Cognitive Development and Information Processing in Children
1/74
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
75 Terms
In which stage of Piaget's cognitive development is Clara if she uses imaginary play but fails conservation of liquid tasks?
Pre-operations
What is object permanence?
The understanding that objects continue to exist even when they cannot be seen.
At what age did Piaget claim there was no object permanence?
For the first 8 months.
What is the A-not-B error in Piaget's stages of object permanence?
A situation where a baby finds an object in location A but fails to find it when hidden in location B.
What is the violation of expectations paradigm?
A method used to test infants' understanding of object permanence by measuring their looking time at unexpected events.
What does the term 'working memory' refer to?
A system that holds and processes information temporarily for cognitive tasks.
What is the capacity of sensory memory?
Holds large amounts of information for a very brief period of time.
How long does unrehearsed information last in short-term memory?
10-15 seconds.
What are memory strategies that improve retention?
Rehearsal, organization, and elaboration.
What is the difference between mediation deficiency, production deficiency, and utilization deficiency?
Mediation deficiency: not utilizing strategies; Production deficiency: not producing strategies; Utilization deficiency: using strategies improperly.
What is metacognition?
Awareness and understanding of one's own thought processes.
What is the developmental course of self-regulation ability?
Improves significantly between ages 4-7.
What is autobiographical memory?
Memory of personal experiences and events.
What is infantile amnesia?
The inability to recall memories from early childhood, typically before age 2-3.
What did the Harvard Baby Music study demonstrate about infant memory?
Infants listen longer to familiarized melodies, indicating memory retention.
How does working memory capacity change with age?
It improves due to better neural development and experience.
What is the role of knowledge in expertise?
A knowledge base increases performance within a domain of expertise.
What is the significance of Piaget's A-not-B task?
It illustrates the development of object permanence and memory in infants.
What are the techniques for processing new information?
Rehearsal, attention, and sensory input.
What happens to memory strategies as children age?
Children become more adept at using strategies effectively.
What is the impact of neural development on memory?
It enhances processing speed and efficiency.
What is the purpose of rehearsal in memory?
To help comprehend and store information permanently.
What is the difference between short-term memory and working memory?
Short-term memory holds information temporarily, while working memory involves processing and manipulating that information.
What is the function of the central executive in memory processing?
It acts as the operating system that manages attention and coordinates information.
What is the significance of the study by Simcock and Hayne (2002) regarding preverbal memory?
It tested children's ability to recall events from early childhood, showing that early memories may be inaccessible without language.
What is the main finding regarding memory improvement with age?
Memory becomes more verbal and organized as children grow older.
What perspective compares the operations of a computer to the workings of the human mind?
The information-processing perspective.
What are the three processing units in the Multistore Model?
Sensory store, short-term store (STS), and long-term store (LTS).
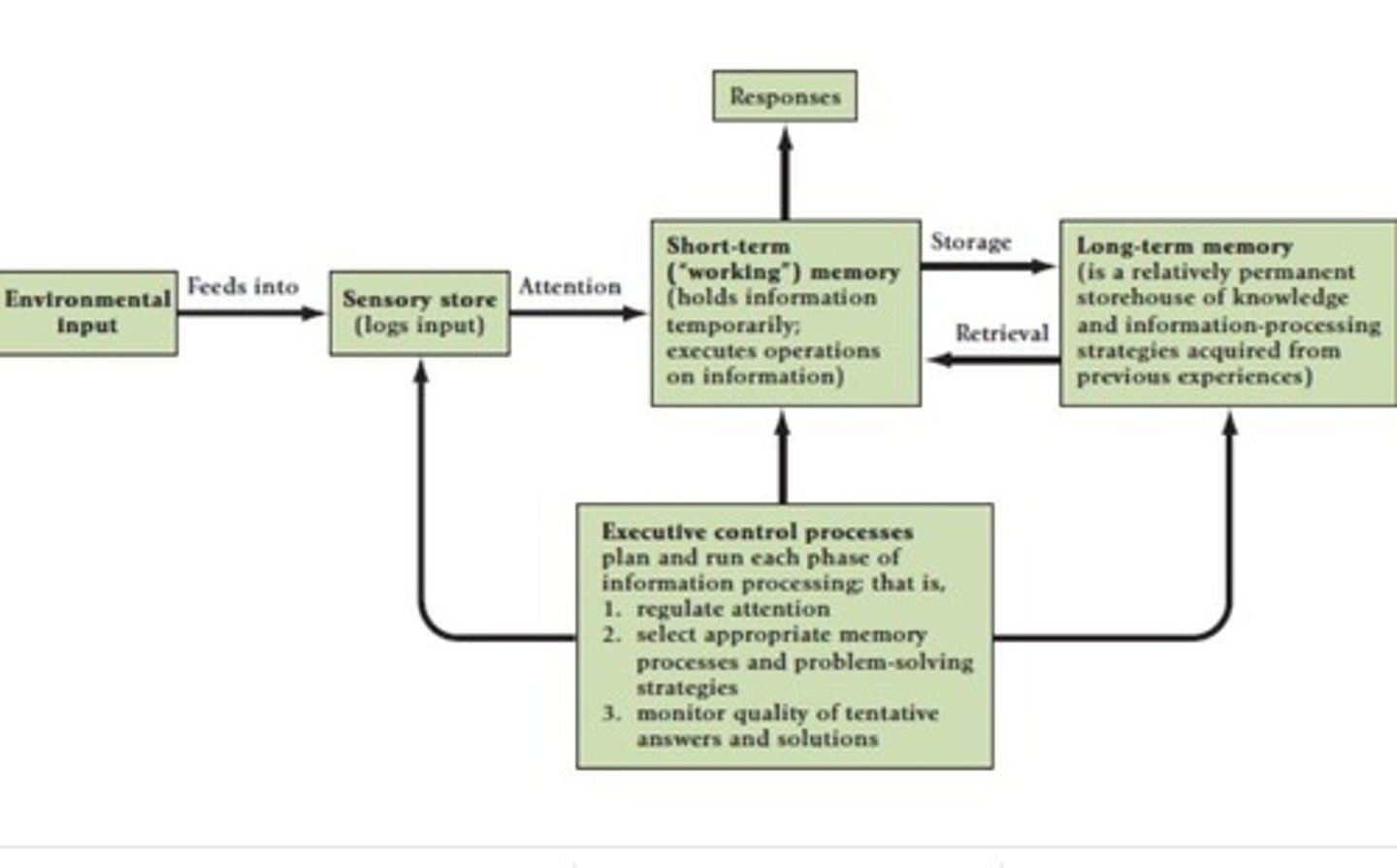
What is the function of the sensory store?
It is the first information-processing store where stimuli are noticed and briefly available for further processing.
What is the role of the short-term store (STS)?
It temporarily stores information and allows for manipulation of that information.
What does the long-term store (LTS) do?
It stores information that has been examined and interpreted for future use.
What is executive function in the context of memory?
A set of self-regulated processes involved in planning and executing strategies based on information gathered from long-term memory.
What is attention in the context of memory?
The process of selecting which stimuli to detect or work on.
Define inhibitory control.
A form of self-regulation that allows individuals to purposely choose not to attend to certain information.
What is set-shifting?
The ability to move from one strategy to another.
What is memory span?
A measure of the amount of information that can be held in the short-term store.
What is span of apprehension?
The number of items that can be kept in mind at one time without mental effort to store the information.
What are memory strategies?
Effortful techniques used to improve memory, such as rehearsal, organization, and elaboration.
What is rehearsal in memory strategies?
A strategy for remembering that involves repeating the items one is trying to retain.
What does semantically organized mean in memory strategies?
Grouping or classifying stimuli into meaningful clusters to aid retention.
What is elaboration in memory strategies?
Adding something to or creating meaningful links between bits of information to aid retention.
What are production deficiencies?
Failures to spontaneously generate and use known strategies that could improve learning and memory.
What is utilization deficiency?
Failure to benefit from effective strategies that one has spontaneously produced.
What is transfer utilization deficiency?
When the mental effort needed to execute a strategy leaves no cognitive resources to transfer that strategy to a new task.
What is the adaptive strategy choice model?
A model describing how strategies change over time, with multiple strategies competing for use.
Define metacognition.
Knowledge about cognition and the regulation of cognitive activities.
What is attention span?
The capacity for sustaining attention to a particular stimulus or activity.
What is selective attention?
The capacity to focus on task-relevant aspects of experience while ignoring distractions.
What is event memory?
Long-term memory for events.
What are autobiographical memories?
Memories for important experiences or events that have happened to the individual.
What is source-monitoring theory?
The process of determining whether the source of one's memories was internal or external.
What is analogical reasoning?
Reasoning that involves using something already known to help reason about something not yet known.
What does cardinality refer to in math skills?
The principle specifying that the last number in a counting sequence indicates the number of items in a set.
What is fuzzy-trace theory?
A dual-process theory of memory where event details and the gist of the event are encoded simultaneously.
What does developmental cognitive neuroscience study?
The study of cognitive development incorporating brain growth and processing.
What analogy do information-processing theorists use to describe the mind?
They compare the mind to a computer with information flowing through a limited-capacity system.
What are the three components of the multistore model?
Sensory register, short-term store (STS), and long-term store (LTS).
What is executive function in cognitive processes?
The active processes that plan, monitor, and control all phases of information processing.
How does age affect information-processing capacity?
Age differences in memory span and span of apprehension indicate substantial differences in short-term store capacity.
What are some frequently used memory strategies?
Rehearsal, semantic organization, and elaboration.
What is a production deficiency in memory strategies?
When children fail to produce a strategy spontaneously but can do so when instructed.
What is a utilization deficiency?
When children experience little or no benefit from using a new strategy.
What influences effective strategy choice in children?
The cognitive resources needed and children's metacognition about their own strategy use.
How does attention span change with age?
Attention spans increase dramatically, becoming more planful and selective.
What role do parents play in the development of autobiographical memory?
They help children recall experiences by discussing past events and providing cues about important information.
What do schema theories emphasize?
How memories of events are manipulated and how scripts of routine actions are extracted.
What is the difference between implicit and explicit cognition?
Implicit cognition occurs without conscious awareness, while explicit cognition involves awareness.
How does children's eyewitness memory accuracy change with age?
It generally increases, with younger children being more susceptible to suggestion.
What is the principle of cardinality in early arithmetic skills?
The understanding that the last number counted represents the total quantity.
How do cultural variations affect mathematics performance?
Cultural differences influence the use of arithmetic strategies and overall performance in mathematics.
What is connectionism in cognitive development?
Using computational modeling to simulate how the brain processes and learns information.
What are the criticisms of the information-processing perspective?
It largely ignores neurological, evolutionary, and sociocultural influences on cognitive growth.
What is the significance of myelinization in attention development?
It contributes to the dramatic increase in attention spans as children age.
What is the role of executive control processes in reasoning?
They improve analogical reasoning by enhancing working memory, inhibition, and cognitive flexibility.
What is the impact of cultural goals on memory organization in children?
Children from autonomy-focused cultures recall events from personal perspectives, while those from collectivist cultures focus on social aspects.