07 Plastics
1/58
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
59 Terms
Historical examples of plastics (2)
Goodyear (1839) and the rubbern (vulcanized caoutchouc)
Celluloid
Def: plastics
Materials whose components consist of such macromolecular organic compounds that are formed synthetically or by transformation of natural products
Plastically moldable under heat and pressure conditions
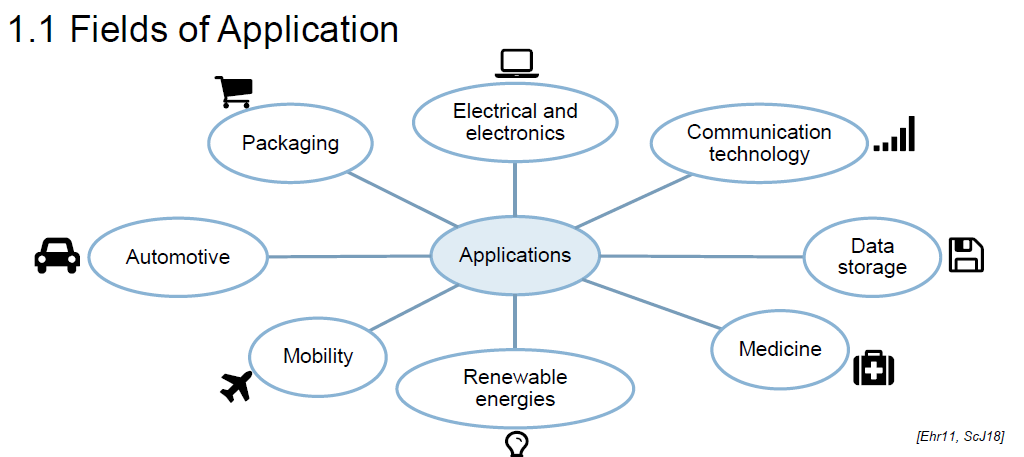
Name the fields of application of Plastics (8)
Packaging
Electrical and electronics
Communication technology
Automotive
Data storage
Mobility
Renewable energies
Medicine
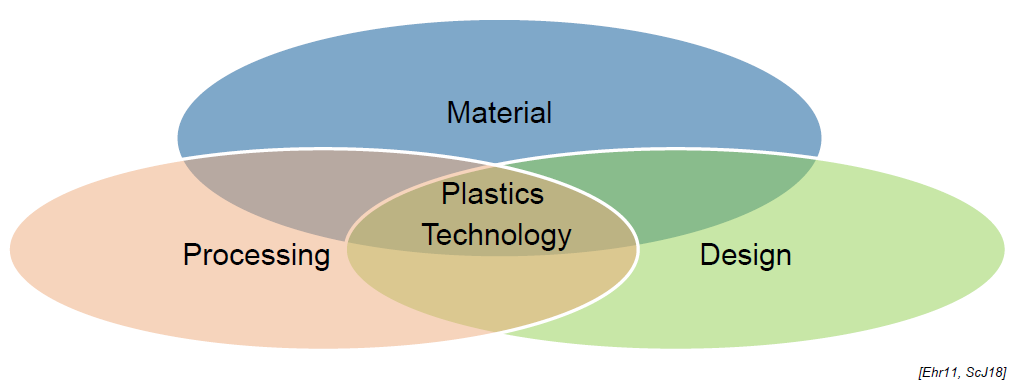
What aspects are related to Plastics Technology? (3)
Material
Processing
Design
What does Plastic Processing depend on? (5 + Ex)
Design requirements
Material properties
Quantity
Reinforcements?
Tool mold or production options
Ex: Vessels
It is not the same a HP vessel made to withstand up to 700 bar
than a tupper (also a vessel) to store food
What is comprised within Plastic Design? (5 + Ex)
Processing
Material
Function
Service requirements (mechanical, chemical and physical reqs.)
Installation space
Ex: Vessels
Pressure vessel carbon winding with different winding methods (polar, helical, hoop)
Injection molding rule (draft angles for demolding)
Organize following materials as a function of their density: Al, Fe, Ceramics, Plastics, Ti
Plastics (0.8 - 2.2 g cm-3) < Al < Ti < Fe < Ceramics
Characterize Plastics (10)
Adjustable spectrum of mechanical properties
Economic
Low processing temperatures
Good thermal insulation
Good electrical insulation
Variety of colors
High chemical resistance
Permeable
Recyclable
Lightweight
What is retardation when talking about polymers?
Analogous to the creep for solid materials
How is visco-elastic behavior described?
Mathematically through Maxwell’s spring-damper model for e.g. polymer melt
Through Kelvin’s mode
What are the main mechanisms of Polymer Synthesis? (3)
Polymerization
Polycondensation
Polyaddition
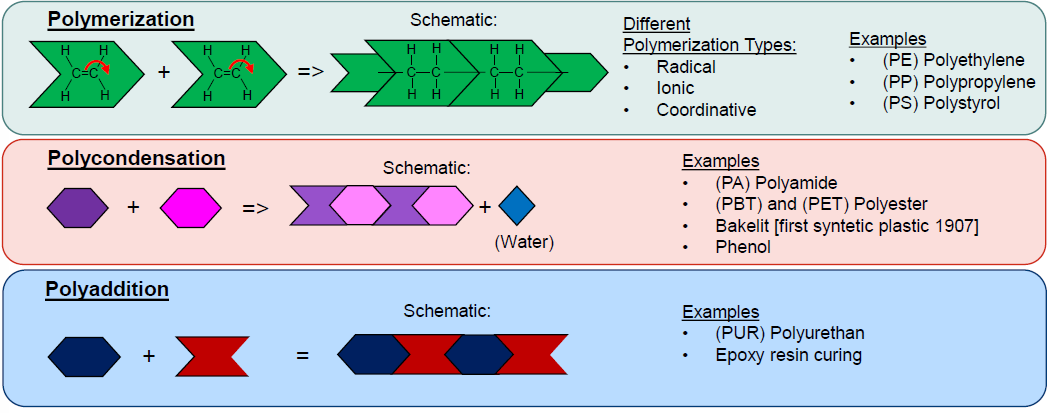
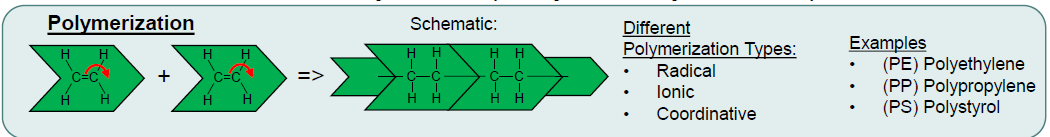
What is Polymerization? (2 + Ex)
Formation of polymers by linking monomers
Can be radiacal, ionic or coordinative
Ex:
Polyehtylene (PE)
Polypropylene (PP)
Polystyrene (PS)
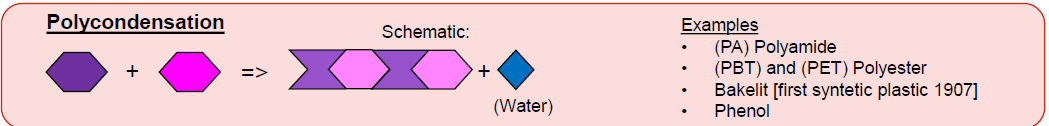
What is Polycondensation? (1 + Ex)
Reaction of monomers + release of small molecules
Ex:
Polyamide
Polyester (Polyethylene Terephthalate = PET)
PBT
Bakelite
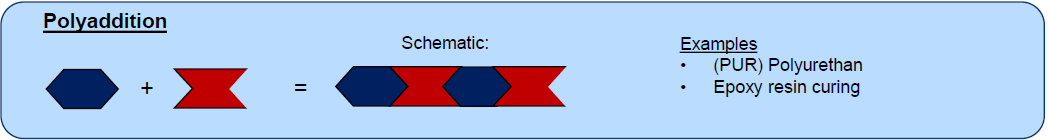
What is Polyaddition? (1 + Ex)
Monomer combination without by-product
Ex:
Polyurethane (PUR)
Epoxy resins
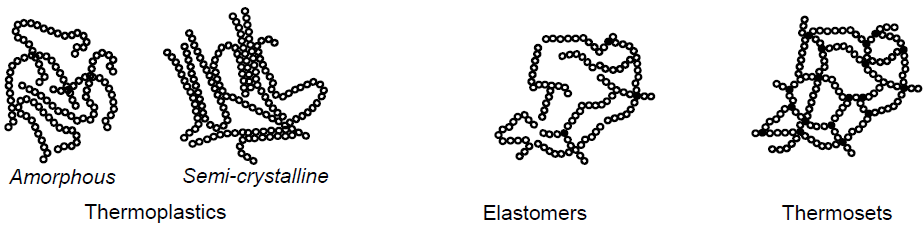
In which groups are plastics divided?
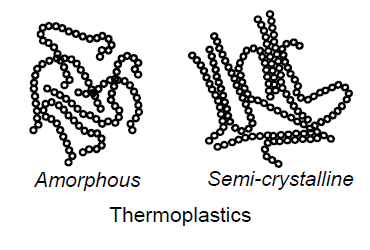
Thermoplastics: Amorphous and Semi-Crystalline
Elastomers
Thermosets
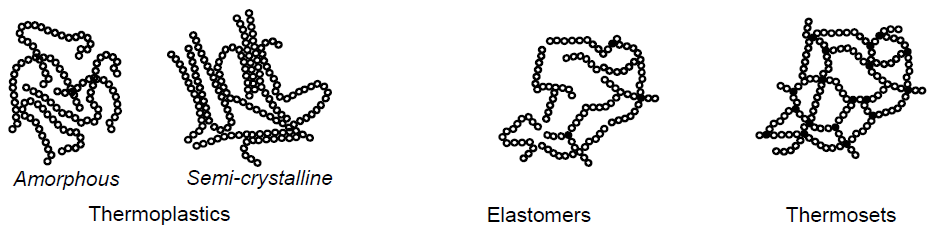
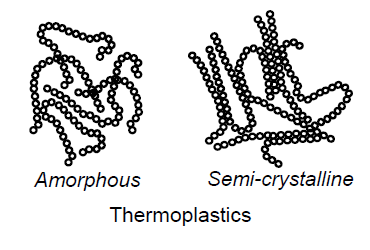
What are thermoplastics? (4)
Plastics with linear ore branched molecules, with almost no crosslinking
Amorphous: generally transparent
Semicrystalline: more visco-plastic
Can be melted as oft as desired
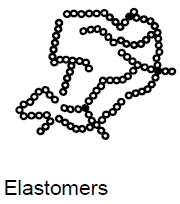
What are elastomers? (4)
Syn: rubber
Low degree of crosslinking
Cannot be melted without undergoing breakdown processes
Usually vulcanized
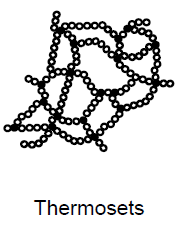
What are thermosets? (4)
Cured plasticas
Cannot be melted without undergoing breakdown processes
Syn: duromers
Constant material properties up to breakdown
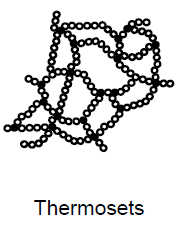
Order the plastic types as a function of the degree of crosslinking of their molecules
Thermoplastics < Elastomers < Thermosets
Which kind of intermolecular forces are present in plastics? (3)
Keesom-Forces (dipole-dipole force between permanent dipoles)
Debye-Forces (permanent dipole to induced dipole)
Van-der-Waals-Forces (induced dipole to induced dipole (between non-polar molecules))
Hydrogen bonds (stronger than Van-der-Waals)
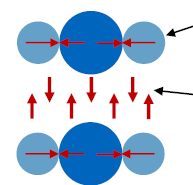
What defines a meltable substance?
Intramolecular forces > Intermolecular forces (able to change state before decomposing in its constituent elements)
What is copolymerization?
Polymers with more than one kind of monomers
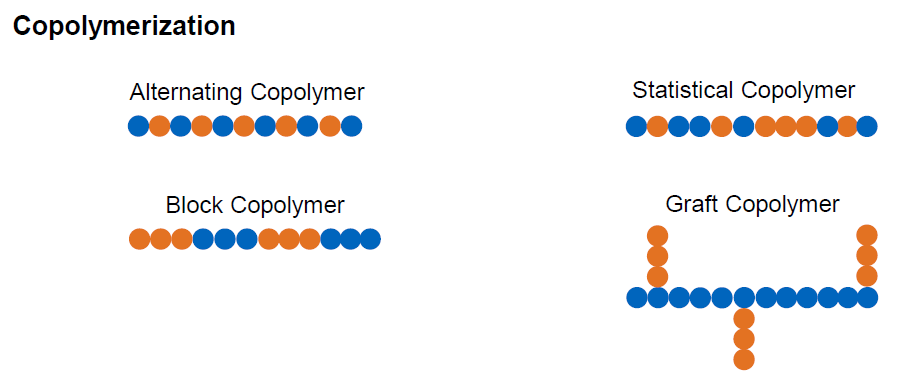
What are the types of copolymerization (4)
Alternating Copolymer
Statistical Copolymer
Block Copolymer
Graft Copolymer
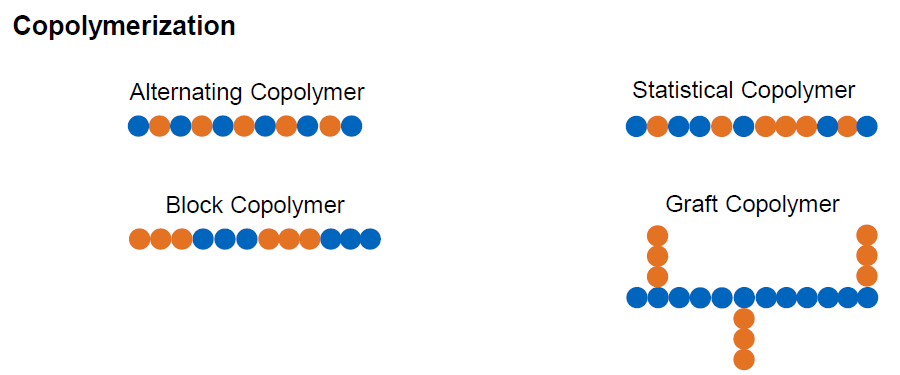
What are alternating copolymer?
Two monomers alternately lined up in the chain

What are statistical copolymer?
Random arrangement of monomers

What are block copolymer?
Monomers arranged in blocks of same monomers

What are Graft copolymers?
2-dimensional arrangement of monomers in blocks
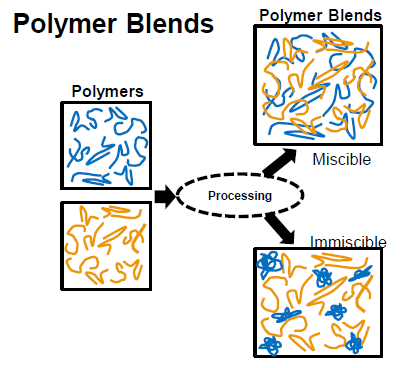
What is the difference of miscible and immiscible blends?
Miscible blends: homogeneous, single-phase, similar thermal properties
immiscible blends: heterogeneous, multi-phase, different thermal properties
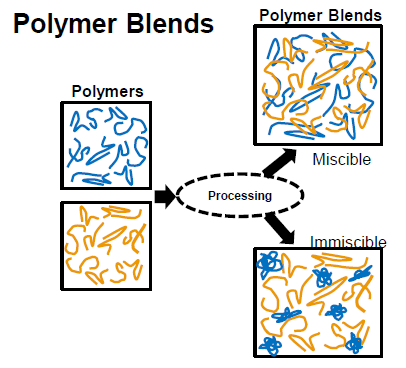
What are polymer blends used for?
To tailor polymers by enhancing desired properties depending on the application
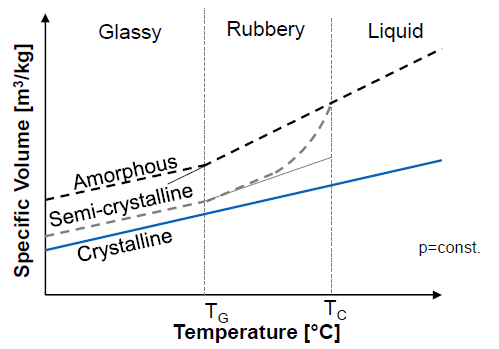
What is TG? (3)
Glass transition temperature (syn: softening temperature)
Polymer changes form flexible to glassy/brittle state
Border between rubbery and glassy
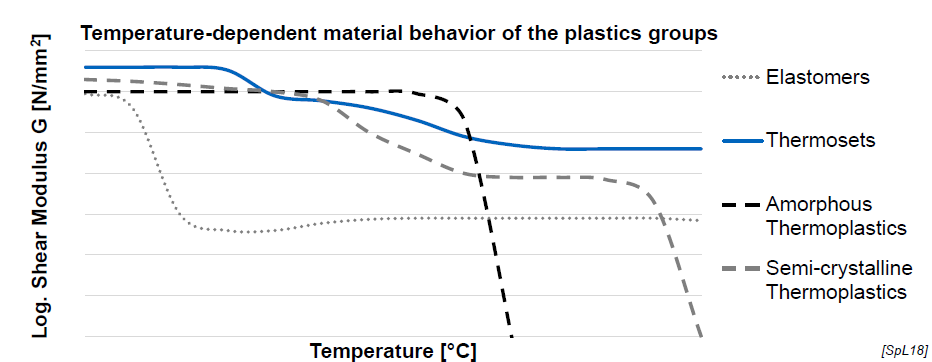
Mechanical Behavior of Plastics as a fct of Temperature (4)
Elastomers: stable after certain point
Thermosets: relatively stable
Amorphous thermoplastics: abrupt drop after certain temperature
Semicrystalline thermoplastics: two quick decrease points
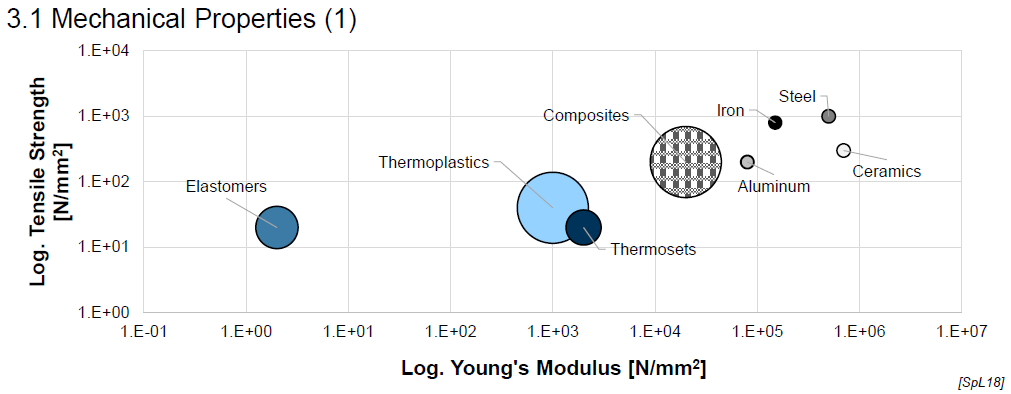
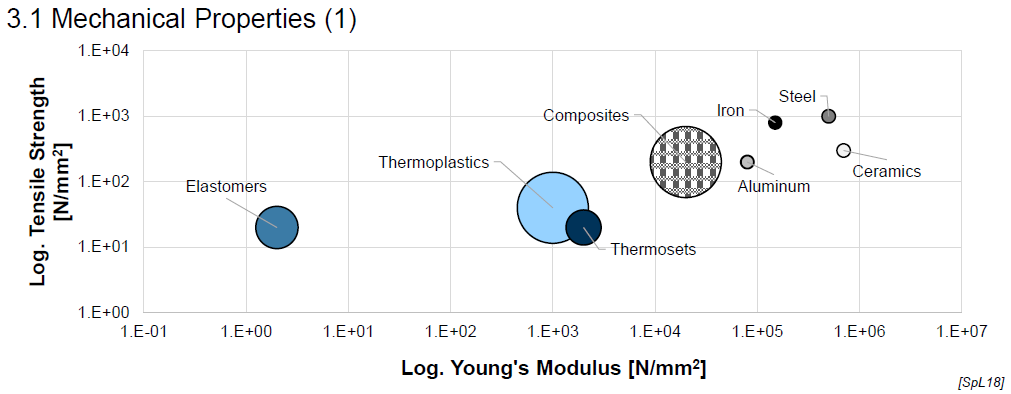
Mechanical Properties of Plastics (E-Modulus) (2)
Wide range of E-modulus
Tailorability
Mechanical Properties of Plastics (Stress-Strain-Diagram) (2)
Plastics are (in gneeral) extremely ductile
Amorphous Thermoplastics: brittle behavior due to random chain arrangement
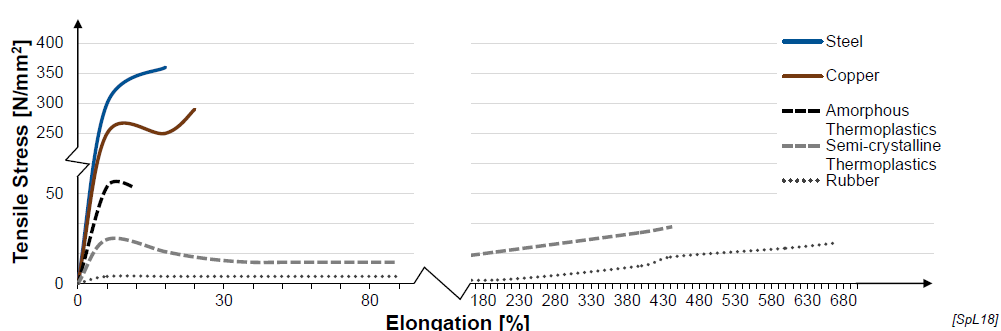
Thermal Properties of Plastics (2)
Poor thermal resistance (relative low service temperatures)
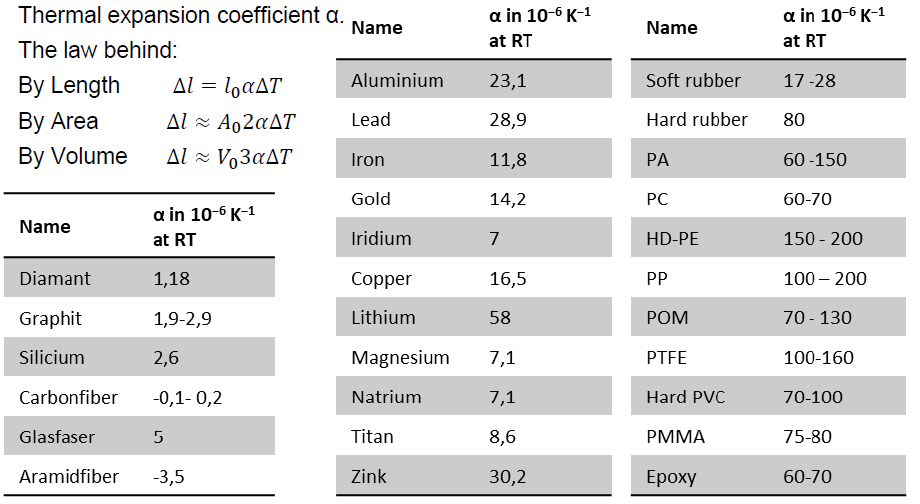
Very high thermal expansion
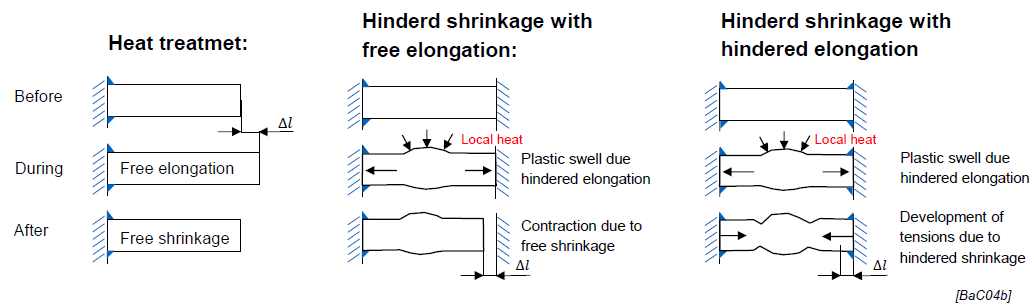
Thermal Properties of Plastics: Effects (1)
Formation of huge residual stresses due to high thermal expansion
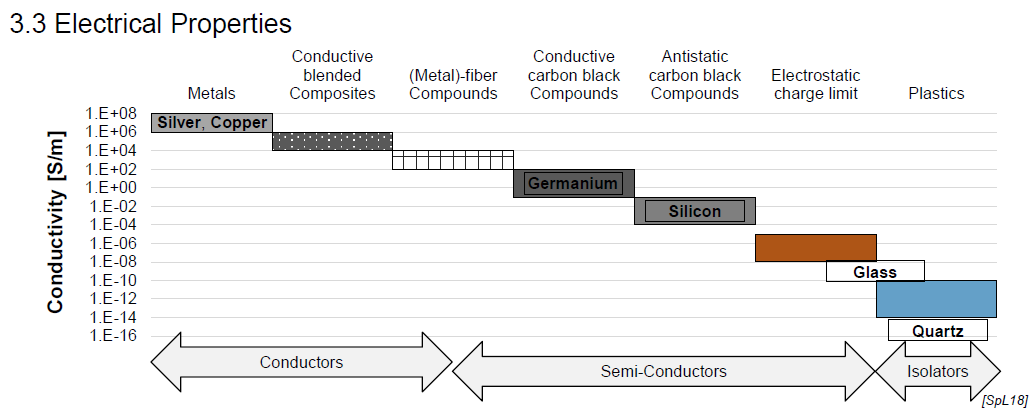
Electrical Properties of Plastics
Extremely low electrical conductivity → very good electrical insulator (e.g. good for lighting strinke protection)
How can plastics originate? (2)
Fossil-based
Bio-based
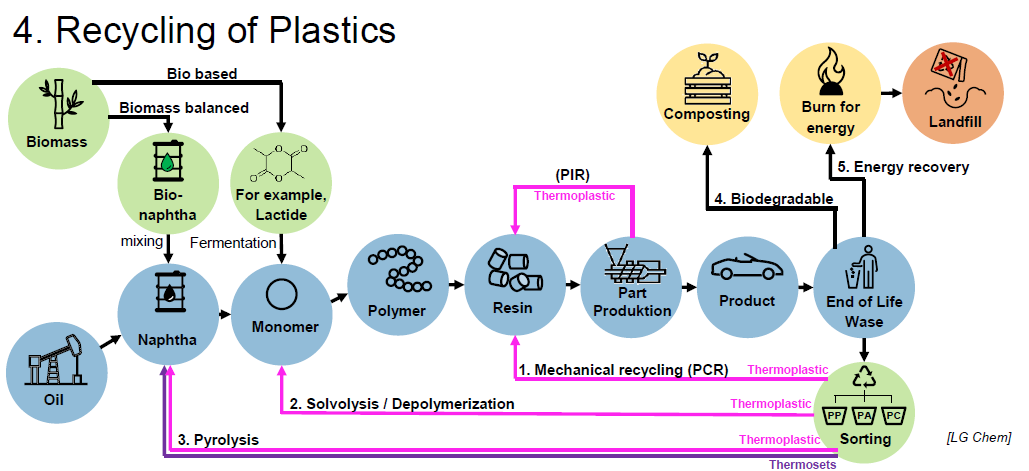
What are recycling methods suitable for plastics? (2)
Mechanical recycling (PCR) (Thermoplastic)
Depolymerization (Thermoplastic)
Pyrolisis (Thermoplasztic and Thermosets)
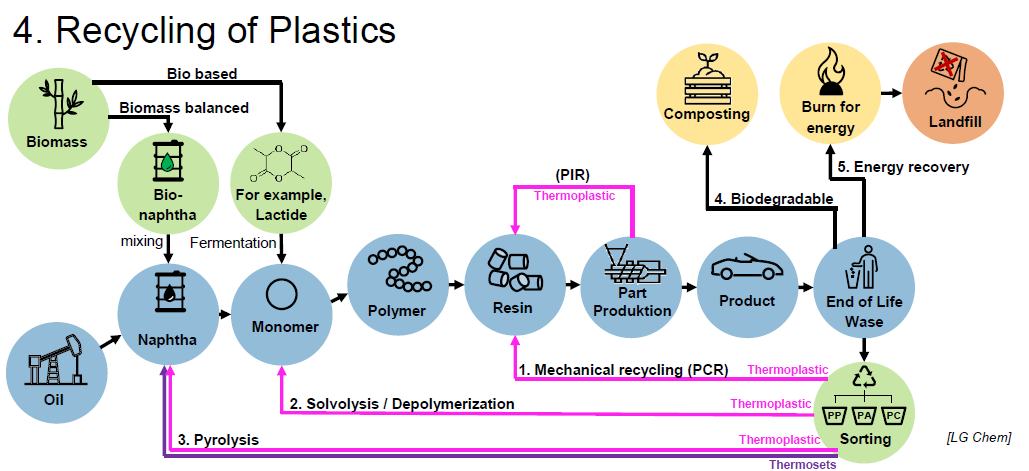
What End-of-Life options are there for plastics? (3)
Composting
Energy recovery (burning)
Landfill disposal
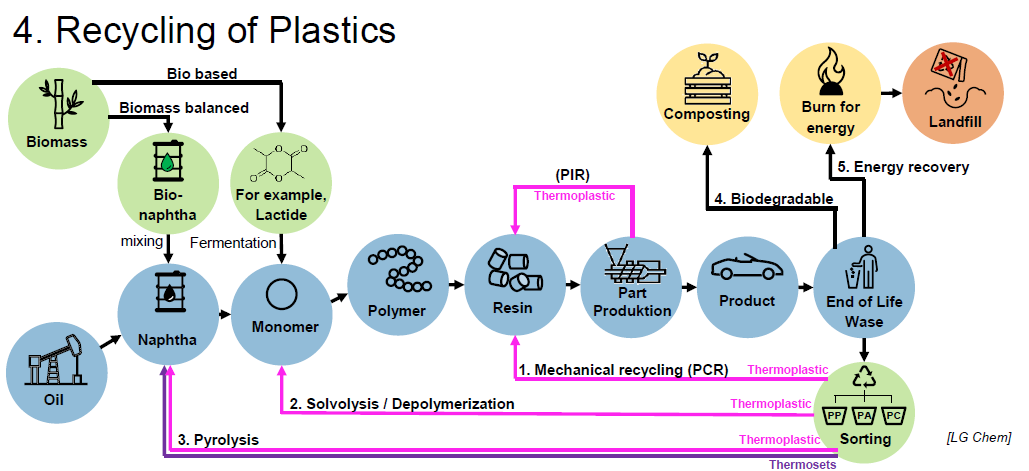
What is necessary for plastic recycling?
Sorting, at least in thermoplastics and thermosets
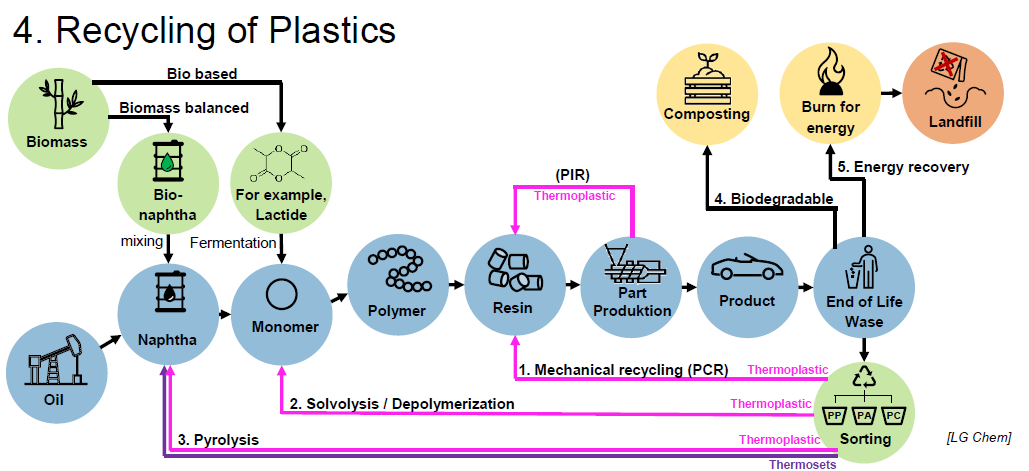
What are the steps of Mechanical Recycling? (4)
Shredding
Washing
Drying
Part Production
What is PIR? (3)
Post Industrial Recyclate
Made from rejected parts/offcuts
Low influence of quality
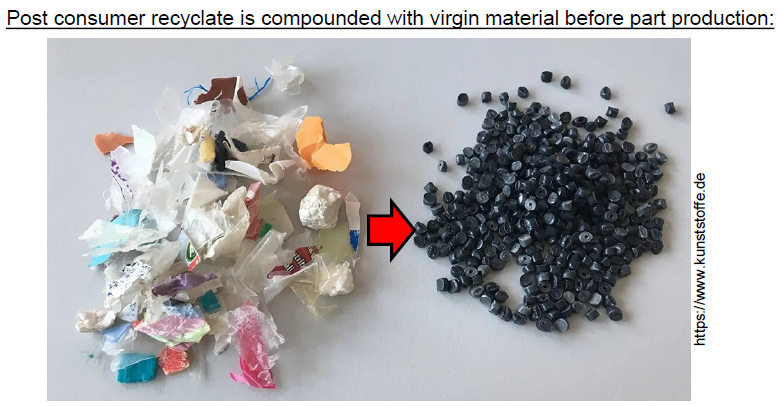

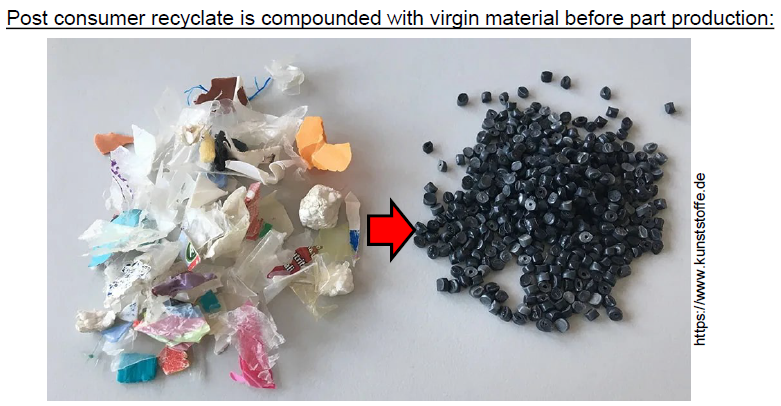
What is PCR? (4)
Post Consumer Recyclate
Polymer sorting
Different fabrication sources
High influence quality

What are the steps for Solvolysis/Depolymerization? (6)
Shredding
Solve
Filter
Precipitation
Drying
Monomer
For which kind of plastics is Solvolysis normally used?
Polycondensation plastics
What are the steps for Pyrolisis? (4)
Shredding
Pyrolisis
Condensation
Fractioning
Gas
Naphtha
Wax
What is Pyrolisis?
Heating up plastic past breakdown temperature in absence of oxygen to get shorter hydrocarbon chains
Order plastics according to their degree of complexity (3)
Vrigin Thermoplastics
Mixed Thermoplastics
FRP
Order recycling processes according to their degree of Utilization and Sustainability (3)
Energy Recovery (not classified as recycling bc it needs high tech filters for the exhaust gases)
Chemical Recycling and Pyrolisis
Mechanical Recycling
SQ: Name the definition of plastics
Materials whose components are macromolecular organic compounds
Formed synthetically or by transformation of natural products
Plastically moldable during processing under certain heat and pressure conditions
SQ: List three field of applications for plastics and give one explicit example in each case
Packaging
Automotive: vibration damping, car interior, insulation
Mobility: FRP, leightweight construction, vibration damping
Renewable energies: connections, organic solar cells, heat exchangers
Medicine: everyday devices like contact lenses, disposable syringes, dressing materials, artifical blood vessels…
Data storage: CD, etc
Communication technology: plastic sheating for message transmision
Electrical and electronics: insulator or sheting materials for cables, organic electronics
SQ: Name five important features of plastics
Leightweight (low density)
Adjustable spectrum of mechanical properties
Economically machined
Good thermal insulator
Good electrical insulator
High chemical resistance
SQ: Name all three types of polymer synthesis and explain one in detail
Polymerization: covalent, ionic or coordination bonding between monomers e.g. Polyehtelene
Polycondensation: reaction of monomers, releasing small molecules like water e.g. Polyamide or Polyester
Polyaddition: monomer combination without by-products e.g. Epoxy Resins
SQ: List all Plastic groups and name one distinctive characteristic of each
Thermosplastics: linear or branched with very low degree of interlocking. Can be melted as oft as desired
Amorphous
Semicrystalline
Elastomers: rubber-elastic materials formed through vulcanization. Low degree of crosslinking. Breakdown before melting
Thermosets: temperature stable up to thermal breakdown, need curing, cannot be melt after curing
SQ: Distinguish Thermoplastics of Thermosets bases on polymer structure
Thermoplastics: consist of linear or branched molecules that are not covalently bonded to each other via crosslinking reactions. This allows them to melt repeatedly
Thermosets: molecular threads that are closely crosslinked. This chemical reaction during curing makes them unable to be melted afterwards
SQ: Name on major advantage and disadvantages of plastics compared to metals
Advantage: Plastics have a considerably higher elongation at break compared to metals like steel or copper
Disadvantage: lower thermal resistance, with continuous usage temperatures ending where metals do not yet show temperature-dependent properties.
SQ: Explain the influence of temperature on plastics
Transition between brittle glassy state to viscous state at glass transition temperature TG
Thermal unstable properties (in general)
Extremely high thermal expansion coefficient
SQ: Explain why it is important to consider different material properties for the design of plastic components
Plastic processing and design depend on specific requirements and material properties, meaning different applications demand specific manufacturing processes.
Design considerations for plastics must focus on processing, material properties, and functionality, including mechanical, chemical, and physical requirements.
Understanding material properties like thermal expansion is crucial, especially when combining plastics with other materials (e.g., metals), to prevent issues like residual stresses and deformation.
SQ: Explain the difference between recycling of virgin and mixed thermoplastics
?