IB BIology 2025 Enzymes
1/41
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
42 Terms
Enzyme
a substance produced by a living organism that acts as a catalyst to bring about a specific biochemical reaction.
Catalyst
(n.) a substance that causes or hastens a chemical reaction; any agent that causes change
Active Site
a region on an enzyme that binds to a protein or other substance during a reaction.
Substrate
reactant of an enzyme-catalyzed reaction
Enzyme-Substrate Complex
A temporary complex formed when an enzyme binds to its substrate molecule(s).
Activation Energy
the minimum amount of energy required to start a chemical reaction
Product
A substance produced in a chemical reaction
Lock-and-Key Model
The model of the enzyme that shows the substrate fitting perfectly into the active site
Induced Fit Model
enzyme model where the substrate induces the enzyme to alter its shape slightly so it fits better
Denaturation
In proteins, a process in which a protein unravels and loses its native conformation, thereby becoming biologically inactive. In DNA, the separation of the two strands of the double helix.
Optimal Temperature
Temperature at which an enzyme works the best
Optimal pH
specific pH at which an enzyme works the fastest
Enzyme Activity
a measure of the ability of an enzyme to catalyse a specific reaction.
enzyme turnover rate
rate at which the enzyme that comes out with the product is recycled through the process again
Cofactor
Non-protein helpers that may be bound tightly to the enzyme as a permanent resident, or may bind loosely and reversibly along with the substrate.
Coenzyme
If the cofactor is an organic molecule.
Prosthetic Group
A non-protein, but organic, molecule (such as vitamin) that is covalently bound to an enzyme as part of the active site.
Competitive Inhibition
substance that resembles the normal substrate competes with the substrate for the active site
Non-Competitive Inhibition
a type of enzyme inhibition where the inhibitor reduces the activity of the enzyme and binds equally well to the enzyme whether or not it has already bound the substrate.
Allosteric Site
The place on an enzyme where a molecule that is not a substrate may bind, thus changing the shape of the enzyme and influencing its ability to be active.
Allosteric Inhibition
inhibition by a binding event at a site different from the active site, which induces a conformational change and reduces the affinity of the enzyme for its substrate
Feedback Inhibition
A method of metabolic control in which the end product of a metabolic pathway acts as an inhibitor of an enzyme within that pathway.
Reversible Inhibition
inhibitor bonds noncovalently to the active site and prevents substrate from binding, when inhibitor leaves enzyme function resumes
Irreversible Inhibition
active site is made unavailable for prolonged period of time or enzyme is permanently altered usually when a covalent bond is formed between the inhibitor and the enzyme itself
Enzyme Kinetics
the study of the rates of enzyme-catalyzed reactions
Vmax
maximum initial velocity or rate of an enzyme-catalysed reaction.
Saturation point - Enzymes
The point is where there are too many substrates for enzymes, and their reaction rate stays the same. All active sites are full of substrates
Inhibitor
A substance that slows down or stops a chemical reaction
Enzyme Specificity
Enzyme specificity is the concept that each enzyme catalyzes only one kind of reaction.
Catalytic Cycle
substrate + enzyme --> enzyme substrate complex --> product + enzyme
Metabolic Pathway
A series of chemical reactions that either builds a complex molecule or breaks down a complex molecule into simpler compounds.
Immobilized Enzymes
are enzymes that can be attached to each other or to inert substances and can be used repeatedly. (to each other, insoluble supports: glass, within a gel: sodium Alginate)
Transition State
a high-energy intermediate state of the reactants during a chemical reaction that must be achieved for the reaction to proceed
competative inhibition
regulatory molecule is similar in size and shape to the enzyme's natural substrate and inhibits catalysis by binding to the enzyme's active site
Non-competative inhibition
The inhibitor binds to the allosteric site, changing the shape of the enzyme so that the substrate can no longer bind the active site.
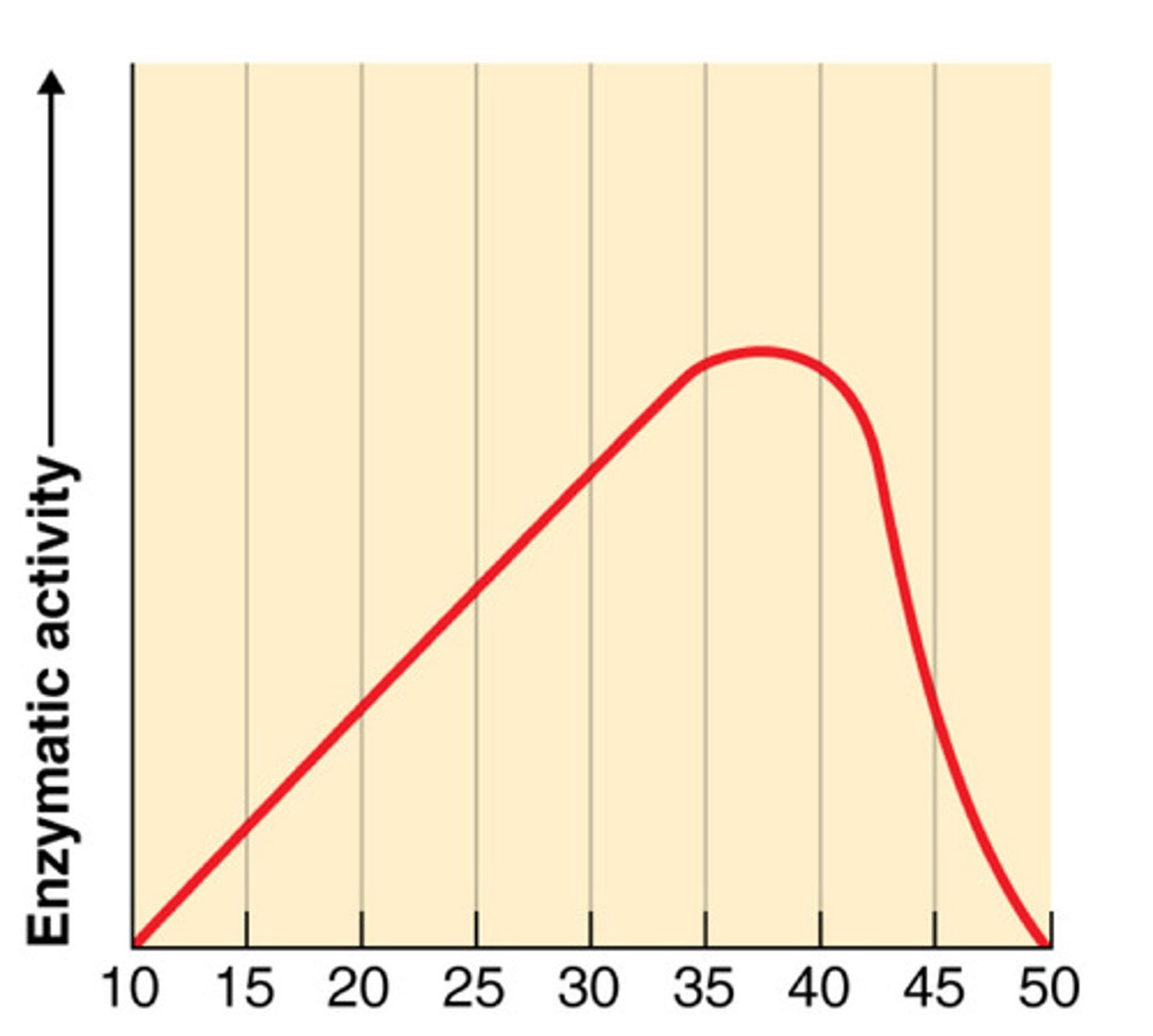
Effect of temperature on enzyme activity
Enzyme activity increases as temperature increased (often doubles with every 10 degree rise) because collisions between substrate and active site occur more frequently due to faster molecular motion
At too high temperatures, enzymes denature and stop working
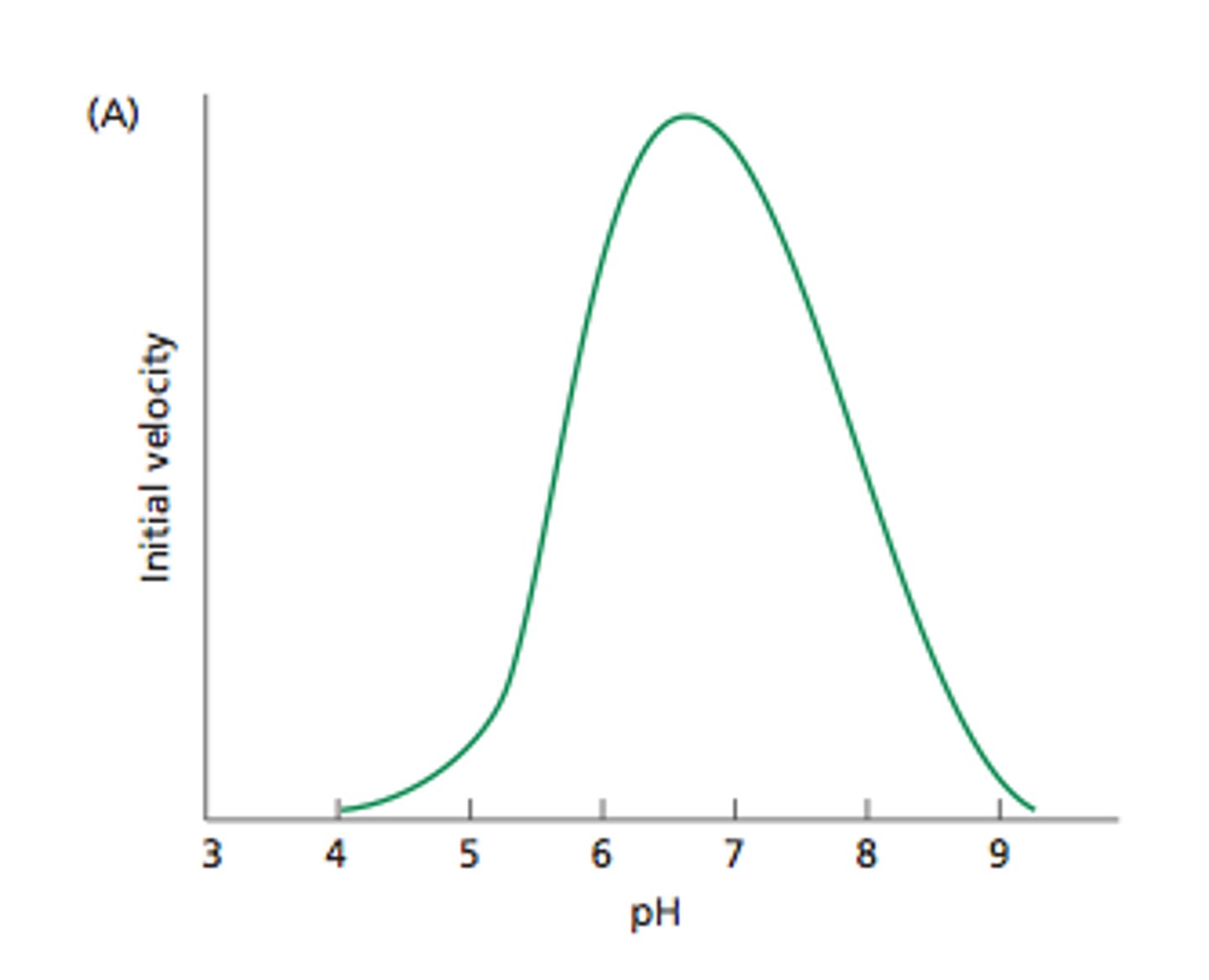
Effect of pH on enzyme activity
All enzymes work best at optimal pH. above and below the optimal pH the rate of reaction decreases. Extreme pH changes can denature the enzyme.
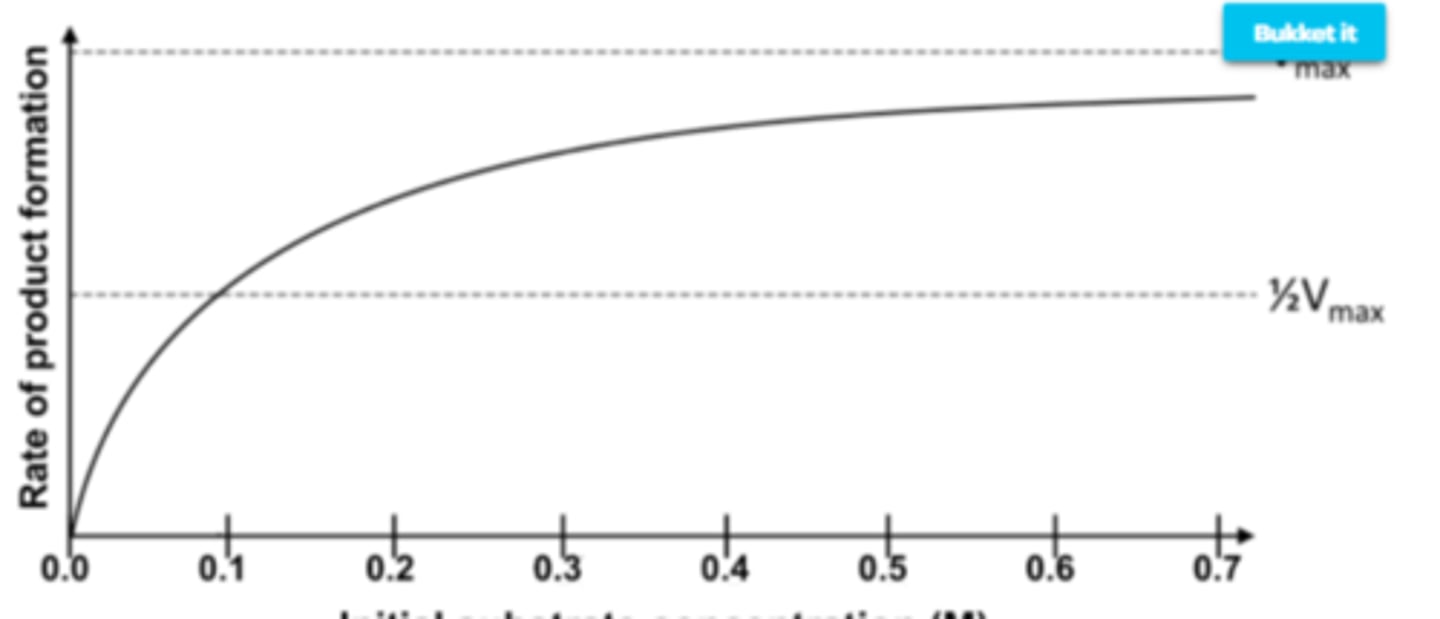
substrate concentration on enzyme activity
As the substrate concentration increases, so does the rate of reaction, until all of the active sites are bound and the rate of reaction levels off.
temp enzyme activity graph
ph enzyme activity graph
Substrate Concentration on Enzyme Activity graph
mechanism-based inhibition
- inhibitor acts as a substrate and forms a covalent bond with the enzyme so the reaction cannot take place as the substrate cannot fit in the enzyme
- often irreversible
eg: covalent "suicide" inhibition