significance tests - what to use (revision)
1/6
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
7 Terms
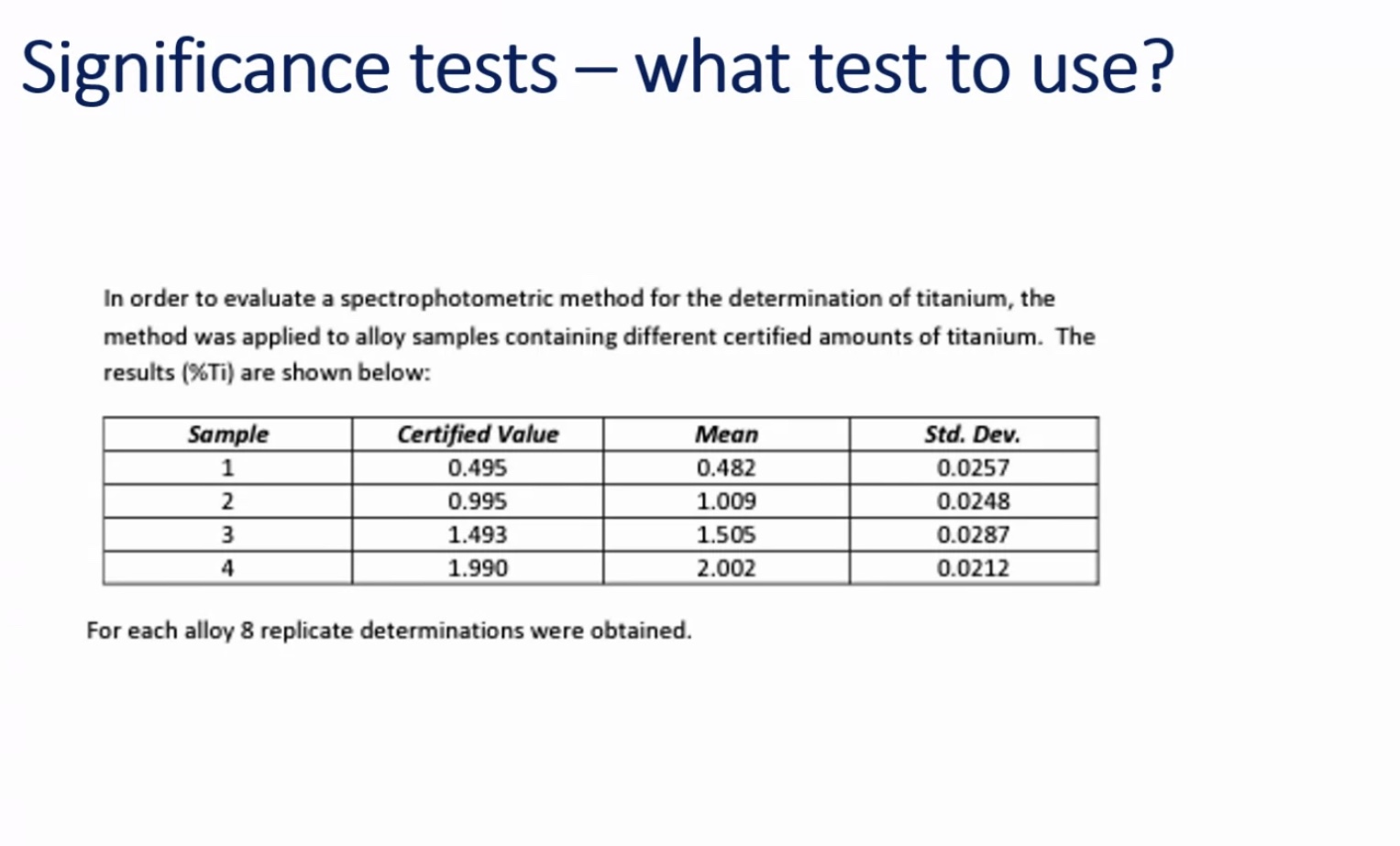
Use a 1 sample t-test:
because there’s only one method.
It’s a certified value.
The question is only looking for a one sided T test on sample 1.
The question is not asking to compare samples, it’s just asking to compare CV on SD, so only have to do sample 1.
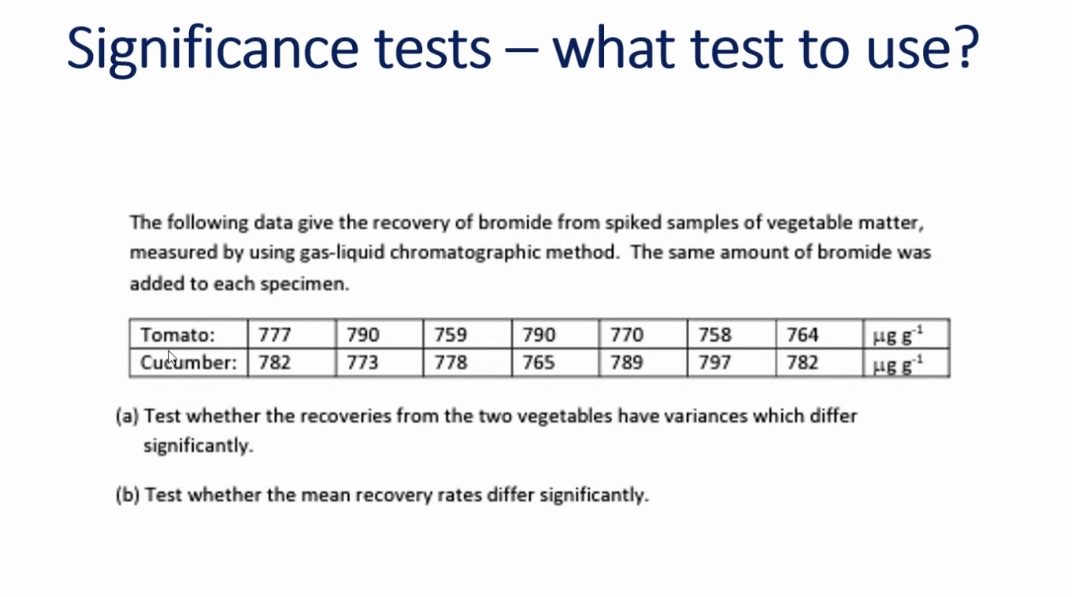
A) f test
Compare data, same method, different samples.
Contents may have an impact on the bromide so we want to check that there is no variance.
B)2 sample t test
a pulled t-test, the variance should not be impacting the mean.
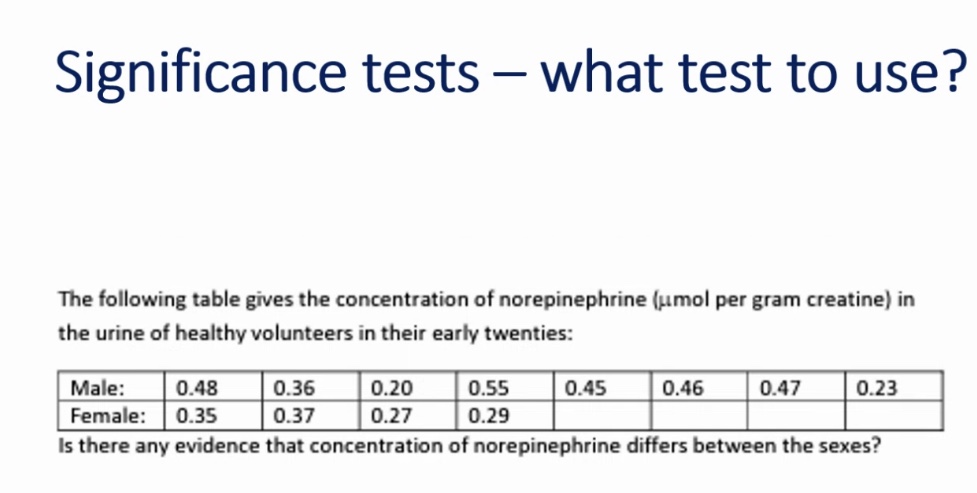
F test
2 sampled t-test (SD the same, then use pulled t-test)
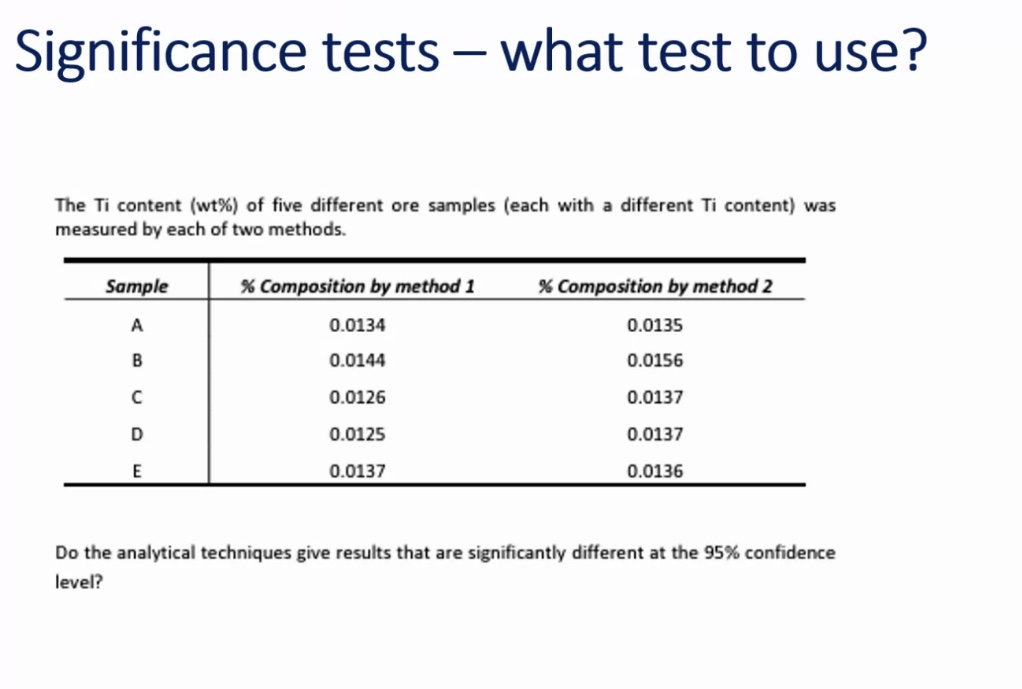
Paired t test because comparing methods.
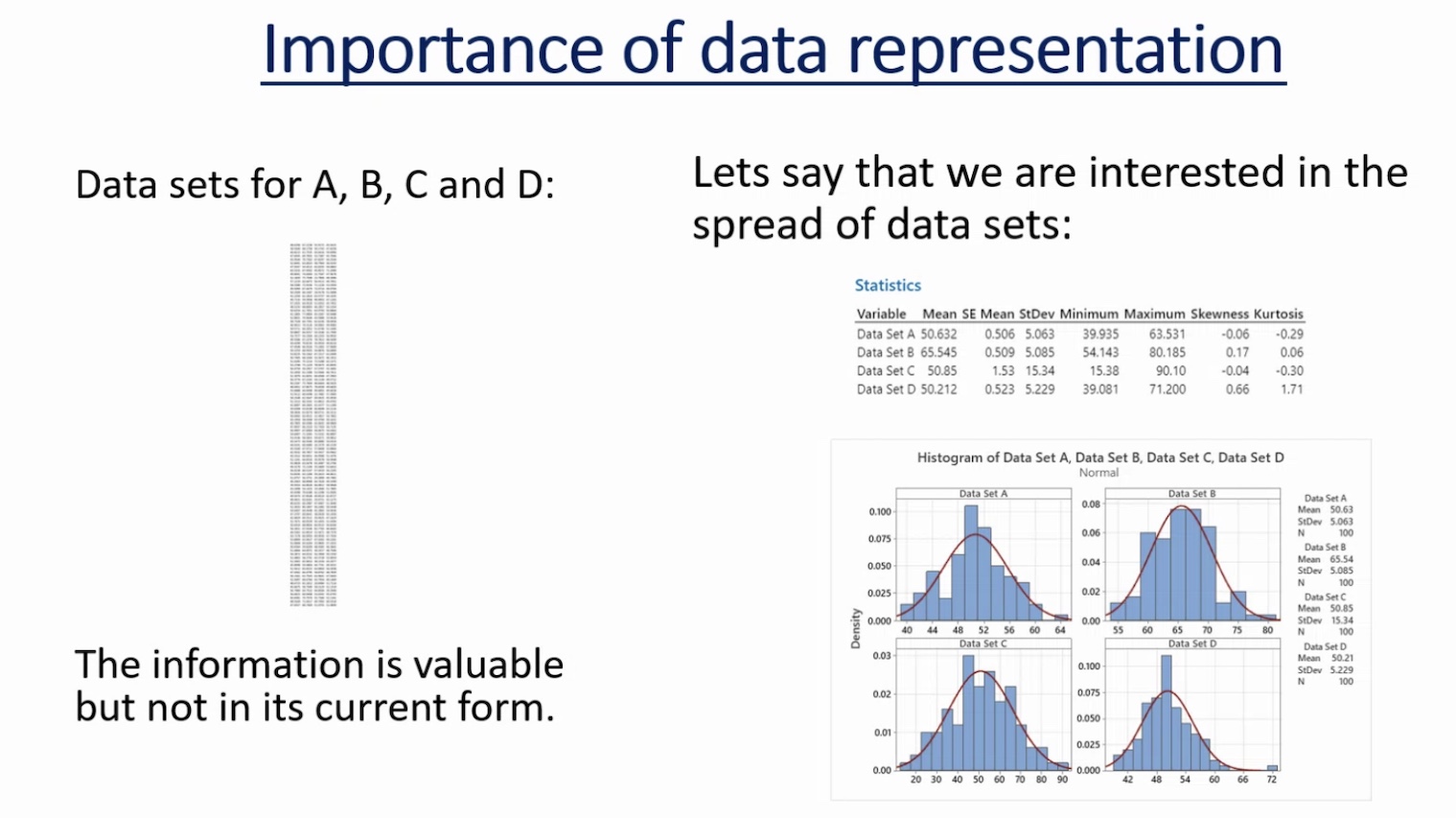
skewness:
equal pairing or to one side? where the mean of the data set is (e.g skewness to the right or left) tells us whether the data set is off.
if there was skewness in the sample, the method may be potentially wrong.
kurtosis:
weight difference, we want a main peak.
if there are lots of ‘main’ peaks it shows that there is a lack of precision, for example data set C is flattened.
box-plots:
visual comparison for data sets, reader friendly.
could use pie charts or histograms.
what is a hypothesis and why is it important?
hypothesis:
a statement that takes away from our own opinion/influence.
data = proof
either accept or reject.
takes away error and human perception
always write a hypothesis:
null; no difference (1st mean - 2nd mean = 0)
alternative; difference (1st mean - 2nd mean = greater )
outlier = if there is a ‘strange’ point in the results, it is called an outlier. if it is needed to be removed the exam question will ask you to do so.
what types of significance tests are there?
f-test:
compare standard deviations
1 or 2 variance (on minitab)
2 variance = 2 data random data sets.
f test to test for variability (the sd)
if there is no variance than you can do t-test.
t-test
compare the mean with a target value
one sample T
(compare manufacturers results to yours)
compare between means of two data sets
two sample T
(two results)
compare different methods
paired T-test
(two different methods)
test for bias (one sided t-test)
one sample t
(assess only one side of the table)