Inorganic qualitative analysis
1/27
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
28 Terms
Define anions and cations
Anions- negative ions
Cations- positive ions
How to test for the Ammonium ion?
Add a small amount of dilute Sodium Hydroxide and warm it gently.
Test gas produced with damp red litmus paper
What colour does the red litmus paper turn into when the ammonium ion test is positive?
When NH4+ ions are present the red litmus paper turns blue
Write down the equation for testing for Ammonium
NH4+ (aq) + OH- (aq) = NH3 (g) + H2O (l)
Ammonium + Hydroxide ion = Ammonia + water
How to test for the carbonate ion?
Add a small amount of dilute acid (e.g. nitric).
What shows when the carbonate ion test is positive and why?
Effervescence/bubbling due to CO2 gas production
What shows when the carbonate ion test bubbled through limewater is positive?
The solution turns cloudy
Write down the equation for the carbonate ion test.
Carbonate ion + 2Hydrogen ion = Carbon dioxide + water
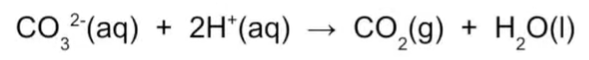
How to test for sulfate ions?
Add a small amount of barium ion (Ba2+) through Barium nitrate (Ba(NO3)2) or Barium chloride (BaCl2)
What can we see if the sulfate ion test is positive and why?
Reaction should produce white precipitate due to BaSO4 (Barium sulfate) production
Write down the ionic equation for the sulfate ion test
Barium ion (aq) + Sulfate ion (aq) = Barium sulfate (s)
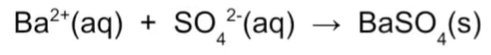
How to test for chloride ions excluding results
Add a small amount of dilute HNO3 (Nitric acid) to remove any carbonate ions
Add a small amount of aqueous AgNO3 (Silver nitrate)
Why do we add dilute nitric acid when testing for halide (Cl, Br and I) ions?
In order to remove any carbonate ions, which would give a precipitate of silver carbonate at the end; a false positive
What is produced when the chloride ion test is positive and why?
Reaction should produce a white precipitate due to AgCl (s)/ silver chloride production
What is the backup test for chloride ions, including results, once the main test is done?
Add a small amount of dilute aqueous ammonia
If chloride ions present the precipitate fully dissolves
How to test for bromide ions excluding result
Add a small amount of dilute nitric acid (HNO3) to remove any carbonate ions
Add a small amount of aqueous silver nitrate (AgNO3)
What indicates a positive bromide ion test result and why?
Reaction should produce a cream precipitate due to AgBr production
ionic formula for chloride ion test
Ag+ (aq) + Cl- (aq) = AgCl (s)
(Silver ion + Chloride ion = Silver chloride)
How to test for iodide ion excluding result
Add a small amount of dilute nitric acid (HNO3) to remove any carbonate ions
Add a small amount of aqueous silver nitrate (AgNO3)
What is produced as a result of a positive iodide ion test result and why?
Reaction should produce a yellow precipitate due to AgI (Silver iodide) production
Backup test for bromide ions?
Add a small amount of dilute aqueous ammonia; precipitate should partially dissolve
Ass a small amount of concentrated aqueous ammonia; precipitate should fully dissolve
Write down the ionic formula for bromide ion test
Ag+ (aq) + Br- (aq) = AgBr (s)
Silver ion + Bromide ion = Silver bromide
Backup test for iodide ion presence?
Add dilute or concentrated aqueous ammonia; precipitate should be insoluble on the addition of both.
What is the correct order for anion tests if testing unknown substances?
1) Carbonate ion
2) Sulfate ion
3) Halide ion
Remember the acronym (Ca-S-H)
Why do we carry out anion tests for unknown substances in a specific order?
Because if they’re carried out in the wrong order, false positive results are obtained.
1) What happens if you incorrectly add barium ions (sulfate test) to carbonate ions during the anion tests?
2) Give the ionic equation for this
1) A white precipitate of barium carbonate would form; however you’d think that a white precipitate of barium sulfate formed instead, giving a false positive sulfate result!!!
2) Ba2+ (aq) + CO32- (aq)= BaCO3 (s) or Barium ion + Carbonate ion = Barium carbonate
1) What happens if you incorrectly add Ag+ ions (Halide tests) to carbonate ions during the anion tests?
2) Write down the equation for this
1) A yellow-grey precipitate of silver carbonate is produced which you would incorrectly think is the yellow silver iodide; false positive iodide result!!!
2) 2Ag+ (aq) + CO32- (aq) = Ag2CO3 (s) or Silver ion + Carbonate ion = Silver carbonate
1) What happens if you incorrectly add Ag+ ions (Halide tests) to sulfate ions during the anion tests?
2) Write down the equation for this.
1) A white precipitate of silver sulfate is formed which you would incorrectly think is silver chloride; false positive chloride result!!!
2) 2Ag+ (aq) + SO43- (aq) = Ag2SO4 (s) or Silver ion + Sulfate ion = Silver sulfate