ECON 101 EXAM 2
1/117
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
118 Terms
Economic growth brings wealth which increases..
societal well being
higher infant survival rates are in
wealthy countries
GDP per capita facts:
most of worlds population is poor compared to America
73% of worlds population live in countries with a GDP per capita thats less than average
Everyone used to be poor facts:
distribution of world income tells us that poverty is normal while wealth is not
for must of human history there wasn’t any long run growth in real per capita GDP
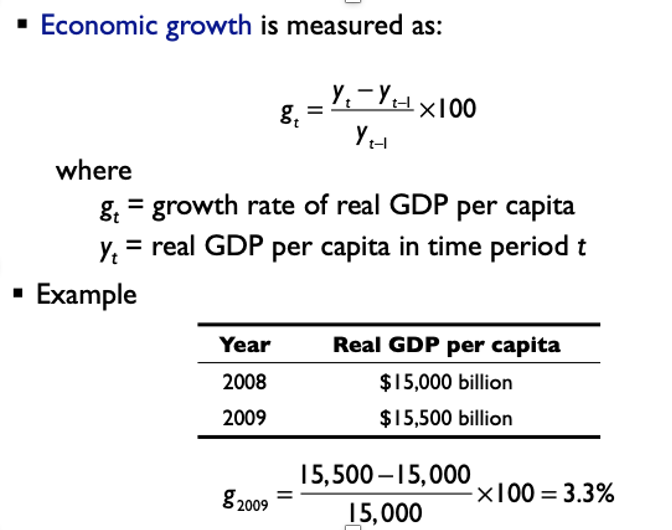
economic growth is measured as
growth rate of real GDP per capita
Rule of 70
length of time necessary for a growing variable to double
Rule of 70 example
Real GDP per capita is growing at annual growth rate of 3.5% then it will double in:
70/3.5= 20 years
Growth miracles
- slow and consistent economic growth
- U.S. is one the wealthiest country ever because it grew slowly but consistently for over 200 years
- From 1950 to 1970 Japan grew 8.5% per year.
growth disasters
- Nigeria's minimal economic growth since 1950
- Argentina's decline in per capita GDP from 1900 to 2000.
Wealth of Nations
causes of growth in GDP per capita:
factors of production
incentives
insistutions
Factors of production
physical capital
human capital
technological knowledge
physical capital
tools such as: machines, structures, and equipment
more/better physical capital makes workers more productive
physical capital is increased by investing
human capital
knowledge and skills that workers get through education, training, and experience
example: degree, internships, problem solving skills, expertise in specific fields
allows workers to use more sophisticated tools
human capital is increased with education
technical knowledge
knowledge about how the world works, that is used to produce goods and services
We increase technological knowledge with research and development.
Improved technological knowledge increases productivity
Institutions
institutions of economic growth include laws, regulations, customs, practices, organizations, and social norms.
Incentives of economic growth
• Property rights
• Honest government
• Political stability
• A dependable legal system
• Competitive and open markets
Property Rights
Institutions crucial for fostering investment in physical and human capital
important for encouraging technological innovation
Honest Government - Impact
Resources spent on bribery can't be invested in machinery or equipment.
Honest Government - Corruption
-Acts as a drain on resources, diverting funds from productive uses.
Political Stability
Civil wars and dictatorships can hinder economic growth.
Dependable Legal system
Facilitates contracts and protects parties against expropriation.
Dependable legal system - Challenges
Uncertain property rights hinder borrowing and investment.
Competitive Open Markets
Key to optimal resource allocation
Competitive Open Markets - barriers
Inefficient regulations and trade restrictions impede efficiency
Ultimate causes of wealth
Natural resources, transport accessibility, geography, history, culture, and luck influence economic growth.
Cutting Edge Growth
growth due to new ideas
Catching up Growth
growth due to capital accumulation
Production Function
expresses a relationship between output of economy and the factors of production
Production Function Equation
Physical Capital (K), Human Capital × Labor (eL), and Ideas (A).
Y = F(A, K, eL)
simplify to y= F(k) if..
A (ideas) and eL(labor) are constant
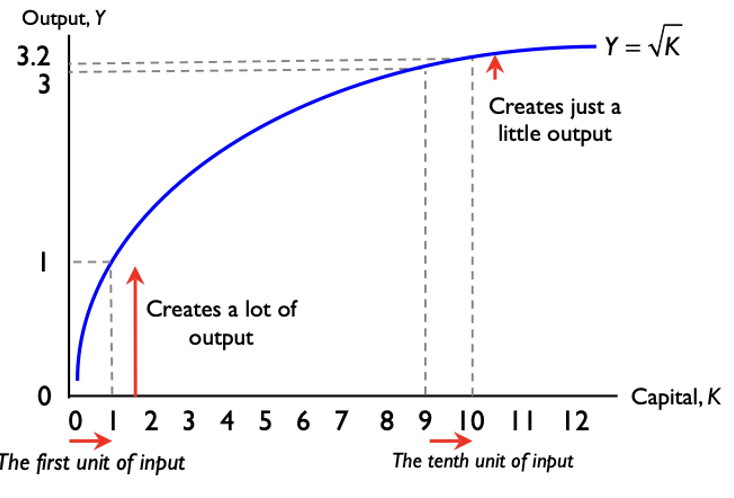
typical production function is
Y = √K
increases in K deliver increases in Y
Capital is..
output that is saved and invested rather than consumed
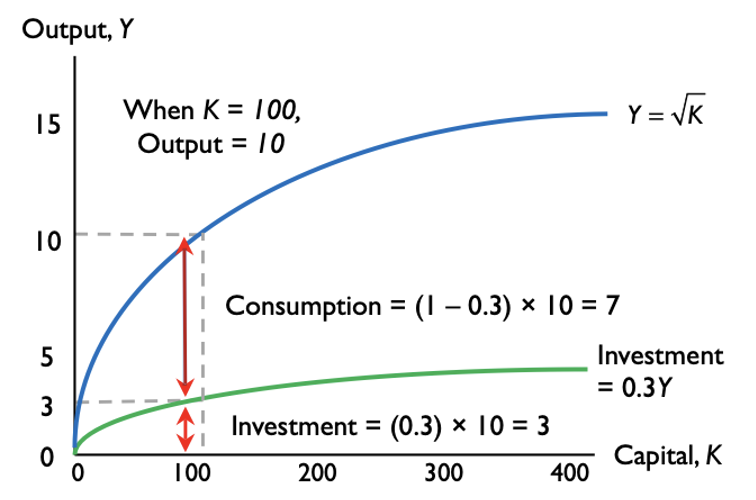
Capital/ Investment example:
Out of 10 units produced, 7 consumed, 3 invested.
Investment Fraction: γ (gamma), where γ = 3/10 = 0.3.
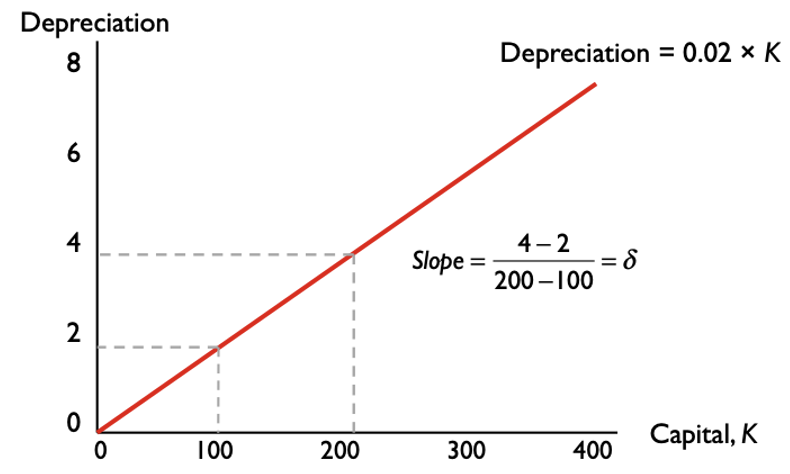
Capital Depreciation definition
Capital wears out over time
ex: If 100 units of capital, 2 might depreciate, leaving 98 for the next period
Depreciation Equation
δ (delta) = 2/100 = 0.02
ex: If 100 units of capital, 2 might depreciate, leaving 98 for the next period
Investment > Depreciation
Capital and output grow
Investment = Depreciation
Capital and output remain constant (steady state)
Investment < Depreciation
Capital shrinks, and output decreases
Higher investment rates lead to..
more capital and increased output
Countries with high investment rates..
have higher GDP per capita
Solow model predicts zero economic growth in the long run but better ideas..
can keep the economy growing even in the long run
Solow model with tech
A stands for ideas that increase productivity; our production function is:
Y=A K
Reasons for patents:
products/methods can be copies
imitators have lower costs and cant copy them
increase incentives to develop new products
governments role in economy:
create incentives to produce new ideas
encourage production of new ideas though subsidies/tax breaks
universities train scientists to research/develop new products
Large markets mean
increased incentives
4 factors that determine Supply of Savings
smoothing consumption
impatience
marketing + psychological factors
interest rates
consumption is most high during..
working years
you can Smooth Consumption by…
saving during working years and spend during retirement
Impatience
the more impatient a person is the more likely their savings will be low, ex: criminal, addict, smoker
Marketing/Psychological Factors
ppl save more if saving is presented as natural/default alternative
ex: retirement savings plan participation was 25% higher in business that used automatic enrollment than opt-in feature
higher interest rate
more amount saved
3 factors that determine Demand of Borrowing
smoothing consumption
investment
interest rates
consumption smoothing
ppl borrow to smooth their consumption
ex: borrowing to invest in their education
Investment - Demand of Borrowing
business borrow to finance large projects
low interest rates
greater demand to borrow
Suppliers of Loanable funds (savers) trading with demanders of loanable funds(borrowers) creates…
market for funds
interest rates adjust to..
equalize savings and borrowing
Surplus is created when
interest rate > equilibrium, and quantity of savings > quantity of savings demanded
Shortages are created when..
interest rate < equilibrium, the quantity of savings < quantity of savings demanded
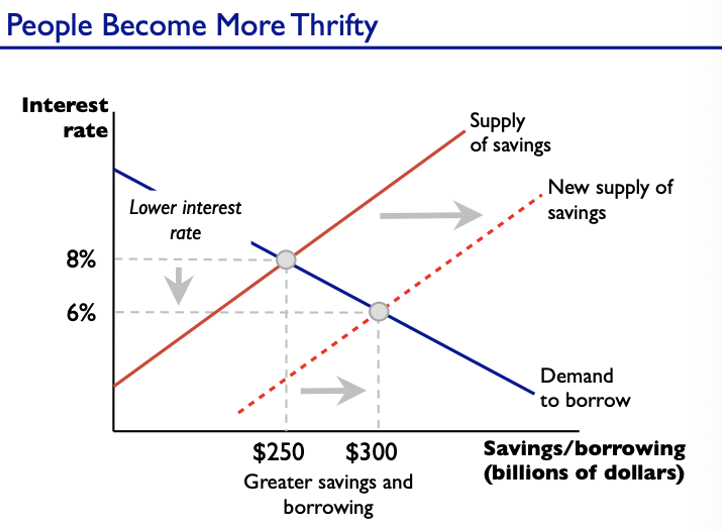
Supply and Demand Shift
changes in economic conditions
ex: ppl becoming more thrifty, investors less optimistic
Financial Intermediaries
banks, bond markets, stock markets
Financial Intermediaries job is..
reduce the costs of moving savings from savers to borrowers and mobilize savings toward productive uses
banks receive savings..
and loan them to borrowers
corporation acknowledges debt by..
issuing bond (corporate IOU)
bonds are a way to raise..
large sum of money for long-lived assets
a risky company has to pay
higher interest
US gov bonds/ treasury securities are desirable because
because they are easy to buy and sell, and the U.S. government is unlikely to default
T- bonds
30 year bonds, pay interest every 6 months
T- notes
range from 2 to 10 years, pay interest every 6 months
T - bills
range from a few days to 26 weeks, interest paid at maturity
Zero coupon bonds/ discount bonds
only pay at maturity
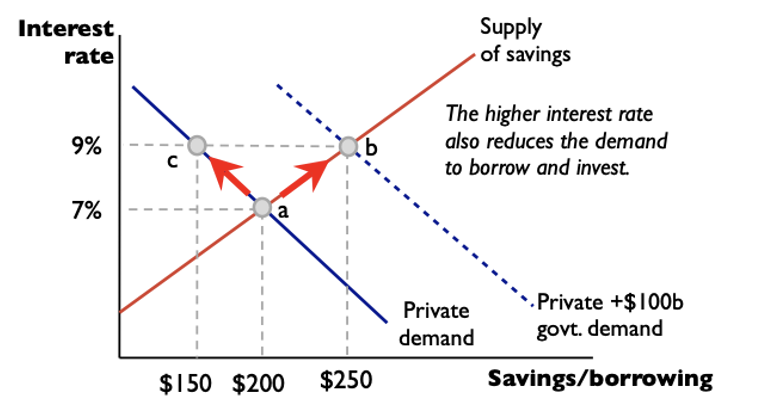
an increase in gov borrowing shifts..
private consumption and investment
Value of bond at maturity is called
Face Value
formula for rate of return (receiving interest rate) on zero coupon bond is…
=(FV- Price / Price ) x 100
arbitrage
buying and selling of equally risky assets
stock
A certificate of ownership in a corporation
stocks are traded in
stock exchanges
Initial Public Offering (IPO)
The first time a corporation sells stock to the public in order to raise capital
Financial Intermediaries are..
bridges between savers and borrowers
Intermediation can fail due to:
- insecure property(bank accounts) rights
- politicized lending
- government bank
- interest rate controls
- inflation
- bank failures and panics
insecure property (bank accounts) rights ..
negatively affect savings and investments
ex: When Argentina froze bank accounts in 2001, many banks went under and Argentinians lost their savings
Price controls on interest rates
cause the loanable funds market to malfunction (shortage of savings)
Usury Laws
impose a maximum amount on the interest rate that can be charged
Government owned banks
have slower growth in per capita GDP
Bank failures/panics cause
people to lose all their savings
Owners equity
The value of the asset minus the debt, or E = V − D.
Leverage Ratio
The ratio of debt to equity, or D/E.
A house worth $400,000 with 20% down and a mortgage of $320,000. What is the equity?
$400,000 – $320,000 = $80,000
A house worth $400,000 with 20% down and a mortgage of $320,000. What is the leverage?
$320,000/$80,000 = 4
2008 Financial Crisis happened because..
failing asset prices and high debt which caused panic
Unemployed workers
adults who dont have a job but are looking for one
To be counted as unemployed you have to be:
16 years+
not in prison
a civilian looking for work
Unemployment Rate equation
(Unemployed/ Unemployed + Employed) ×100= Unemployed / Labor Force ×100 =
January 2019, there were 6.5 million people unemployed in the U.S. and 156.7 million employed. Together, the employed and the unemployed make up the labor force of 163.2 million. What is the unemployment rate?
(6.5 / 6.5 + 156.7) x 100 = (6.5/163.2) x 100 = 3.98%
Unemployment means the economy is..
underperforming
Discouraged workers
Workers who have given up looking for work but still want a job
Underemployment
ppl who have jobs and are employed but dont work as much as they would like to
ex: taxi driver with PhD in Physics
Frictional unemployment is..
short term unemployment
Frictional unemployment is caused by..
ordinary difficulties of matching employee to employer
ex: finding a job that you want at a wage that you will accept and that
the employer will pay
Large portion of the total unemployment in U.S. is..
frictional unemployment