OpenStax Chapter 3 Section 3.2 Comparing Prokaryotic and Eukaryotic Cells
1/23
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
24 Terms
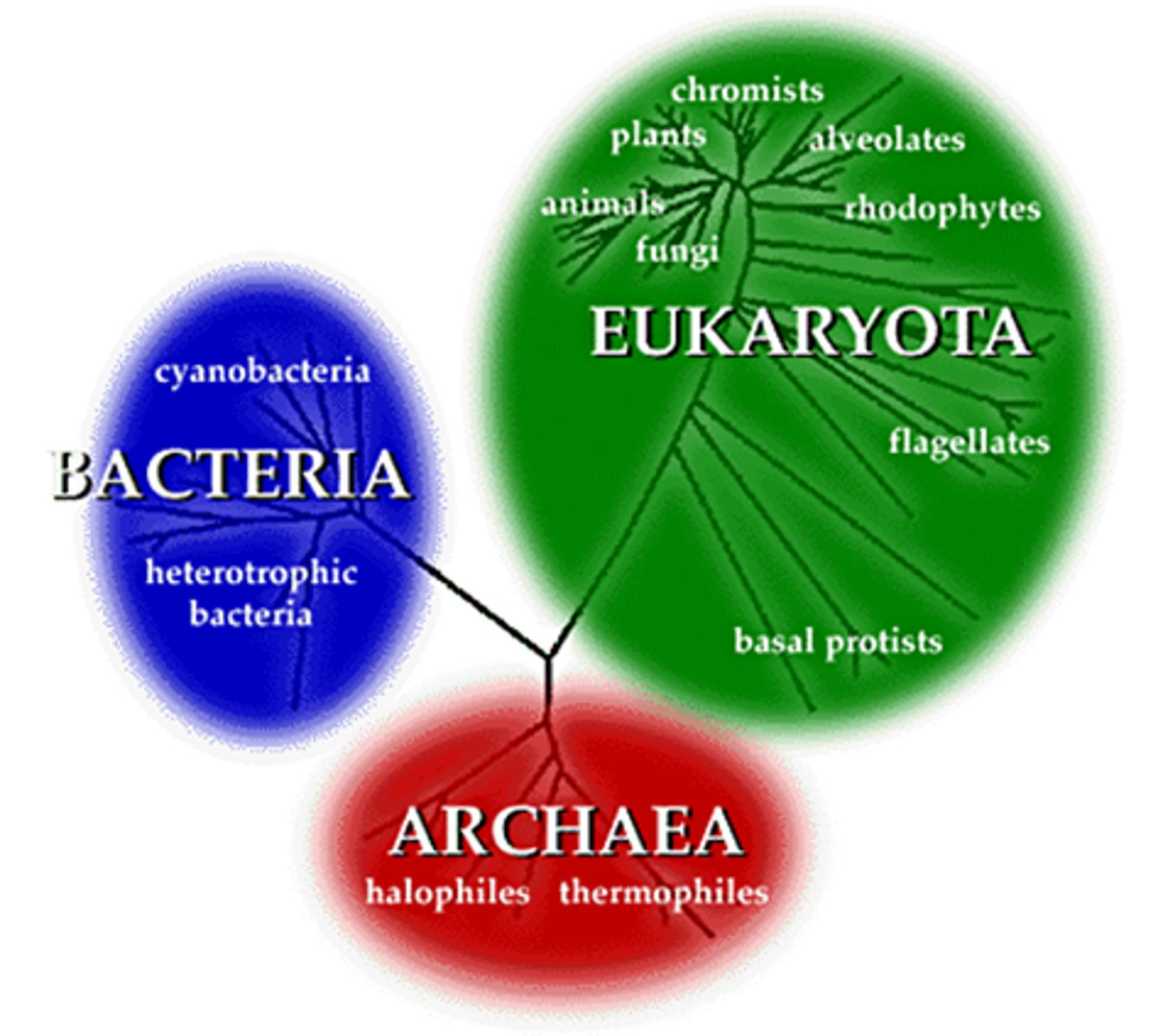
Prokaryotic Organisms
Single-celled organisms of the domains Bacteria and Archaea.
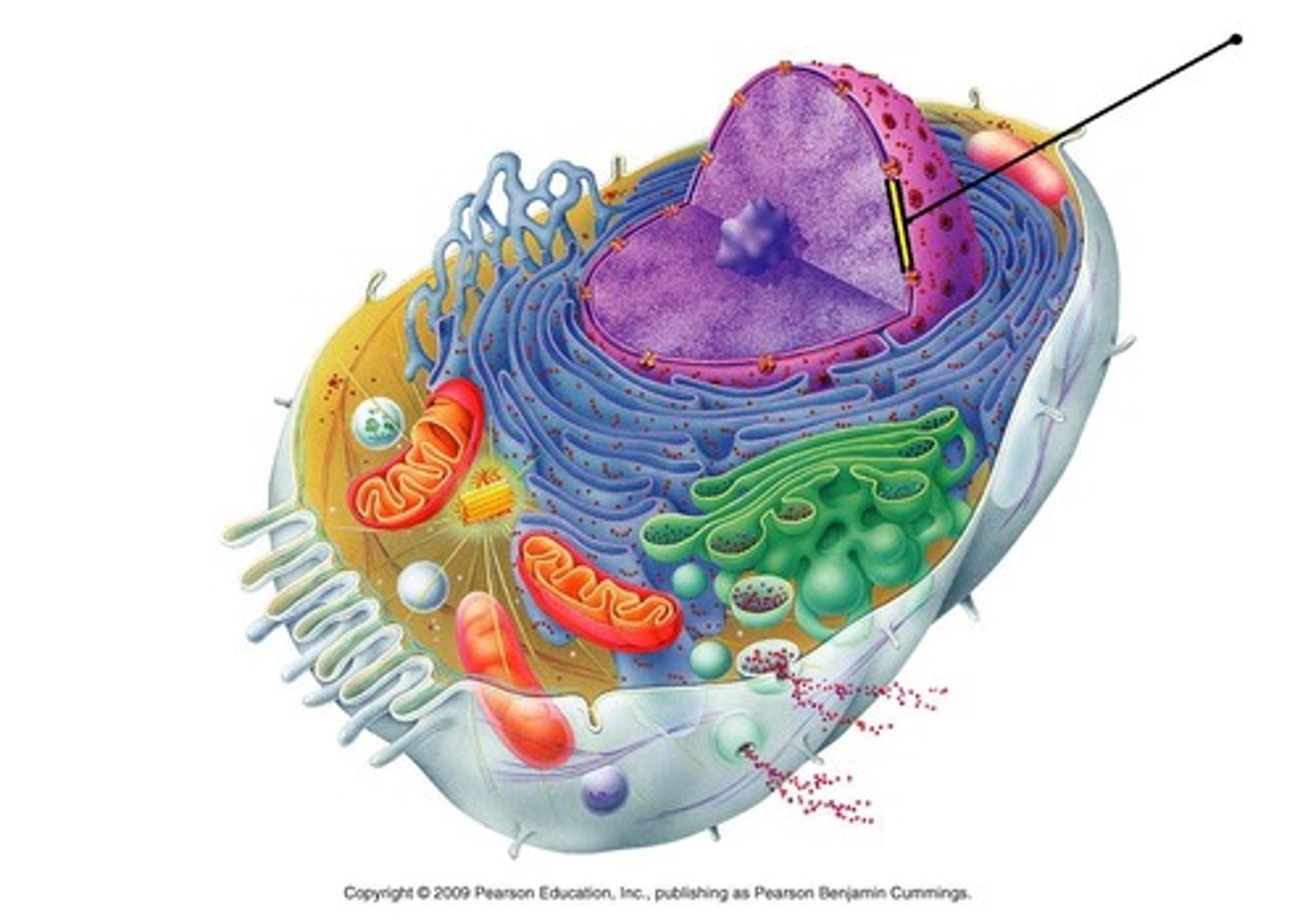
Eukaryotic Organisms
Animal cells, plant cells, fungi, and protists classified as ______________.
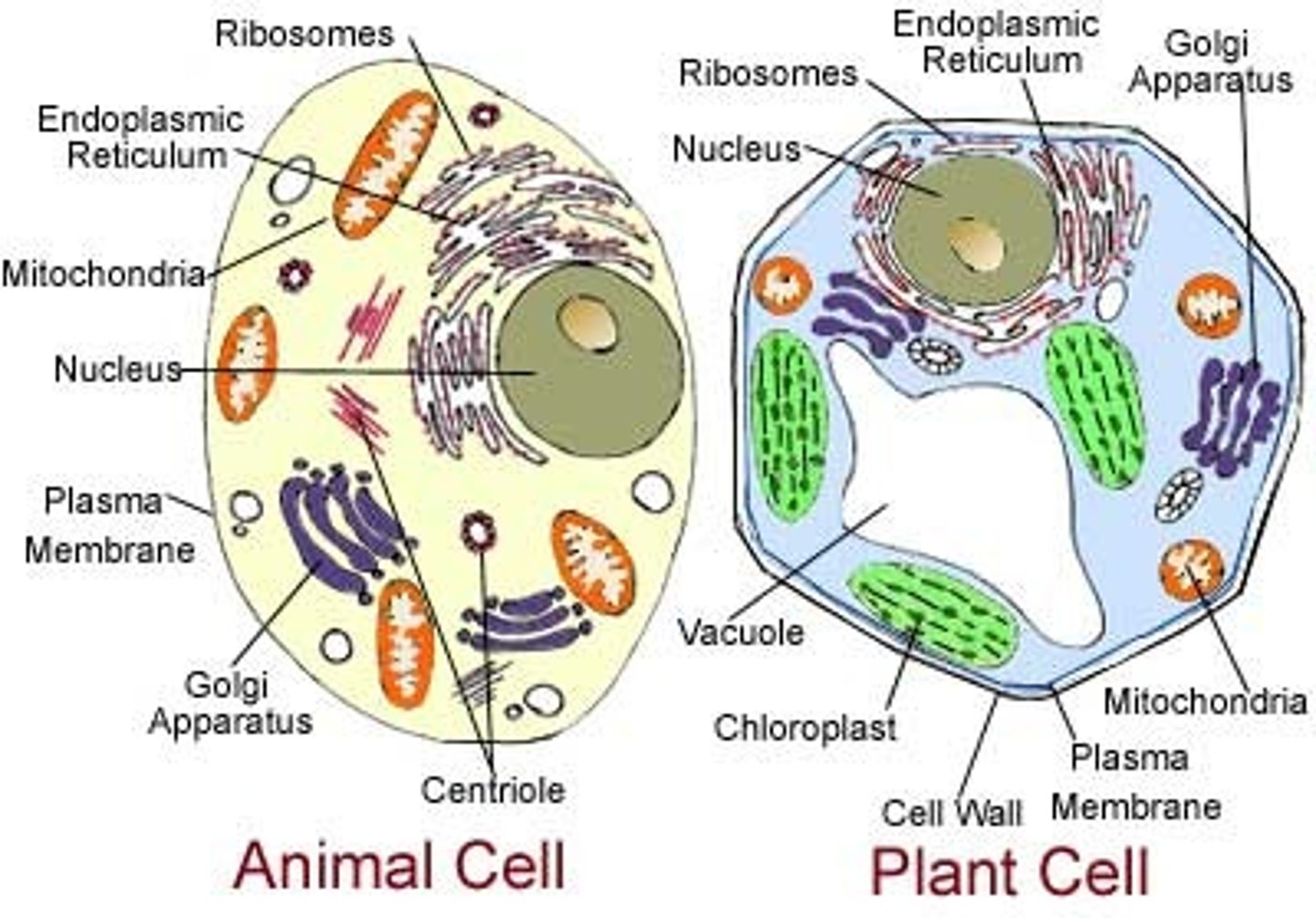
Plasma Membrane
Outer covering of a cell that separates the cell's interior from its surrounding environment.
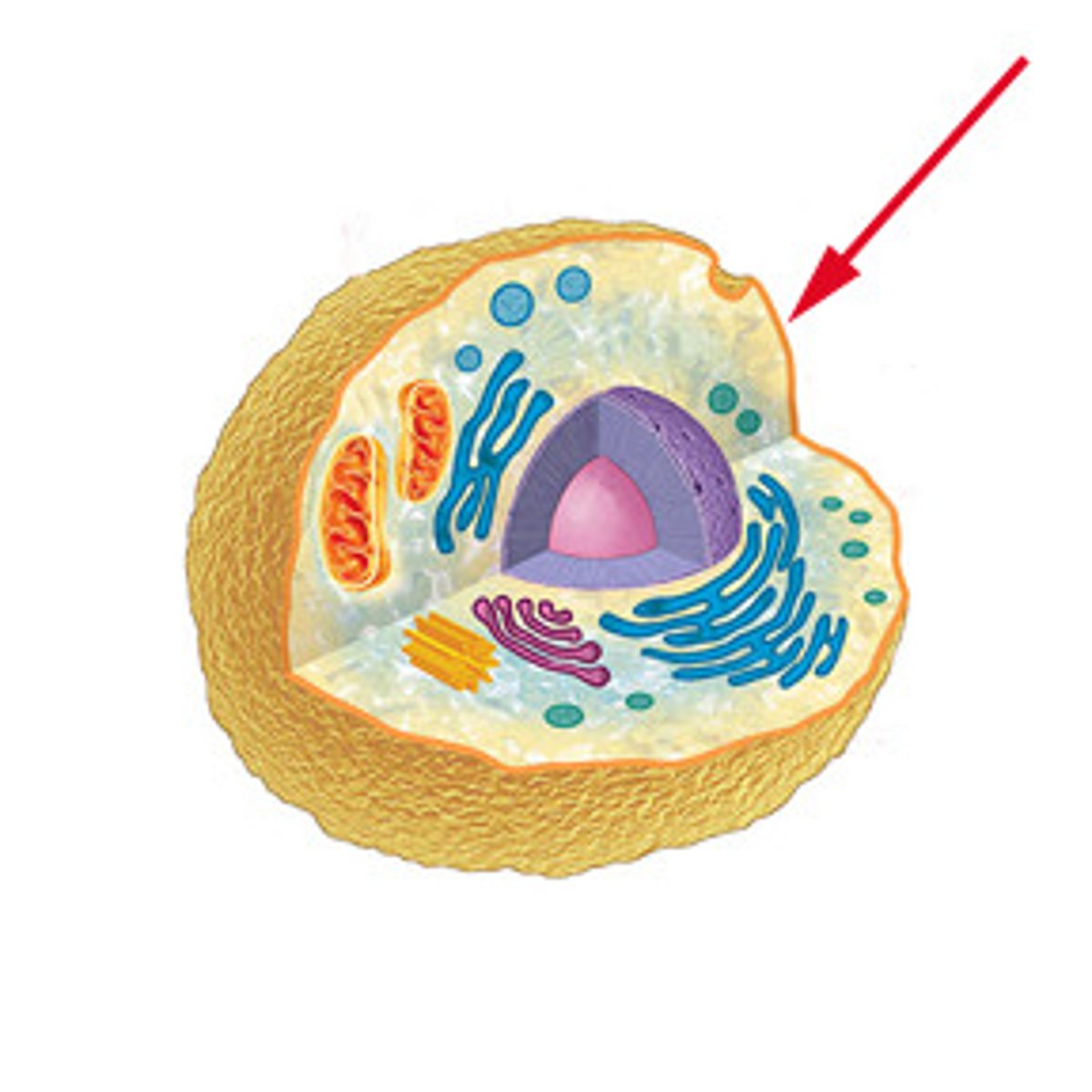
Cytoplasm
Jelly-like region within a cell where other cellular components are found.
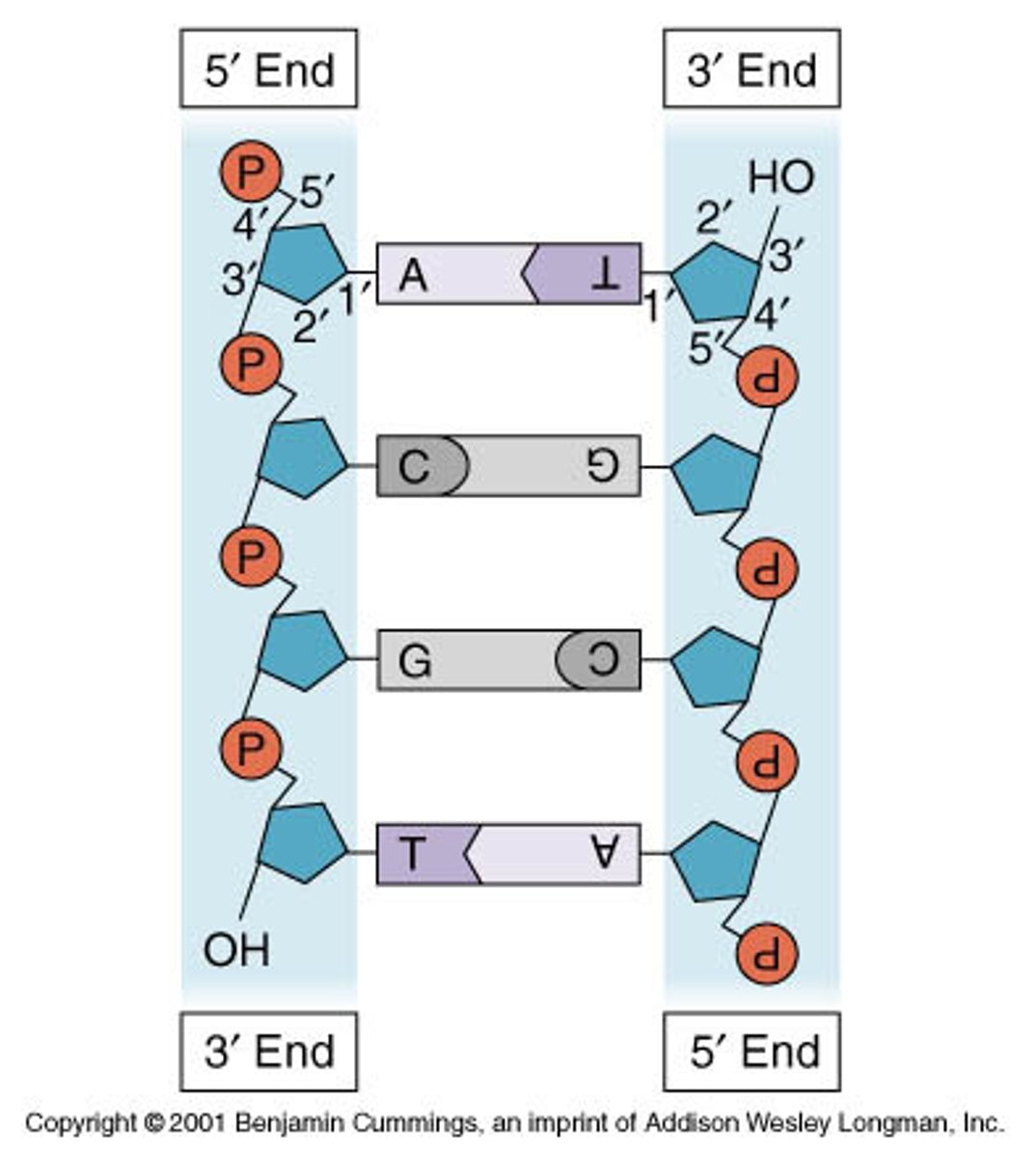
DNA
Genetic material of the cell.
Ribosomes
Particles within a cell that synthesize proteins. Prokaryotes & Eukaryotes both have them.
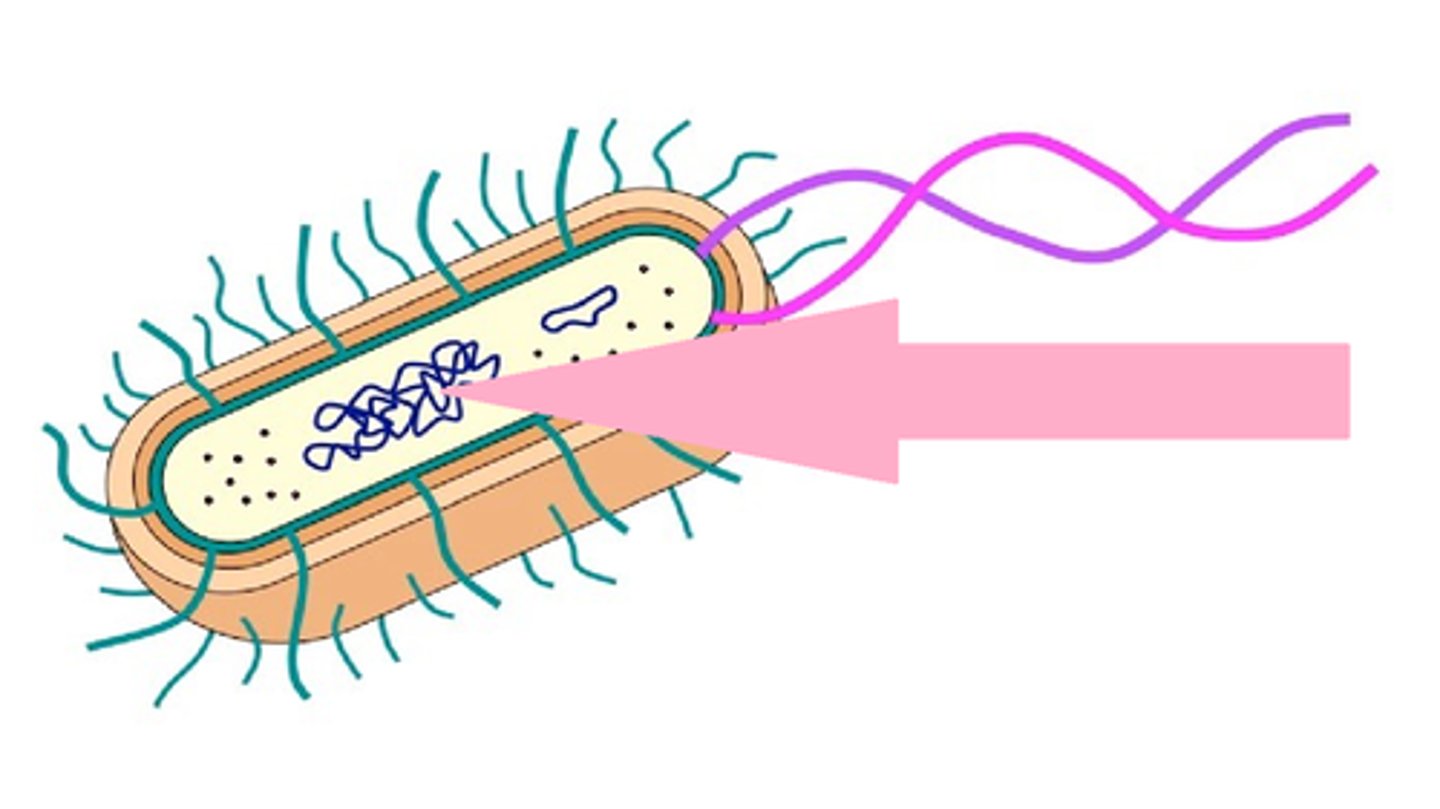
Nucleoid
Central part of a prokaryotic cell where DNA is found.
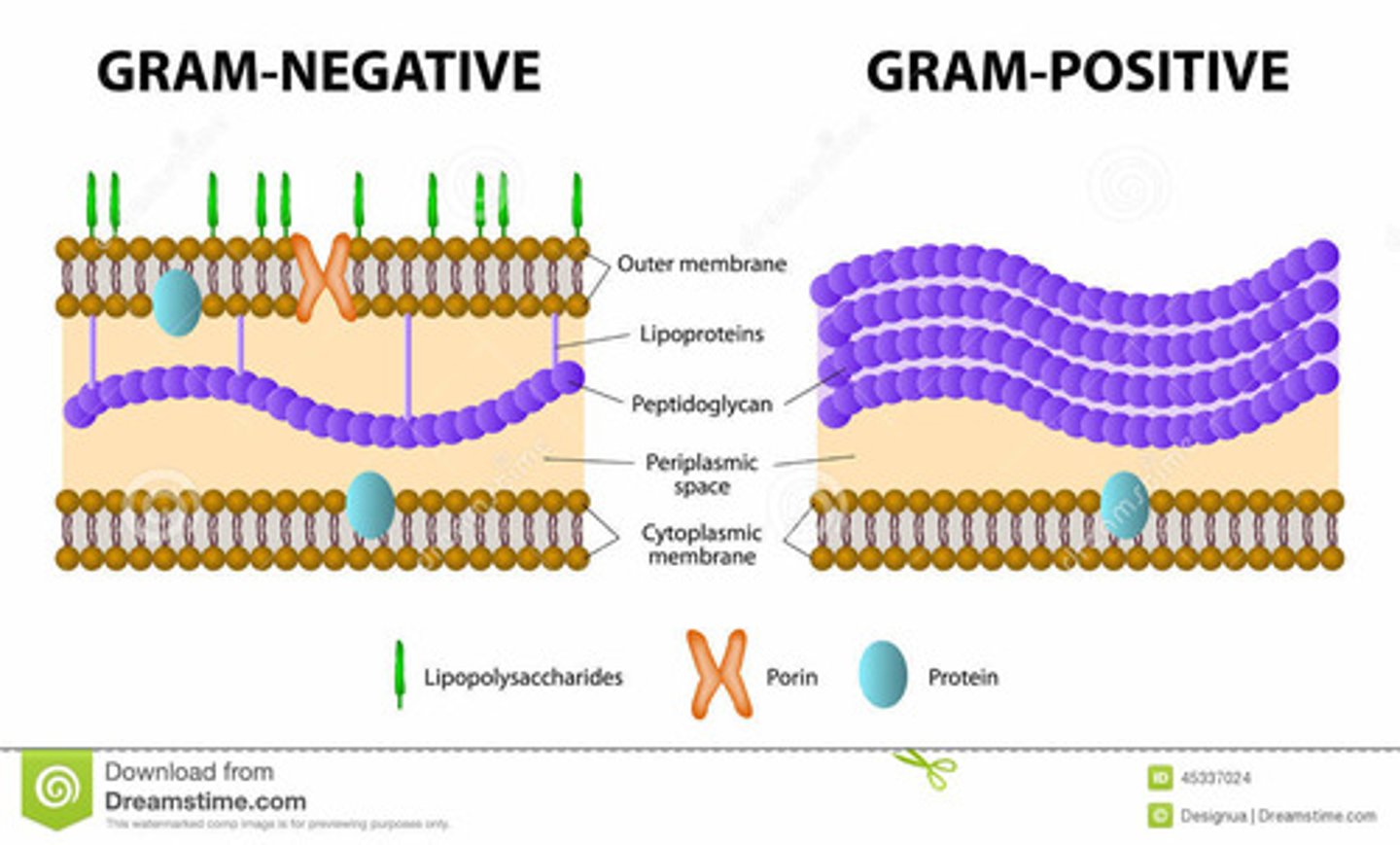
Cell Wall
Outer layer that provides protection and maintains shape generally only plants, fungi, algae, most bacteria, and archaea have this.
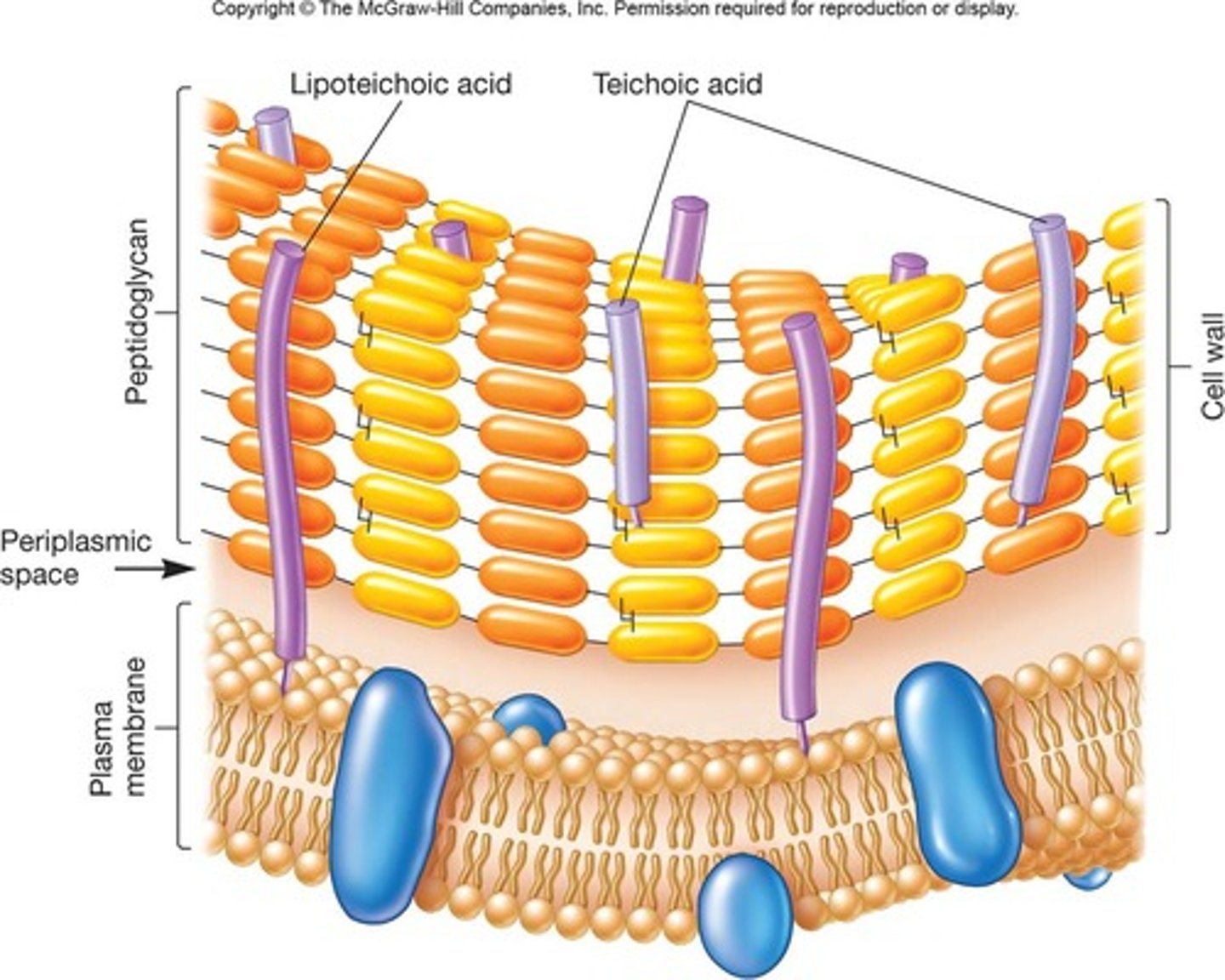
Peptidoglycan
Material in the cell wall of bacteria, comprised of sugars and amino acids.
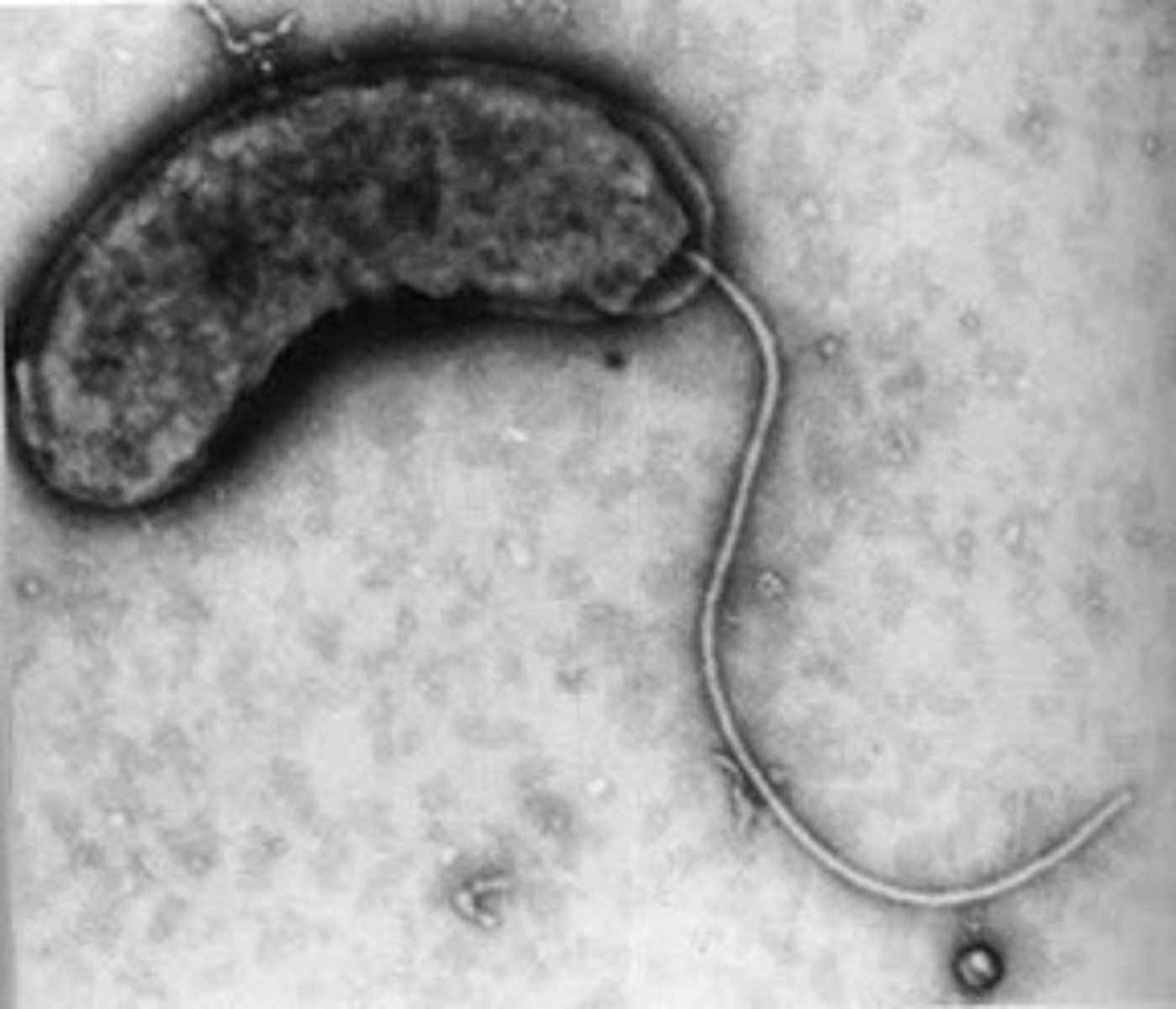
Flagella
Hair-like appendage that protrudes from microbe used for locomotion
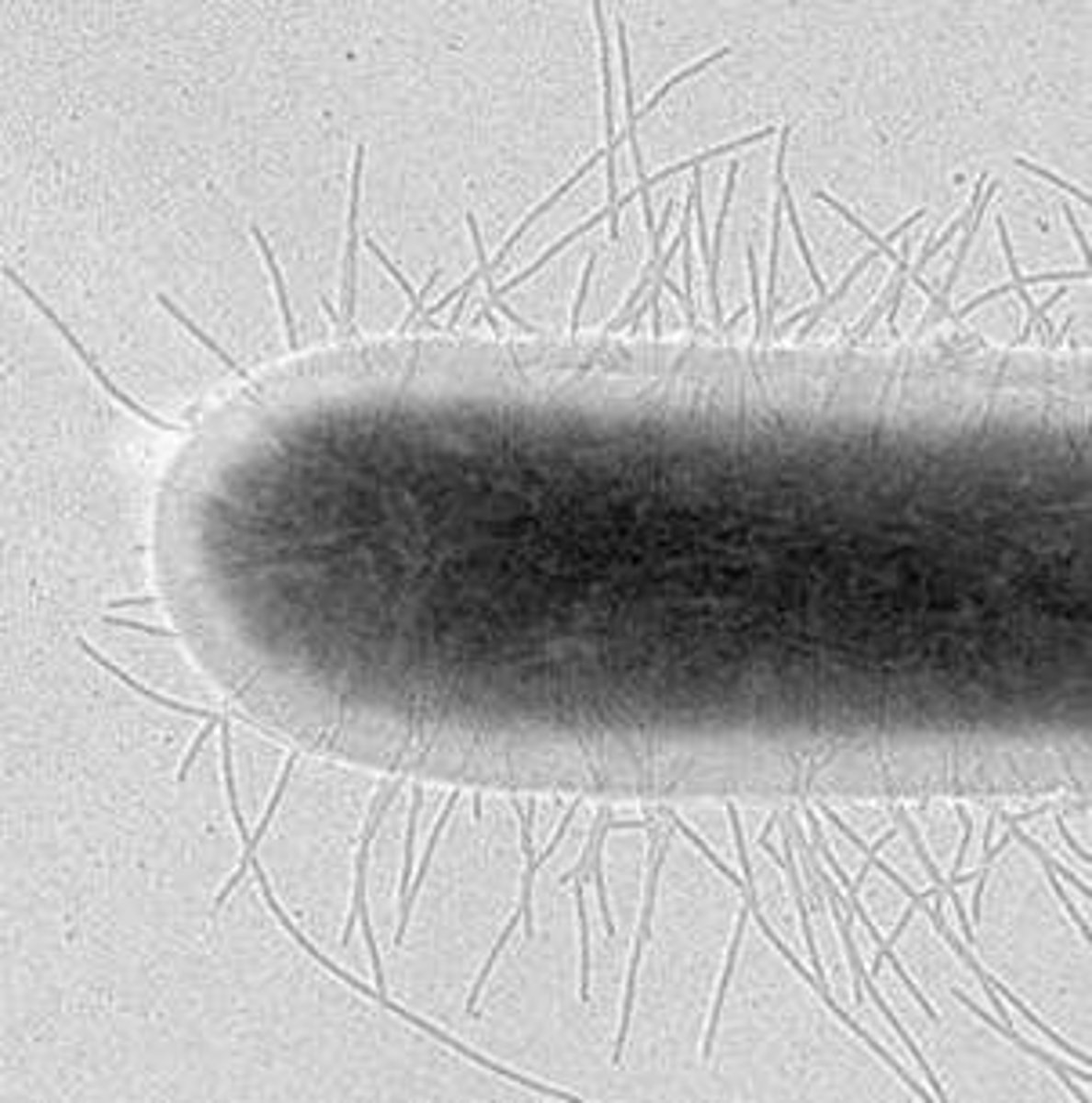
Pili
Hair-like structure on many bacteria and archaea that can mediate DNA transfer, adhesion, or biofilm formation
diameters ranging from 0.1-5.0 µm
Prokaryotic Cell Size
Cellular Transport
Process by which ions, molecules, and wastes move into, within, and out of cells.
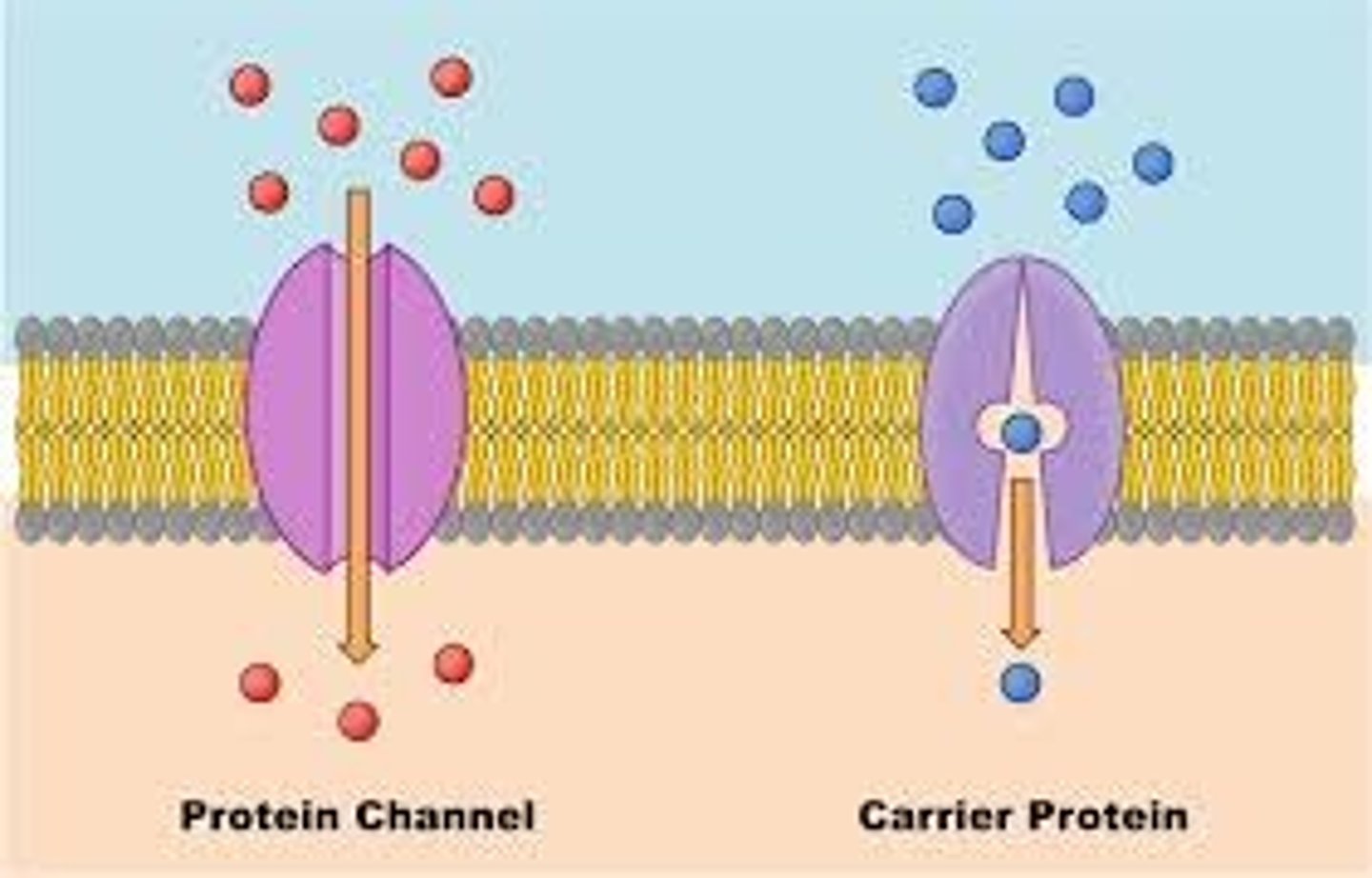
Form Follows Function
Principle: Within an organism, structures are formed in direct correlation to what they are meant to do
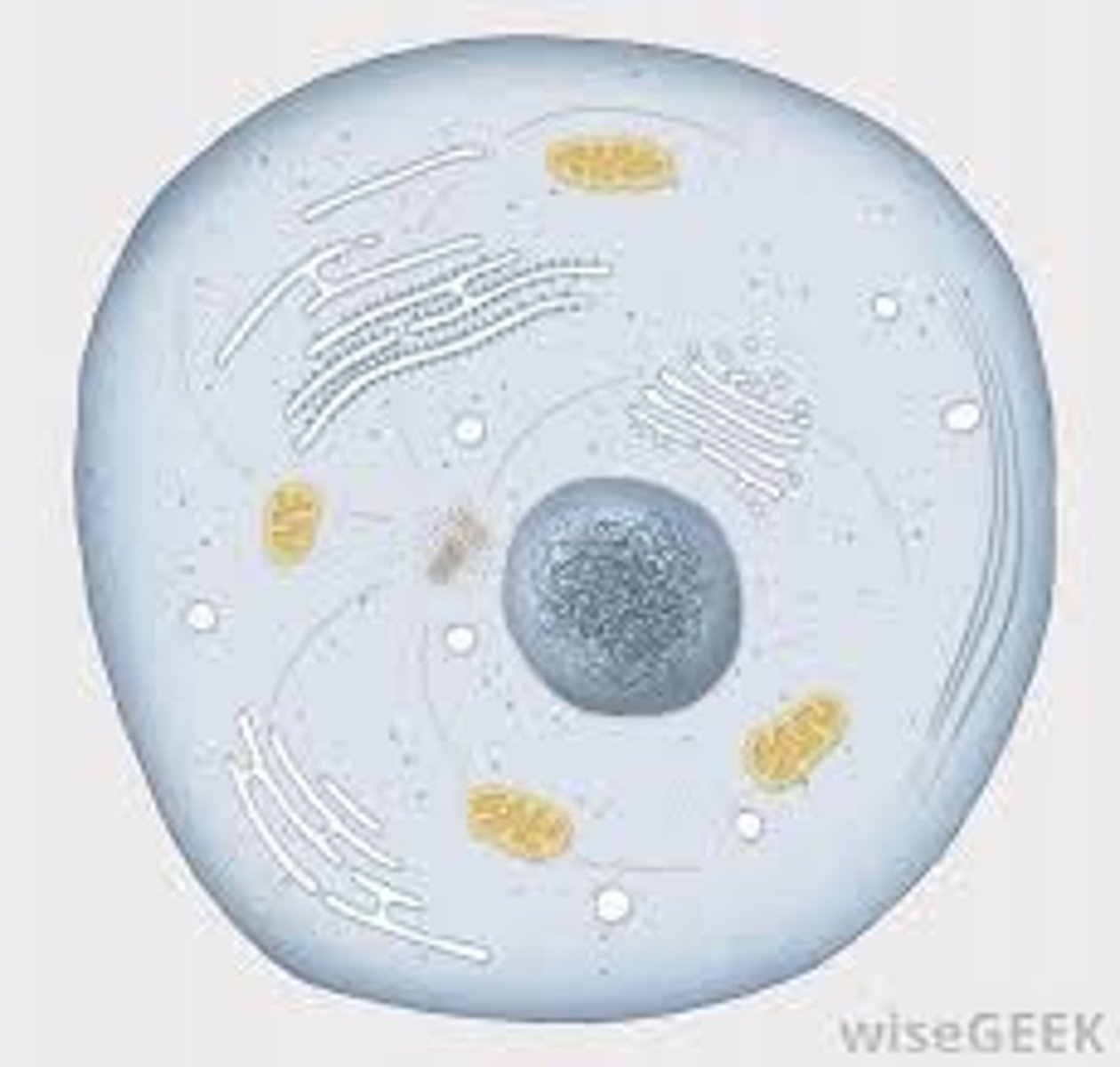
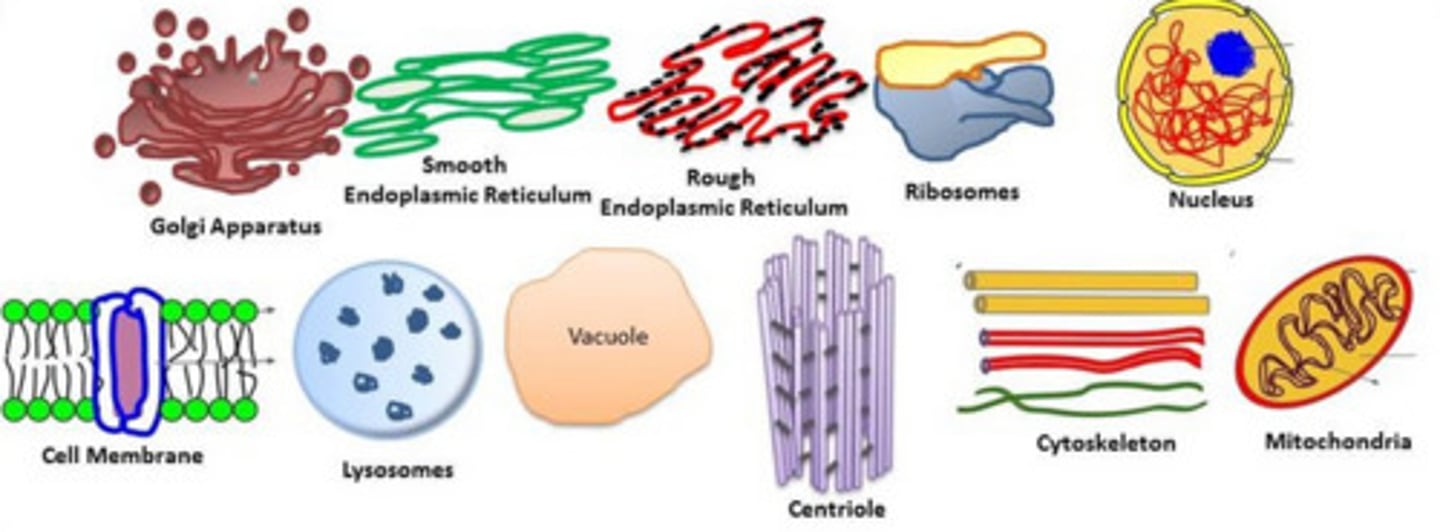
Organelles
Membrane-bound compartments in eukaryotic cells with specialized functions.
diameters ranging from 10-100 µm
Eukaryotic Cells size range
Logarithmic Scale
Scale where each unit is a multiple of the previous one, showing exponential growth.
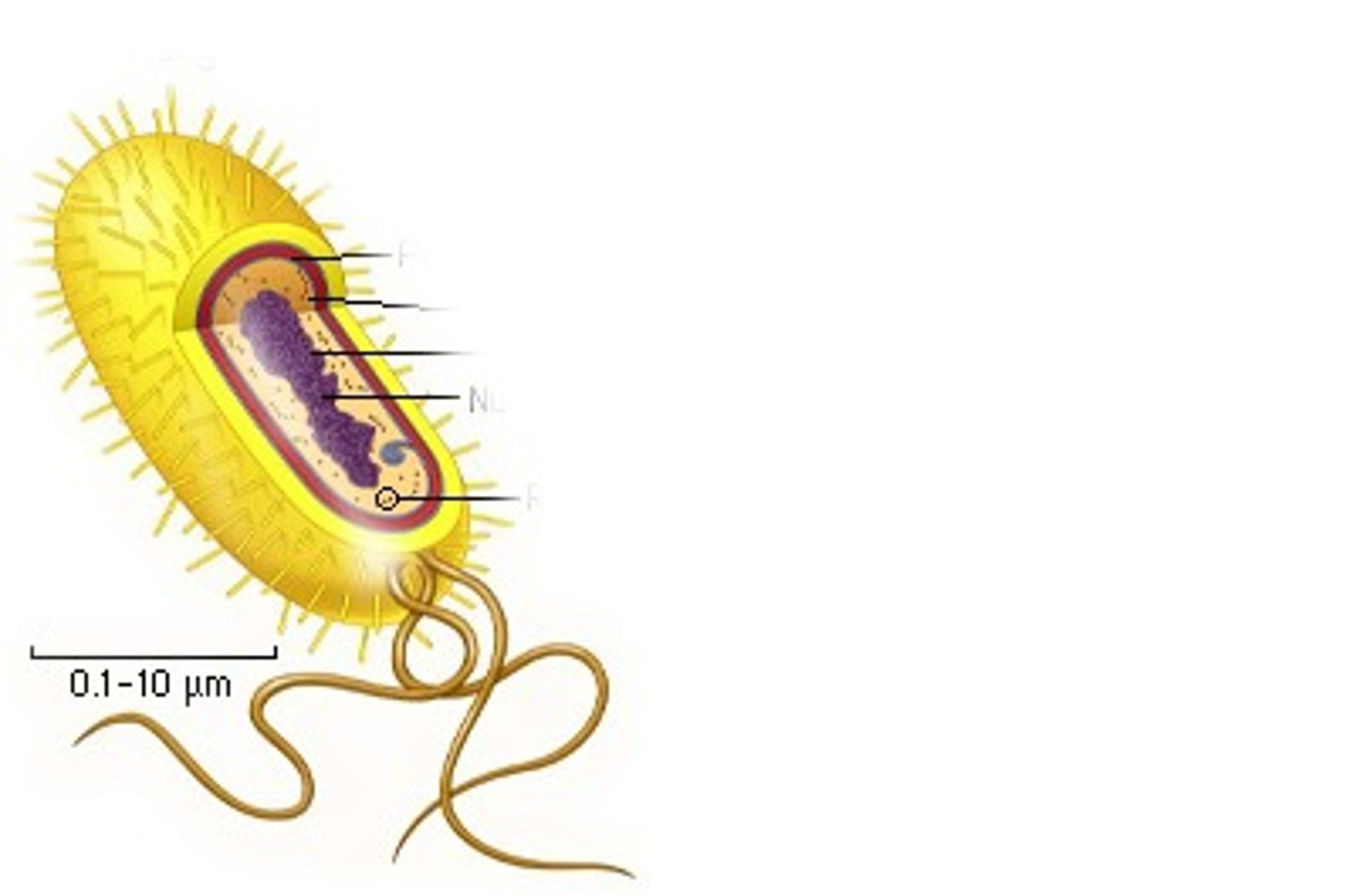
Prokaryotic
Cells without a true nucleus.
Eukaryotic
Cells possessing a true nucleus.
Pro
Prefix meaning 'before' in Greek.
Eu
Prefix meaning 'true' or 'good' in Greek.
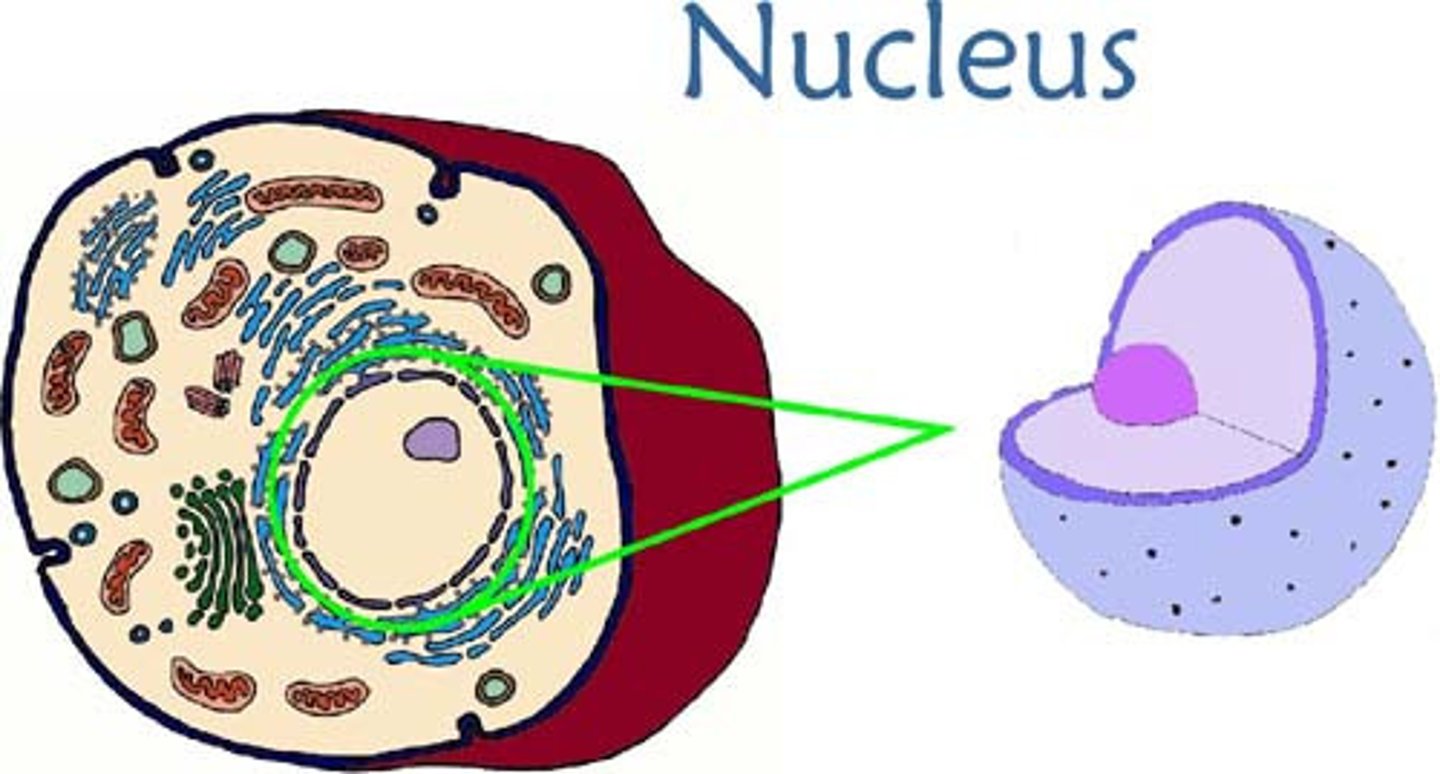
Nucleus
Membrane-bound organelle containing genetic material.
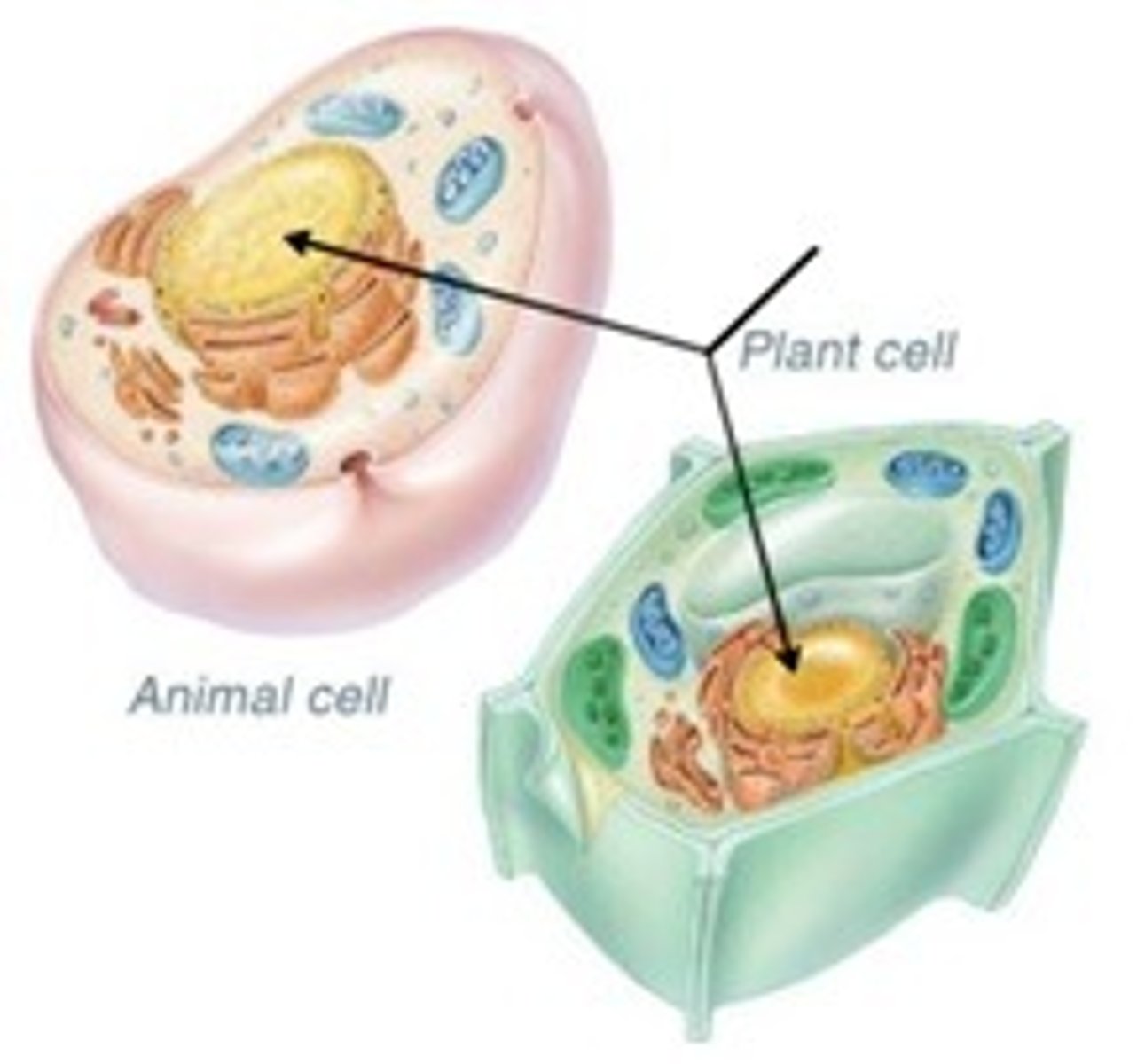
nucleolus
Spherical body within the nucleus of most eukaryotic cells, involved in the synthesis of ribosomal RNA
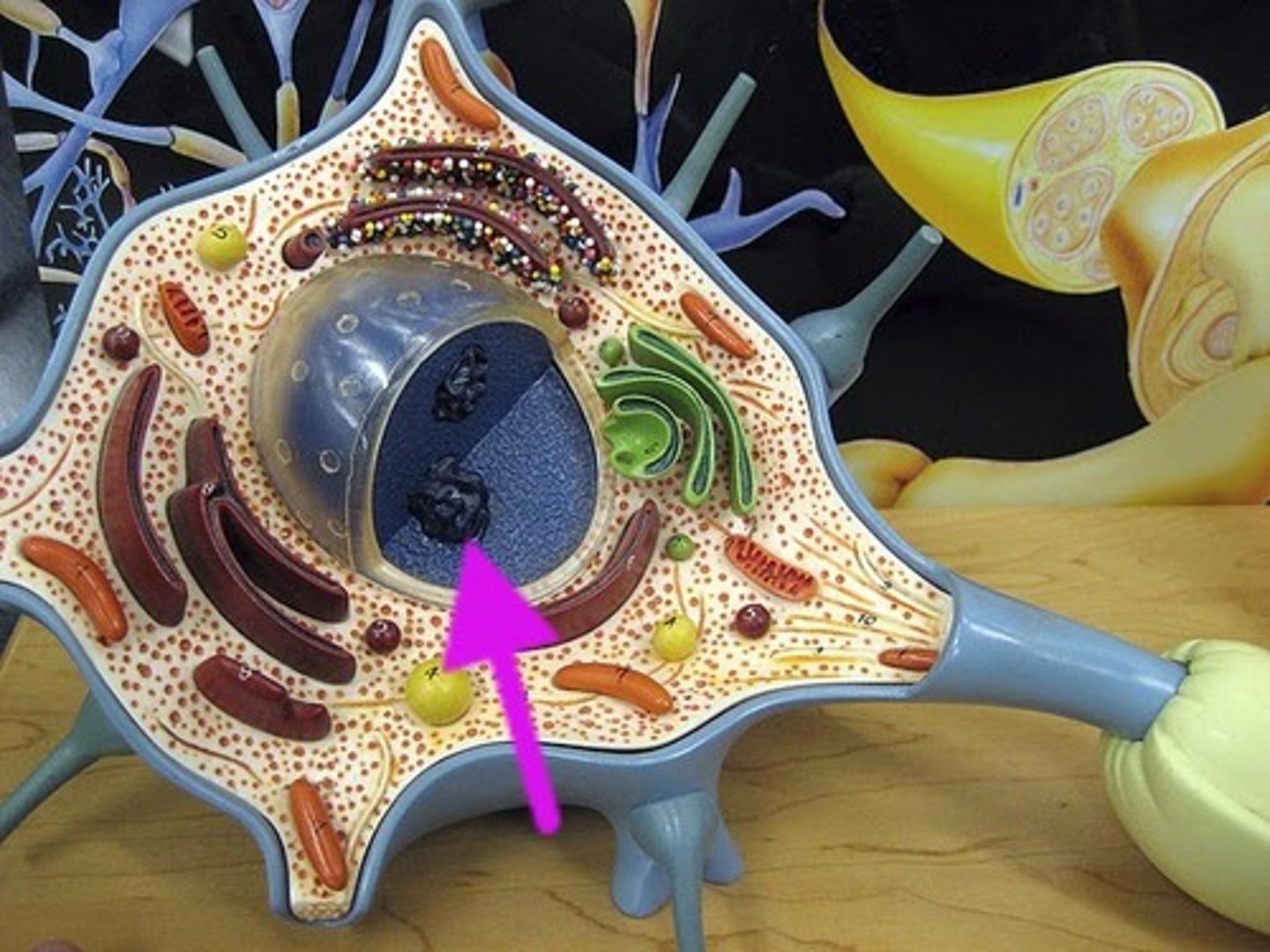
nucleus
"Karyose" comes from a Greek word which means "kernel," as in a kernel of grain. In biology, we use this word root to refer to the __________.