Cost of capital Quicknotes
1/35
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
36 Terms
rate of return necessary to maintain market value or stock price of a firm.
Computed as a weighted average of the various long-term capital sources such as: Long-Term Debt, Preferred Stock, Common Stock and Retained Earnings
OTHER NAMES: Minimum Acceptable Rate of Return, Required Rate of Return, Hurdle Rate, Desired Rate, Standard Rate, Cut-Off Rate
COST OF CAPITAL

What is the cost of capital of each source of capital?
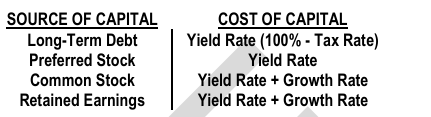
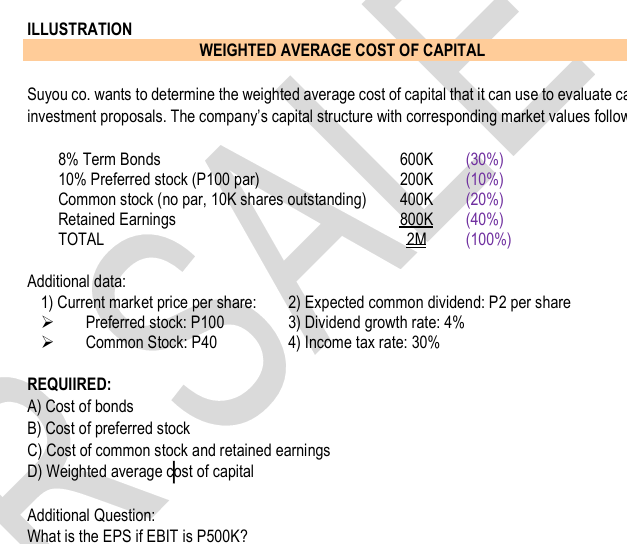
ILLUSTRATION WEIGHTED AVERAGE COST OF CAPITAL Suyou co. wants to determine the weighted average cost of capital that it can use to evaluate capital investment proposals. The company’s capital structure with corresponding market values follows:
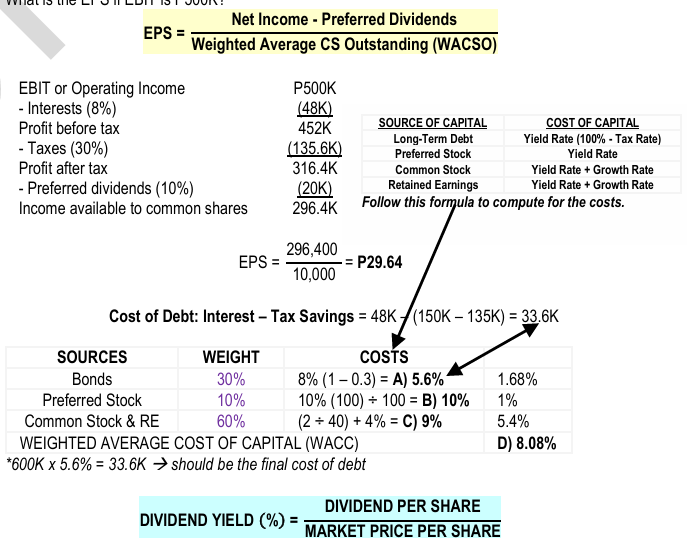
Formula for EPS

– based on a debt instrument’s EFFECTIVE interest rate.
YIELD RATE
To approximate the YIELD-TO-MATURITY (YTM) rate on debt instrument: YTM =z
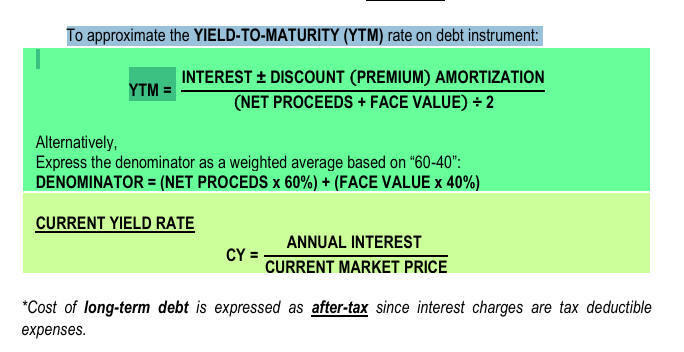
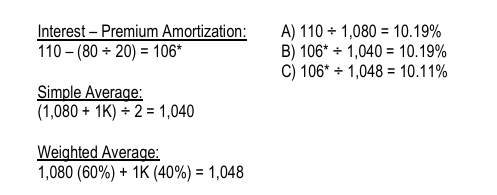
ILLUSTRATION COST OF DEBT: CURRENT YIELD vs. APPROXIMATE YIELD-TO-MATURITY Cici Co. has an outstanding P1K par value bond with 20 years to maturity. The bond carries an annual interest payment of P110 and is currently selling for P1,080.
REQUIRED: Determine the following:
A) Current Yield
B) Approximate Yield-to-Maturity (using simple average).
C) Approximate Yield-to-Maturity (using weighted average).
A) 110 ÷ 1,080 = 10.19%
B) 106* ÷ 1,040 = 10.19%
C) 106* ÷ 1,048 = 10.11%
The yield rate that must be used for preferred shares is the
DIVIDEND YIELD.
Formula for dividend rate and dividend per share
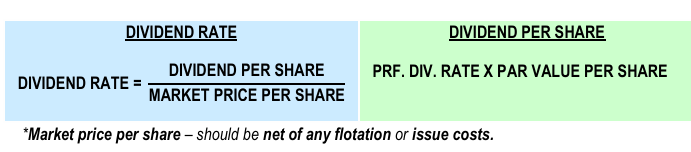
– cost of issuing or floating securities in the market.
FLOTATION COST
ILLUSTRATION:
COST OF PREFERRED STOCK
Aamon Co. pays an annual dividend of P10 per share for its preferred stock with a P100 par value. Aamon can sell each share of preferred stock for a price of P125.
REQUIRED: Determine the following:
A) Cost of preferred stock (assuming a tax rate of 25%).
B) Cost of preferred stock (assuming a flotation cost of P25 per share).
A) 10 ÷ 125 = 8%
B) 10 ÷ (125 – 25)
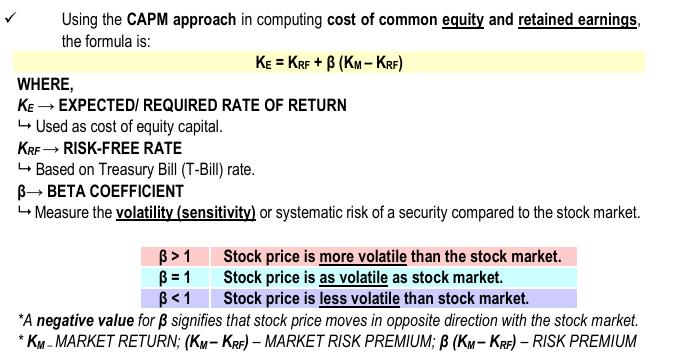
In COST OF COMMON STOCK (CS) & RETAINED EARNINGS (RE) KE
Yield rate is the Dividend Yield.
Dividend per share must be based on the __________
next dividend to be paid i.e., expected dividend.
EXPECTED DIVIDEND PER SHARE =

ILLUSTRATION
COST OF COMMON EQUITY: GORDON GROWTH MODEL (GGM)
Joy Co.’s common stock is selling for P50 per share with 20% flotation cost and a dividend per share of P2. Both earnings and dividends are expected to grow by 5%. Tax rate is 30%.
REQUIRED: Determine the following.
A) Cost of common stock (assuming the P2 dividend is yet to be paid).
B) Cost of common stock (assuming the P2 dividend was just paid recently).
C) Cost of retained earnings (assuming the P2 dividend is yet to be paid).
D) Cost of retained earnings (assuming the P2 dividend was just paid recently).
A) (2 ÷ 40**) + 5% = 10%
B) (2.1* ÷ 40**) + 5% = 10.25%
C) (2 ÷ 50) + 5% = 9%
D) (2.1* ÷ 50) + 5% = 9.2%


ILLUSTRATION COST OF COMMON EQUITY:
CAPITAL ASSETS PRICING MODEL (CAPM)
Use the Security Market Line equation for CAPM in each of the following independent cases.

CAPITAL ASSET PRICING MODEL (CAPM): A RISK-BASED APPROACH
A security risk consists of two components:
(1) Diversifiable risks and (2) Non diversifiable risks.
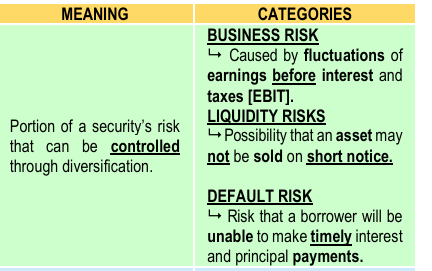
DIVERSIFIABLE RISK (Controllable or Unsystematic Risk or Company-Specific Risk)
Results from forces outside the firm’s control.
CATEGORIES
MARKET RISK
Stock’s price will change due to changes in stock market.
INTEREST RATE RISK
Resulting from fluctuations in the value of an asset as interest rates change.
PURCHASING POWER RISK
A rise in price will reduce the quantity of goods that can be purchased.
NON-DIVERSIFIABLE RISK (Non-controllable risk or Systematic Risk or Market-related risk)
Using the CAPM approach in computing cost of common equity and retained earnings, the formula is:
In business, it refers to the usage of fixed costs, representing risks to the firm.
LEVERAGE
– represents risk of being unable to cover fixed operating costs.
OPERATING LEVERAGE
DOL formula

– represents risk of being unable to cover fixed financial obligations.
FINANCIAL LEVERAGE
DFL Formula

– measure of total risk, determines how EPS is affected by a change in sales.
TOTAL LEVERAGE
Total Leverage
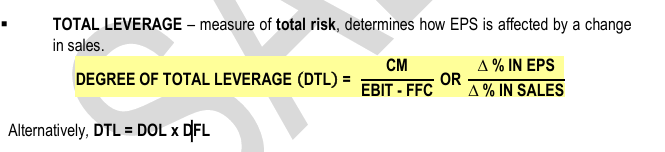
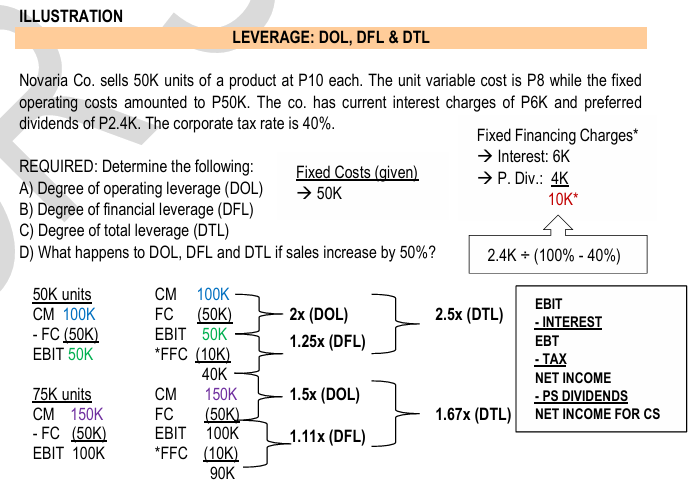
ILLUSTRATION LEVERAGE:
DOL, DFL & DTL Novaria Co. sells 50K units of a product at P10 each. The unit variable cost is P8 while the fixed operating costs amounted to P50K. The co. has current interest charges of P6K and preferred dividends of P2.4K. The corporate tax rate is 40%.
REQUIRED:
Determine the following:
A) Degree of operating leverage (DOL)
B) Degree of financial leverage (DFL)
C) Degree of total leverage (DTL)
D) What happens to DOL, DFL and DTL if sales increase by 50%?
– refers to the mix of the long-term financing that comprises a firm’s sources of funds that mature beyond one year.
CAPITAL STRUCTURE
CAPITAL STRUCTURE =
= FINANCIAL STRUCTURE – CURRENT LIABILITIES
– mix of debt and equity financing that maximizes a firm’s market value while minimizing its overall cost of capital.
OPTIMAL CAPITAL STRUCTURE (TARGET CAPITAL STRUCTURE)
– cost to the firm of the next peso of new capital raised after exhausting internal source of financing (e.g., retained earnings).
MARGINAL COST OF CAPITAL (MCC)
– offers the lowest cost of capital due to its tax deductibility.
DEBT FINANCING
– when WACC is minimized and the market value of assets is maximized, an optimal capital structure exists.
TRADITIONAL THEORY OF CAPITAL STRUCTURE
VALUE OF THE FIRM = M
= MARKET VALUE OF DEBT + MARKET VALUE OF COMMON EQUITY
OR, EBIT ÷ WACC
WHERE,
MARKET VALUE OF DEBT = INTEREST ÷ COST OF DEBT
MARKET VALUE OF COMMON EQUITY = (EBIT – INTEREST) ÷ COST OF COMMON EQUITY