AP HuG Final: Units 1-4
1/274
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
275 Terms
Physical Georgraphy
The study of natural processes and distribution of environmental features (ex. landforms, plants, animals, climates, etc)
Human Geography (Why of where)
Study of events and processes that have shaped how humans understand, use, and alter Earth
Spatial Perspctive
Where something happens; looks at where and why they are located, how they live
Ecological perspective
Relationship between living things and their environment; help understand complex relationships —> important to geographers
Absolute location - absolute direction
Exact location of a place on the earth described by global coordinates - literal measurements and directions (ex. 500 feet north)
Relative location - relative direction
The position of a place in relation to another place - right or left based on where you are
Location
The position that something occupies on Earth's surface
Place
Diff from location, refers to a larger spot relative to its qualities
Site
The absolute location of a place, described by local relief, landforms, and other cultural or physical characteristics (ex. on Lake Michigan)
Situation
Relative location of a place (ex. near Lake Michigan)
Sense of place
Feelings evoked by people as a result of certain experiences and memories associated with a particular place
Mental map
An internal representation of a portion of Earth's surface based on what an individual knows about a place, containing personal impressions of what is in a place and where places are located
Space
The physical gap or interval between two objects
Distribution
The arrangement of something across Earth's surface
Density
Number of things (animals, people, etc.) in a specific area
Pattern
Manner in which things are arranged in space; depends on what humans need/want--> shows in patterns (organization)
Flow
Movement of goods, people, and info along with the economical , social, and political effects they have
Environmental determinism
The belief that the physical environment exclusively shapes humans, their actions, and their thoughts
Possibilism
The theory that humans have a better ability to make a result over environmental determinism
Sustainability
Use of the Earths material in ways they are maintained for future/continuous use (renewable resources, non-renewable resources, sustainable development)
Distance decay
The farther the distance between two things causes them to interact less with each other than if they were closer (ex. living across an ocean)
Time-space compression
Processes causing relative distance to shrink (ex. planes faster than boats, technology, etc.)
Scale
Area or size in correlation to the study being conducted
Scale of analysis
How zoomed in or out you are when looking at geographic data (ex. national, local, global) at the issue level
Region
An area distinguished by a unique combination of trends or features that separate it from other parts
Formal/uniform region
An area with shared traits (ex. Chi--> mayor, political, region)
Functional/nodal region
An area organized around a node or focal point (ex. loop being based downtown)
Perceptual/vernacular region
An area based on feelings toward the place (ex. Chicago may be bigger or smaller depending on the person)
Geographic data
Data collected geographically...
Quantitative vs. qualitative data
One has number based data, the other observation and fact based
Census
Population collection done every ten years
GIS
A computer system that stores, organizes, analyzes, and displays geographic data
Topography
The arrangement of the natural and artificial physical surface of an area
Geovisualization
Creation and use of visual representations to facilitate thinking, understanding, and knowledge construction about human and physical environment
Remote sensing
The acquisition of data about Earth's surface from a satellite orbiting the planet or other long-distance methods
GPS
A system that determines the precise position of something on Earth through a series of satellites, tracking stations, and receivers (ex. google maps)
Cartographer
Map drawer
Isoline map
Map that uses lines to show similar data points (ex. that one weather one)
Graduated symbol map
Map that uses different sized dots/symbols to represent date (ex. dots on capital cities)
Cartogram map
Map with distorted sizes based on data (ex. a state being misshapen in chi as more live here than skinny suburbs)
Dot map
Map that uses dots to show data (ex. not bigger or smaller just clustered and what not)
Choropleth map
A thematic map that uses tones or colors to represent spatial data as average values per unit area
Population distribution
Where people live within an area; depending on cluster ness of a population the environment can change
Globalization
The worldwide growth of economics and stuff that further develops the world
Periphery, semi-periphery, and core
States relativity to economic status and worldwide participation (in a sense)
Population distribution factors
Physical: climate, landforms, bodies of water,
soil; social: culture, economics, history, politics
Arithmetic density
the total number of people per unit area of land; also called crude density
Physiological density
The number of people per unit of area of arable land, which is land suitable for agriculture
Agricultural density
The ratio of the number of farmers to the total amount of arable land
Carrying capacity
The largest population that an area can support
Sex ratio
The ratio of males to females in a population
Demographics
Statistical data relating to the population and particular groups within it
Crude birth rate
The total number of live births in a year for every 1,000 people living in a population
Total fertility rate
The average number of children born to a woman during her childbearing years
Mortality
Death
Crude death rate
The number of deaths per year per 1,000 people.
Infant mortality rate
The percentage of children who die before their first birthday within a particular area or country
Life expectancy
The average number of years an individual can be expected to live, given current social, economic, and medical conditions
Population pyramid
A bar graph representing the distribution of population by age and sex
Rate of natural increase (RNI)
The difference between CBR and CDR in a group of people; doesn't always tell the whole story--> only data
Doubling time
Number of years in which a population growing at a rate will double DT=70/RNI
Urbanization
Growth and development of cities; relates to industrialization because the cities develop from industry
Factors that influence population growth and decline
Economic, political, environmental, cultural, changing role of female, voluntary migration, forced migration
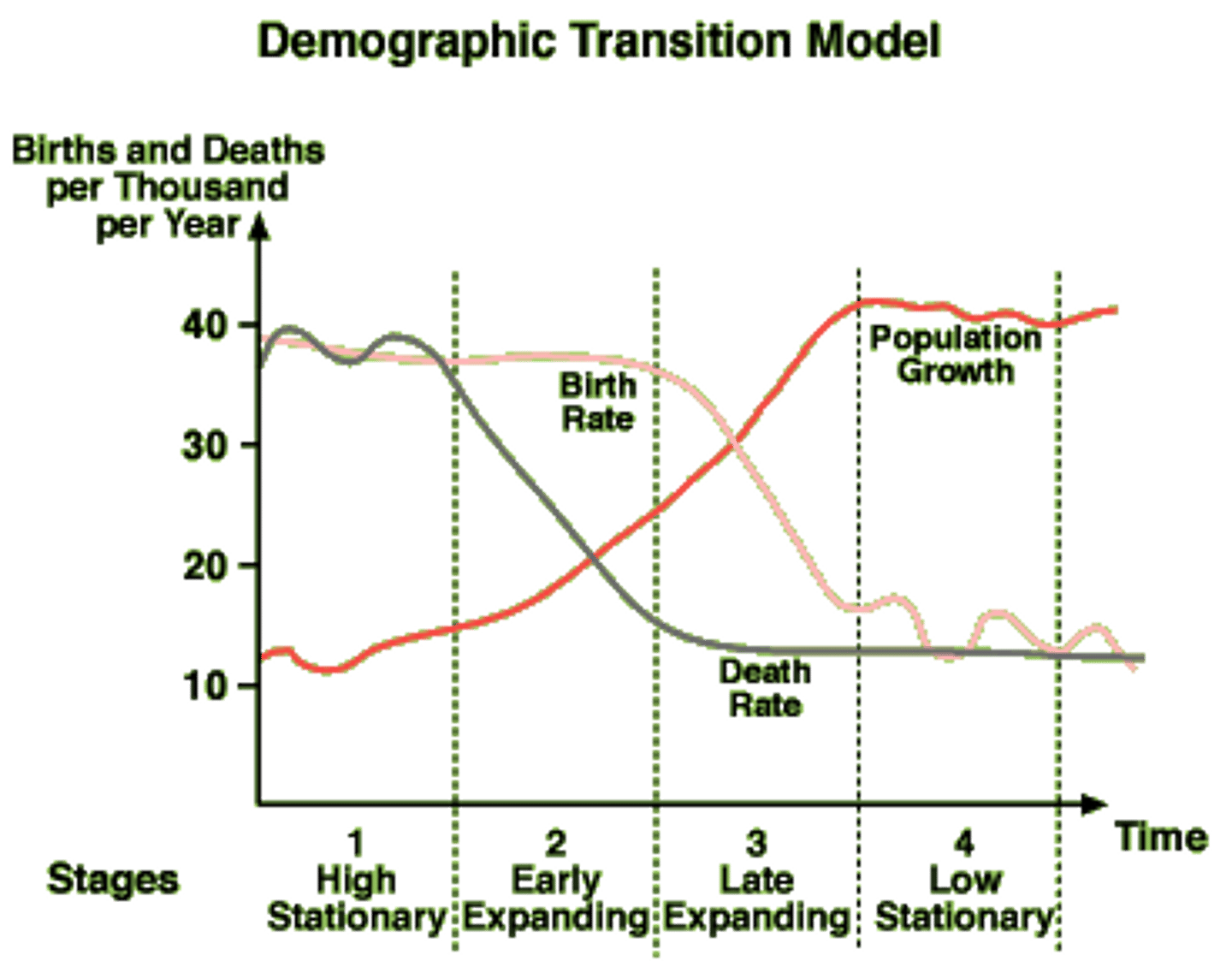
DTM
Know the stages
Degenerative disease
Any disease in which deterioration of the structure or function of tissue occurs
Infectious disease
A disease that is caused by a pathogen and that can be spread from one individual to another
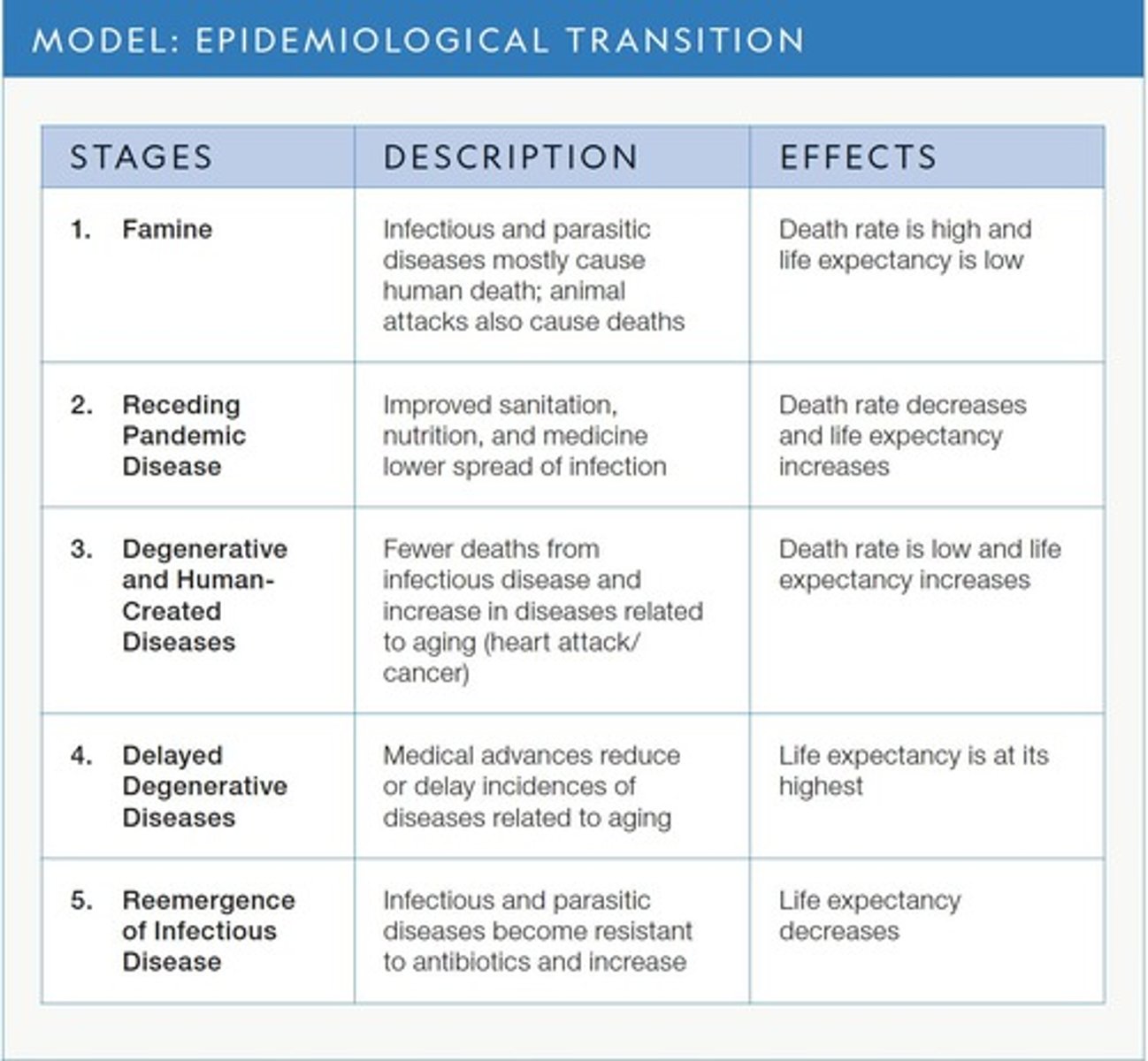
ETM
Know the stages
Pronatalist policy
Government policy that supports higher birth rates
Antinatalist policy
Government policy that supports lower birth rates
Human trafficking
The illegal trade of human beings, a modern-day form of slavery, for the purpose of commercial sexual exploitation, forced labor, or involuntary military combat
Repatriation
A refugee or group of refugees returning to their home country, usually with the assistance of government or a non-governmental organization (not deportation, voluntary)
Interregional migration
Migration outside a region
Intraregional migration
Migration within the same state, not across national borders
Dependency ratio
Ratio used to measure the demand for workers; # of people unable to work (-14 - +64) divided by working age (15+ - -65) times 100
Migration
A general term for movement
Immigration
The act of moving permanently to a new country
Emigration
The act of leaving one's own country to settle permanently in another; moving abroad
Net migration
The difference in number between emigrants and immigrants in a location
Ravenstein's laws of migration

Gravity model
A model that holds that the potential use of a service at a particular location is directly related to the number of people in a location and inversely related to the distance people must travel to reach the service
Push factor
A negative factor that pushes you to leave (economic, political conditions and conflict, cultural, demographic, environmental)
Pull factor
A positive factor that pulls you in (economic, political conditions and conflict, cultural, demographic, environmental)
Transnational migration
Migration through different countries; lots of people who migrate transnationally "belong" to two countries by heart
International migration
Movement and flow inside a country instead of transnational
Friction of distance
The increase in time and cost that usually comes with increasing distance
Transhumance
Nomad migration practices of moving at different elevations depending on the time of year and how it benefits living
Chain migration
When new immigrants tell their family or friends about their positive experiences so there begins a chain of people immigrating to the same place
Step migration
When someone wants to migrate but it takes multiple steps to get to the final destination (ex. limits, obstacles, conflicting opportunities, etc.)
Intervening obstacle
An obstacle that hinders or blocks migration often being negative to the steps
Intervening opportunity
An opportunity that makes the migrator feel the need to stay as it could have a positive outcome
Rural to urban migration
Moving from a small nobody town to a big city
Guest workers
A temporary laborer from a different country
Circular migration
The temporary movement of a migrant worker between home and host countries to seek employment
Refugee
Someone forced to leave their home due to threat of death
Asylum
Right to protection in a new country
Internally displaced persons
Forced to flee homes but still stuck inside of the same state
Malthus's theory of population
Theory based on the premise that exponential population growth will outpace the increase in resources and food supply (the end of supply is where the lines cross) - he is incorrect as he did not foresee the development of agricultural possibilities

Overpopulation
The number of people in an area exceeds the capacity of the environment to support life at a decent standard of living
Neo-Malthusian
Concerns about the use of sustainability on the planet; claim that Earth can only support a finite population even with the developments made today
Xenophobia
A fear or hatred of foreigners or strangers