and without ≈ 98%
• Difference ≈ 3.5L of fluid/day
What is the zona fasciculata and its key features?
Large lipid containing cells (75% cortical volume)
What is the zona reticularis and its key features?
Compact cells with less lipid (10% cortical volume)
What does the zona fasciculata and zona reticularis both produce?
cortisol and androgens
What do both fasciculata and reticularis both lack?
CYB11B2 gene (P450aldo)
What is cortisol?
AKA hydrocortisone
Major glucocorticoid
>90% bound to plasma proteins
Half-life 60-80 minutes
Effects virtually all tissues mainly by binding to its receptor and controlling gene transcriptionWha
What are the effects of cortisol?
Stimulates hepatic gluconeogenesis
Inhibits glucose uptake in muscles and adipose tissue
Stimulates muscle catabolism
Inhibits bone formation
Leads to loss of collagen and connective tissue
Increases vascular sensitivity to epinephrine and norepinephrine
Can modulate behaviour and cognitive function
Inhibits gonadal release of testosterone, oestrogens and progestins
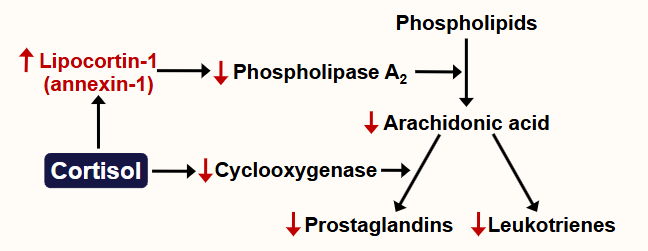
What process are glucocorticoids involved in and what happens?
Anti-inflammatory and immunosuppression
Inhibits cytokine production and thus T cell proliferation (rapid increase)
Inhibits prostaglandin and leukotriene production
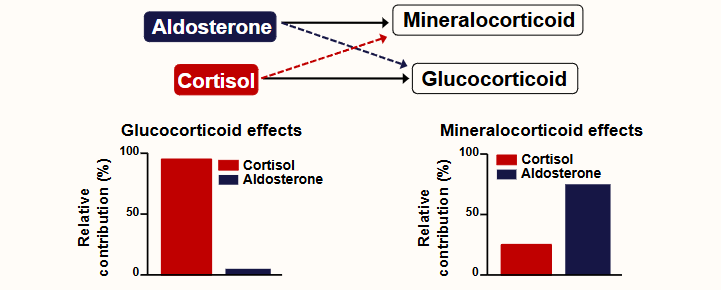
What are the key differences in Aldosterone and Cortisol effects?
Cortisol: Drives glucocorticoid effects; also binds mineralocorticoid receptors.
Aldosterone: Drives mineralocorticoid effects.
Cortisol is 100× more abundant, but
11β-HSD enzyme blocks its mineralocorticoid action.