Biochem Lect 26: Glycolysis Part II
1/47
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
48 Terms
2 phases of glycolysis (overall summary)
Phase 1 = glucose → 2 G3P (-2 ATP)
Phase 2 = 2 G3P → 2 pyruvates (+4 ATP, +2 NADH)
Overall Summary for Phase II
everything is doubled!!!
6) G3P → 1,3BPG (“six, redox”)
7) 1,3BPG → 3PG
8) 3PG → 2PG = “3 to 2”
9) 2PG → PEP
10) PEP → Pyruvate
Phase II enzymes
6) G3P dehydrogenase
7) Phosphoglycerate kinase
8) Phosphoglycerate mutase
9) Enolase
10) Pyruvate kinase
Phase II Extra (total)
6) +2 NADH
7) +2 ATP
8)
9)
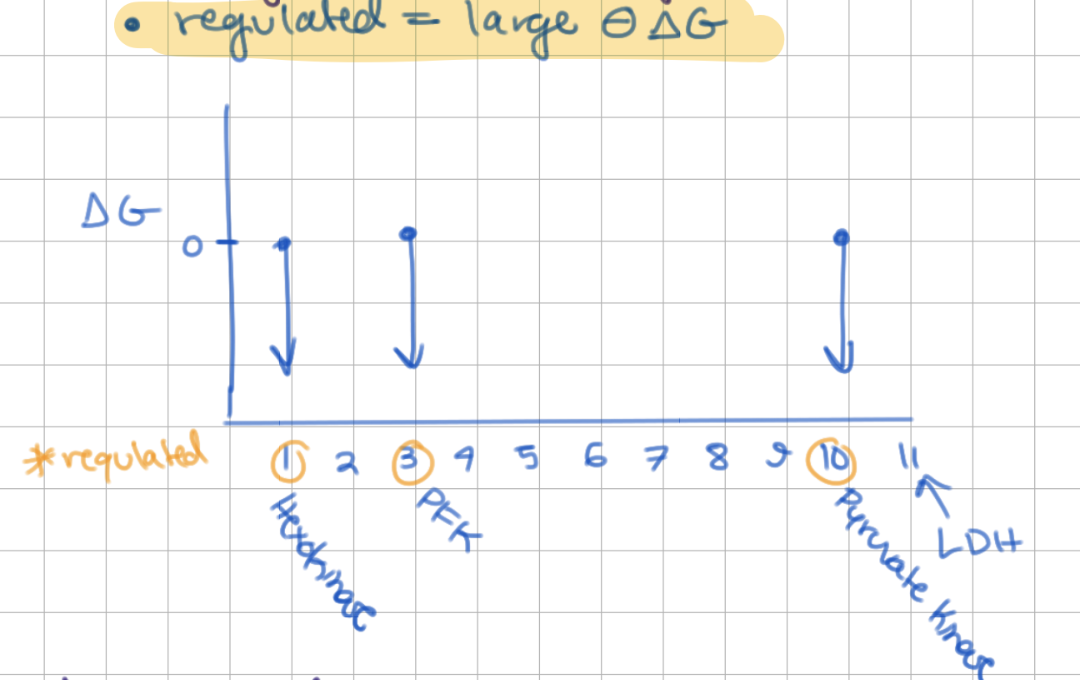
10) +4 ATP (regulated/-ΔG/irreversible)
Reaction 6
Redox reaction*
Glyceraldehyde 3 Phosphate (G3P) → 1,3 Biphosphoglycerate (1,3 BPG)
Enzyme = G3P dehydrogenase
+1 NADH
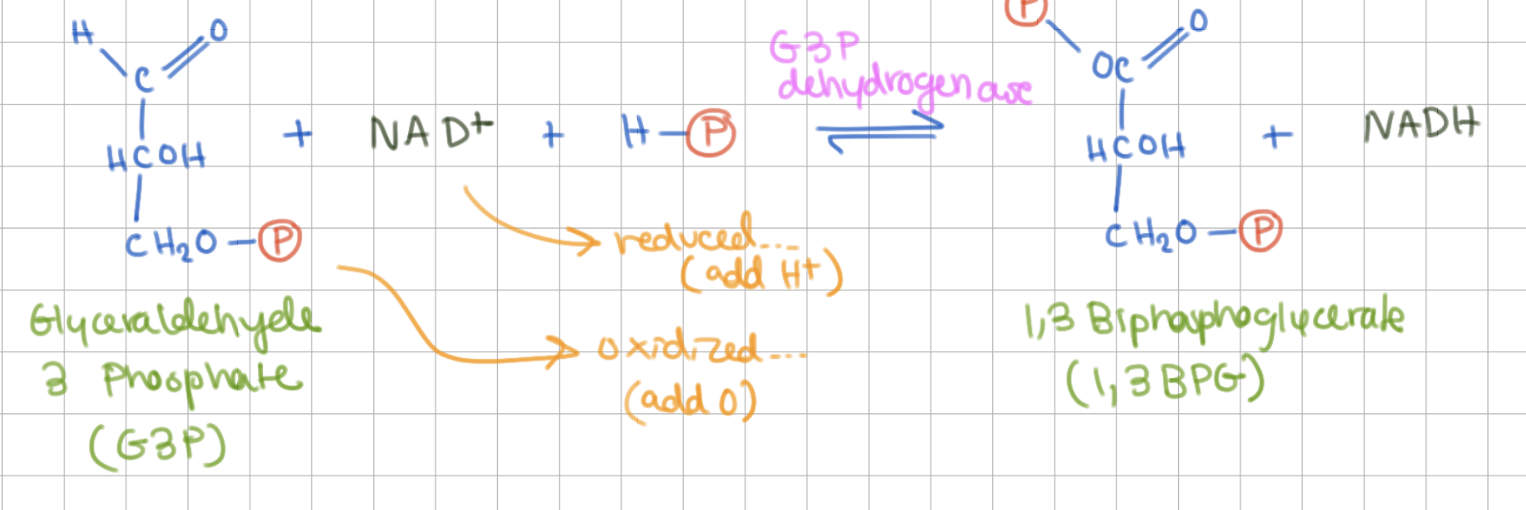
Step 6 mechanism (3 steps + notes)
involves covalent catalysis
inorganic phosphate provides P
1) SH of Cys attacks G3P → thiohemiacetal
2) thiohemiacetal loses H+ to NAD+ → thioester
3) phosphorolysis (Pi attacks and cleaves SH)

Reaction 7
Small ATP Formation
1,3 Biphosphoglycerate (1,3 BPG) → 3 Phosphoglycerate (3PG)
Enzyme = Phosphoglycerate kinase
+1 ATP
-
spontaneous reaction (-ΔG)!
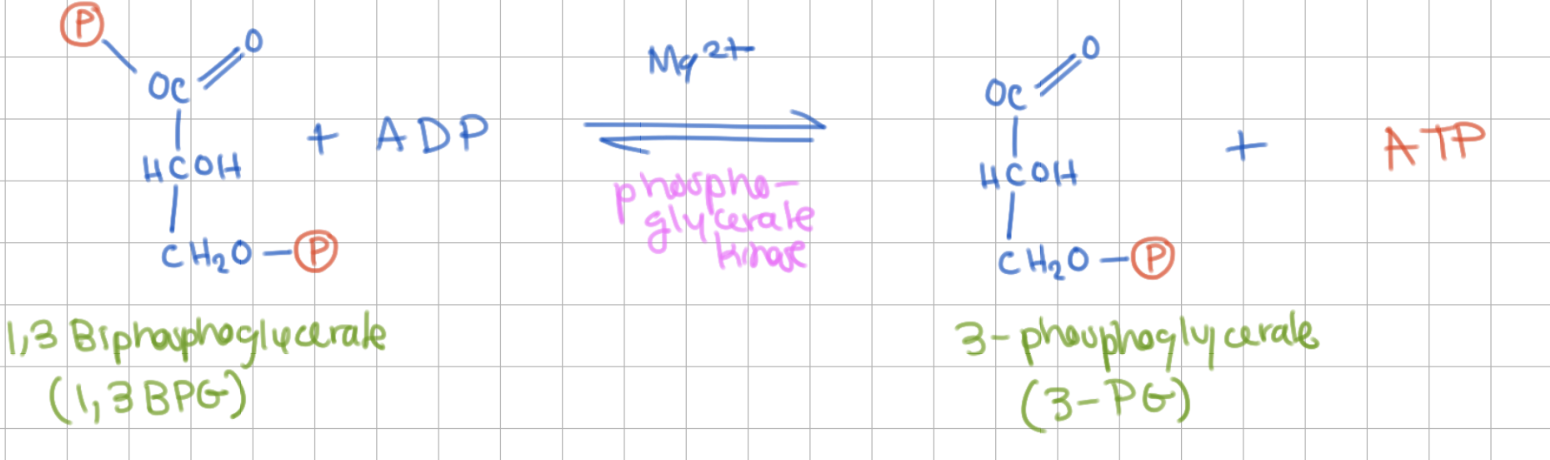
Step 7 involves _______ phosphorylation
substrate level
-
phosphate is added from substrate to create ATP
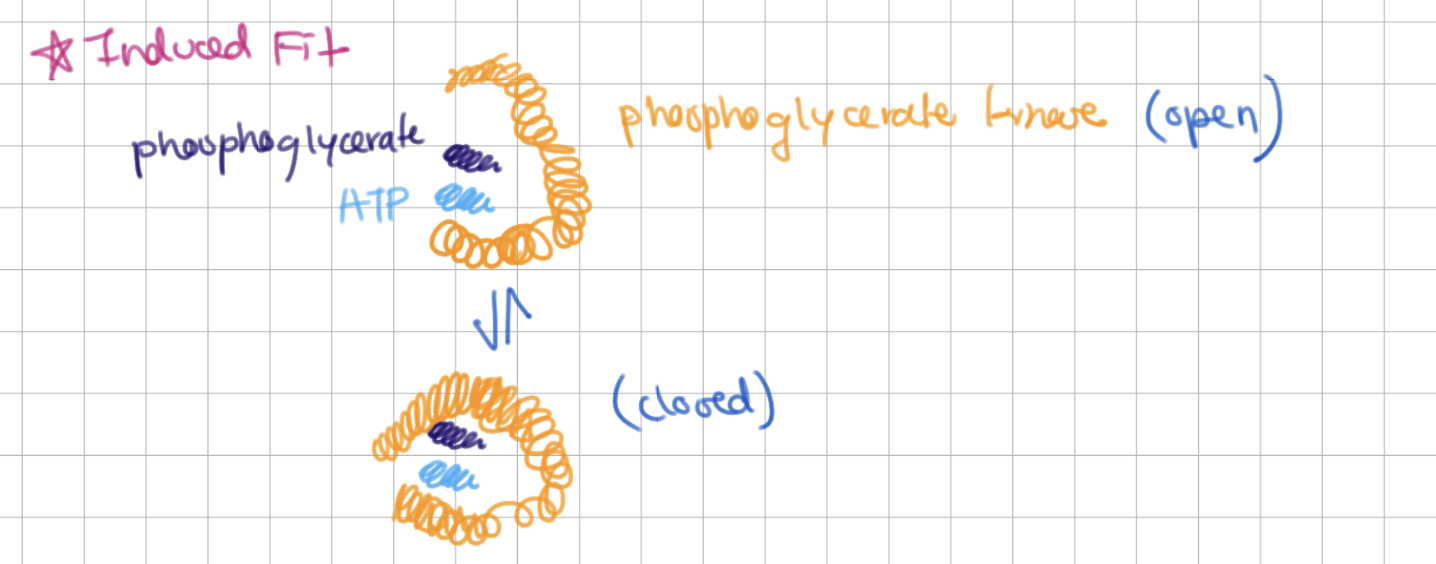
phosphoglycerate kinase induced fit
nothing rlly to note tbh
What is 2,3 BPG?
regulator of hemoglobin (found a lot in erythrocytes)
-
made from 1,3 BPG
2,3 BPG is made from _____ and _____
1,3BPG and 3PG
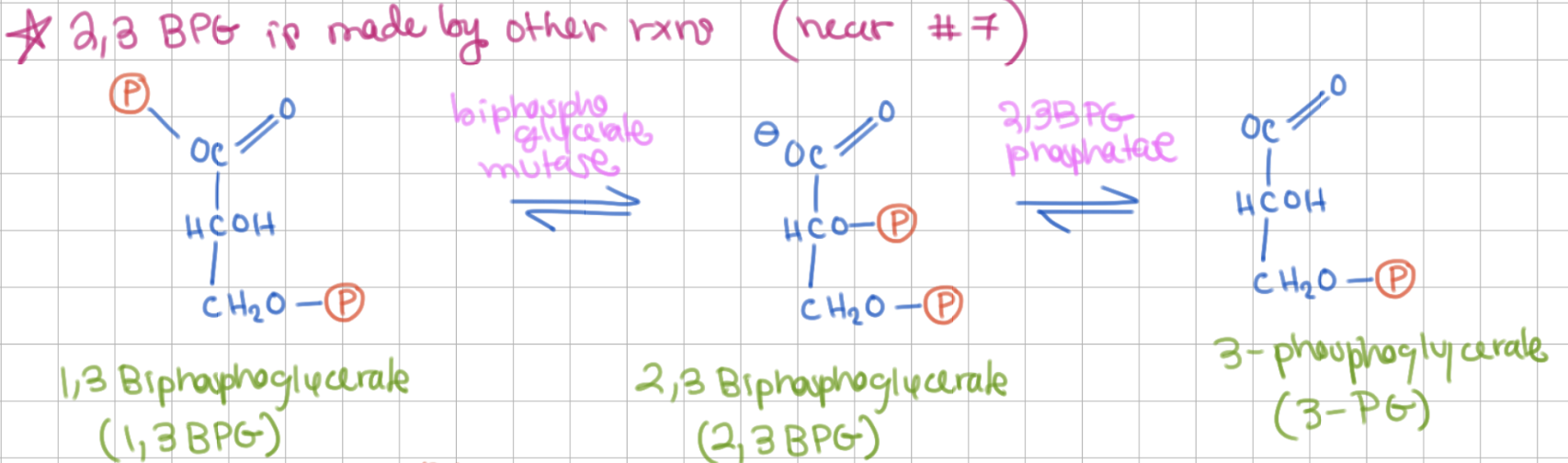
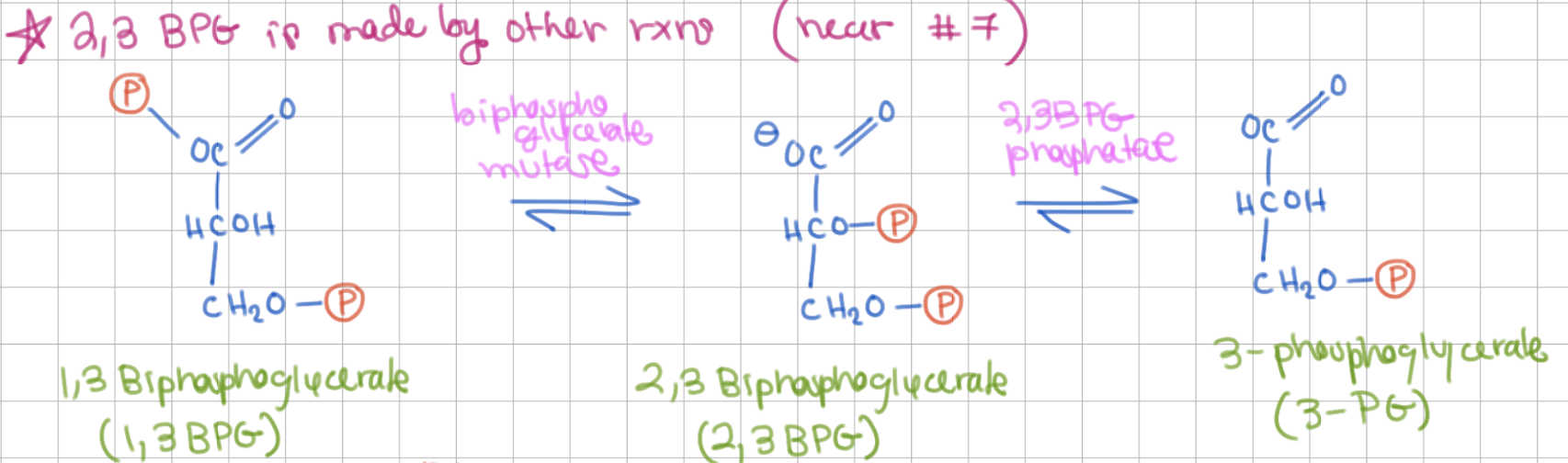
1,3 BPG ←→ 2,3BPG involves what enzyme?
BPG mutase
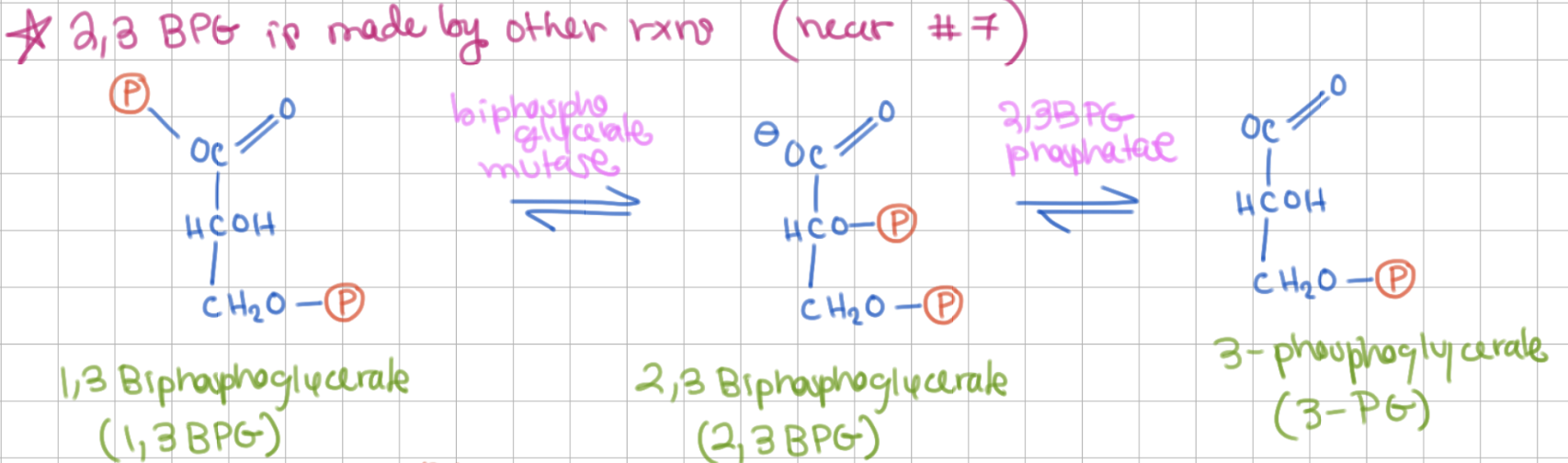
2,3 BPG ←→ 3PG involves what enzyme?
2,3 BPG phosphatase
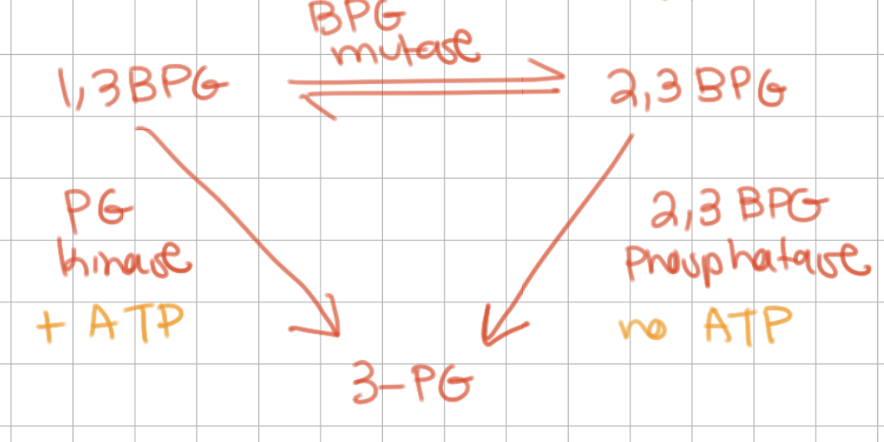
summary of equilibrium between 1,3 BPG / 2,3 BPG / 3 PG (view image)
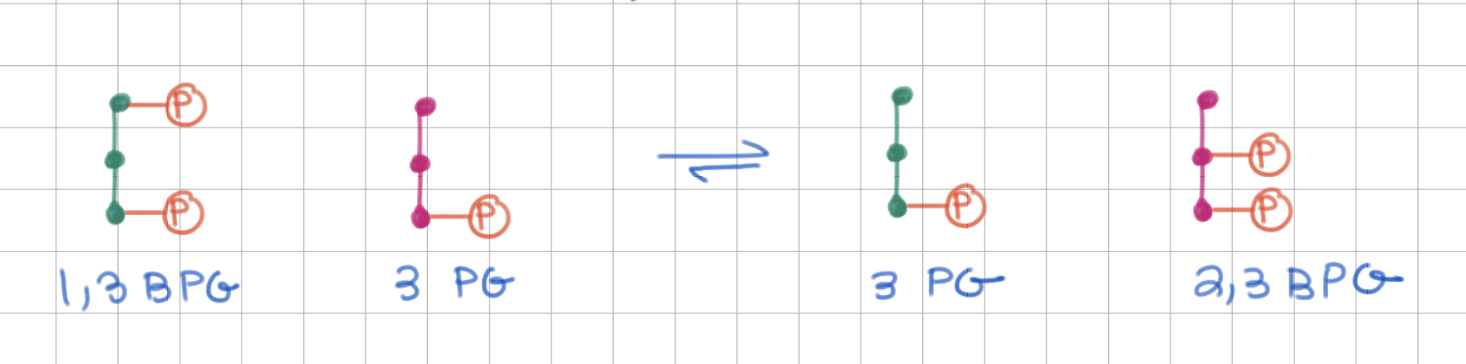
1,3 BPG ←→ 2,3 BPG requires ____
3PG
-
intermolecular switch
Reaction 8
“3 to 2”
3 Phosphoglycerate (3PG) → 2 Phosphoglycerate (2PG)
Enzyme = Phosphoglycerate mutase
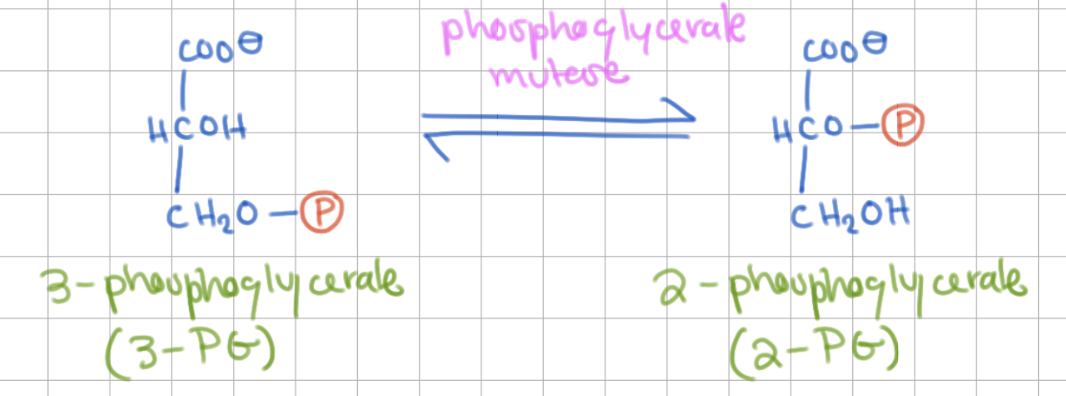
Is step 8 intramolecular or intermolecular?
intramolecular
(Step 7 was intermolecular)
What residue is in the active site of PG mutase?
Histidine
Step 8 mechanism (3 steps) *
1) histidine gets phosphorylated by 2,3 BPG
2) phosphohistidine adds phosphate to C2
3) phosphohistidine removes phosphate from C3

Phosphohistidine is…
a phosphorylated histidine intermediate
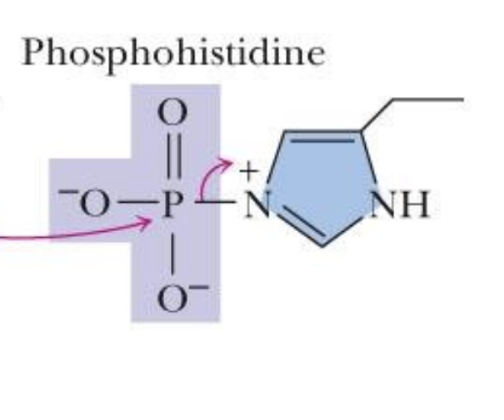
Zelda Rose showed that a little _____ is needed to ________
2,3 BPG; phosphorylate His
Reaction 9
2PG → PEP
2 Phosphoglycerate (2PG) → Phosphoenolpyruvate (PEP)
Enzyme = Enolase
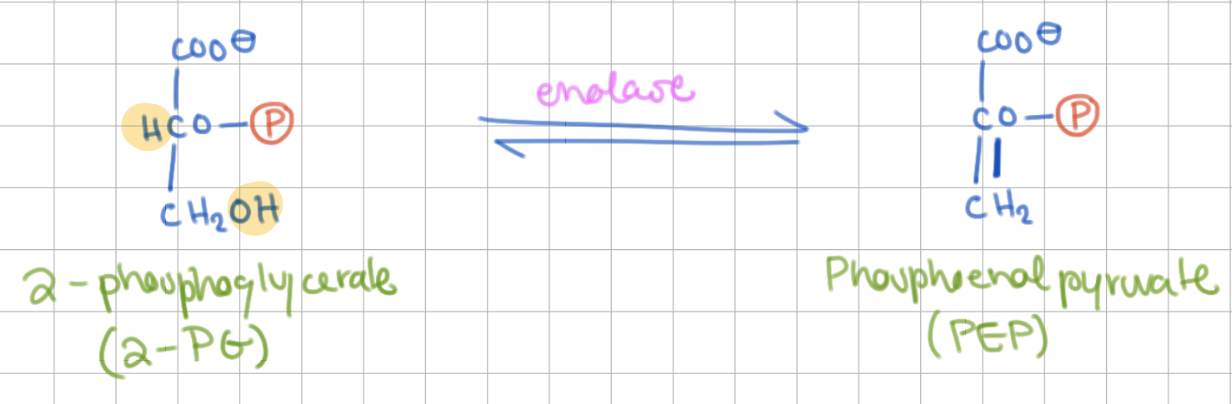
Step 8 purpose
make high energy phosphate (enol) for ATP synthesis (step 10)
enolase structure
assymetric dimer
one subunit holds 2PG, other holds PEP
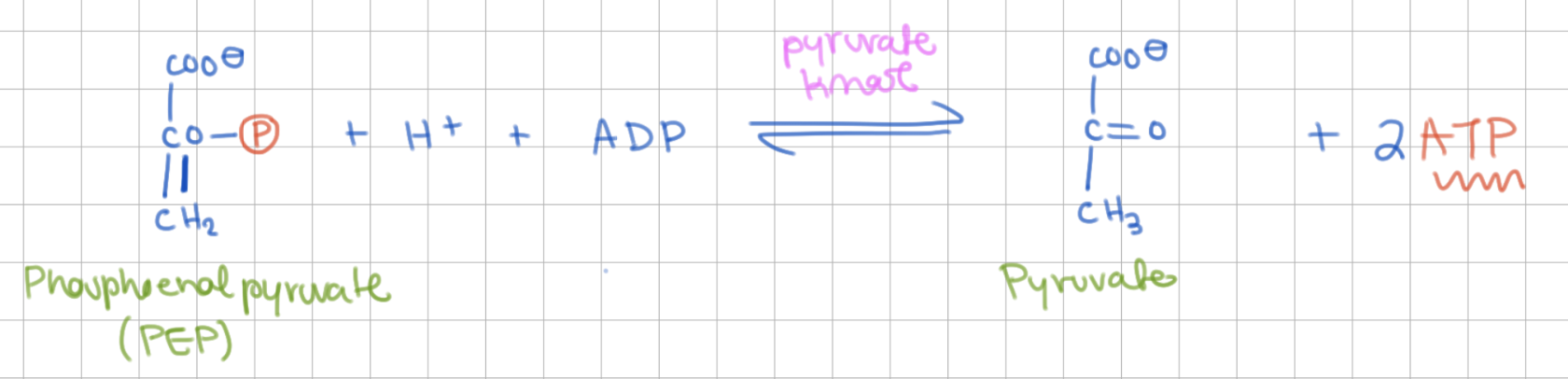
Reaction 10
ATP Formation
PEP → Pyruvate
Enzyme = Pyruvate Kinase
+2 ATP
very spontaneous reaction (- large ΔG)
Step 10 regulation (4+1)
ATP ______/AMP ______
acetyl CoA ______
F1,6BP ______
alanine ______ (related to pyruvate)
liver PK is regulated by _______________
ATP inhibits/AMP activates
acetyl CoA inhibits
F1,6BP activates
alanine inhibits (related to pyruvate)
liver PK is regulated by covalent modification (phosphorylation)
pyruvate’s _______ is spontaneous and helps reaction to be thermodynamically favorable
keto-enol tautomerism

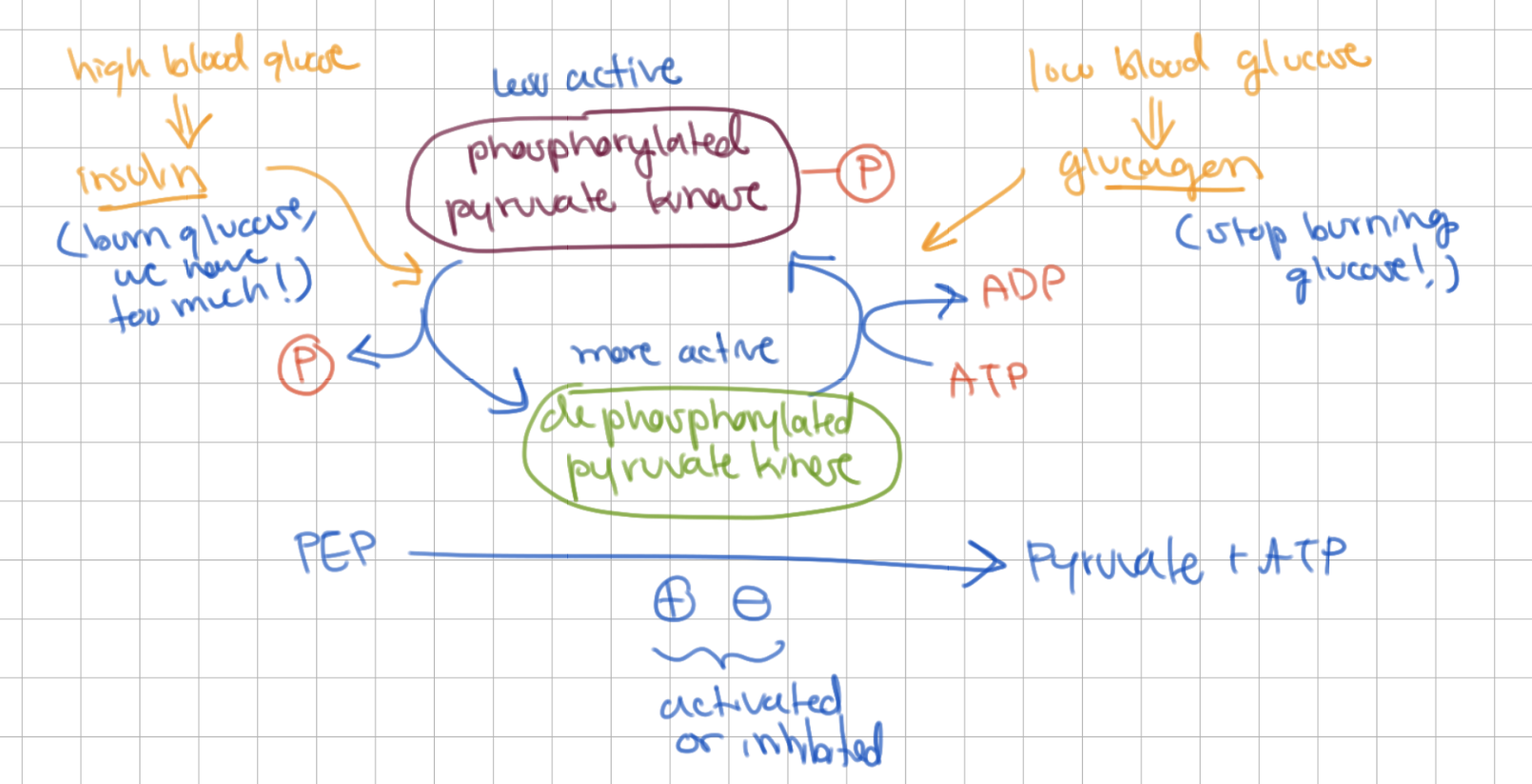
in liver, high blood glucose → insulin → pyruvate kinase is ______ → more/less active
dephosphorylated, more
in liver, low blood glucose → glucagon → pyruvate kinase is ______ → more/less active
phosphorylated, less
summary of liver PK regulation (image)
Metabolic fates of NADH (2)
1) aerobic → NADH oxidized in ETC => more ATP
2) anaerobic → NADH oxidized by lactate dehydrogenase (LDH) => more NAD+ (for more glycolysis)
Metabolic fates of Pyruvate (3) - review
1) aerobic = TCA cycle → acetyl-CoA
2) anaerobic = lactic acid fermentation (ex: muscle) → lactate
3) anaerobic in yeast = alcoholic fermentation → ethanol + CO2
lactic acid bacteria produce…
lactate (yoghurt, sauerkraut…)
Main difference between glucose → pyruvate vs glucose → lactate
no NADH produced when making lactate
Which steps of glycolysis are regulated?
1, 3, 10
Which steps of glycolysis is the “payout” (ATP produced)?
7, 10
Fermentation
ATP produced where organic molecules are electron donor/acceptors
-
(unlike respiration where O2 is electron acceptor)
-
ex: acetone, butanol
The Entner-Doudoroff pathway
tequila fermentation
-
makes more ethanol and at higher concentration
Alternatives to glucose for glycolysis (3 main)
1) Galactose (via Leloir Pathway)
2) Glycerol
3) Lactose
Leloir Pathway
use galactose instead of glucose for glycolysis
-
galactose → gluc 6P
3 main steps of Leloir pathway
1) galactose → galactose 1P
2) galactose 1P → glucose 1P
3) glucose 1P → glucose 6P
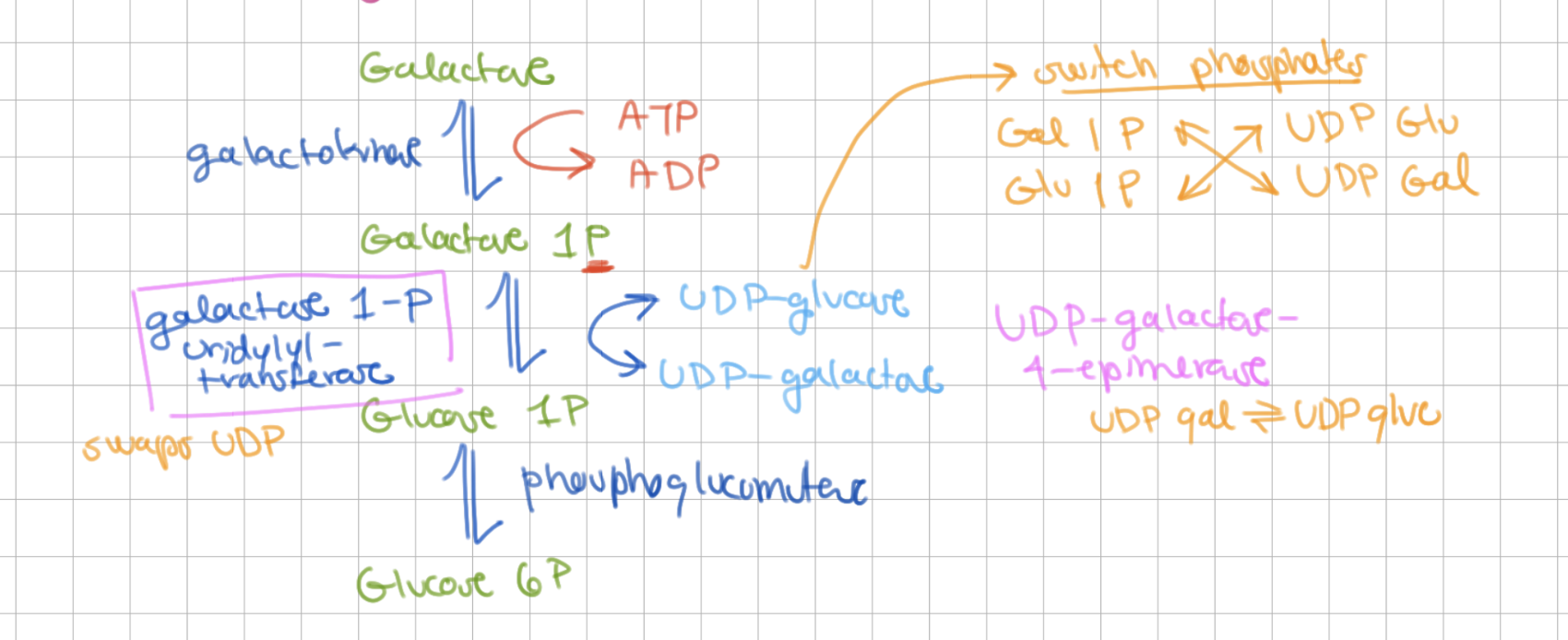
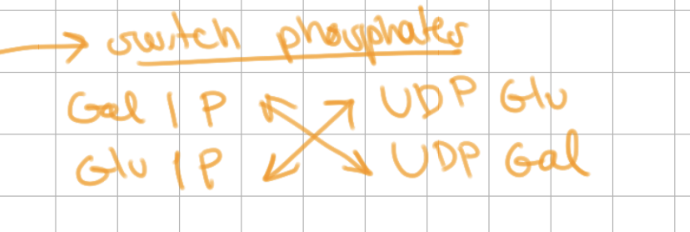
How does step 2 of Leloir pathway occur?
UDP glucose and 1P galactose swap phosphates => UDP galactose and 1P glucose
In step 2 of Leloir pathway, which enzyme swaps UDP?
galactose 1P uridyl transferase
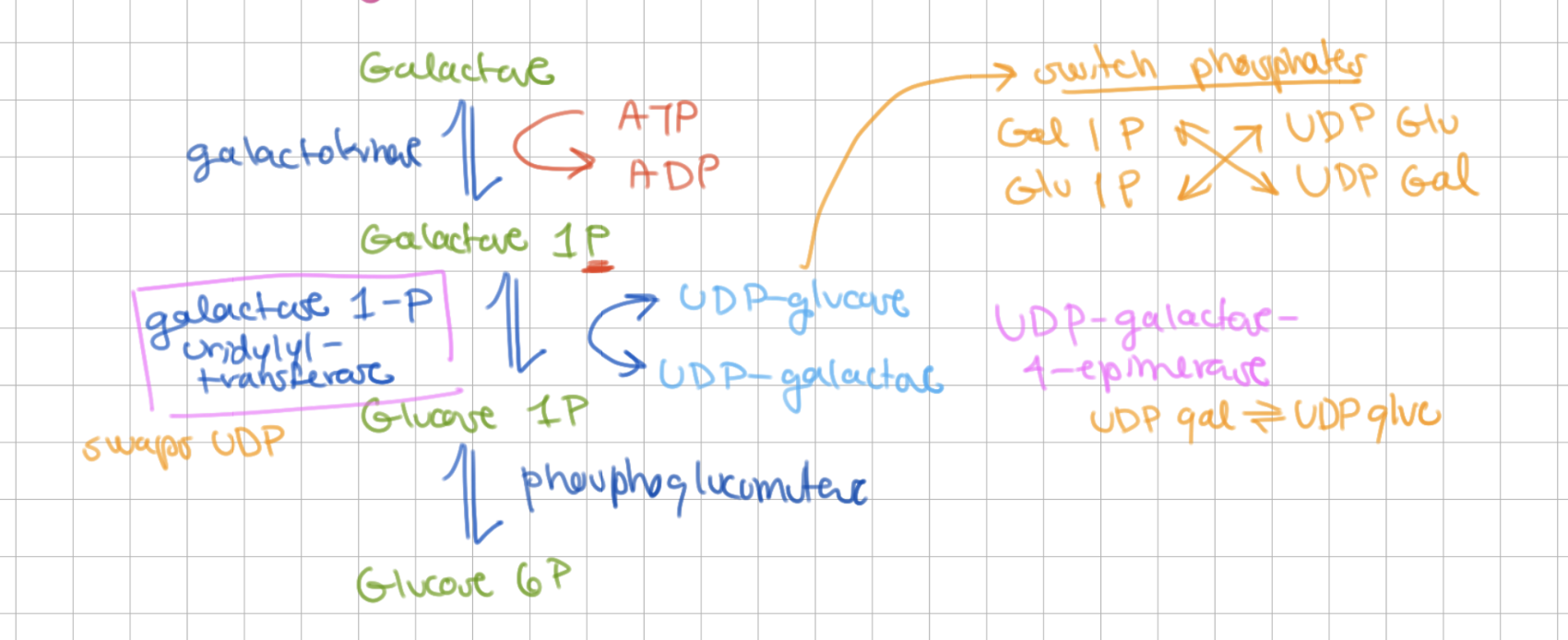
In step 2 of Leloir pathway, which enzyme switches UDP galactose with UDP glucose?
UDP galactose 4 epimerase
Glycerol can also enter glycolysis as ____ in 2 steps:
DHAP
1) phosphorylate glycerol
2) redox → DHAP + NADH
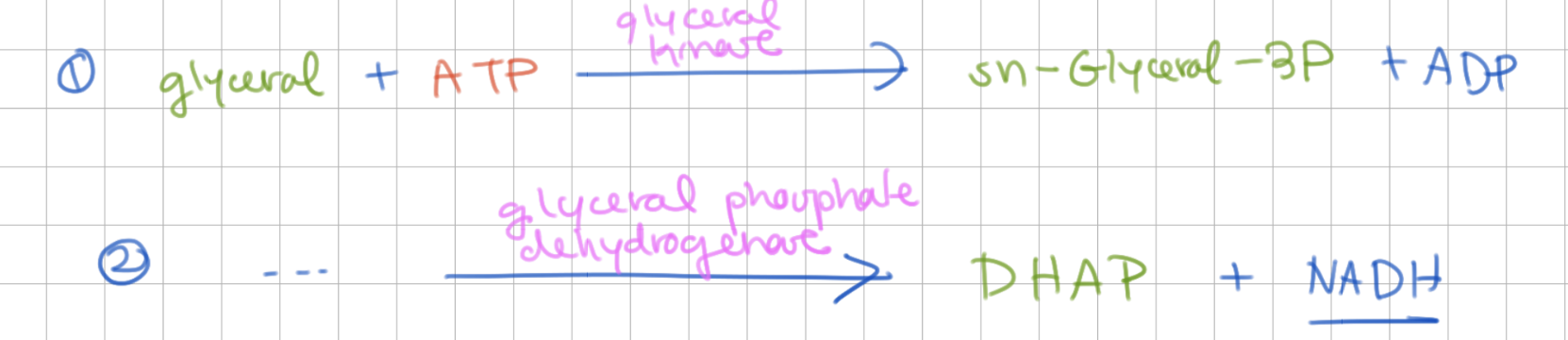
Glycerol → DHAP requires 2 enzymes:
1) glycerol kinase
2) glycerol phosphate dehydrogenase
Lactose can be converted to glucose via…
cleavage
-
lactose = disaccharide of galactose + glucose
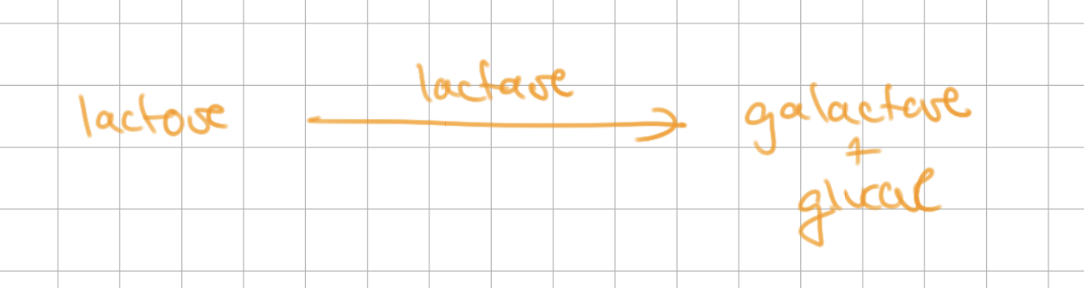
____ synthesizes lactose and _____ breaks down lactose
lactase synthase, lactase