Vas week 2 : Carotid duplex bookwork
1/28
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
29 Terms
what is most common area for atherosclerosis in the extracranial arteries
proximal ICA (because of the bulb)
Occlusion of the ______ may result in loss of end diastolic flow in the CCA
ICA
homogenous plaque is best described as having
uniform echo pattern
to calculate the ICA/CCA ratio, the following measurements are used
Highest PSV from pre-bulb distal CCA and proximal ICA
Exams performed within the first few days post-carotid endarterectomy (CEA) when a patch was placed may encounter _____ during B-mode imaging from air entrapment
shadowing
what is the most common mechanism for carotid artery stenosis?
atherosclerosis
the PSV should be relatively _______ throughout the carotid arteries
uniform
vertebral artery stenosis usually occurs
proximal segment
posterior cerebrovascular circulation disorders are primarily caused by disease in which arteries
vertebral
The ICA positioned
posterolateral
identify normal velocities in the internal carotid
<125 cm/sec (book has 180cm/s)
When scanning post-stent placement, the proximal and distal ends of the stent should not reveal any major ___ _____
flow abnormalities
which vessel typically responds to the temporal tap? why?
The ECA because we are tapping the superficial temporal (STA) and its connected to the ECA so it will respond to the temporal tap.
What is the luminal diameter for the ECA
small
Doppler waveforms normally demonstrate ______ resistance in the ECA and _____ resistance in the ICA and vertebral artery’s
High, low
Correct Doppler setup requires a ____ spectral Doppler angle or less with the angle cursor set _____ to the vessel wall or to flow
60 degrees, parallel
when there is a contralateral occlusion and velocities are much higher on the other side, this may be a sign of ____ ____
Compensatory flow
a 24 year old female presents with complaints of unilateral headache. she has a history of a motor vehicle accident with the past 7 days. Discuss which mechanism of disease the patient should be carefully examined for and why
Carotid dissection. can be spontaneous or result from trauma or an iatrogenic complication. ICA dissection typically starts in the first 2-4 cm of the ICA, so this region needs to be carefully examined for a dissection
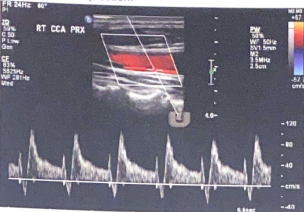
Explain the spectral tracing from a carotid dissection
Flow of the false lumen that has a different flow pattern. we can see this as the gate is in the dissected part and the flow is different because the waveform for it has a abnormal end diastolic flow.
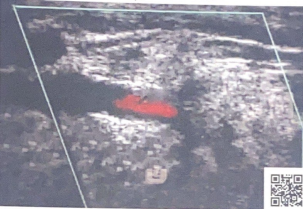
explain the disease process in the vertebral artery documented in this clip (Cant see it in the photo but the video has the flow jump from antegrade to retrograde as it pulses)
Since the usual antegrade flow is switching to retrograde, it suggests subclavian steal
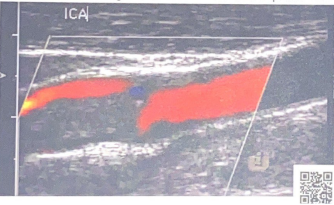
describe the degree of stenosis in this ICA clip
Near occlusion, we can only guess because we do not have velocity information from PW
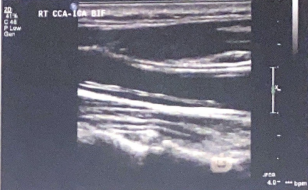
Note the double white line in the arterial lumen. what condition is suspected in this B-mode image?
carotid artery dissection
describe 4 possible abnormal findings in the ICA, post CEA
Restenosis
residual plaque
tissue flaps
hematoma
describe the duplex evaluation/ protocol for carotid stents. What images should be captured?
in addition to standard duplex examination, also capture following:
*native artery prox to stent
*Prox stent attachment site
*Prox, mid, distal stent
*distal stent attachment site
*native artery distal to the stent
When scanning post stent placement, the prox and distal ends should not show any flow abnormalities. Make comparisons to previous studies and observe for flow changes over time
Describe fibromuscular dysplasia (FMD) of the extracranial arterial system. What abnormalities would be found on the carotid duplex exam?
FMD is a non-artherosclerotic arterial disease (congential). Affects large and medium sized vessels. Usually occurs in females where it is usually in the mid ICA. Coexisting FMD in the renal and carotid arteries is not uncommon. when a series of hemodynamically significant velocity increases are noted in the mid/distal segment of the ICA followed by turbulence than FMD is suspected. Shows up as ‘string of beads” in b-mode and color Doppler imaging.
Which artery has branch vessels in the neck, the ICA or ECA?
ECA
Luminal diameter for the ICA
Large
Normal PSV for ECA
<200 cm/s (book answer)
What is the anatomical location of the ECA
Anterolateral