RADT W5L1 Ch 6, 8 - Dental Xray Image Characteristics, Digital Imaging
1/19
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
20 Terms
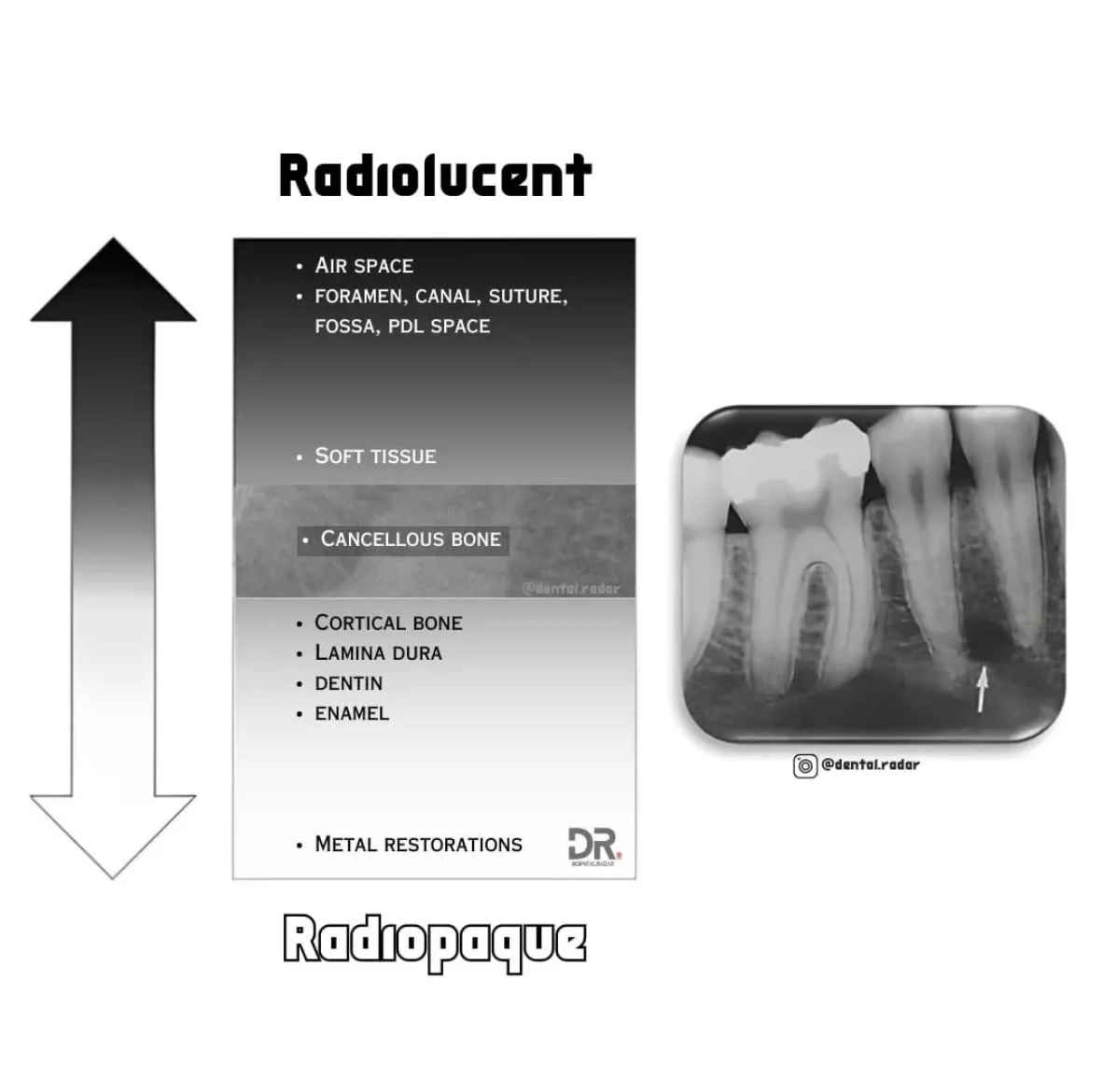
Define Radiolucent
Radiolucent structures appear black or dark on a radiograph because it permits passage of xray beam with little resistance.
ex. tissues, air spaces, dental pulp, periodontal ligament space = radiolucent
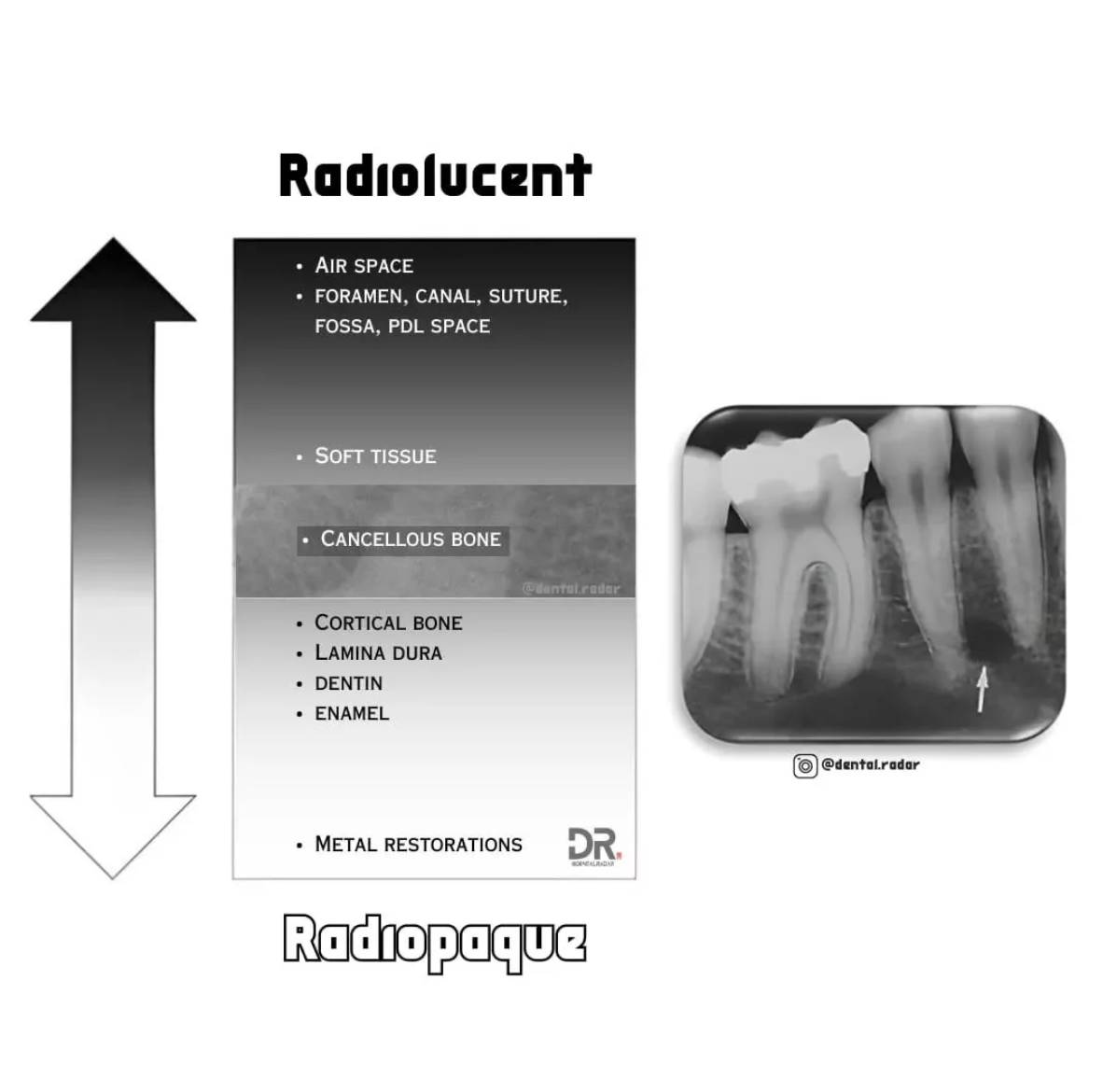
Define Radiopaque
Radiopaque structures appear white or light on a radiograph because it absorbs or resists the passage of the xray beam.
ex. enamel, dentin, bone, hard or thick tissues, maxillary sinus
Fill in the Blanks:
if mA is increased, the image will appear ___.
If kVp decreases, the image will appear ___.
If exposure time decreases, the film density will ____ resulting in a ____ image
If a client has increased amount of dense tissue/dense bone, fewer xrays will reach the film, therefore, the radiograph will have less density and appear____.
darker
lighter
decrease, brighter image
brighter/lighter
Define Short-Scale Contrast
Short-scale contrast only shows 2 densities = black and white.
low kVp (less than 70kvp) = short-scale contrast=higher contrast
Define Long-scale contrast
Long-scaled contrast shows many densities = many shades of grey on radiograph = lower contrast
high kvp (greater than 90kvp) = long scale = low contrast
not enough radiopaque on film
Define Film contrast
Characteristics of a film that influences contrast
ex. film processing and quality of the film
Define Subject contrast
Characteristics of the subject that influecne contrast
ex. thickness, density of the subject
this can be altered by adjusting kVp[
if kVp is too high for the subject = little contrast (too dark)
What is the fx of a Stepwedge?
Used to demonstrate short-scale and long-scale contrast
Monitor the quality of film and film processing
What is penumbra?
when the xray image appears fuzzy (not sharp)
The sharpness of a radiograph is influenced by…? (3)
focal spot size → smaller focal spot = sharper image
film composition → faster films with larger crystals = less sharp
large crystals do not produce object outlines well
movement
How is magnification created in radiographs?
Created from the divergent paths of the xray beam
affected by the target-receptor distance and the object-receptor distance
Longer PID = less image mag
Shorter PID = more image mag
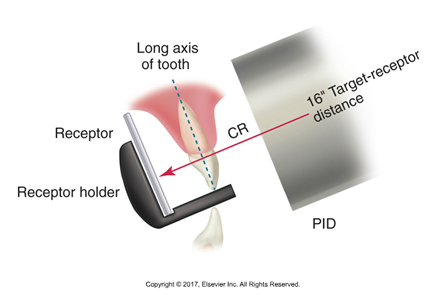
Correcting Vertical Angulation
Maxillary arch: Increase the positive vertical angulation. Imagine the PID (position indicating device) as if it's pointing slightly downwards towards the floor.
Mandibular arch: Increase the negative vertical angulation. The PID would be angled slightly upwards.
How does Digital Radiography compare to conventional radiography?
Requires less x-radiation b/c the sensory is more sensitive to xrays
50-90% shorter exposure time than conventional radiography
pt’s exposure to radiation is significantly reduced
Digital xray unit allows exposures of 1/100th of a second. The xray unit can also…
be used for conventional radiography
What is the most common image receptor used for digital dental imaging?
Charged-couple device (CCD)
also used in fax machines, cameras, microscopes, telescopes
has a solid-state detector with a silicone chip/electric circuit sensitive to xrays
What are pixels?
Small boxes or “wells” where electrons produced by xrays are deposited. They are arranged in order and a image is projected.
Why is a complementary metal oxide semiconductor (CMOS) better than a CCD?
CMOS aka active pixel sensor has 25% greater resolution, lower cost of production and greater durability than CCD (charged-couple device)
Compare and contrast Direct and Indirect Digital Imaging
Direct Digital Imaging:
Components: xray, intraoral sensor with fiber optic cable, computer monitor
captures radiographic image and transmits image to computer
software used to store radiograph
Indirect Digital Imaging:
Components: CCD camera, and computer
once film/sensor has been exposed, radiograph is digitized using CCD camera
What is storage phosphor imaging?
Aka Photo-stimuable phosphor imaging
A type of wireless indirect digital imaging where a reusable imaging plate coated with phosphorus is used instead of a sensor w cable.
Used similarly to intraoral films
Phosphorus coated plate resembles an intensifying screen used in extraoral xrays
** we use this in Rad lab
What are some disadvantages to digital imaging in comparison to film-based imaging?
Disadvantages:
Initial set-up costs
Image quality not as good as conventional
Sensory size/thickness
Infection control
Wear and tear
legal issues