KIN 223 Block Exam 4 Multiple Choice
1/270
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
271 Terms
An end plate potential is an event that involves a gain of
- positive charge along the inside of the cell membrane, as potassium rapidly enters
- negative charge along the inside of the cell membrane, as sodium rapidly enters
- negative charge along the inside of the cell membrane, as potassium rapidly enters
- positive charge along the inside of the cell membrane, as sodium rapidly enters
positive charge along the inside of the cell membrane, as sodium rapidly enters
If you were studying the functions of skeletal muscle, you would be studying all of the following except
- protecting internal organs
- holding the head erect
- helping maintain a constant body temperature
- movement
- production of blood cells
production of blood cells
Which of the following refers to a sustained muscle contraction?
- Relaxation
- Tetanus
- Fatigue
- Latency
- Summation
Tetanus
A power stroke involves
- an actin molecule pulling a myosin molecule toward the M-line
- a thick filament pushing an actin filament towards the nearest Z-line
- a thin filament shortening in length and thereby shortening the sarcomere
- a myosin head pulling a thin filament toward the center of the sarcomere
a myosin head pulling a thin filament toward the center of the sarcomere
Which of the following connects muscle to bone?
- Epithelial tissue
- Menisci
- Tendons
- Ligaments
- Cartilage
Tendons
With increased age, skeletal muscles show
- an increase in muscle fiber diameter
- a tendency to fatigue less rapidly
- increased glycogen reserves
- a decrease in the number of myofibrils
- no change in oxygen storage capability
a decrease in the number of myofibrils
Which of the following statements is true concerning calcium ions?
- In skeletal muscle, it binds with tropomyosin
- In skeletal muscle, it binds with calmodulin
- In smooth muscle, it binds with calmodulin
- In smooth muscle, it binds with troponin
- In smooth muscle, it binds with myosin light-chain kinase
In smooth muscle, it binds with calmodulin
Oxidative fibers are
- white and fatigable
- red and fatigable
- white and fatigue-resistant
- red and fatigue-resistant
red and fatigue-resistant
Which of the following structures has the active sites to which the heads of the thick filaments will bind?
- Tropomyosin
- Troponin
- Myosin
- Actin
- Sarcoplasm
Actin
The increase in muscle tension that occurs with an increase in the intensity (voltage) of a stimulus is called
- tone
- incomplete tetany
- recruitment
- wave summation
recruitment
For a sprint lasting 60 seconds, ATP is supplied primarily by
- phosphate transfer and glycolysis
- conversion of lactate to pyruvate
- phosphate transfer only
- aerobic respiration only
phosphate transfer and glycolysis
Which is a characteristic of skeletal muscle from the selections below?
- Under autonomic nervous control
- Lack of striations
- Multinucleated
- Contains intercalated discs
Multinucleated
The membranous network that wraps around myofibrils and holds relatively high concentrations of calcium is known as the
- T-tubule
- Golgi body
- sarcomere
- sarcolemma
- sarcoplasmic reticulum
sarcoplasmic reticulum
During relaxation, passive tension in _________ is released.
- dystrophin
- myoglobin
- connectin
- myosin
connectin
What is the letter associated with the dark bands in a sarcomere?
- M
- H
- A
- Z
- I
A
In general, a skeletal muscle is composed of
a: connective tissue sheaths
b: nerves
c: arteries
d: veins
e: muscle fibers
- a, b, d, e.
- a, b, c, d.
- b, c, d, e.
- a, b, c, d, e.
- a, b, c, e.
a, b, c, d, e.
In a lab, wave summation is demonstrated by increasing the _________ of the stimulus.
- capacitance
- intensity
- warm up time
- frequency
frequency
"Intermediate fiber" is another name for
- a fast-twitch, glycolytic fiber
- a slow-twitch, oxidative fiber
- a fast-twitch, oxidative fiber
- a slow-twitch, glycolytic fiber
a fast-twitch, oxidative fiber
The calcium ions involved in skeletal muscle contraction bind to a(n) _________ subunit.
- elastin
- tropomyosin
- actin
- troponin
- myosin
troponin
In a 1500-meter run, an event that may take about 5 to 6 minutes, ATP is supplied by which energy sources?
- Phosphagens and anaerobic sources
- Aerobic sources only
- Phosphagens, anaerobic, and aerobic sources
- Phosphagens only
Phosphagens, anaerobic, and aerobic sources
The sequence for skeletal muscle contraction is
- increased cytosolic calcium, which binds to calmodulin in cytosol, which moves tropomyosin from blocking active sites on actin filament, which binds with myosin head groups, resulting in contraction
- increased cytosolic calcium, which binds to calmodulin in cytosol, complex binds with myosin light-chain kinase, which uses ATP to phosphorylate myosin head groups, which bind to actin filaments, resulting in contraction
- increased cytosolic calcium, which binds to troponin, complex binds with myosin light-chain kinase, which uses ATP to phosphorylate myosin head groups, which bind to actin filaments, resulting in contraction
- increased cytosolic calcium, which binds to troponin, which moves tropomyosin from blocking active sites on actin filament, which binds with myosin head groups, resulting in contraction
increased cytosolic calcium, which binds to troponin, which moves tropomyosin from blocking active sites on actin filament, which binds with myosin head groups, resulting in contraction
Select all that are true regarding a resting muscle fiber.
- The charge difference across the sarcolemma is zero
- There is more sodium outside the cell as compared to the sarcoplasm
- Chemically gated ion channels are open
- Voltage-gated ion channels are closed
- The charge difference across the sarcolemma is zero
- There is more sodium outside the cell as compared to the sarcoplasm
- Voltage-gated ion channels are closed
The muscle that extends from the clavicle to the first rib, and whose main action is to stabilize and depress the clavicle, is the
- trapezius
- rhomboid major
- subclavius
- pectoralis major
subclavius
A nursing baby is using what muscle to suckle?
- Platysma
- Buccinator
- Mentalis
- Levator labii superioris
- Risorius
Buccinator
Which muscle does not attach proximally to the ischial tuberosity?
- Biceps femoris
- Semitendinosus
- Semimembranosus
- Adductor longus
- Quadratus femoris
Adductor longus
What is the action of the gastrocnemius muscle?
- Adduction of leg
- Flexion of leg
- Extension of leg
- Rotation of leg
- Abduction of leg
Flexion of leg
What two muscles attach distally to the calcaneal tendon?
- Extensor hallucis longus and fibularis longus
- Flexor digitorum longus and flexor hallucis longus
- Gastrocnemius and soleus
- Tibialis posterior and popliteus
- Tibialis anterior and extensor digitorum longus
Gastrocnemius and soleus
These two muscles are known as the triceps surae and together are the most powerful plantar flexors of all of the leg muscles.
- Gastrocnemius and soleus
- Tibialis anterior and extensor digitorum longus
- Tibialis posterior and popliteus
- Flexor digitorum longus and flexor hallucis longus
- Extensor hallucis longus and fibularis longus
Gastrocnemius and soleus
There are three gluteal muscles. Select the one that is correctly matched with its primary action.
- Gluteus minimus: rotates the thigh
- Gluteus maximus: abducts the thigh
- Gluteus medius: abducts the thigh
Gluteus medius: abducts the thigh
For elbow flexion,
- biceps brachii is the antagonist and triceps brachii is the agonist
- triceps brachii is the synergist and biceps brachii is the antagonist
- deltoid is the agonist and biceps brachii is the synergist
- biceps brachii is the synergist and triceps brachii is the agonist
- biceps brachii is the agonist and triceps brachii is the antagonist
biceps brachii is the agonist and triceps brachii is the antagonist
Crural muscles are those that move the
- wrist
- hip
- vertebral column
- thigh
- ankle, foot, and toes
ankle, foot, and toes
These muscles elevate the ribs and have their origin on the inferior border of the superior rib and their insertion on the superior border of the inferior rib.
- Serratus posterior inferior
- Transversus thoracis
- Internal intercostals
- External intercostals
- Diaphragm
External intercostals
Which of the following muscles is the longest muscle in the body and is nicknamed the "tailor's muscle" because it flexes and laterally rotates the thigh while also flexing and medially rotating the leg (helping us to sit cross-legged, as tailors used to do)?
- Rectus femoris
- Gracilis
- Sartorius
- Vastus lateralis
Sartorius
Which is the longest muscle of the body?
- Sartorius
- Biceps brachii
- Quadriceps femoris
- Brachioradialis
- Gracilis
Sartorius
Which muscle is the prime extensor of the elbow joint?
- Deltoid muscle
- Triceps brachii
- Brachioradialis
- Biceps brachii
- Brachialis
Triceps brachii
The muscles of the anterior compartment of the leg function to
- plantarflex the foot and flex the toes
- dorsiflex the foot and extend the toes
- dorsiflex the foot and flex the toes
- plantarflex the foot and extend the toes.
dorsiflex the foot and extend the toes
A muscle whose action opposes that of the prime mover is known as a(n)
- agonist
- antagonist
- synergist
- extensor
antagonist
This muscle has its inferior attachment on the manubrium and sternal end of the clavicle and its superior attachment on the mastoid process.
- Scalene
- Sternocleidomastoid
- Splenius cervicus
- Longissimus capitis
- Splenius capitis
Sternocleidomastoid
The muscle that compresses the cheek against the teeth when we chew is the
- masseter
- mentalis
- buccinator
- orbicularis iris
buccinator
Which muscle does not move the mandible?
- Lateral pterygoid
- Temporalis
- Masseter
- Medial pterygoid
- Genioglossus
Genioglossus
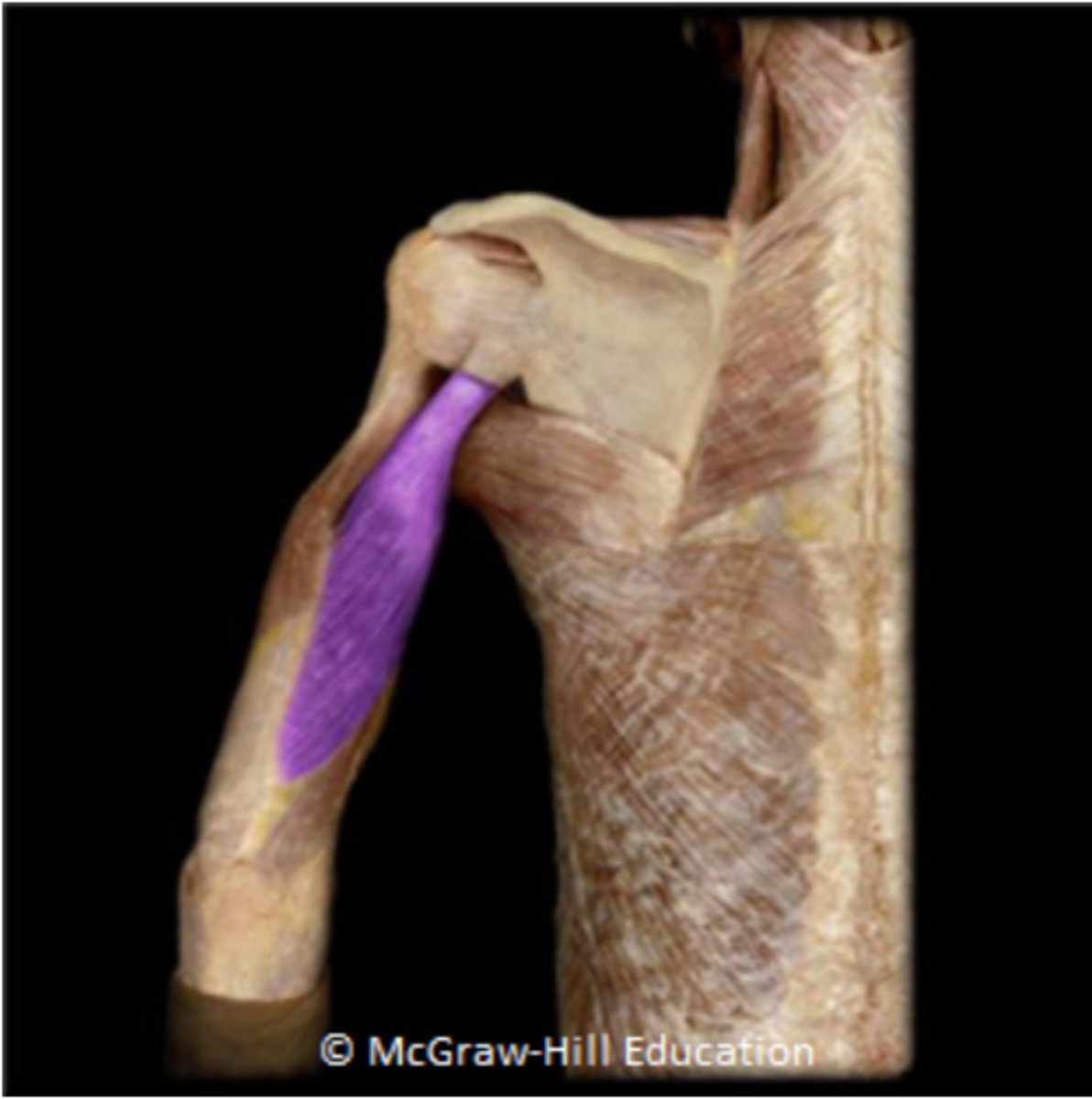
What is the proximal attachment of the highlighted muscle?
- Olecranon of ulna
- Coracoid process of scapula
- Medial border of scapula
- Superior clavicular border
- Infraglenoid tubercle of scapula
Infraglenoid tubercle of scapula
All of these muscles, except one, have their proximal attachment on the scapula. Select the exception.
- Pectoralis major
- Coracobrachialis
- Subscapularis
- Triceps brachii
- Infraspinatus
Pectoralis major
What are tendinous intersections?
- Narrow, vertical, fibrous strips used to attach muscle sheaths of the left and right rectus abdominis
- Fibrous, perpendicular insertions between successive sheets or blocks of muscle
- Flat sheets of connective tissue used for muscle insertion
- Round tendonlike structures attaching muscle to bone
- Thin layers of muscle used to attach two other muscles together
Fibrous, perpendicular insertions between successive sheets or blocks of muscle
The multiple nuclei in skeletal muscle cells are the result of the
- spontaneous development of nuclei in embryonic cells
- cytokinesis of embryonic satellite cells
- stimulation of fibroblasts by hormones
- fusion of myoblasts
- action of testosterone on mesenchyme cell
fusion of myoblasts
Consider the difference between lifting a light pad of paper versus a heavy textbook. The primary way the level of force of muscle contraction is controlled is by
- altering the number of crossbridges each individual fiber uses
- activating the motor units at a different frequency
- activating different regions of the muscle
- recruiting a different number of motor units
recruiting a different number of motor units
Stimulation of muscle fibers at a rate of 20 to 50 stimuli per second does not allow for complete relaxation of the fibers before the next stimulatory event. This results in _________ and can lead to incomplete tetany.
- wave summation
- a muscle twitch
- tone
- tetany
wave summation
An individual is better at performing repeated muscle contractions under aerobic conditions if he or she has a greater percentage of ____________ fibers in the muscles used in that activity.
- type I
- type IIb
type I
Your school wins the homecoming football game against its biggest rival. You watch as the small cheerleader tries to lift up the heaviest linebacker in her excitement. As she strains against his 300-pound load and does not move him, what type of muscle contraction are her muscles experiencing?
- Isotonic
- Concentric
- Isometric
- Eccentric
Isometric
The branch of the nervous system that helps govern smooth muscle contraction is the __________ nervous system.
- somatic
- autonomic
autonomic
When an impulse arrives at the knob of the motor neuron, calcium
- is released from synaptic vesicles
- exits through voltage-gated channels and triggers transmitter release
- exits through active transport pumps and brings transmitter with it
- enters through voltage-gated channels and triggers the release of transmitter
- enters through active transport pumps and triggers the release of transmitter
enters through voltage-gated channels and triggers the release of transmitter
If you were studying the neurotransmitter released from axon terminals at a neuromuscular junction, you would be studying
- acetylcholine
- lactic acid
- creatine phosphate
- calcium ions
- ATP
acetylcholine
For relaxation to occur,
- extracellular calcium levels fall, calcium is pumped into the myofibril, and tropomyosin slides away from actin
- calcium leaves the sarcoplasmic reticulum, and troponin binds calcium and blocks the binding sites on actin
- calcium enters the myofibril, it detaches from myosin, and the binding sites on myosin become inactive
- sarcoplasm calcium levels fall, calcium is removed from troponin, and tropomyosin building blocks binding sites on actin
sarcoplasm calcium levels fall, calcium is removed from troponin, and tropomyosin building blocks binding sites on actin
Smooth muscle found in both the iris and ciliary muscle of the eye and arrector pili muscles in the skin is ______________ smooth muscle.
- single-unit
- multiunit
- visceral
- varicosity-controlled
multiunit
What part of a muscle twitch begins as a repetitive power stroke, then pulls the thin filaments past the thick filaments, shortening the sarcomeres?
- Latent period
- Contraction period
- Relaxation period
- Threshold
Contraction period
The type of muscle fibers that are striated, form Y-shaped branches, and are joined by intercalated discs are
- voluntary
- skeletal and voluntary
- skeletal
- smooth
- cardiac
cardiac
All the muscle fibers under the control of a single motor axon are referred to as
- the myosin
- a motor unit
- the sarcolemma
- a myofibril
- the prime mover
a motor unit
Which fibers dominate many of the back and calf muscles that contract almost continually to maintain posture?
- Slow-twitch
- Fast-twitch
- Intermediate
Slow-twitch
The narrow space that separates the motor neuron and the skeletal muscle fiber in a neuromuscular junction is called the
- synaptic cleft
- motor end plate
- synaptic knob
- synaptic vesicle
synaptic cleft
Release of crossbridges and a decline in muscle tension characterizes the _________ period of a twitch.
- latent
- relaxation
- contraction
relaxation
A decrease in muscular activity or damage to neurons that attach to skeletal muscle can lead to a reduction in the size of muscle called
- myasthenia gravis
- atrophy
- dystrophy
- rigor mortis
- denervation
atrophy
Which of the following will increase during strenuous muscular activity?
- Actin
- Oxygen
- Lactate
- Carbon monoxide
- Myosin
Lactate
What are the causes of muscle fatigue? Select all that apply
- Lack of ATP
- Crossbridge recycling/elevated phosphate ion concentration
- Change in Na+ or K+ ion concentration
- Insufficient Ca2+ at the neuromuscular junction
- Change in Na+ or K+ ion concentration
- Insufficient Ca2+ at the neuromuscular junction
Muscles of the pectoral girdle attach proximally on the
- axial skeleton and attach distally on the clavicle and scapula
- axial skeleton and attach distally on the humerus
- clavicle and scapula and attach distally on the axial skeleton
- humerus and attach distally on the clavicle and scapula
- humerus and attach distally on the axial skeleton
axial skeleton and attach distally on the clavicle and scapula
Which of the following thigh muscles has its insertion in the head of the fibula?
- Gracilis
- Sartorius
- Biceps femoris
- Adductor magnus
Biceps femoris
Besides the supinator, which other muscle is a powerful supinator of the forearm?
- Brachialis
- Pronator quadratus
- Pronator teres
- Biceps brachii
- Triceps brachii
Biceps brachii
The muscles that protract the scapula include
- serratus anterior and trapezius
- trapezius and subclavius
- serratus anterior and pectoralis minor
- rhomboid major and teres minor
serratus anterior and pectoralis minor
Which muscles help us in the initial breakdown of food?
- Muscles of mastication
- Muscles that move the tongue
- Muscles of the pharynx
- Extrinsic eye muscles
- Muscles of facial expression
Muscles of mastication
If the right sternocleidomastoid contracts unilaterally, the resulting movement will be
- lateral extension of the head to the left and rotation of the head to the right
- lateral extension of the head to the right and rotation of the head to the left
- lateral flexion of the head to the left and rotation of the head to the right
- lateral flexion of the head to the right and rotation of the head to the left
lateral flexion of the head to the right and rotation of the head to the left
Muscles that protract the scapula would be ______________ thoracic muscles.
- posterior
- anterior
anterior
The muscle that has its superior attachment on the mastoid process and has a bilateral action of flexing the neck is the
- middle scalene
- splenius capitis
- sternocleidomastoid
sternocleidomastoid
Muscles whose functions are to depress either the hyoid bone or the thyroid cartilage of the larynx are the ____________ muscles.
- stylohyoid
- mylohyoid
- infrahyoid
- suprahyoid
infrahyoid
The deepest of the abdominal muscles are the ______________ muscles.
- tendinous intersections
- external oblique
- rectus abdominus
- internal oblique
- transversus abdominus
transversus abdominus
If you had all of your fingers (including the thumb) spread out wide, which muscle or group would bring your thumb toward your first finger?
- Dorsal interossei
- Adductor pollicis
- Lumbricals
- Palmar interossei
- Abductor pollicis longus
Adductor pollicis
The muscle that forms a partition between the thoracic and abdominal cavities is the
- diaphragm
- scalenes
- internal intercostal
- interspinales
- transversus thoracis
diaphragm
Which muscle forms the traditional "six-pack" of a well-toned abdominal wall?
- Longissimus
- Rectus abdominis
- Internal oblique
- External oblique
- Transversus abdominis
Rectus abdominis
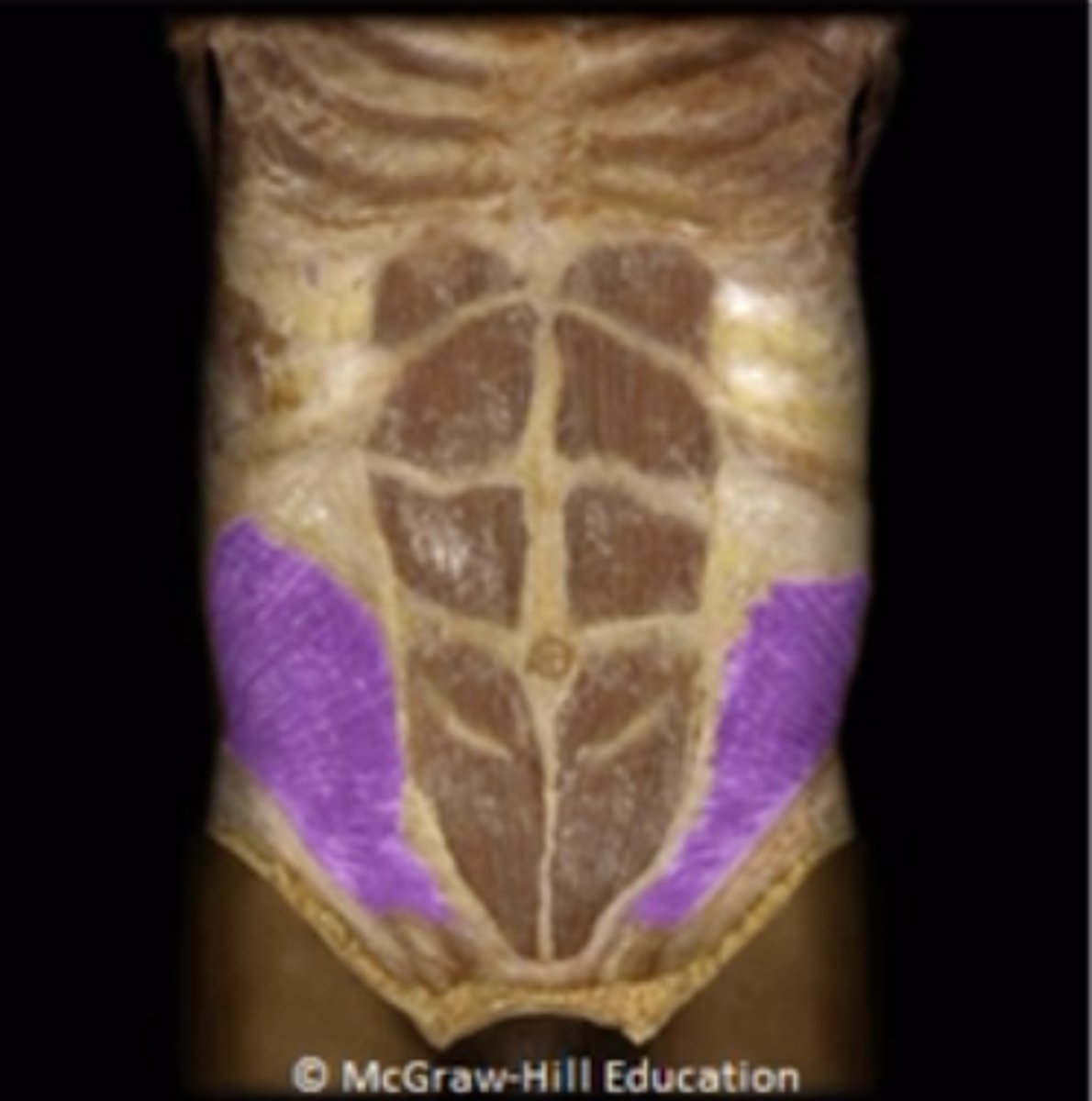
Which structure is highlighted?
- Rectus abdominis
- External abdominal oblique
- Transverse abdominis
- Internal abdominal oblique
- Anterior rectus sheath
Internal abdominal oblique
If you had all of your fingers (including the thumb) spread out wide, which muscle or group would bring fingers 2-5 together?
- Dorsal interossei
- Adductor pollicis
- Abductor pollicis longus
- Lumbricals
- Palmar interossei
Palmar interossei
Of the following, the muscle or group that does not have its proximal attachment on the calcaneus is the
- abductor hallucis
- lumbricals
- quadratus plantae
- flexor digitorum brevis
- extensor digitorum brevis
lumbricals
During wave summation
- stimuli arrive at the muscle fiber at a rate that allows it to contract and then completely relax between each stimulus
- a second stimulus arrives at the muscle before complete relaxation of the first contraction, causing the second contraction to have greater tension than the first one
- a muscle fiber under continuous stimulation and contraction becomes unable to contract at all until it has rested
- the stimuli arrive at the muscle fiber so rapidly that there is no muscle relaxation between stimuli, but rather a continuous contraction of the muscle fiber
a second stimulus arrives at the muscle before complete relaxation of the first contraction, causing the second contraction to have greater tension than the first one
The structure responsible for attaching muscle to bone is a
- ligament
- myofibril
- sphincter
- tendon
- fascia
tendon
Which protein makes up the thick filaments?
- Troponin
- Actin
- Myopathy
- Myosin
- Tropomyosin
Myosin
Acetylcholine exerts its effect by
- allowing calcium to enter the cell
- binding to receptors at the motor end plate
- stimulating the motor neuron's synaptic knob
- activating acetylcholinesterase
binding to receptors at the motor end plate
The contractile unit of a myofibril is called the
- M line
- sarcoplasm
- sarcolemma
- sarcoplasmic reticulum
- sarcomere
sarcomere
During tetany,
- stimuli arrive at the muscle fiber at a rate that allows it to contract and then completely relax between each stimulus
- the stimuli arrive at the muscle fiber so rapidly that there is no muscle relaxation between stimuli, but rather, a continuous contraction of the muscle fiber
- a muscle fiber under continuous stimulation and contraction becomes unable to contract at all until it has been rested
- a second stimulus arrives at the muscle before complete relaxation of the first contraction causing the second contraction to have greater tension than the first one
the stimuli arrive at the muscle fiber so rapidly that there is no muscle relaxation between stimuli, but rather, a continuous contraction of the muscle fiber
A typical skeletal muscle cell contains approximately ___________ mitochondria.
- 30
- 3
- 300
- 3000
300
For relaxation to occur,
- ACh receptors open and Ca++ channels on the sarcoplasmic reticulum close
- ACh receptors open and Ca++ channels on the sarcoplasmic reticulum open
- ACh receptors close and Ca++ channels on the sarcoplasmic reticulum close
- ACh receptors close and Ca++ channels on the sarcoplasmic reticulum open
ACh receptors close and Ca++ channels on the sarcoplasmic reticulum close
Which type of smooth muscle is innervated most similar to skeletal muscle, with muscle cells arranged as motor units and each cell stimulated by a single motor neuron?
- Multiunit smooth muscle
- Single-unit smooth muscle
Multiunit smooth muscle
Phosphate transfer is used for
- immediate ATP needs and is dependent on oxygen
- long term ATP needs and is not dependent on the presence of oxygen
- immediate ATP needs and is not dependent on oxygen
- long term ATP needs and is dependent on oxygen
immediate ATP needs and is not dependent on oxygen
The repolarization of the action potential involves the opening of
- chemically gated K+ channels
- chemically gated Na+ channels
- voltage-gated Na+ channels
- voltage-gated K+ channels
voltage-gated K+ channels
The action potential of a muscle fiber occurs
- along the sarcolemma and down T-tubules
- within the sarcoplasmic reticulum
- in the mitochondria
- at the end plate
along the sarcolemma and down the T-tubules
A term that describes the change in muscle following a lack of exercise is
- convergence
- myofascia
- atrophy
- hypertrophy
- proliferation
atrophy
Which are possible functions of skeletal muscles?
a: Maintenance of posture
b: Both highly coordinated and localized simple movements
c: Temperature regulation
d: Support of certain body organs
e: Regulation of the movement of material through certain body tracts
- a, b, c, e
- a, b, c
- a, b, c, d, e
- a, b, c, d
- a, b, e
a, b, c, d, e
The ending "glossus" on the name of a muscle refers to
- the tongue
- swallowing
- the jaw
- mastication
- the neck
the tongue
The function of the biceps femoris is to
- extend the thigh and flex the leg
- flex the thigh and extend the leg
- adduct the thigh and extend the knee
- flex the hip and ankle
- flex the thigh (with no action at the leg)
extend the thigh and flex the leg
The diamond-shaped region between the lower appendages is called the
- anal triangle
- genital triangle
- linea alba
- perineum
perineum
If you severely injured your adductor pollicis, which movement might be affected?
- Adduction of fingers 2-5
- Adduction of the pinky finger (finger 5)
- Adduction of the wrist
- Adduction of the thumb
Adduction of the thumb
Which muscle is the most powerful muscle of mastication and functions to elevate and protract the mandible?
- Medial pterygoid
- Masseter
- Lateral pterygoid
- Temporalis
Masseter
The condition known as "tennis elbow" is caused by trauma or overuse of the common tendon muscles that cause wrist extension. In other words, it is caused by damage to the
- common extensor tendon of the anterior forearm muscles
- common flexor tendon of the anterior forearm muscles
- common flexor tendon of the posterior forearm muscles
- common extensor tendon of the posterior forearm muscles
- None of the choices is correct.
common extensor tendon of the posterior forearm muscles
The type of muscles in which the fascicles are at an oblique angle to the tendon and the muscle fibers resembles a large feather is called
- pennate
- parallel
- circular
- convergent
pennate
Which cranial nerve innervates the superior oblique muscle?
- The trochlear nerve
- The glossopharyngeal nerve
- The trigeminal nerve
- The oculomotor nerve
- The abducens nerve
The trochlear nerve