Week 1: Economic growth intro slides
1/6
Earn XP
Description and Tags
What GDP is; how and why we measure it
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
7 Terms
What are 5 basic economic growth facts
Agricultural advances means more food and less hunger. Industrial revolution of economic growth → raising living standards and longer lives. Small differences in growth rates have a big impact. There have been growth successes and disasters.
What are the physical ingredients of economic growth
Labour and total hours worked (population = higher GDP, but not greater GDP per person. Demographics affect economic growth; women’s increased employment foreign investment builds cpa economic growth)
Capital accumulation (physical capital is a complement to labour; investment depends on saving rate; foreign investment builds capital stock).
What are the productive ingredients of economic growth?
Human capital (education increases economic growth)
Technological progress (new ideas/technologies make it possible to produce more from given physical input; computers embody technological progress)
How does economic growth change relative to distribution and pollutants
Shifts the whole distribution. Tails differs a lot across countries with similar average incomes. Pattern seen globally, especially at low income levels, where increases in GDP are associated with significant decreases in the prevalence of extreme poverty. Also true for health outcomes, especially easily preventable deaths. Historically GDP is also associated with increasing pollutants including greenhouse gases. Many economies are now achieving growth with lowered carbon emissions.
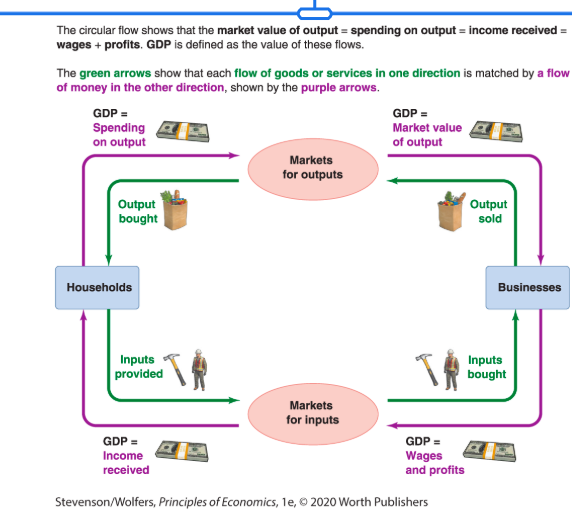
Draw the circular flow and describe what this shows

What are the costs of unemployment?
Labour market hysteresis - the effects of even a temporary spell of unemployment are typically long-lasting. On average, unemployment has a long term impact on earnings and career opportunities. These impacts are worse for those who lost their jobs during recessions. These effects are true for individuals but also region towns or countries experiencing periods of high unemployment.
Fiscal costs - high unemployment means high costs for government services and transfers (including universal credit for example but also through the demand for a broader range of public services). At the same time, high unemployment means less tax revenue, not just through taxes but also employer taxes, VAT and other taxes.
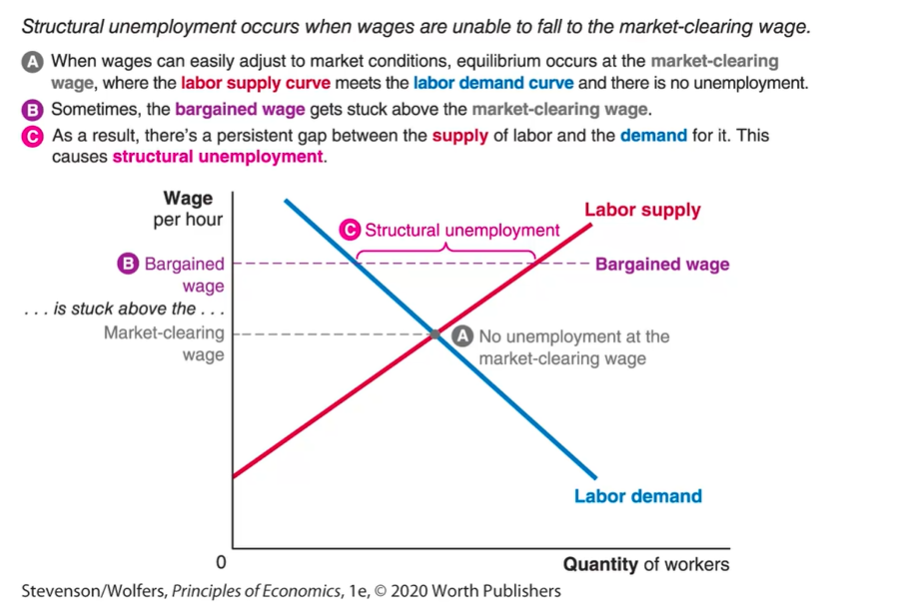
Describe when structural unemployment happens and draw the diagram for this