Earth Systems
1/24
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
25 Terms
Concept of a “system”
provides framework for understanding how each part of the Earth works and why it is changing
Concept of a “system”
provides framework for understanding how each part of the Earth works and why it is changing
System
a group of interdependent materials that interact to form a united whole and are influenced by related forces.
Materials in a System
change in an effort to reach and maintain equilibrium.
move to a lower level of energy to attain balance and peace
Earth Systems: Closed
Type of system that exchanges only energy (no matter) with its surroundings
Eg. Earth and the Sun
Earth Systems: Open
Type of system that exchanges both heat and matter with surroundings; applies to most earth systems
Eg. river systems, volcanic systems, etc.
State of equilibrium
(Direction of Change in Earth Systems)
There is a universal tendency for systems to move toward a/an _________
Equilibrium
A condition in which the net result of the forces acting on a system is zero
Fundamental law
Any system tends to run down: to lose energy to the surroundings.
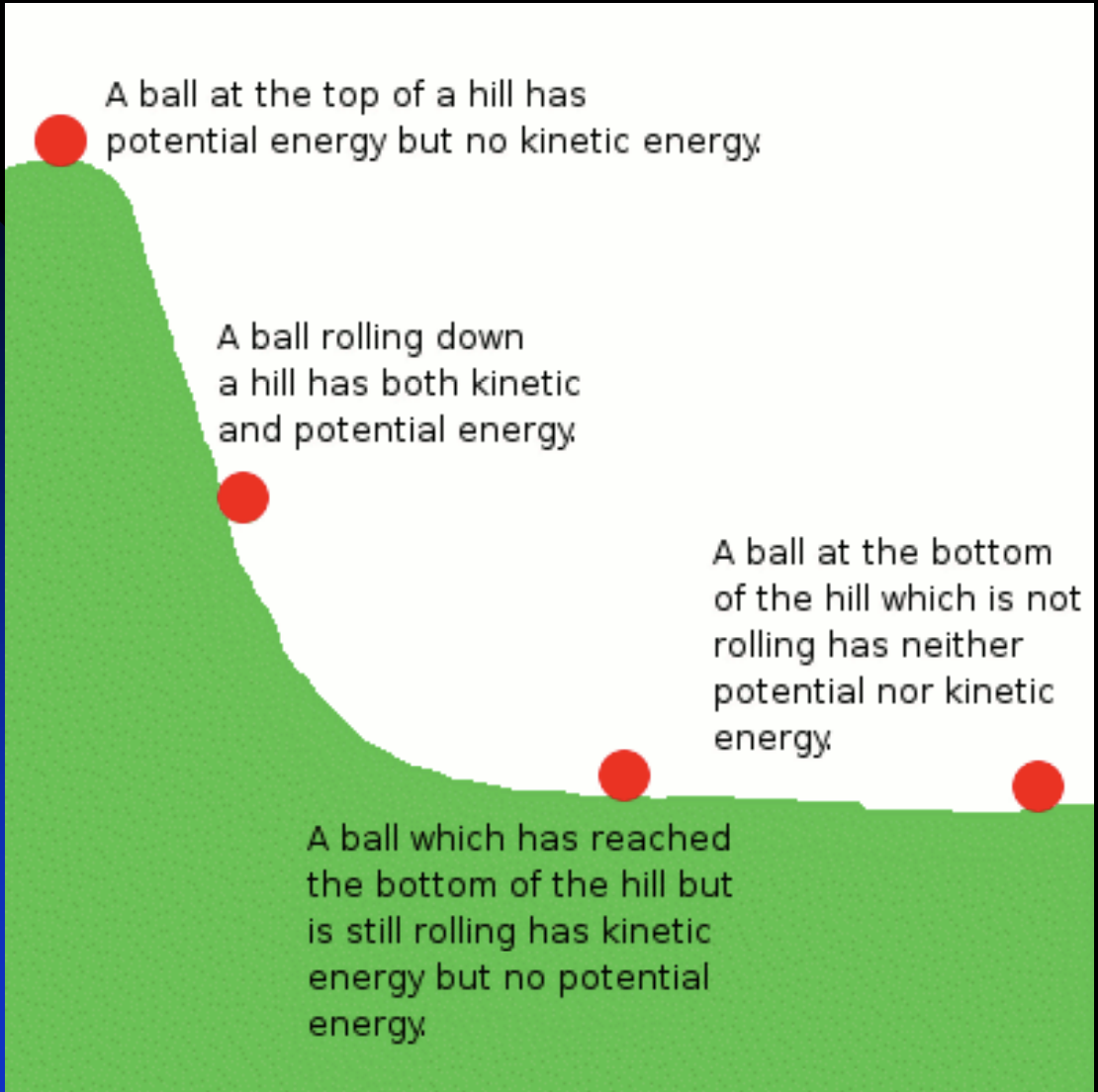
Direction of Change in Earth Systems
For spontaneous change to occur, the total energy of a system must decrease. The most stable state is the one with the lowest energy.
James Lovelock and Lynn Margulis
Proponents of Gaia Hypothesis
Gaia Hypothesis
The biosphere is a self-regulating system that controls its physical and chemical environments
We don’t have to do much to maintain the system
The Daisyworld Model of Earth Systems
Daisies represent the materials on the surface of earth (oceans, lands, clouds) where white daisies reflect light and black daisies absorb heat
The Earth can only survive because the Sun exists.
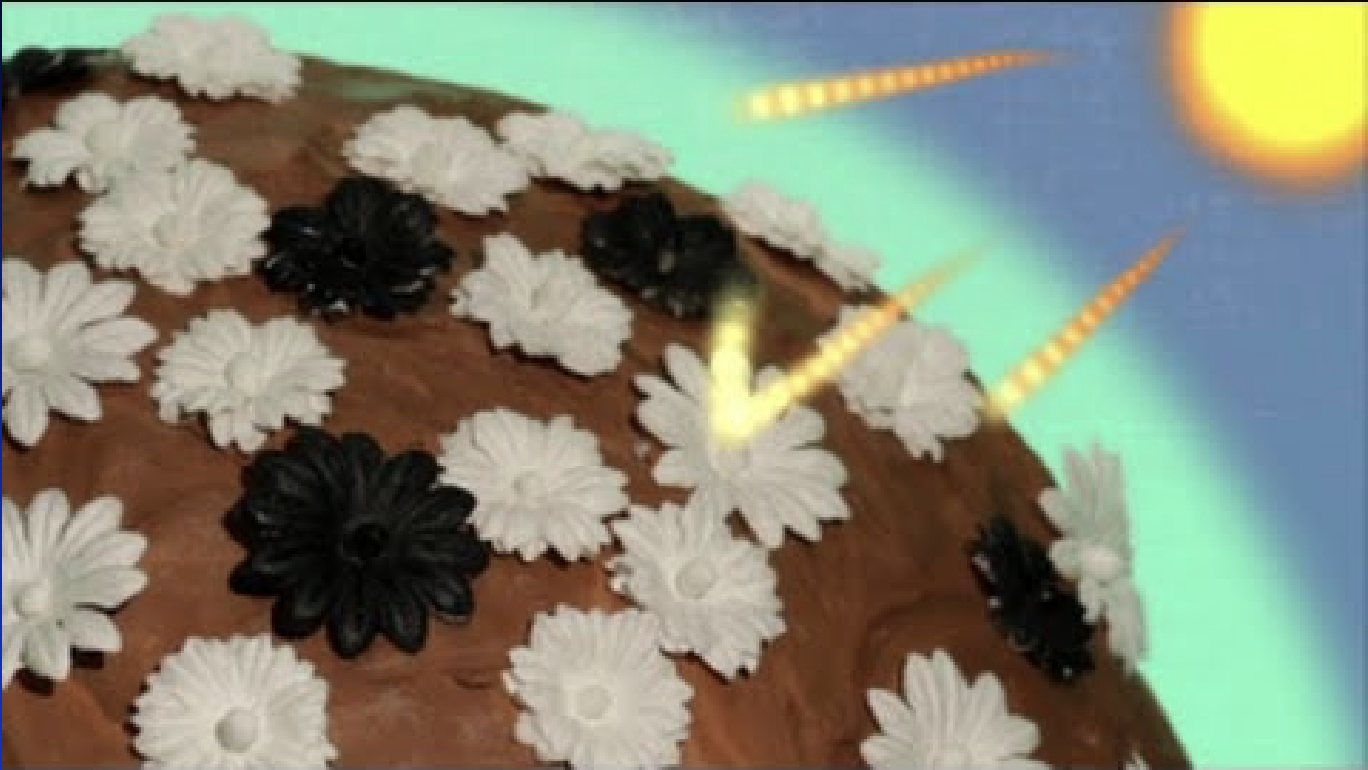

Mechanisms for Manipulating the Environment (Natural Manipulation)
Negative and Positive Feedback
Negative feeback
attainment of equilibrium involves a response that opposes the change; “mitigates” the impact(s) of the process. ( more solar radiation = global warming then more white daisies = reflect radiation, lower surface temperature)
Positive feedback
the reaction invokes a response that amplifies the change; “enhances” the impact(s) of the process.
Major Earth Systems
Hydrologic System
Tectonic System
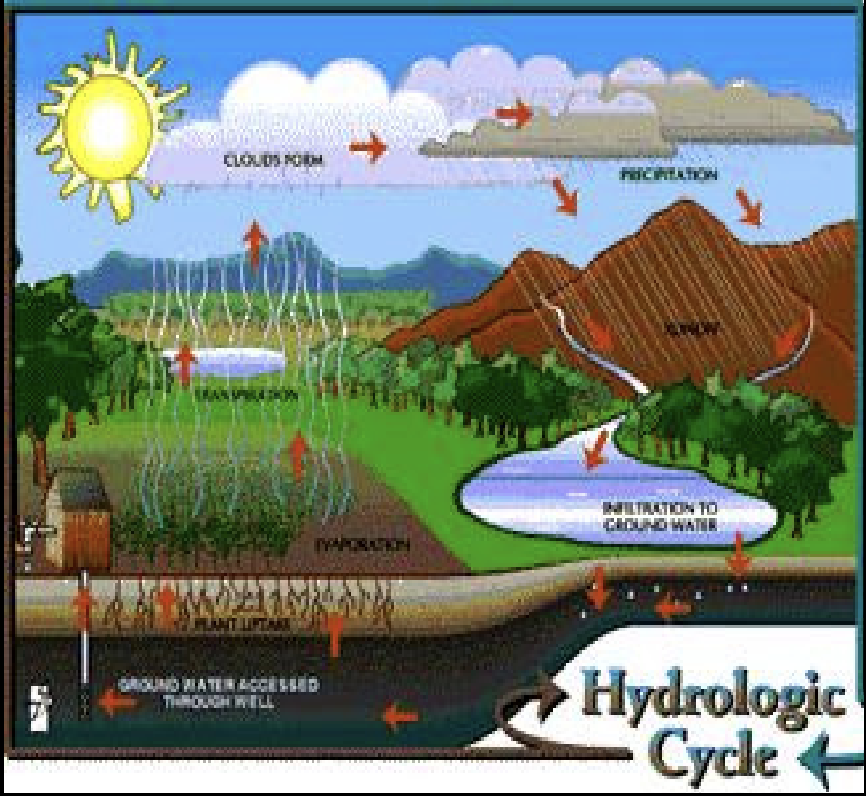
Hydrologic System
A complex cycle through which water moves from the oceans, to the atmosphere, over the land, and back to the oceans again.
Water moving as surface runoff, groundwater, glaciers,ocean waves and current- erodes, transports, and deposits surface rock materials
Hydrologic Cycle
Precipitation = Runoff + Evapotranspiration + Infiltration
Precipitation = _______________
If water did not return to the oceans, sea level will drop by 1 m/year; all ocean basins will dry out in 4,000 years!
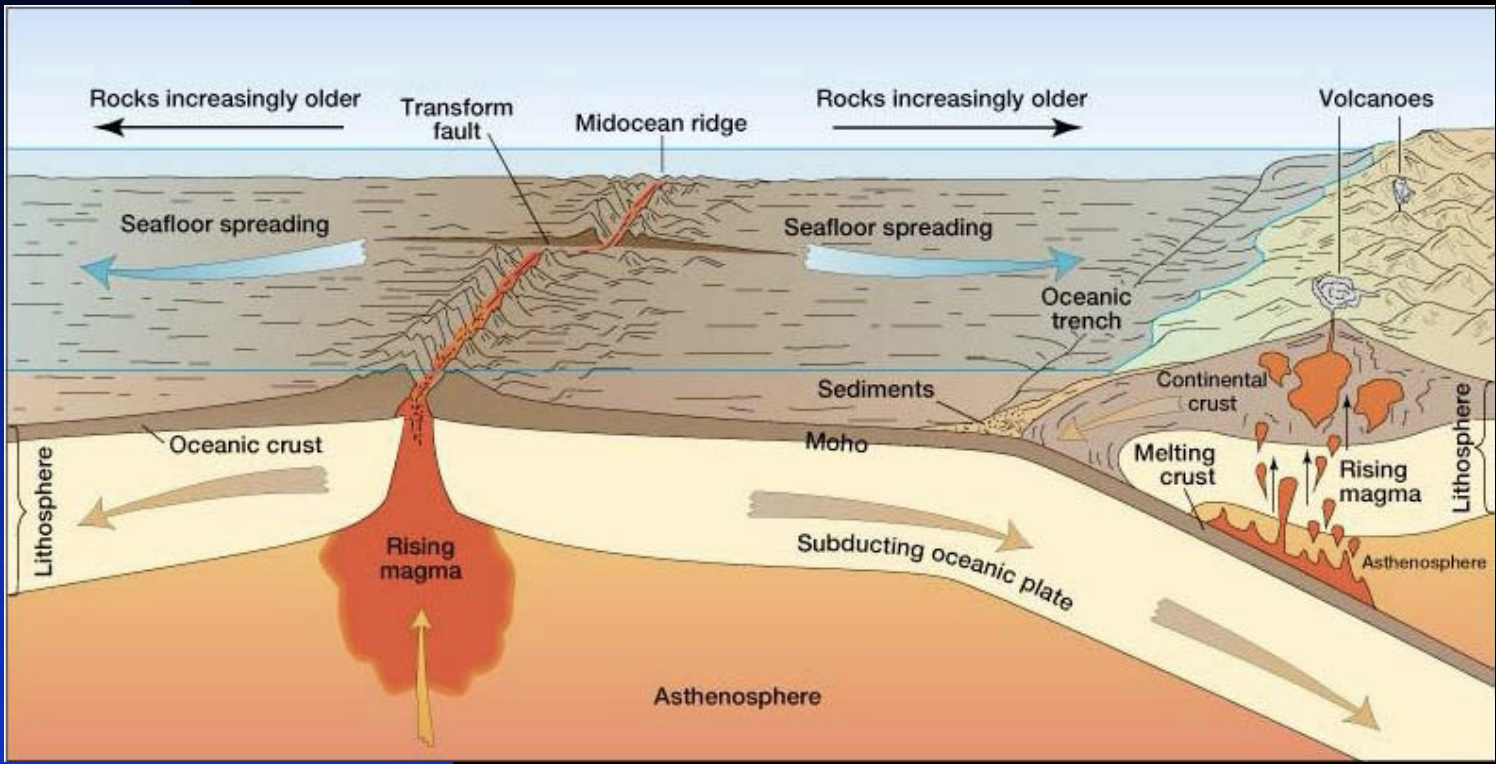
Tectonic System
Involves the movement of the lithosphere which broken into a mosaic of separate plates which move independently, separating, colliding, and sliding past one another.
The margins of the plates are sites of considerable geologic activity such as seafloor spreading, continental rifting, mountain building, volcanism, and earthquakes.
Major Tectonic Plates
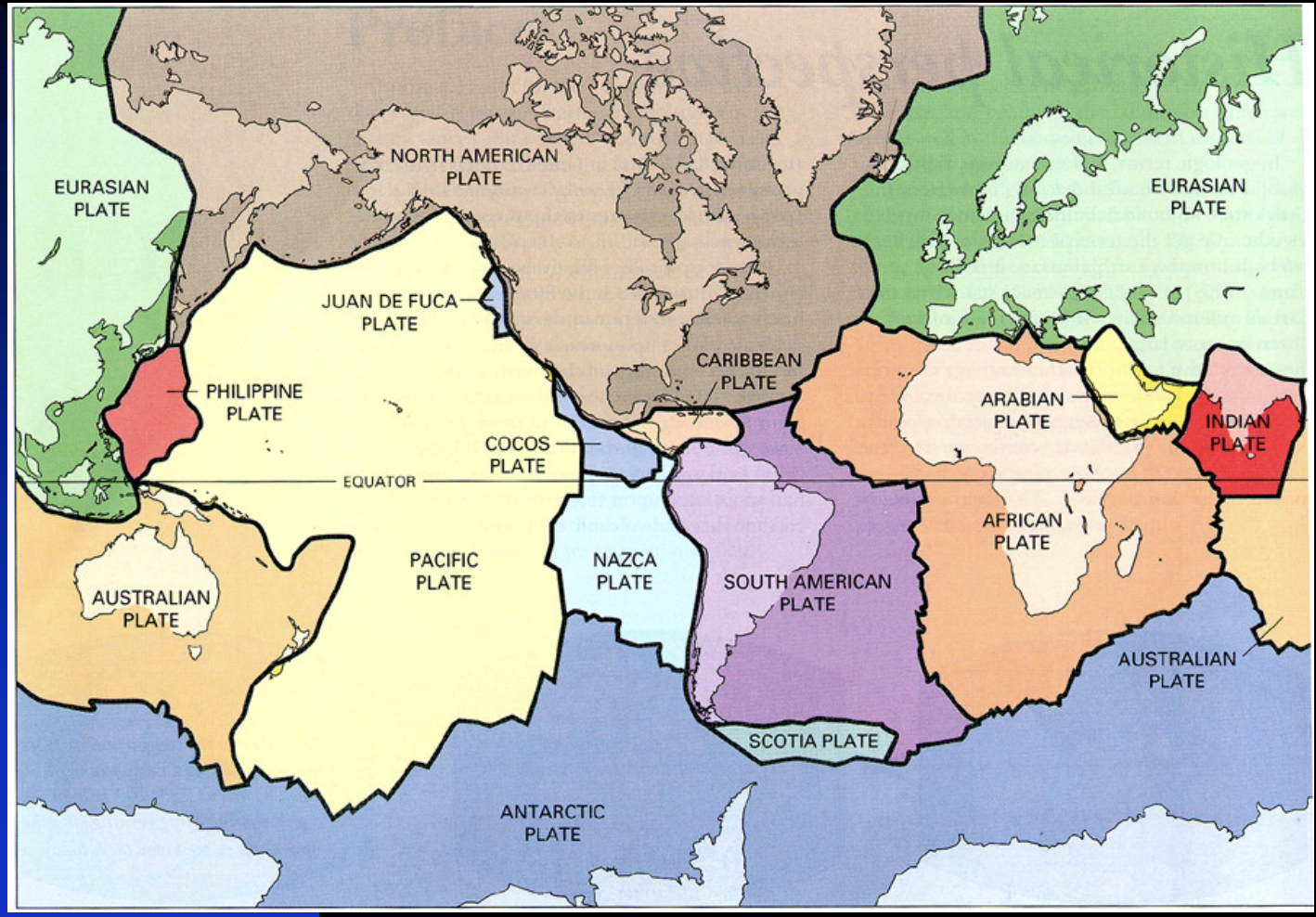
Plate Motions and Boundaries
Earth Systems
biosphere
atmosphere
hydrosphere
geosphere
Earth Systems
The Earth is an interacting system of matter and energy, that as part of its functioning produces phenomena like volcanoes, glaciers, mountain ranges, oceans, and continents.
Earth Systems
The Earth is an interacting system of matter and energy, that as part of its functioning produces phenomena like volcanoes, glaciers, mountain ranges, oceans, and continents.
Internal heat (from radioactive decay)
The reason why there is still energy in Earth’s system, keeping it moving. Drives plate tectonics.
Solar energy
External source of energy for Earth’s Systems. Maintains ocean and atmosphere circulation and helps to drive erosion.