Chapter 6: The Human Population and Its Impact
How Many People Can the Earth Support?
Natural Capital Degradation
- Reduction of biodiversity
- Increase NPP use
- Elimination of natural predators
- Interfering with biochemical cycling
- Relying on fossil fuels
Human Population Growth Continues but It Is Unevenly Distributed
- Cultural carrying capacity: the number and type of a given species that people will tolerate over time
What Factors Influence the Size of the Human Population?
The Human Population Can Grow, Decline, or Remain Fairly Stable
- Population change: (births + immigration) – (deaths + emigration)
- Crude birth rate: The number of live birth's per 1,000 people in a population in a given year
- Crude death rate: The number of deaths per 1,000 people in a population in a given year
Women Having Fewer Babies but Not Few Enough to Stabilize the World’s Population
- Fertility rate: Number of children born to a woman during her lifetime
- Replacement-level fertility rate: The average number of children a couple must have to replace themselves
- 2.1 in developed countries
- up to 2.4 in developing countries
- Not immediate so many are younger than 15 years old
- Total Fertility Rate (TFR): The average number of children born to women in a population during their reproductive years.
- Plays a role in determining population size
Factors That Affect Birth and Fertility Rates
- Children might be a part of the labor force
- Cost of raising children
- Education and employment of women are slowly increasing
- Availability of abortions
- Religious or cultural beliefs
- Availability of birth control
Factors That Affect Death Rates
- Life expectancy: The average number that an individual is likely to live
- Global life expectancy from 48 in 1955 to 69 in 2010
- Infant mortality rate: Number of live births that die in the first year
- A strong indication of the quality of life in the area
- Longer lives because…
- Increased food supply
- More nutritions
- Available medical resources
- Improvements in sanitization
How Does a Population’s Age Structure Affect Its Growth or Decline?
A Population’s Age Structure Helps Us Make Projections
Age Structure Categories:
- Prepreproductive age (0-14)
- Reproductive ages (15-44)
- Postreproductive ages (45 and older)
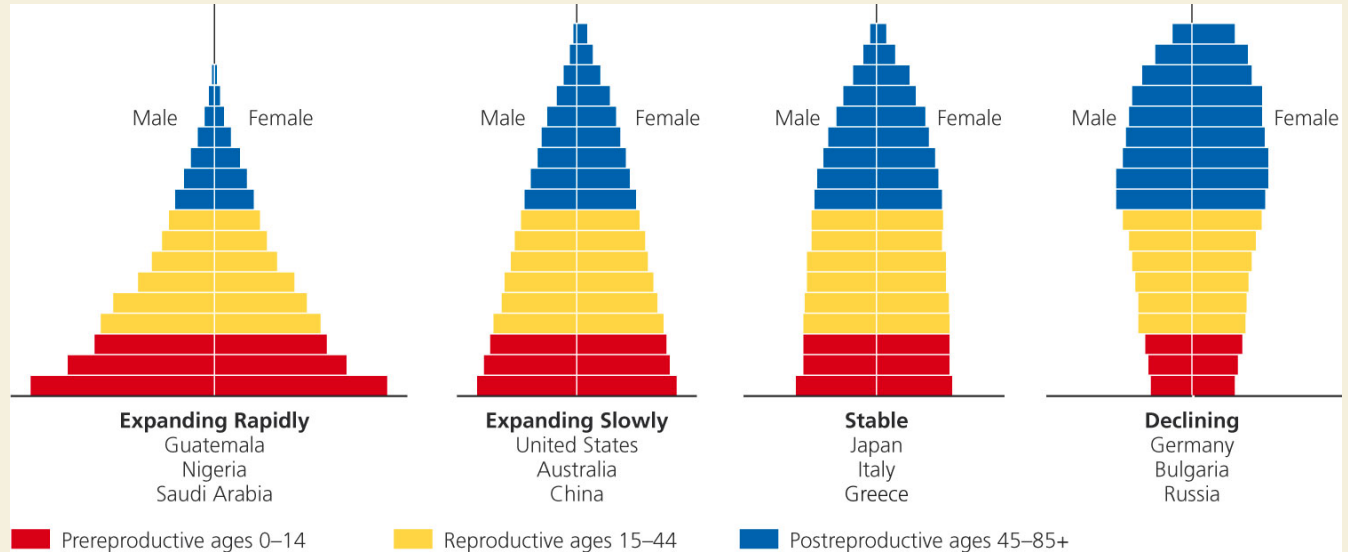
Some Problems With Rapid Population Decline
- Threaten economic growth
- labor shortage
- Fewer business formations
- Retirement age increases
- Pensions can be cut
How Can We Slow Human Population Growth?
As Countries Develop, Their Populations Tend to Grow More Slowly
- Demographic transition: First death rate declines and then the birth rate declines.
- Four Stages
- Preindustrial: The population grows slowly and has a high death and birth rate.
- Transitional: The population grows rapidly and the birth rate is high. Death rate drops.
- Industrial: Population growth slows as both birth and death rates drop because of improved food production, health, and education
- Postindustrial: Population growth levels off and then declines as birth rates equal and the fall below death rates
Women
- Do most of the housework and care for children
- Unpaid health care
- Discriminated against legally and religiously
- Women make up 64% of the 800 million illiterate adults
- Illiterate women TFR→ 5-7 Children
- Literate women TFR→ 2 or fewer children
- Family Planning: Provides educational and clinical services that help couples choose how many children they want to have and when to have them