POCS AFP
5.0(1)
Card Sorting
1/46
Earn XP
Description and Tags
Last updated 2:10 AM on 12/6/22
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
47 Terms
1
New cards
What does POCs stand for
Porous organic cages
2
New cards
generally what type of material are POCs
a type of crystalline microporous materials
3
New cards
What are the desirable properties of POCs
uniform micropores, high surface areas, and thermal and chemical stability
4
New cards
What differentiates POCs from other conventional porous materials, such as zeolites, metal organic frameworks, porous polymers, and carbon molecular sieves.
The unique structure of POCs and their distinctive solid state molecular packing
5
New cards
generally, what do POCs consist of and what can they do
They consist of covalently bonded organic cages that can assemble into crystalline microporous materials displaying three-dimensional connectivity and uniform pore size.
6
New cards
What are the general characteristics of POCS
Discrete organic building blocks
Intrinsic cavities
Extrinsic voids
Imine linked tetrahedral structure
Intrinsic cavities
Extrinsic voids
Imine linked tetrahedral structure
7
New cards
What are the general advantages of POCs
Dissolvable in common organic solvents
Thermal stability
Chemical stability
High surface areas (~40-800 m2/g)
Thermal stability
Chemical stability
High surface areas (~40-800 m2/g)
8
New cards
How are POCs typically synthesized
via [4+6] cycloimination reactions. Depending
on the amine and trialdehyde employed different cages can be formed.
on the amine and trialdehyde employed different cages can be formed.
9
New cards
what is the most studied prototypical type of POC.
CC3
10
New cards
How is CC3 formed
by the coordination of 1,3,5-triformylbenzene with trans-1,2-diaminocyclohexane,
11
New cards
What is the limiting pore size (window diameter) of CCS
~3.6 Ǻ
12
New cards
What has CC3 been used fo r
- to separate mesitylene from 4-ethyl toluene,
- separation of rare gases, including Xe and Kr ,
- sulfur hexafluoride separation
- gas chromatography separations involving chiral alcohols
- as membrane for the separation of several binary gases (ideal selectivites)
- as proton conductor
- as a noble metal catalytic support.
- separation of rare gases, including Xe and Kr ,
- sulfur hexafluoride separation
- gas chromatography separations involving chiral alcohols
- as membrane for the separation of several binary gases (ideal selectivites)
- as proton conductor
- as a noble metal catalytic support.
13
New cards
What in the XRD indicates a decrease in the
interplanar spacing.
interplanar spacing.
displacement to higher 2 theta angles
14
New cards
What may be related to small changes in the unit cell volume of CC3
the displacement of XRD peaks as a function of synthesis time
15
New cards
What suggest different degrees of packing of CC3 as well a contraction-expansion within this POC
The flexible nature of the CC3 crystals together with these changes in interplanar spacings
16
New cards
How many growth regimes are there for the crystal size of CC3
Three main growth regimes observed
17
New cards
When does the first regime occur
from 8hr to 18hr
18
New cards
what happens in the first regime
rapid crystal growth
amorphous agglomerates densify and transform into larger irregular crystals
amorphous agglomerates densify and transform into larger irregular crystals
19
New cards
when does the second regime happen
from 18 hr to 60 hr
20
New cards
what happens during the second regime
there is an intermediate stage in which crystal size decreases gradually with time
21
New cards
what might be causing the crystal size to decrease in the second growth regime
crystal fragmentation (most likely based on SEM)
crystal dissolution,
crystal dissolution,
crystal dissolution,
crystal dissolution,
22
New cards
When does the last regime take place
60 hr to 360 hr
23
New cards
what happens during the last regime
there is a regrowth stage
a progressive increase in crystals size as a function of synthesis time
a progressive increase in crystals size as a function of synthesis time
24
New cards
What is likely responsible for the continuous crystal growth in the final regime
Ostwald ripening mechanism in which small crystals disappear at expense of growing larger crystals which are favored energetically
25
New cards
What happens during the fragmentation event
crystals detach from larger crystals
26
New cards
When regarding crystal fragmentation what may explain the decrease in crystal size
The regular hexagonal voids left by fragmented crystals with comparable sizes of those crystals synthesized at 30 h
27
New cards
What is CO2 uptake highly dependent on from CC3
crystal size
28
New cards
How does the concentration of solute change for the stirring and non-stirring case
in the non-stirring case the concentration of solutes is high, and gradually decreases
in the stirring case, this concentration rapidly decreases and become steady.
in the stirring case, this concentration rapidly decreases and become steady.
29
New cards
What should affect the overall crystallization process affecting the resultant crystal size, shape, and distribution
The kinetics of the stirring/non-stirring concentration gradient
30
New cards
In principle what is the most thermodynamically stable and simplest form that a colloidal particle can adopt in solution during nucleation and growth
spherical
31
New cards
Why is the spherical shape likely preferred in the non-stirring case
the higher concentration of solutes leads to:
faster supersaturation (solute concentration/solubility ratio)
lower local thermal energy associated to the stagnant solution (non-stirred case) leading to the lowest energy spherical shape configuration.
faster supersaturation (solute concentration/solubility ratio)
lower local thermal energy associated to the stagnant solution (non-stirred case) leading to the lowest energy spherical shape configuration.
32
New cards
What are the different formation stages for different crystal formation stages for CC3
rapid crystal growth stage
intermediate stage in which crystal size decreased with time.
regrowth stage leading to a continuous crystal size increase.
intermediate stage in which crystal size decreased with time.
regrowth stage leading to a continuous crystal size increase.
33
New cards
Adsorption properties of the resultant CC3 phases for CO2 and N2 were highly dependent on what
synthesis time.
34
New cards
What are the advantages of the microwave synthesis of POCs
• Narrow size distribution of crystals
• Higher heating rates vs conventional heating
• No contact between energy source and chemicals
• No wall or heat diffusion effects
• Selectively heats
• No “hotspots”
• Higher heating rates vs conventional heating
• No contact between energy source and chemicals
• No wall or heat diffusion effects
• Selectively heats
• No “hotspots”
35
New cards
What were the conclusions of the microwave synthesis of POCs
• Microwave irradiation greatly reduced crystallization time for two prototypical POCs: CC3 and CC2.
• Size control of CC3α achieved
• Highly crystalline at short times!
• Typical reported surface areas obtained
• Microporous topology maintained
• Size control of CC3α achieved
• Highly crystalline at short times!
• Typical reported surface areas obtained
• Microporous topology maintained
36
New cards
What the proposed steps for the formation of CC3 via EISA
initial homogenous solution on Al foil.
homogenous solution on Al Foil. High RH
MSE
Flexible State
POC Nanocrystalline islands
homogenous solution on Al Foil. High RH
MSE
Flexible State
POC Nanocrystalline islands
37
New cards
What were the conclusions of CC3 formed by EISA
- The solvent diffusion rate was controlled by the relative humidity in the system.
- Novel synthetic method for the formation of a prototypical type of porous organic cage denoted as CC3.
- The formation of CC3 crystals was promoted via EISA approach which relies on the gradual evaporation of dichloromethane from a diluted concentration of CC3 precursors deposited on
aluminum foil.
- The slow solvent evaporation allowed enough time for the organization and formation of CC3 porous organic cage.
- HRTEM, SAED, SEM, and XRD patterns were used as key techniques to follow the formation of this porous organic cage.
- Novel synthetic method for the formation of a prototypical type of porous organic cage denoted as CC3.
- The formation of CC3 crystals was promoted via EISA approach which relies on the gradual evaporation of dichloromethane from a diluted concentration of CC3 precursors deposited on
aluminum foil.
- The slow solvent evaporation allowed enough time for the organization and formation of CC3 porous organic cage.
- HRTEM, SAED, SEM, and XRD patterns were used as key techniques to follow the formation of this porous organic cage.
38
New cards
What are the uses of high purity Xe
Buildings - Commercial lighting
Automotive – Head lights
Space Industry – Propellant
Medical – Anesthesia, Imaging
Science – NMR
Automotive – Head lights
Space Industry – Propellant
Medical – Anesthesia, Imaging
Science – NMR
39
New cards
What are the advantages of membranes
Low energy consumption
Continuous process
No phase changes
No chemical additives
Continuous process
No phase changes
No chemical additives
40
New cards
What is the importance of separation processes
Chemical separations account for
about half of US industrial energy
use and up to 15% of the nation’s
total energy consumption.
about half of US industrial energy
use and up to 15% of the nation’s
total energy consumption.
41
New cards
Why would you want to use POCs as membranes
they should display the most desirable properties of polymers (facile processability and flexibility) and inorganic materials (hierarchically ordered pores with molecular sieving properties) leading to highly selective and permeable membranes
42
New cards
Why was CC3 chosen as the POC membrane for Xe separation
its limiting pore aperture is ~3.6 A can be used as a molecular sieve
Xe has a kinetic diameter ~4.1 A
He, CO2, Kr, and CH4 have kinetic
~ 2.6 Å, 3.3 Å, 3.6Å, and 3.8 Å respectively
Xe has a kinetic diameter ~4.1 A
He, CO2, Kr, and CH4 have kinetic
~ 2.6 Å, 3.3 Å, 3.6Å, and 3.8 Å respectively
43
New cards
draw how CC3 membranes were made by secondary seeded growth
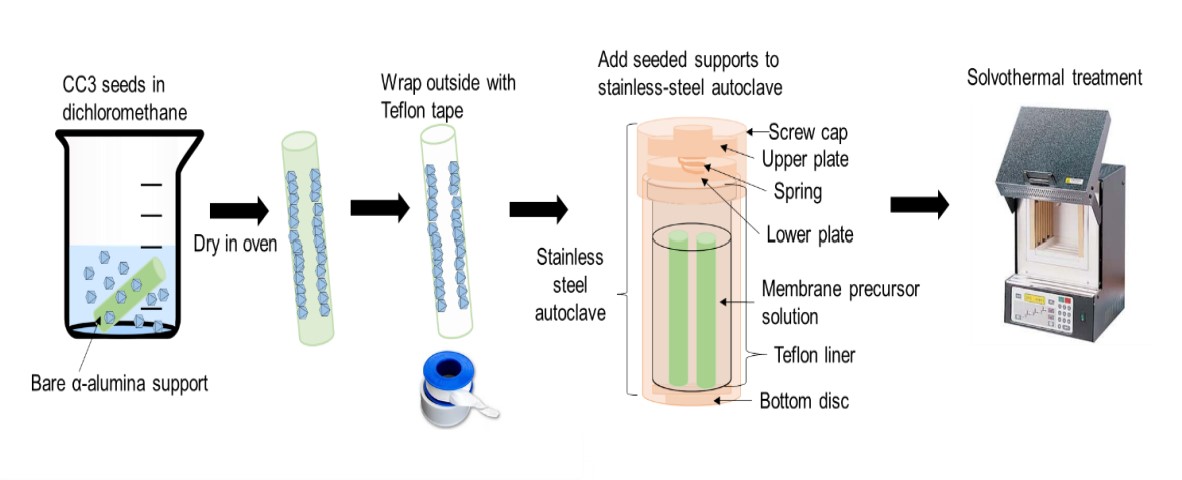
44
New cards
What is the key factor that leads to a higher-than-expected selectivity for Ch4/Xe
pore shape selectivity based on molecular configuration
leading potentially to entropic selectivity
leading potentially to entropic selectivity
45
New cards
What are the factors that affected the separation mechanism
molecular sieving,
adsorption,
diffusivity differences **
adsorption,
diffusivity differences **
46
New cards
What were the conclusion of CC3 as separation membranes for Xe
-The quality of the membranes was dependent on the crystal size, and size distribution of the seeds employed for membrane synthesis. Smaller CC3 seeds with narrow size distribution led to enhanced membrane separation performance.
-Mechanistically, the membranes separated He, CO2, Kr, and CH4 from Xe mainly via differences in diffusivities.
-CC3 membranes displayed low to moderate ideal selectivities of the light gas over Xenon and unprecedented high gas permeances in the 773 to 2114 GPUs range.
-These membranes may be promising for extracting Xenon from different important gas sources, including air, natural gas, and nuclear based mixtures
-Mechanistically, the membranes separated He, CO2, Kr, and CH4 from Xe mainly via differences in diffusivities.
-CC3 membranes displayed low to moderate ideal selectivities of the light gas over Xenon and unprecedented high gas permeances in the 773 to 2114 GPUs range.
-These membranes may be promising for extracting Xenon from different important gas sources, including air, natural gas, and nuclear based mixtures
47
New cards
How might POCS be used for hydrogen isotope separations
Quantum size effects are observed when the difference between the size of the molecule and pore diameter is comparable to the De Broglie wavelength.
Quantum size effects are observed when the difference between the size of the molecule and pore diameter is comparable to the De Broglie wavelength.
Quantum size effects are observed when the difference between the size of the molecule and pore diameter is comparable to the De Broglie wavelength.