Marine Plants and Algae Contd- marine science
1/59
Earn XP
Description and Tags
need spring break
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
60 Terms
Photoynthesis Formula
carbon dioxide + water —>light and chlorophyl—> glucose + oxygen
Diatom
What type of algae that sometimes connects in chains?
__ keep growing until they run out of a limiting resource like nitrogen or phosphorus
plankton
Areas of upwelling because the nutrients fuels their spread
Where do algae blooms occur?
Support a strong food web
How can algae blooms be beneficial?
During spring, diatom blooms in polar areas as water warms and sunlight increases, supporting swarms of krill, which attract annually attract migrating whales and other creaures to feed
How can diatom growth be beneficial to polar areas?
Harmful Algae Blooms (HAB)
Occur when a bloom has negative affects on the ecosystem
The algae secrete brevatoxins that can bioaccumulate or cause fish death, which depletes the oxygen do to the e high amount of decomposition and blocks sunlight to organisms can’t growth/waters cool
What causes Harmful Algae Blooms?
Karenia brevis
What toxin is responsible for Red Tide?
Respitory issues in humans
Cause and Effect of Red Tides: Brevatoxins from waves crashing in air result in…
Organisms such as dolphins, manatees, and turtles die
Cause and Effect of Red Tides: Because animals are trapped in the aquatic environment…
seafood unsafe to eat
Cause and Effect of Red Tides: the animals in seafood accumulate brevatoxins making….
massive fish kills
Cause and Effect of Red Tides: Fish don’t have oxygen because the microbes take it all in, causing…
No, not directly correlated. However, if the pollution is close to the ocean, there is more of a possibility of an influence.
Does land-based pollution cause FL red Tide?
Provide habitat and structure (including nursery habitats)
Major source of food
Produce oxygen
Absorb carbon dioxide and store it (blue carbon)
How are marine plants and and macroalgae growth in the seafloor important?
Nursery Habitats
places for young marine species to safely grow into adulthood
Blue Carbon
any carbon stored by the ocean
macroalgae
Seaweed is the nickname for ___
Macroalgae
refers to seaweeds that are visible to the naked eye
red, brown, green
Types of macroalgae
epiphytes
What are macroalgae hosts of?
Calcified
Hardened by deposition of or conversion into calcium carbonate
Epiphytes
tiny organisms living attached to seaweed
yes
Can seaweed be calcified?
Many are eaten by humans, some toxic, some unpalatable as a defense mechanism; if not controlled, they can smother coral reefs due to fast growth
Are seaweed harmless or cause harm? How?
Kelp
organisms that form algae dense forests off the West cost of the US and are home to Californian and Alaskan sea otters
Seaweed are heavily grazed on by urchines who are kept under control by sea otters, whoneeded the seaweed for a protected home
Describe the ecosystem of the kelp forests
30
How many species of kelp are there?
Cold, nutrient rich water OR shallow sunlit water; rocky bottom so holdfasts can attach
Conditions for kelp to grow
Giant Kelp
Largest and fastest growing seaweed that grow 100+ meters tall and is dominant along the California coast
Has multiple air bladders and blades along the stripe
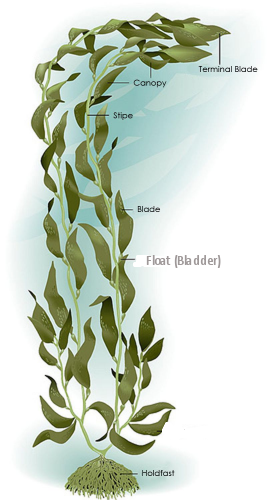
Describe the distinguishing anatomy of a giant kelp
Bull Kelp
A seaweed that grows 30-60 ft tall and is the dominant kelp along the Oregon and Alaskan coastline
Has a single stipe and bulb with multiple blades
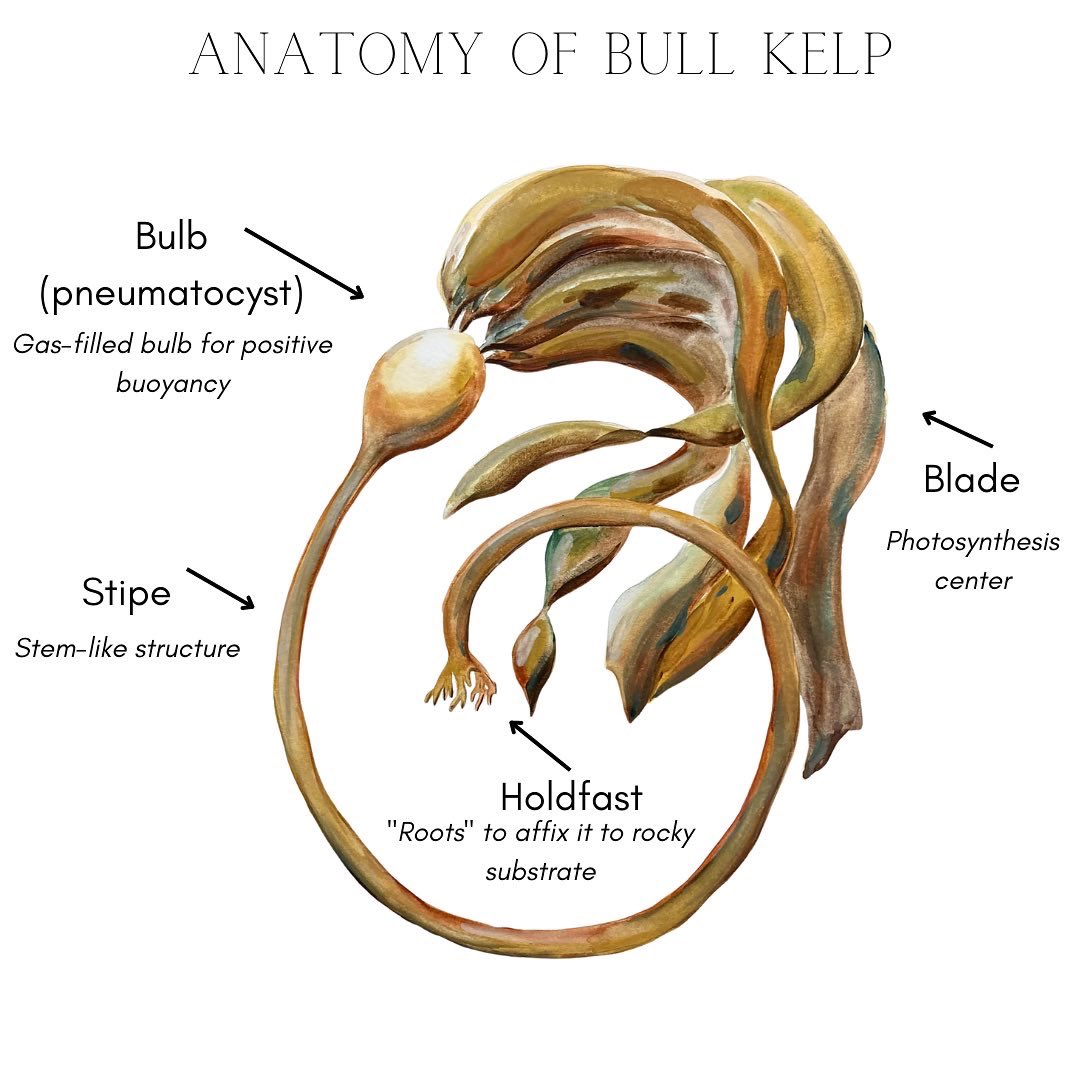
Describe the distinguishing anatomy of a bull kelp
Mangroves
A tree plant adapted to live in salty, brackish water in the intertidal zone at subtropical and tropical latitudes
A high tide, many species take shelter in mangrove roots and at low tide, some species forced out of mangroves
How does tide affect the marine use of mangroves?
protect coastlines from storm erosion (surge, winds, etc) and regular erosion over time and provide habitat for many organisms above and below waters
Importance of mangroves
Roots provide structure for epiphytes to attach
How are the roots of the mangrove tree used?
No, only attach on surface of roots to filter water
Are epiphytes parastitic?
Roots block and filter out salt from the water and their leaves excrete salt
What adaptations allow mangroves to thrive in conditions that would kill other plants?
55 worldwide; 4 in FL
How many species of magnroves are there worldwide? How many in FL?
No, can’t withstand freezing temps
Can mangroves survive polar conditions?
Red and black
Which mangroves species are most common in FL
Types of mangroves
Red and black
Red Mangroves
(rhizophora mangle) a type of mangrove tree that has large prop roost that extend into the water
Propagules are carried by currents until they take root in shallow mud
How do red mangroves reproduce?
Black Mangroves
(Avicennia germinas) a type of mangrove that grows on higher ground than reds and is submerged at highest tides
Have pneumatophores that stick up from the root to take in oxygen in shallow water and low tide (they close during high tide)
How do black mangroves take in oxygen if they are mostly submerged?
Seagrass
Not truly a grass, but a marine flowering plant that is found in shallow lagoons and bays, often near mangroves and coral reefs
By spreading pollen or spreading rhizome roots
How do seagrass reproduce?
Anchor the plant into substrate and absorb nutrients from sediment; prevent erosion
Seagrass Structure:
What are the roots for?
Flowers produce pollen that is carried by water currents
Seagrass Structure:
Flowers purpose
Run horizontally under sediment to hold in place and allow asexual reproduction
Seagrass Structure:
Rhizomes purpose
Helps water clarity in estuaries, absorb nutrients, trap sediments, crucial nursery habitat
Impact of Seagrass
Sun and sand
What type of climate is needed for seagrass to root and grow?
Prop Scars
Torn seagrasses as a result of boat motors
7
How many species of seagrass are in FL?
Manatee Grass
one of the most common seagrasses; cylindrical blades and grow up to 20 in
Turtle Grass
one of the most common seagrasses and most common in Caribbean; flat bladed grass up to 14 in
Salt Marsh Grasses
A grass found in coastal low-lying areas (commonly Gulf coast) that is a nursery habitat for 75% of fisheries species and is flooded + drained daily by tide
Act as a buffer to wave action and trap sediments
How do salt marsh grasses prevent erosion of the coastline?