Orgo I Chapter 4: Organic Compounds: Cycloalkanes and Their Stereochemistry
1/20
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
21 Terms
cycloalkanes (alicyclic compounds)
saturated cyclic hydrocarbons
general formula of cycloalkanes
(CH2)n
True or False: cycloalkanes are more flexible than open chain alkanes
False, open chain alkanes have relatively free rotation around single bonds, while cycloalkanes are more fixed to their plane
True or False: the larger cycloalkanes the more rotational freedom
True
cis cyclo isomer
same face of the ring, both out of or into the page
trans cyclo isomer
opposite faces of the ring, one is out of the page and one in
stereoisomer
atoms connected in the same order but differing in three-dimensional orientation
If two substituents are both out of or both into the page are they cis or trans
cis
angle-strain
strain induced in a molecule when bond angles are forced to deviate from the ideal 109 tetrahedral value
torsional strain
strain due to eclipsing of bonds between neighboring atoms
steric strain
the strain due to repulsive interactions when atoms approach each other too closely
what are the property results of cyclopropane's bent bonds
cyclopropane bonds are weaker and more reactive
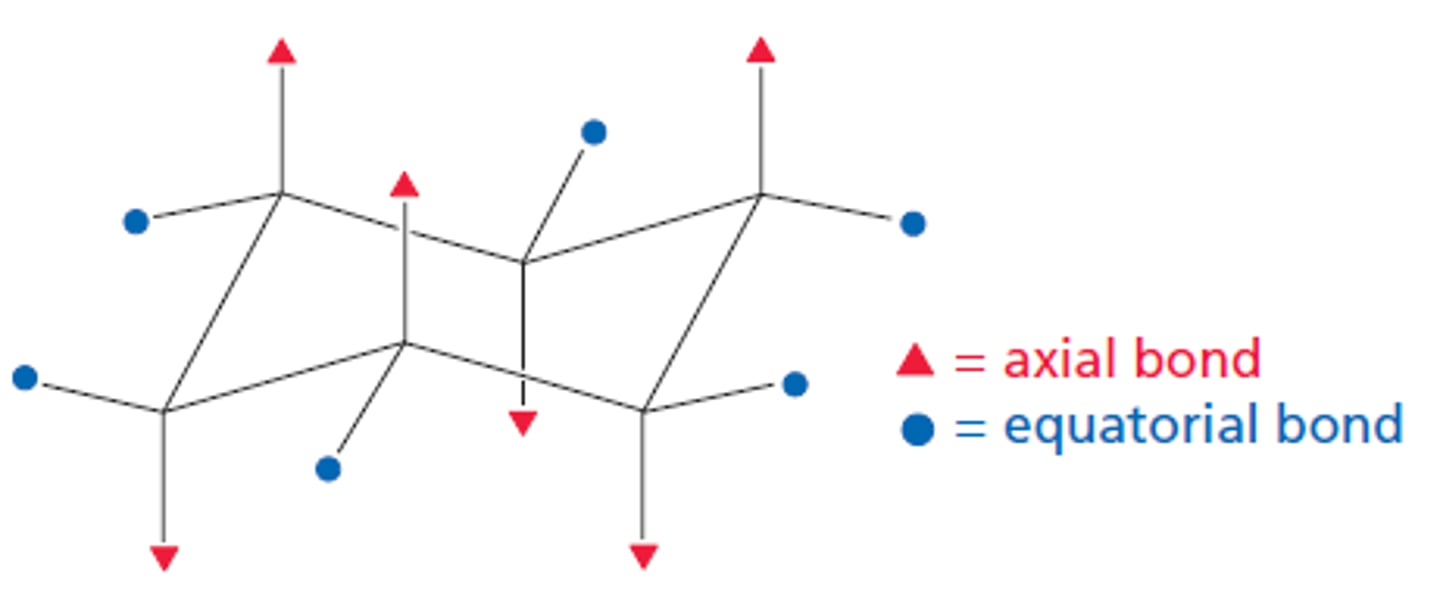
chair conformation
strain free 3-D shape for cyclohexanes
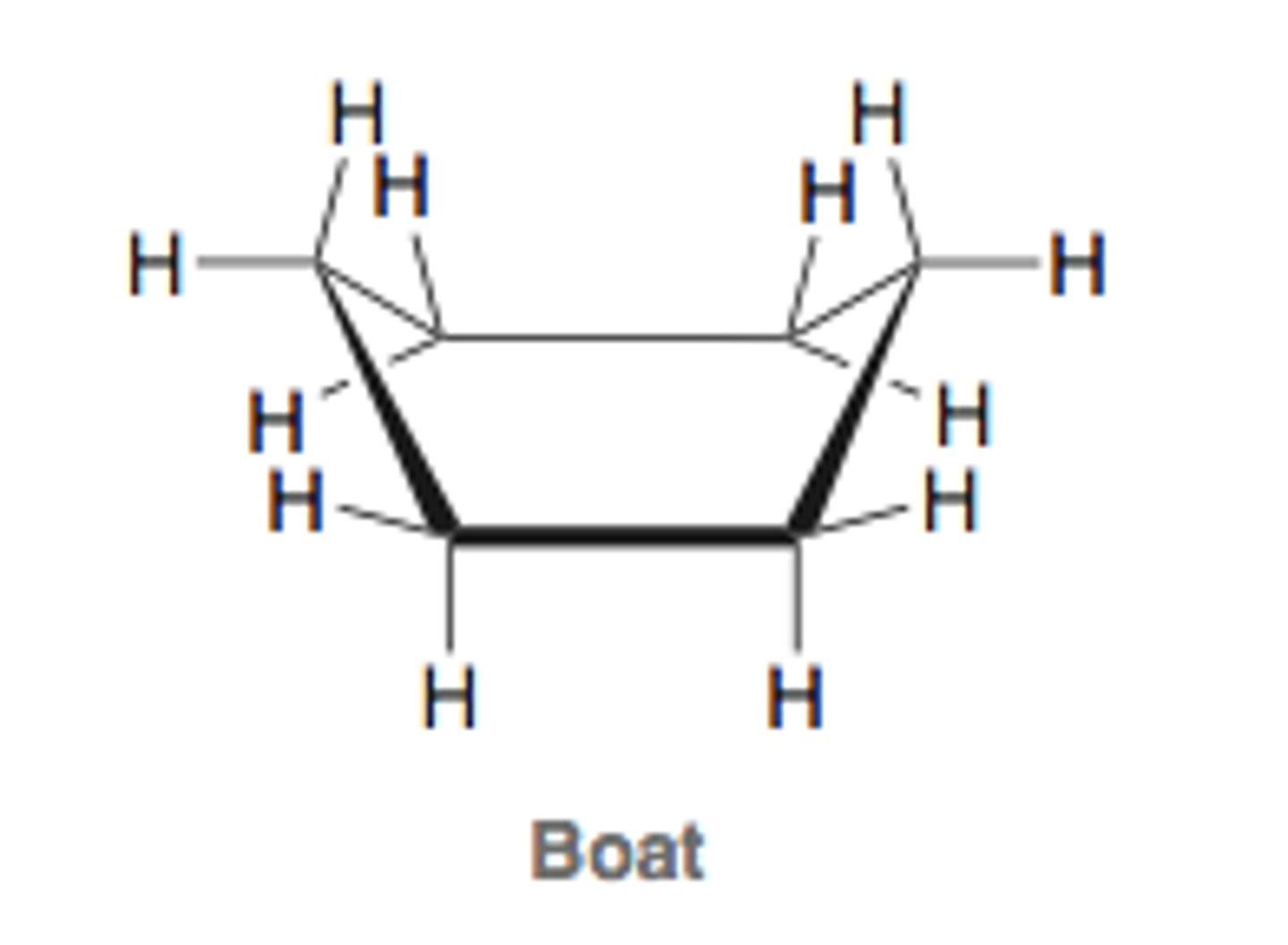
boat conformation
no angle strain lots of eclipsing interactions
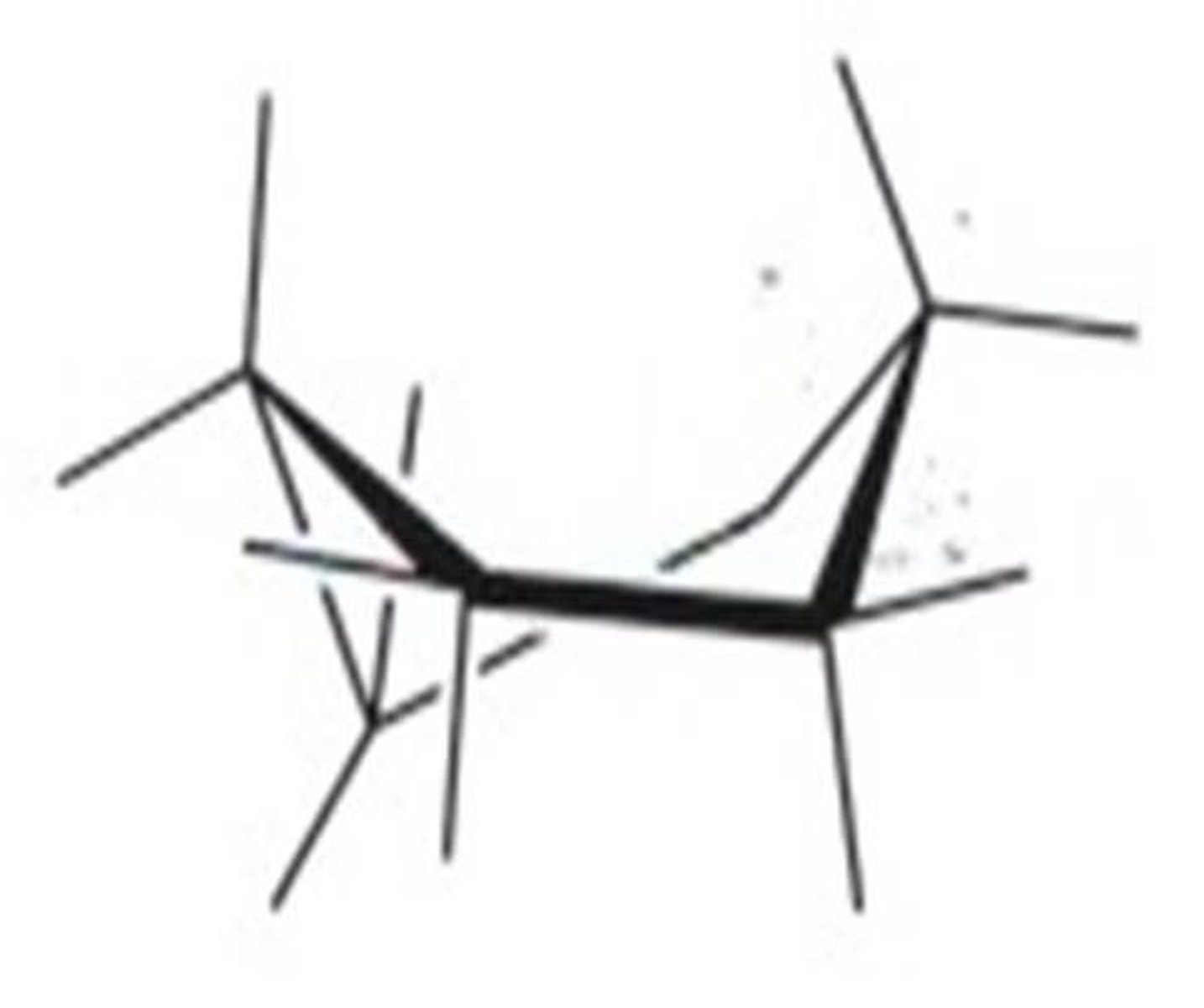
twist-boat conformation
nearly free of angle strain but has both steric and torsional strain
are monosubstituted cyclohexanes generally more stable in the axial or equatorial position
equatorial
1,3-diaxial interaction
the strong steric strain between two axial groups on cyclohexane carbons with one carbon between them
how much energy for H-H eclipsed interaction?
4.0 kJ/mol
how much energy for CH3-H eclipsed interaction?
6.0 kJ/mol
how much energy for CH3-CH3 gauche interaction?
3.8 kJ/mol
how much energy for CH3-CH3 eclipsed interaction?
11.0 kJ/mol