Biological Molecules
1/40
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
41 Terms
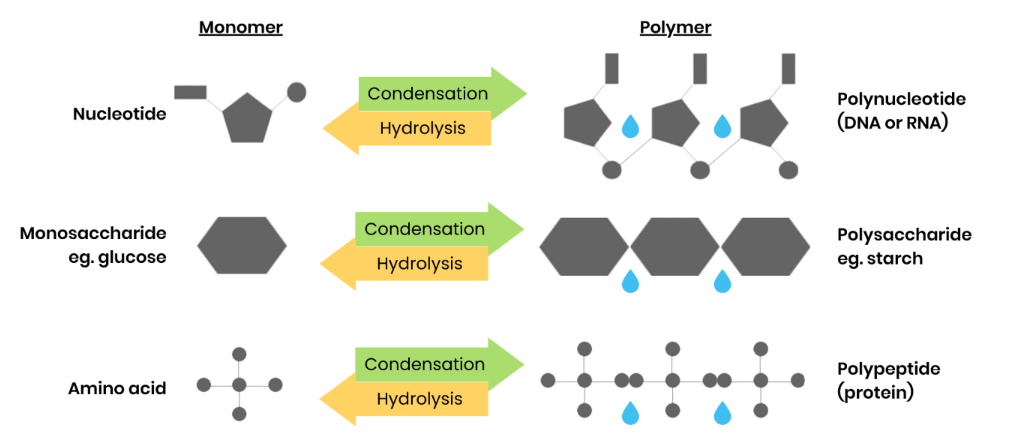
What are monomers and polymers?
● Monomers - smaller, repeating molecules / units from which larger molecules / polymers are made
● Polymers - molecules made from many (a large number of) identical / similar monomer molecules
What happens in condensation reactions
● 2 molecules join together
● Forming a chemical bond
● Releasing a water molecule
What happens in hydrolysis reactions
● 2 molecules separated
● Breaking a chemical bond
● Using a water molecule
Give examples of polymers and the monomers from which they’re made
What are monosaccharides? Give 3 common examples
● Monomers from which larger carbohydrates are made
● Glucose, fructose, galactose
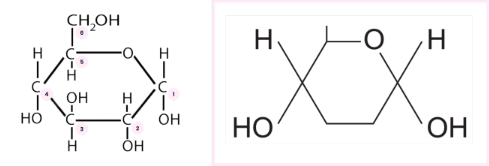
Describe the structure of α-glucose
● Left - full structure, carbon atoms labelled
● Right - simplified structure as in the specification to be memorised for exam
Describe the difference between the structure of α-glucose and β-glucose
● Isomers - same molecular formula but differently arranged atoms
● OH group is below carbon 1 in α-glucose but above carbon 1 in β-glucose
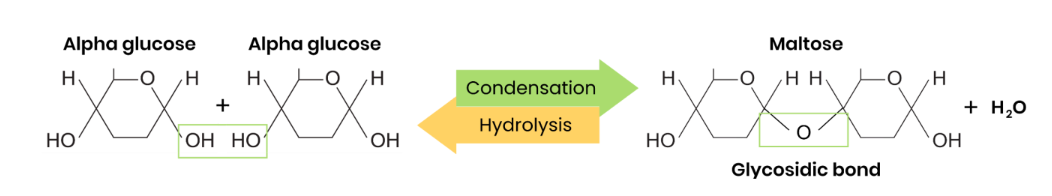
What are disaccharides and how are they formed?
● Two monosaccharides joined together with a glycosidic bond
● Formed by a condensation reaction, releasing a water molecule
List 3 common disaccharides & monosaccharides from which they’re made
Maltose = Glucose + glucose
Sucrose = Glucose + fructose
Lactose = Glucose + galactose
Draw a diagram to show how two monosaccharides are joined together
What are polysaccharides and how are they formed?
● Many monosaccharides joined together with glycosidic bonds
● Formed by many condensation reactions, releasing many water molecules
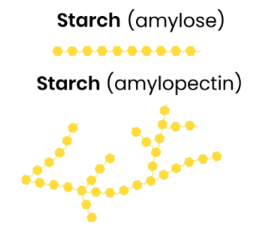
Describe the basic function and structure of starch
Energy store in plant cells
● Polysaccharide of α-glucose
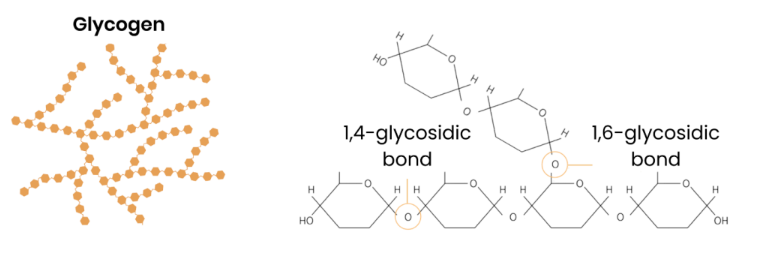
● Some has 1,4-glycosidic bonds so is unbranched (amylose)
● Some has 1,4- and 1,6-glycosidic bonds so is branched (amylopectin)
Describe the basic function and structure of glycogen
Energy store in animal cells
● Polysaccharide made of α-glucose
● 1,4- and 1,6-glycosidic bonds → branched
Explain how the structure of starch relates to its function - amylose
● Helical → compact for storage in cell
● Large, insoluble polysaccharide molecule → can’t leave cell / cross cell membrane
● Insoluble in water → water potential of cell not affected (no osmotic effect)
Explain how the structure of glycogen relates to its function - and amylopectin
● Branched → compact / fit more molecules in small area
● Branched → more ends for faster hydrolysis → release glucose for respiration to make ATP for energy release
● Large, insoluble polysaccharide molecule → can’t leave cell / cross cell membrane
● Insoluble in water → water potential of cell not affected (no osmotic effect)
Describe the basic function and structure of cellulose
Function
● Provides strength and structural support to plant / algal cell walls
Structure
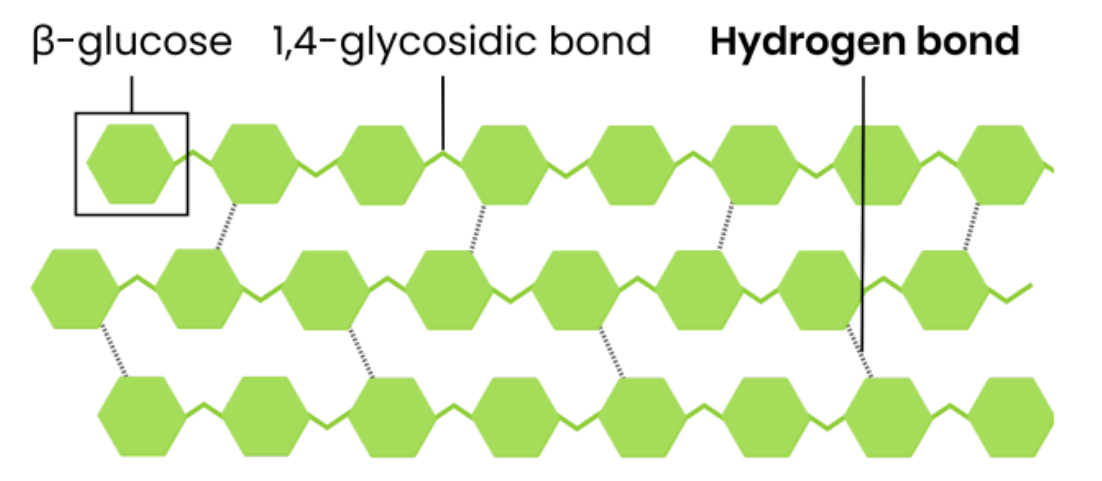
● Polysaccharide of β-glucose
● 1,4-glycosidic bonds so forms straight, unbranched chains
● Chains linked in parallel by hydrogen bonds, forming microfibrils
Explain how the structure of cellulose relates to its function
● Every other β-glucose molecule is inverted in a long, straight, unbranched chain
● Many hydrogen bonds link parallel strands (crosslinks) to form microfibrils (strong fibres)
● Hydrogen bonds are strong in high numbers
● So provides strength to plant cell walls
Identify the reducing sugars
monosaccharides, maltose, lactose
Describe the test for reducing sugars
1. Add Benedict’s solution (blue) to sample
2. Heat in a boiling water bath
3. Positive result = green / yellow / orange / red precipitate
Identify non-reducing sugars
sucrose
Describe the test for non-reducing sugars
1. Do Benedict’s test (as above) and stays blue / negative
2. Heat in a boiling water bath with acid (to hydrolyse into reducing sugars)
3. Neutralise with alkali (eg. sodium bicarbonate)
4. Heat in a boiling water bath with Benedict’s solution
5. Positive result = green / yellow / orange / red precipitate
Suggest a method to measure the quantity of sugar in a solution
● Carry out Benedict’s test as above, then filter and dry precipitate
● Find mass / weight
Suggest another method to measure the quantity of sugar in a solution
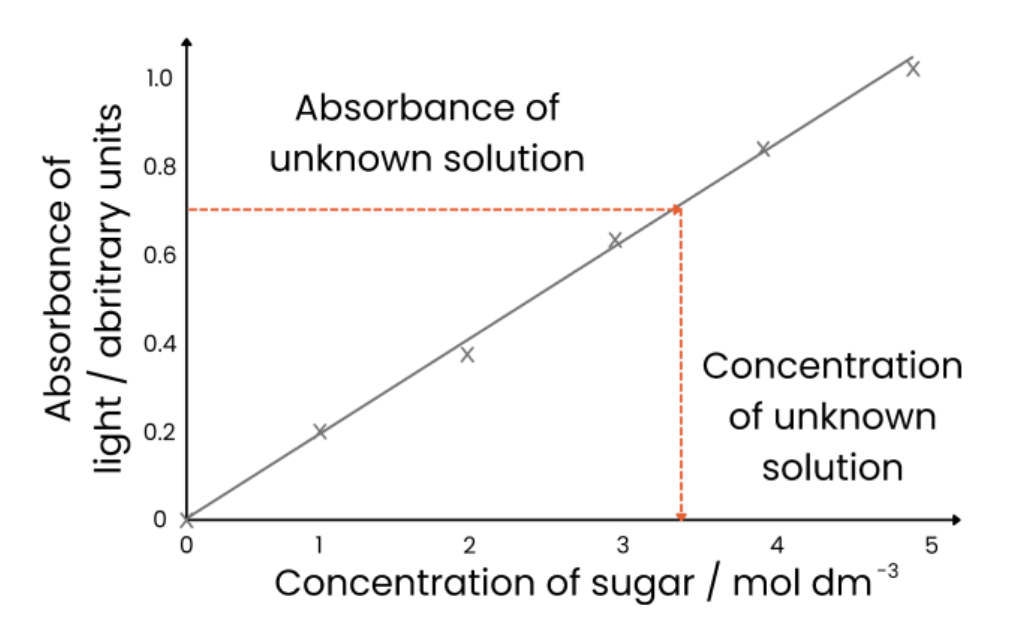
1. Make sugar solutions of known concentrations (eg. dilution series)
2. Heat a set volume of each sample with a set volume of Benedict’s solution for the same time
3. Use colorimeter to measure absorbance (of light) of each known concentration
4. Plot calibration curve - concentration on x axis, absorbance on y axis and draw line of best fit
5. Repeat Benedict’s test with unknown sample and measure absorbance
6. Read off calibration curve to find concentration associated with unknown sample absorbance
Describe the biochemical test for starch
1. Add iodine dissolved in potassium iodide (orange / brown) and shake / stir
2. Positive result = blue-black
Name two groups of lipid
Triglycerides and phospholipids.
Describe the structure of a fatty acid (RCOOH)
● Variable R-group - hydrocarbon chain (this may be saturated or unsaturated)
● -COOH = carboxyl group
Describe the difference between saturated and unsaturated fatty acids
● Saturated - no C=C double bonds in hydrocarbon chain → all carbons fully saturated with hydroge
● Unsaturated - one or more C=C double bond in hydrocarbon chain (creating a bend / kink)
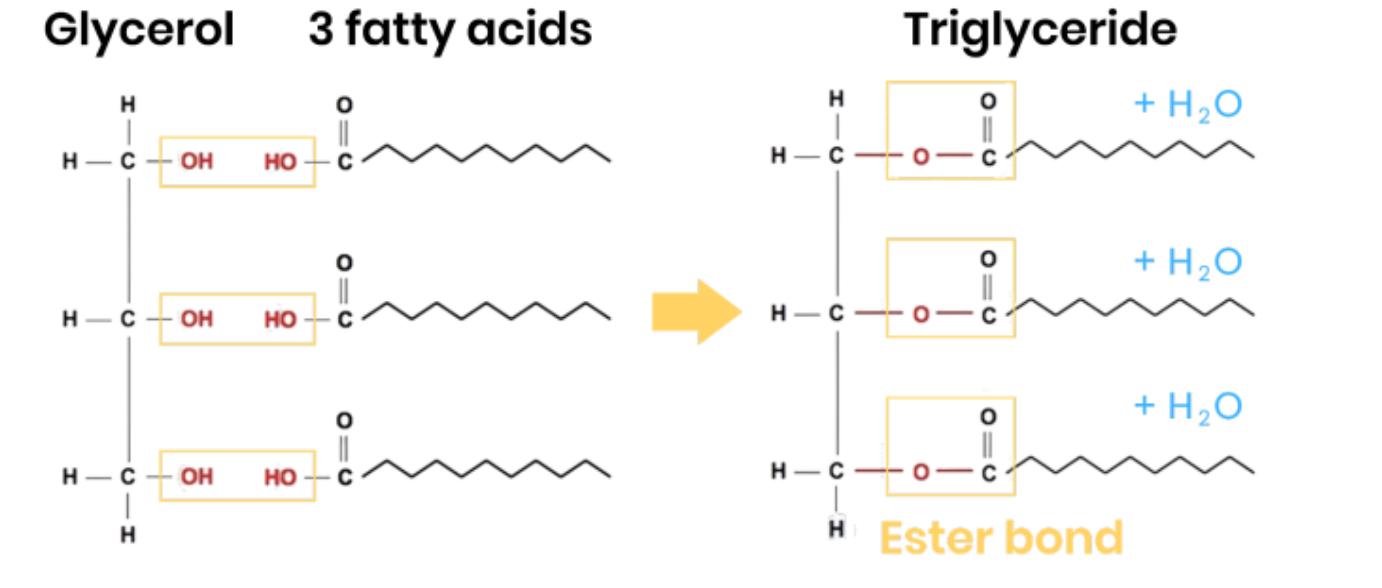
Describe how triglycerides form
● 1 glycerol molecule and 3 fatty acids
● 3 condensation reactions
● Removing 3 water molecules
● Forming 3 ester bonds
Explain how the properties of triglycerides are related to their structure
function = energy storage
● High ratio of C-H bonds to carbon atoms in hydrocarbon chain
○ So used in respiration to release more energy than the same mass of carbohydrates
● Hydrophobic / non-polar fatty acids so insoluble in water (clump together as droplets, tails inwards)
○ So no effect on water potential of cell (or can be used for waterproofing)
Describe the difference between the structure of triglycerides and phospholipids
One of the fatty acids of a triglyceride is substituted by a phosphate-containing group
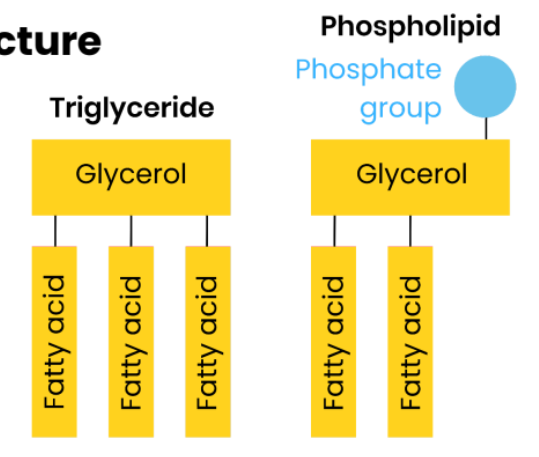
Describe how the properties of phospholipids relate to their structure
Function: form a bilayer in cell membrane, allowing diffusion of lipid-soluble (non-polar) or very small substances and restricting movement of water-soluble (polar) or larger substances.
● Phosphate heads are hydrophilic
○ Attracted to water so point to water (aqueous environment) either side of membrane
● Fatty acid tails are hydrophobic
○ Repelled by water so point away from water / to interior of membrane
Describe the test for lipids
1. Add ethanol, shake (to dissolve lipids), then add water
2. Positive result = milky white emulsion
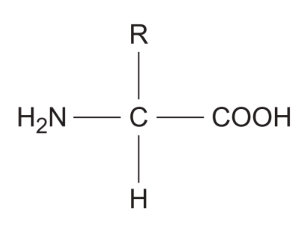
Describe / draw the general structure of an amino acid
● COOH = carboxyl group
● R = variable side chain / group
● H2N = amine group
How many amino acids are common in all organisms? How do they vary?
The 20 amino acids that are common in all organisms differ only in their side group (R).
Describe how amino acids join together
● Condensation reaction
● Removing a water molecule
● Between carboxyl / COOH group of one and amine / NH2 group of another #
● Forming a peptide bond
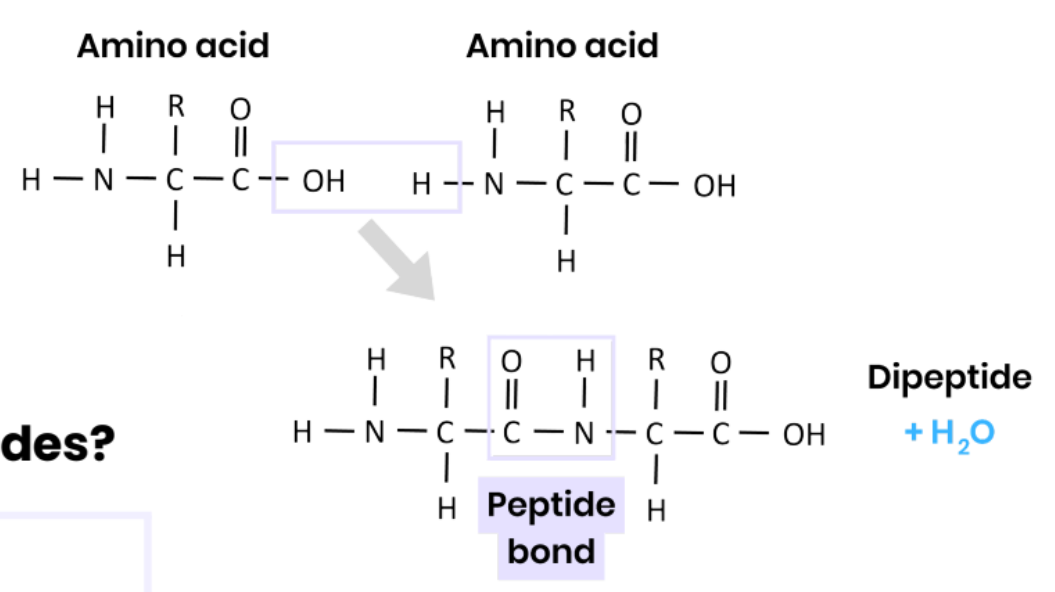
What are dipeptides and polypeptides?
● Dipeptide - 2 amino acids joined together
● Polypeptide - many amino acids joined together
A functional protein may contain one or more polypeptides.
Describe the primary structure of a protein
Sequence of amino acids in a polypeptide chain, joined by peptide bonds
Describe the secondary structure of a protein
● Folding (repeating patterns) of polypeptide chain eg. alpha helix / beta pleated sheets
● Due to hydrogen bonding between amino acids
● Between NH (group of one amino acid) and C=O (group)
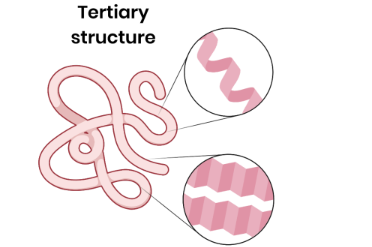
Describe the tertiary structure of a protein
● 3D folding of polypeptide chain
● Due to interactions between amino acid R groups (dependent on sequence of amino acids)
● Forming hydrogen bonds, ionic bonds and disulfide bridges
Describe the quaternary structure of a protein
● More than one polypeptide chain
● Formed by interactions between polypeptides (hydrogen bonds, ionic bonds, disulfide bridges)
Describe the test for proteins
1. Add biuret reagent (sodium hydroxide + copper (II) sulphate)
2. Positive result = purple / lilac colour (indicating presence of peptide bonds)