Recession and Furcations
1/15
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
16 Terms
what is the difference berween gingival shrinkgaer and true recession
shrinkage happens cos of perio or side effect of tx and id pappilae move back
recession is inflammation free and id papillae are at normal level
u dont lose teeth from recession
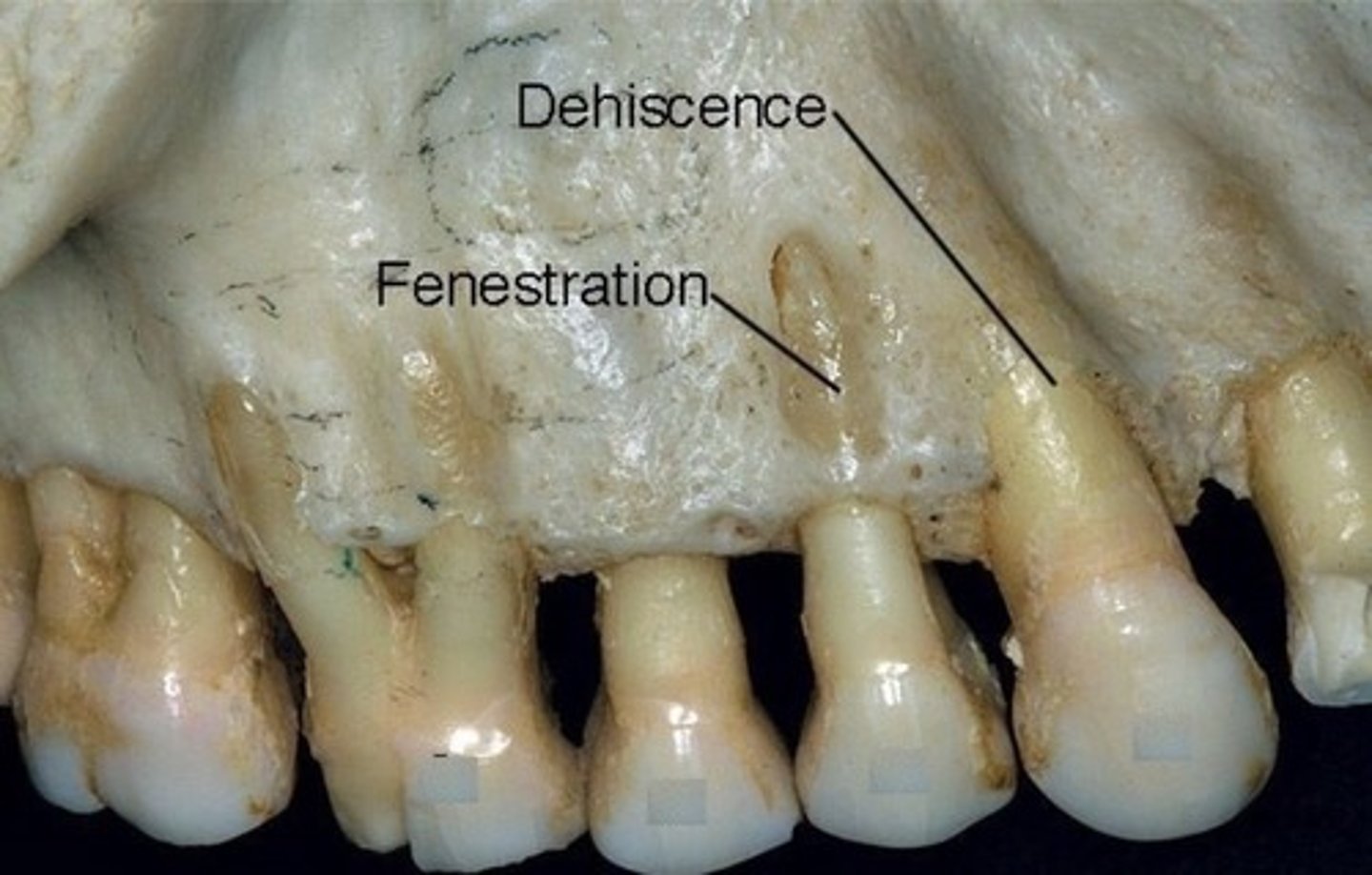
what is dehiscence
lack of bone
tooth is normally procline through a thin sheet of bone
associated with recession as the ginivae is pulled down to the level of the bone
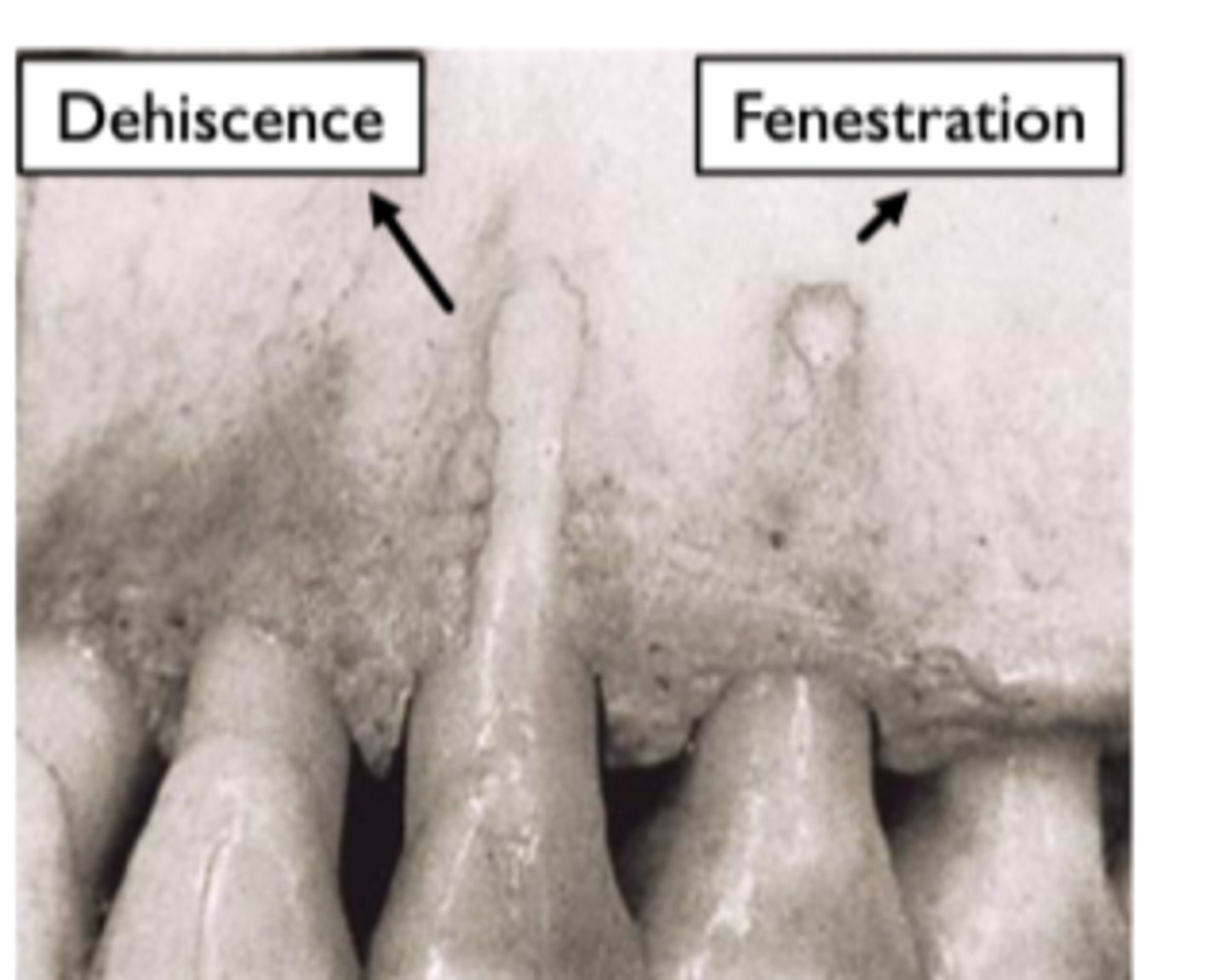
what is fenestration
window in bone
usually buccal aspect
related to recession as the gingivae shinks to where the bone is gone
what are causes of true recession
morphology and anatomy of tooth and bone
chronic minor trauma ie improper tb technique
accidental injury
mild chronic inflammation esp in anteriors
frenum pulls
ortho
excessive perio scaling
parafunction - teeth not functioning properly
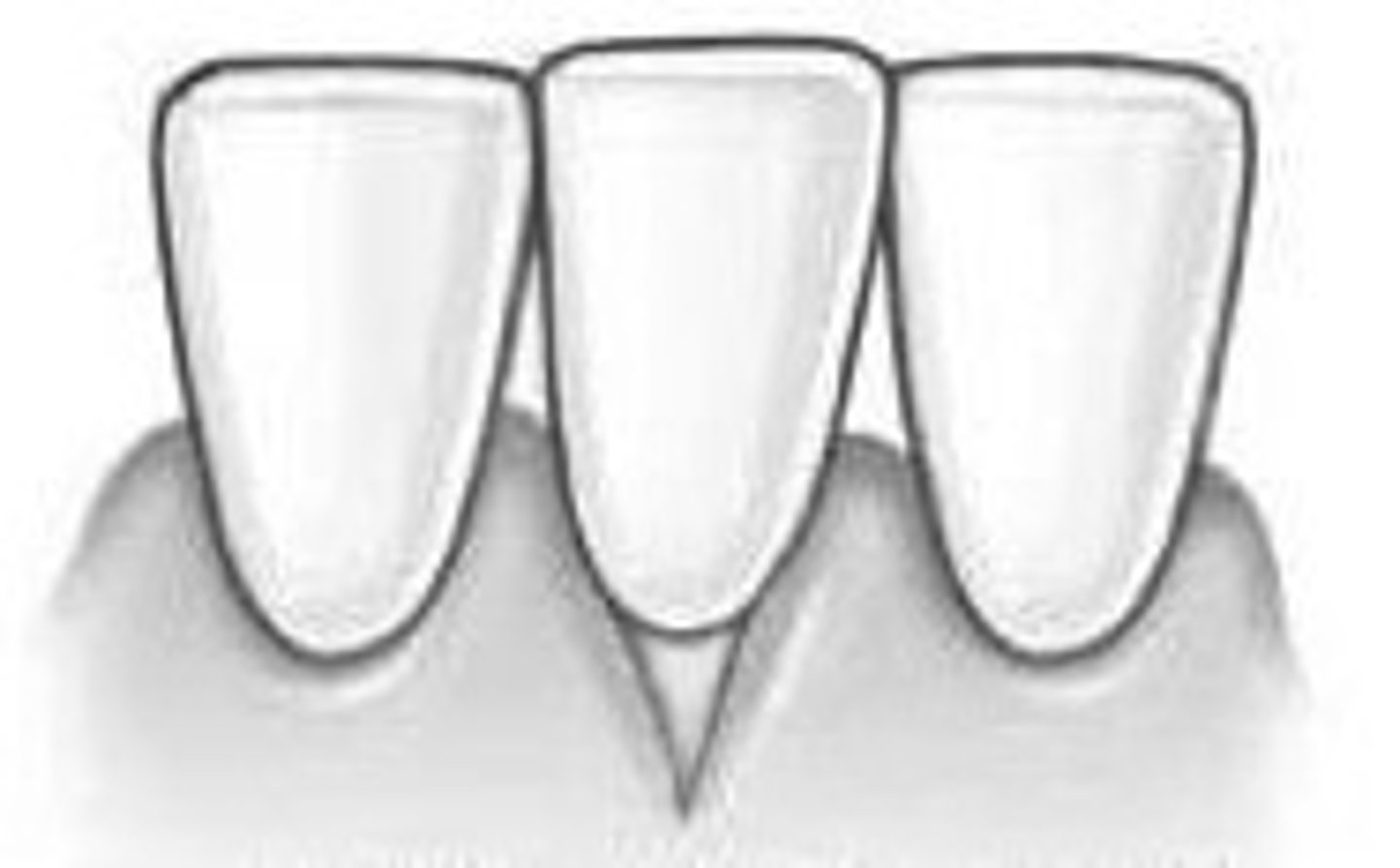
what is a stillmans cleft
localised recession that is a v shape
what is a mcalls festoon
refers to the gingivae that rolls back
can have the same time as a stillmans cleft or without
what issues r with recessiom
dentine hypersensitivity
root caries
tb abrasion - if root recessed then if tb abrasdion happens it will erode away quickly
where does localised recession occur
anywhere but usually lower ants
caused by fraenul pull and thin buccal bone
how do we monitor recession
LOA and pocket depths on perio chart
clinical photos
study models
how do we treat recession
eliminate causal factors
ie modify tb technique
eliminate areas of mild inflam eg replace faulty margins of restoration or remove calc
frenectomy
monitor
treat any associated issues eg
dentine hypersensitivity
prevent caries on roots - ensur good oh anf flouride
perio surgery - soft tissue grafts
what is furcation involvement
horizontal loss of support in areas where multirooted teeth converge
diagnosed via both radiograph and clinical exam
ie xray may have arrowhead lesion but cant see soft tissue
if not seen in mouth = not furcation
what is pre/molar tooth morphology
max -
1st premolar 2 roots
2nd premolar 1 root
molars 3 someyimes 2
mand -
1 and 2nd premolar 1 root
molar 2 roots
what is hamp et al
record tooth site and severty
1 - 1/3rd width
3 - full way through
why are furcations bad
reduces prognosis of a tooth ;
difficult to clean so hard to control disease
loss of vitality may happen due to accessory channels running from pulp chmaber to furcation nd bacteria can get in
how do we manage and treat furcation
manage -
grade every checkup and review/kuo
vitality test every year
treat - perio surgery
how do we treat diff grades of furcation
OHI for all
1 - pmpr furcatonplasty
2 - furcationplasty
guided tissue regern
root resection
extraction
3 - tunnel prep
root resection
extraction